About 30% of the population suffers from hidden forms of iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia. They have low ferritin in their blood. High levels of ferritin are characteristic of inflammatory and infectious diseases, and cancer pathologies. Determining the concentration of ferritin in blood serum allows hematologists at the Yusupov Hospital to effectively differentiate iron deficiency anemia from other types of anemia. Laboratory technicians perform ferritin analysis at an affordable price using modern diagnostic equipment and precise reagents. This allows you to obtain accurate research results, allowing you to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Patients with critical ferritin levels are kept in wards with European comfort levels during treatment. They are provided with dietary food, the quality of which does not differ from home cooking, and individual personal hygiene products. Complex cases of diseases, the manifestation of which is increased or decreased ferritin in the blood, are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council, in which candidates and doctors of medical sciences, doctors of the highest category take part.
Leading hematologists collectively develop management tactics for each patient. Complex therapy for diseases in which low or high ferritin in the blood includes modern medications that are effective and have minimal side effects.
What is ferritin in the blood
Iron ions are part of proteins that transport oxygen, iron seroproteins and cytochromes, iron-containing enzymes. Ferritin is a highly informative marker that characterizes iron metabolism. It is a water-soluble complex of iron hydroxyphosphate with the protein apoferritin. The largest amount of ferritin is found in the cells of the liver, spleen, bone marrow and reticulocytes, where the processes of production, maturation and degradation of red blood cells intensively take place. Ferritin is actively involved in the metabolism and redistribution of iron in the body.
The serum ferritin level allows us to estimate the total iron stores in the human body. In healthy people, the ferritin content in blood plasma is 20-350 ng/ml. Lack of iron in the body leads to negative consequences. The development of iron deficiency anemia is indicated by a drop in concentration below 10 ng/ml. Iron deficiency in the third trimester of pregnancy is found in almost 90% of women and persists after childbirth during breastfeeding in 55% of them.
With excessive accumulation of iron, ferritin concentration increases to several thousand ng/ml. Increased ferritin in the blood of women is the cause of toxicosis. You can take a blood test for ferritin at the Yusupov Hospital.
Interpretation of results
Blood test for ferritin
used to diagnose anemia caused by infectious diseases, the development of a malignant neoplasm or an inflammatory process. It is also prescribed when differential diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia is necessary. Reference values differ depending on gender. For women they are 10-150 ng/mg, and for men 20-350 ng/mg. If acute inflammation develops in the body, ferritin concentration increases significantly. A slight decrease in its amount in pregnant women is within normal limits and does not indicate the presence of pathology. Iron deficiency anemia is characterized by a lack of ferritin.
An increase in indicators is possible in the following cases:
- liver pathologies;
- acute inflammatory process;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- leukemia;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- general exhaustion of the body.
This test is not intended for self-diagnosis and should only be interpreted by a physician. Self-medication can cause irreparable harm to your health, so you should not risk it; you should consult a doctor. When interpreting the results, data from other studies, individual characteristics of the organism and a number of other factors are taken into account. If deviations from the norm are detected in the early stages, in many cases, taking a course of a vitamin-mineral complex is sufficient to normalize them, but such a drug must be prescribed by a doctor. For the most reliable assessment of iron metabolism, as a rule, a complex of laboratory tests is carried out, rather than a single analysis.
Ferritin - what is it and how is it determined?
Determination of ferritin concentration is carried out using three types of analysis:
- Radioimmune;
- Immunoenzyme;
- Fluorescent.
The principle of radioimmunoassay is as follows: ferritin of the sample being determined reacts with antibodies that are immobilized on a solid-phase carrier, and then binds to antibodies labeled with iodine-125. Labeled antibodies that have not reacted with ferritin remain in solution and are removed. The radioactivity of the “labeled antibody + ferritin with immobilized antibody” complex is measured on a gamma counter. In this case, the measured radioactivity is proportional to the amount of ferritin in the test sample.
Most immunological research methods use the polyvalency of ferritin in its reaction with antibodies. They are based on the principle of two-center immunometric analysis. In this embodiment, each ferritin molecule binds two antigenic centers with two antibody molecules: with an antibody that contains a label (enzymatic, isotopic or fluorescent), and with an antibody that is attached to a polymer carrier. Most diagnostic tools use formed solid-phase carriers (balls, tubes, paper disks, stars) coated with antibodies as a separation system. Modern diagnostic kits use monoclonal antibodies.
Enzyme immunoassay methods for determining serum ferritin use special test systems. They are highly sensitive. Immunofluorescent methods are based on the detection of molecules labeled with a fluorescent label, which is characterized by a high ability to generate a signal. The most promising variant of the research method is considered to be one in which porphyrins or polymacrocyclic compounds are used as labels.
There are diagnostic test systems that are based on the principle of enhanced chemiluminescence. The rapid chemiluminescent ferritin assay measures ferritin in serum and plasma in a two-step, one-hour procedure.
Complexes with this research
Anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause Control of age-related changes during the postmenopausal period 8,260 R Composition
Male anti-aging diagnostics Monitoring of basic indicators in men aged 40+ 8,680 R Composition
Advanced female anti-aging diagnostics Advanced monitoring of basic blood parameters in women aged 40+ RUR 20,600 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Monitoring the diet of a nursing mother RUB 1,960
- Women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 7,860
- Vegetarians and vegans RUB 3,750
- Advanced anti-aging diagnostics in postmenopause RUR 21,000
- Advanced male anti-aging diagnostics RUB 24,320
Increased or decreased ferritin
In healthy adults, serum ferritin levels vary by gender and age. In men, the concentration of serum ferritin varies from 30 to 200 μg/L. In women of childbearing age, the concentration of ferritin in the blood serum is in the range of 10-90 mcg/l, in postmenopause it reaches average values that are typical for men. In children, serum ferritin levels increase sharply during the first three months of life. This is due to the rapid development of organs and tissues. Subsequently, from the age of six months until puberty, the level of ferritin in the blood serum remains unchanged, varying in the range of 34.4-4.1 μg/l.
What does ferritin show? Hematologists, by determining the level of ferritin in the blood, assess the iron reserves in the patient’s body. Serum ferritin is the earliest and most reliable sign of tissue iron deficiency. It precedes the development of iron deficiency anemia itself. With tissue iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia, there is a decrease in ferritin in men below 30 mcg/l, in women and children below 10. When anemia is relieved and the iron depot is replenished, the level of serum ferritin is restored to normal. For this reason, hematologists at the Yusupov Hospital use it as a method of objectively assessing the adequacy of the treatment provided.
To obtain a reliable result of a ferritin test, the patient needs to prepare:
- Donate blood for testing on an empty stomach;
- Do not smoke 30 minutes before blood collection;
- On the eve of the study, avoid physical and psycho-emotional stress.
A high level of ferritin is observed in post-transfusion hemosiderosis and hemochromatosis (a hereditary disease characterized by increased absorption of iron from the digestive tract, increased deposition in tissues and organs). Scientists have found that ferritin also has other functions not directly related to iron metabolism. H-isoforms of ferritin play the role of suppressors in the proliferation of blood cells. They slow down the division of myeloid and lymphoid cells.
Ferritin levels increase during acquired immunodeficiency virus infection. The concentration of total ferritin also increases during an acute inflammatory process, which allows us to consider ferritin as an acute-phase protein.
Ferritin has cytoprotective properties. It is found in large quantities in pancreatic cells. It is used to retain zinc, which is abundant in insular cells. Zinc competes with iron for binding sites in ferritin and transferrin.
Ferritin is associated with tumor necrosis factor, which is released by certain cells as a result of the following stimuli:
- Viruses;
- Ultraviolet irradiation;
- Interleukins;
- Oxidative stress.
High ferritin in the blood is determined in malignant tumors of the ovaries, breast, and hepatocellular cancer. An increase in the concentration of serum ferritin in liver diseases is associated with the process of release of ferritin from liver cells during their destruction.
A significant increase in serum ferritin is observed in the following malignant neoplasms:
- Prostate cancer;
- Lymphogranulomatosis;
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas;
- Testicular cancer;
- Pancreatic cancer.
An increase in ferritin is observed in patients suffering from blood diseases: acute leukemia, chronic myeloid leukemia, acute erythromyelosis.
Ferritin: price of analysis, where to take it in Odintsovo and Zvenigorod
You can always check your health at VERAMED clinics.
Our own laboratory and cooperation with leading clinical laboratories in the region allow us to perform diagnostics quickly and efficiently. Doctors at our clinics will advise, identify the problem, and prescribe medications or a diet that will compensate for excess or deficiency of iron. In medical departments, you can donate blood for any tests, including ferritin. The call center operators will tell you the current cost of analysis: 8(495)150-03-03.
Elevated ferritin levels
If ferritin levels are elevated, then iron is in excess or an acute inflammatory reaction has occurred , in which ferritin is mobilized into the blood without excess iron.
Ferritin also increases under oxidative stress. It is enhanced by antioxidant responsive element (ARE). ()
Ferritin, in turn, can increase of inflammatory mediators IL-1b, iNOS, RANTES, IkappaBa and ICAM1 in the liver ()
Because ferritin is also an acute-phase reactant of inflammation (part of the body's response), it is often elevated in various diseases. Ferritin levels greater than 1000 μg/L are a nonspecific marker of diseases, including infections and cancer. ()
However, even ferritin a little more than 300 mcg/l may indicate some inflammation in the body. Inflammatory cytokines stimulate the production of ferritin, which acts as an acute phase reactant in relation to inflammation or infection. ()
Circulating ferritin production is enhanced by the cytokines interleukin IL-1β and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). ()
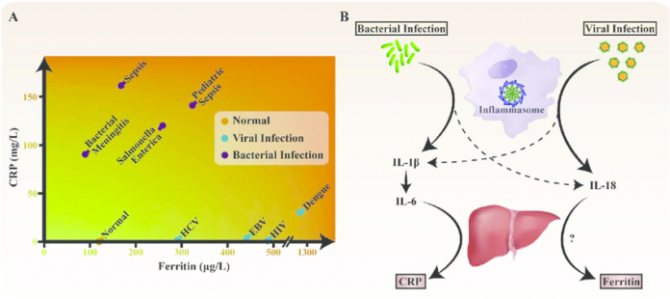
by varying levels of ferritin and C-reactive protein in the blood (source)
Viral infections are typically characterized by high plasma ferritin with concomitant low levels of circulating C-reactive protein (CRP). While bacterial infections are usually characterized by high levels of CRP in the blood. The production of inflammatory interleukin IL-1β/IL-6 in response to bacterial infections promotes elevated CRP levels, while viral infections are characterized by increased interleukin IL-18 culminating in excessive ferritin levels.
It is important to note that IL-1/IL-6/CRP and IL-18/ferritin levels do not fully reflect the duality of bacterial-viral infection, as some bacterial infections are known to increase IL-18 levels in the blood, and viral infections are known to , can also increase IL-1β levels. ()
Rules for preparing for the test
The main goal of preparation is to minimize possible distortions in the analysis:
- Do not take iron supplements for a week.
- For 5 days, do not take penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics, antifungal medications, hepatoprotectors that contain aluminum or silymarin.
- 3 days before the test, stop drinking alcohol; if the daily dose of alcohol in terms of ethanol exceeds 300 ml, do not test for ferritin for 7-10 days.

- Stop smoking one day before and eliminate red meat from your diet; liver, except chicken, 3 days in advance; Do not consume chicken liver the day before.
- Do not eat food 12 hours before.
- Do not drink liquid 1 hour before.
- Don't worry for half an hour.