Ultrasound diagnostics is a highly accurate, painless and accessible method of studying the body in all respects, actively used in various fields of medicine. Ultrasound also occupies an important place in ophthalmological practice - it is one of the main tools that complements generally accepted methods for diagnosing eye pathologies.
Ultrasound research is based on the principle of echolocation. The eyeball is a set of environments with different acoustic impedances. By assessing the characteristics of the reflection of ultrasonic waves from various intraocular structures, it is possible to obtain information about their structure and determine normal and pathologically altered biological environments.
Ultrasound diagnostics allows for highly accurate measurements of the eyeball, obtaining information about the state of the anatomical and optical elements of the eye and assessing the nature of blood flow in the orbital vessels.
Possibilities of ultrasound diagnostics in ophthalmology
Ultrasound of the eye differs from other methods of ophthalmological diagnostics in its versatility - it is used to detect a wide range of eye diseases. Ultrasound allows you to assess both the general condition of the internal structures of the eye and measure its specific biometric parameters.
The main indications for an eye ultrasound are:
- closed eye injuries and damage to the optic nerve;
- progressive deterioration of vision;
- retinal disinsertion;
- pathology of the ciliary body;
- entry of foreign bodies into the eye (including those that are not detected by x-ray);
- clouding of optical media of various nature;
- suspicions of intraocular neoplasms, etc.
Ultrasound scanning is of particular value in the dynamic assessment of treatment results. It is used in calculating the optical power of artificial lenses, as well as for measuring and differentiating intraocular tumors. Ultrasound diagnostics is an indispensable tool in preparation for some ophthalmological operations.
How is the research going?
Each eye is examined separately in just one visit to the ophthalmologist. The patient only needs to place his chin on a special panel and fix his gaze on the luminous mark. The device scans all the necessary parameters and then produces printed results. It takes only 10 minutes to measure the radius of curvature of the cornea, the length of the eye axis, the diameter of the cornea and pupil and other parameters.
The measurement is carried out in a non-contact manner, so the patient does not experience pain or discomfort. He does not need to prepare for the procedure in any way; he just needs to make an appointment with an ophthalmologist. When measuring, there is no risk of infection, and the results are as accurate as possible, which greatly simplifies the selection of the most suitable artificial lens parameters.
Most often, the procedure is used when installing an artificial lens. This operation, in turn, is performed to treat cataracts and correct myopia and farsightedness. Given the large number of people suffering from these pathologies, biometrics is a fairly popular service.
Ultrasound eye diagnostic methods: scanning modes A and B
In ophthalmological practice, several ultrasound diagnostic methods (scanning modes) are used, each of them has its own technical features, differs in diagnostic capabilities and is intended for specific medical cases.
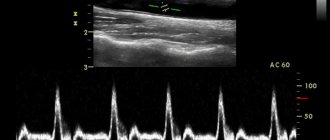
Ultrasound in A-mode . Scanning the eye in one-dimensional mode. The data on the monitor is displayed in the form of a graph, based on which the specialist assesses the biometric parameters of the eye. Ultrasound scanning in A-mode is classified into a separate direction - echobiometry.
Examination in A-mode allows you to accurately measure the axial length of the eye, the depth of its anterior chamber, and lens parameters. These data are crucial in preparing for cataract extraction, for accurately calculating the optical power of an artificial lens, and in diagnosing refractive errors. Ultrasound diagnostics in A-mode also makes it possible to detect and evaluate intraocular tumors.
Ultrasound in B-mode . Advanced scanning method. With its help, the monitor no longer produces a graph, but a two-dimensional image detailing the internal structures of the eyeball: lens, retina, eye muscles, etc. Research in B-mode allows highly accurate assessment and differentiation of intraocular changes: determining the nature of the pathology, its shape , length. Unlike the static A-mode, B-scan displays the intraocular picture in dynamics, which significantly expands its diagnostic potential.
Along with these two methods, which are considered to be the gold standard of ophthalmological diagnostics, other scanning modes are also used:
Combined method is a mode that combines the capabilities of A- and B-diagnostics.
Ultrasound biomicroscopy is an ultrasound method that allows high-resolution study of the structures of the anterior segment of the eye - we are talking about the cornea, iris, lens, and anterior chamber angle.
Three-dimensional echography is a highly informative method that provides three-dimensional acoustic visualization of intraocular structures. The image is given in volume. It is broadcast in real time, which allows you to assess the general condition of the eye over time.
Doppler ultrasound is a method that allows one to evaluate blood flow parameters in the orbital vessels.
Interpretation of indicators, normal indicators
After biometrics, the ophthalmologist receives data on the parameters of the eyeball. He compares them with normal values, determining the healthy or pathological condition of the eyes. Therefore, the following standards were identified:
- the length of the ocular axis of adult patients over 18 years of age is 23-24 mm;
- the length of the ocular axis in children under 4 years of age is 20-22 mm;
- the length of the ocular axis of patients from 4 to 18 years is 22-23 mm.
The identified deviations in the listed parameters indicate the development of the following pathologies:
- farsightedness – decrease by 1-2 mm;
- myopia – an increase of 1 mm or more.
The parameters of other areas of the eye are highlighted:
- The normal thickness of the lens is 4.26 mm, volume – 230 mm. cubic;
- anterior chamber depth – 2.57 mm;
- refractive power of the cornea – 48.22 mm.
A slight increase or decrease in the indicator does not always indicate the development of pathology. This can only be judged if a full diagnosis has been carried out, consisting of several tests.
How is an ultrasound examination of the eyes performed?
The procedure is carried out in a sitting or lying position. It does not require any special preparation and its duration on average ranges from 15 to 30 minutes.
Diagnostics in A-mode is carried out by contact method. The patient is with his eyes open. The sterile probe of the ultrasound machine comes into contact with the eye and is slowly moved across the surface. Tear fluid acts as a natural contact medium. To reduce discomfort and lacrimation due to direct contact of the sensor with the eye, an anesthetic drug is instilled into the patient before the procedure.
Diagnosis in B-mode is carried out with eyes closed. An easily washable water-soluble gel is applied to the eyelids, acting as a contact medium. The specialist moves the sensor across the eyelid, periodically indicating what actions the patient needs to perform with his eyes. The procedure does not involve the use of an anesthetic.
What is echobiometry of the eye?
An A-scan of the eye is a one-dimensional ultrasound scan, during which all data is displayed on the monitor in the form of a corresponding graph. Diagnostics can be carried out using ultrasound equipment or optical methods.
| Methods | Distinctive features |
| Ultrasound A-scan of the eye | The procedure involves the use of ultrasonic waves and their ability to be reflected from the structures of the human body. On average, it lasts from 15 to 30 minutes, during which the ophthalmologist conducts examinations with a special sensor. The patient's eyes must be open. |
| Optical biometrics | The procedure does not require direct contact with the ocular surface, and this is its advantage. The process involves a special device that allows scanning without contact. The device itself determines how the eye scans and produces results accordingly. No contact eliminates the risk of infection or injury to the eye structures. |
Combination of ultrasound with other diagnostic methods
The high information content of ultrasound does not exclude the need for additional diagnostic methods. In general cases, ultrasound is preceded by taking an anamnesis and conducting a general clinical and ophthalmological examination by the doctor.
If the presence of a foreign object is suspected, an x-ray of the eye is first taken. If the patient is suspected of having intraocular tumors, ultrasound is preceded by diaphanoscopy of the eyeball. To confirm the presence of a space-occupying lesion in the orbit, exophthalmometry and radiography are additionally performed.
Fill out an application on the website, we will contact you as soon as possible and answer all your questions.
Make an appointment
Features of the procedure
- To carry out calculations using this device, the use of anesthesia and drops is not required.
- With the help of a biometer, the entire examination takes place contactlessly, without penetration into the structure of the eye.
- The accuracy of the results of measuring the length of the anteroposterior axis of the eye using this device does not depend on accommodation (focus) and pupil diameter.
- IOL-Master makes it possible to obtain reliable measurement results in patients of any age.
- The integrated biometer personalization system ensures that every surgeon can achieve ideal surgical results.
- All necessary measurements are carried out immediately on one device - the patient does not need to switch to another device.
- The results can be stored in the database for a long time.
What does an ultrasound of the eye show?
Ultrasound of the eye orbits provides a large amount of data about the condition of the eye, due to the fact that it shows the dynamics of the processes occurring inside it. The examination provides information about the structure of the eye, its size, lens injuries, foreign bodies or tumors. Using ultrasound, retinal detachment and some other pathologies are diagnosed. Ultrasound of the eyeball is often used to monitor the patient’s condition; deciphering examination data, for example, allows one to assess the rate of progression of myopia. In addition, an ultrasound of the eye is often prescribed before surgery is performed.
Ultrasound biometrics of the eye. Features and types of eye biometrics
Using eye biometry, you can measure its length and depth of the anterior chamber, find out the parameters of the lens and the thickness of the cornea. The examination is performed with optical and ultrasonic instruments. The results of the procedure are needed for the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and monitor the condition of the cornea. Using biometrics, a specialist can select the most suitable contact lenses for a patient. Also during the manipulation, the doctor can diagnose glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure).
Eye biometrics allows for personal identification, since the iris of the eye is unique for each person. The procedure is used quite often, is accurate and fast. Abroad, with the help of manipulation, the received data is recorded in a single database, which allows them to be viewed and analyzed in the future. Also in some countries, eye biometrics are done to obtain a biometric passport.
There are 2 types of biometrics: ultrasound and optical. Ophthalmologists most often use the first type. With its help, the parameters of the organ of vision are recorded and then analyzed by a specialist. As a result of the diagnosis, it is possible to calculate the optical power of the intraocular lens, objectively assess the progress of myopia, and monitor the effectiveness of therapy aimed at stabilizing myopia (myopia).
Optical examination by doctors is considered more modern and progressive. It belongs to non-contact diagnostic methods in ophthalmology. As a result of optical biometry of the eye, it is possible to measure the posterior and anterior axis of the organ of vision, the depth of the anterior chamber, and conduct keratometry (assessment of the curvature of the corneal surface).
The optical procedure helps select intraocular lenses for the patient, taking into account the individual parameters of the organ. The main condition for successful manipulation is the transparency of the optical media.
Biometrics of the eye: indications for performance
The study must be carried out before surgical, laser operations, or implantation. For premature babies, the study is carried out at 6 months and 1 year. Up to 5 years - with deterioration of vision, congenital lesions, the appearance of opaque tears, suspected ophthalmological pathologies. Indications for examination are:
- control over developing myopia;
- ophthalmological diseases (cataracts, glaucoma, etc.);
- keratoconus (deformation, thinning of the cornea);
- selection of contact lenses;
- postoperative keratectasia;
- examination of the cornea after transplantation;
- rapid eye fatigue;
- rapid deterioration of vision;
- heaviness of the eyelids when blinking;
- frequent headaches radiating to the eyes;
- deformation or clouding of the cornea;
- distorted, doubled image;
- suspected retinal detachment;
- progressive myopia;
- diagnosis of oncological diseases.
Eye biometrics is carried out as a preventative measure for eye diseases. The method is necessarily used for diabetes mellitus, age-related macular degeneration, and foreign objects getting inside.