Question answer
An adult has low lymphocytes in the blood. Which doctor should I contact?
A decrease in the level of lymphocytes can be caused by a number of reasons, both physiological and pathogenic in nature. If there are no external manifestations of a specific disease, and repeated blood sampling and analysis shows an identical value below normal, then you should contact a hematologist - a specialist in the etiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases directly or indirectly related to the blood system.
Segmented lymphocytes are greatly reduced. What to do?
You cannot have low segmented lymphocytes, since such cellular elements do not exist in nature.
Most likely, we are talking about segmented neutrophils - a mature subtype of granulocytic leukocytes present in the peripheral blood and, accordingly, the basic leukocyte formula, induced in the red bone marrow and migrating into the blood after reaching the band state. They are responsible for protecting the body from bacterial and fungal infections through NETosis. A decrease from the level is called neutropenia and occurs against the background of the development of chronic forms of bacterial and acute forms of viral/fungal infections, radiation therapy, aplastic anemia, as well as severe post-infectious conditions.
I can recommend contacting a hematologist for a comprehensive diagnosis and prescribing appropriate therapy.
What does a low level of lymphocytes in the blood mean during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, at certain stages, a low level of lymphocytes is normal. The mechanism of this process is associated with the physiological characteristics of the immune mechanism. It is well known that the above-mentioned cellular elements are divided into several types - the functionality of the B and T components is aimed at searching for and destroying foreign antigens, including the basis of the biological material of the father. With the onset of conception and hormonal changes, the body of the fair sex produces T-suppressors in large quantities, suppressing the work of the H/T components of the immune system, which allows the embryo to develop unhindered, while its protection against infections and other diseases is formed due to an increase in the concentration of phagocytes and neutrophils.
The overall relative and absolute level of lymphocytes begins to decrease from the fourth to fifth week of pregnancy and begins to gradually increase at the end of the second trimester. Accordingly, a reduced concentration of the described cellular elements is the norm from the beginning of the second month after conception until the 26th week.
Questions answered by: Evgeniy Pogolosov
Leukocytes in the blood
A decrease in leukocytes in the blood is called leukopenia; this condition is detected by the results of a general and detailed blood test. This group is heterogeneous. It includes several populations of cells involved in inflammatory reactions, immune and autoimmune processes.
Based on the presence or absence of granules inside the cell, which are clearly visible under a microscope after special treatment, granulocytes and agranulocytes are distinguished.
The normal ratio of white blood cells of different populations is considered (%):
- granulocytes; band neutrophils (immature) – 2 – 4;
- segmented neutrophils (mature) – 47 – 67;
- eosinophils – 0.5 – 5;
- basophils – 0 -1;
- lymphocytes – 25 – 35;
Leukocytes are involved in anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic processes, their number in the body is constantly changing. If the changes remain within normal limits, then such physiological conditions are not dangerous and do not threaten a decrease in immunity.
The following ranges of values are considered the norm for different types of white cells (number of cells * per 109/l or thousand/μl):
- leukocytes – 4-9;
- neutrophils; stab - 0.08 - 0.35;
- segmented – 2 – 5.9;
Total white blood cells may be normal, but a complete blood count sometimes reveals that neutrophils are reduced, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes or monocytes are reduced or increased.
If leukocyte counts are low, a detailed analysis must be done to identify the cause of the decrease in different cell populations in the blood.
The norm of lymphocytes in the blood. Which level is reduced?
Below are the standard absolute and relative norms for the content of lymphocytes in the blood. If the tests show lower values, this condition is called lymphopenia and requires at least additional diagnostics, and in most cases, the prescription of specific therapy.
In adults
The absolute value of the lymphocyte level is from one to 4.5 X 10⁹ units/liter.
- Lymphocytes: increased and decreased levels, functions, how to bring them back to normal
The relative value of the level of lymphocytes is from twenty to 34 percent.
In children
In children, there are much more lymphocytes in the blood than in adults, and specific norms depend on the age of the child:
Age—relative/absolute value of lymphocyte level:
- Children under one year - from 55 to 75 percent / 4–10.5 X 10⁹ units/l.
- Children under four years of age - from 45 to 65 percent / 2-8 X 10⁹ units/l.
- Children under six years of age - from 35 to 55 percent / 1.5–7 X 10⁹ units/l.
- Adolescents up to ten years - from 30 to 50 percent / 1.5-6.5 X 10⁹ units/l.
- Young people under 21 years of age - from 30 to 45 percent / 1–4.8 X 10⁹ units/l.
Based on the data presented above, the normal level of lymphocytes in the blood decreases with age - their highest concentration occurs in children under 12 months.
What does it mean?
A low lymphocyte count indicates that the patient has developed lymphopenia. This condition is usually associated with the migration of the above-described cellular structures from the lymphatic localized fluid into the tissues - thus, the analysis reveals a lack of the latter in the blood.
The above condition cannot be considered a disease - it is a symptom caused by a number of reasons, among which there may be both physiological and pathogenic factors, most often infectious-toxic fast processes.
This diagnosis is made after an initial and repeated blood test and determination of the patient’s exact immune status. Symptoms of lymphopenia are often very mild or absent altogether. The problem may be indicated by constant changes in the size of the tonsils and lymph nodes, the appearance of associated diseases such as eczema, pyoderma, alopecia, and frequent repeated infectious lesions over a short period of time.
Why are there fewer lymphocytes?
As already mentioned, lymphocytes are one of the types of leukocyte cells.
And they are the ones who perfectly distinguish where the proteins are foreign and where they are their own. They are responsible for cellular immunity. And very often the analysis demonstrates that lymphocytes are reduced, that is, the patient has lymphopenia. The norm of these cells can change significantly throughout life.
For each age category, a certain percentage of deviation from the total number of all elements of the leukocyte formula is allowed:
- in children, the indicator should not decrease by more than 30%;
- in 5-7 year old children – by 50%;
- in the blood of adolescents and adults - a maximum of 20%.
A low ratio may be a temporary phenomenon. This happens in the presence of an infectious focus that is actively suppressed by immune cells. But in general, lymphopenia is diagnosed in an immunodeficient state.
It is important to find out as early as possible the factor that reduces the size of lymphocytes, because if the deviation from the norm lasts too long, infectious pathologies, oncology and other equally serious diseases cannot be ruled out.
The reduction in the number of elements is provoked by:
- Hepatological lesions of chronic form.
- AIDS.
- Aplastic anemia.
- Septic processes.
- Miliary tuberculosis.
- Severe infectious pathologies.
- Chemotherapy, as well as radiation.
- Destruction of lymphocytes.
- Immune disorders of hereditary origin.
- Kidney failure.
- Lupus erythematosus.
- Lymphogranulomatosis.
- Splenomegaly.
- Itsenko-Cushing syndrome.
- Lymphosarcoma.
- Intoxication with corticosteroid drugs.
- Infectious diseases that occur acutely, as well as purulent-inflammatory processes.
Under no circumstances should treatment be delayed for diseases that are accompanied by lymphopenia. The prognosis for such pathologies can be extremely unfavorable. And in order for the level of lymphocytes to normalize, one should not deal with lymphopenia, but eliminate the disease that affected the concentration of cells.
Even if a general analysis showed a change in the number of elements of the leukocyte formula, the doctor will not prescribe a treatment course without additional examinations. Therefore, there is no need to panic ahead of time. After all, there are deviations that are not considered dangerous. Therefore, you should wait for all the diagnostic results and then begin to cure the disorders.
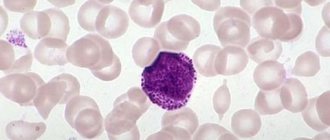
The role of lymphocytes in the body
Scientists have isolated several types of lymphocytes. Each of them differs in the way they act on pathogenic microorganisms.
- T lymphocytes. This group is the most numerous. It is divided into 3 more subspecies. Each of them plays a role. Killer T cells kill infectious agents, as well as altered (tumor) cells. Helper T cells improve immunity, while suppressor T cells suppress the immune response.
- B lymphocytes. Their number is 10-15% of the total concentration. The functions of B-lymphocytes are among the most important. They consist of resisting viruses, bacteria and developing cellular immunity. It is these substances that make vaccination effective.
- NK lymphocytes. This prefix is translated from English as “natural killers.” The proportion of these leukocytes is estimated at 5-10% of the total mass. The main function of agents is to kill elements of their own body if they are infected.
Lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow. From the blood, most of the lymphocytes pass to the thymus (thymus gland), where they are converted into T-lymphocytes, which protect the human body from foreign agents. The rest become B lymphocytes, which complete their formation in the lymphoid tissues of the spleen, tonsils and lymph nodes.
B lymphocytes synthesize antibodies upon contact with infectious agents. There is a third type of lymphocyte. These are the so-called natural killers. They also provide protection to the body from cancer cells and viruses.
- How to reduce lymphocytes in the blood?
Different roles of lymphocytes
h27,0,0,0,0—>
May protect against cancer
h317,0,0,0,0—>
A higher level of CD8+ T-type lymphocytes (directly in the tumor) indicates an increase in the overall survival of cancer patients. (20)
p, blockquote53,0,0,0,0—>
Specialized tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte therapy can treat liver cancer and may help stop the cancer from coming back. (21)
p, blockquote54,0,0,0,0—>
Supports Gut Health
h318,0,0,0,0—>
- The norm of leukocytes in the blood of children in the table, low and increased values in a child
Lymphocytes in the intestine play an important role in maintaining the homeostasis of this organ. They are also critical for early response to intestinal infections. (22)
p, blockquote55,0,0,0,0—>
Protects against damage due to arthritis
h319,0,0,0,0—>
Patients with arthritis and high levels of lymphocytes in their joints had less cartilage and bone damage than people with low levels of lymphocytes. (23)
p, blockquote56,0,0,0,0—>