The length of the nasal bone in an embryo is one of the most important indicators of proper fetal development. If the nasal bone on ultrasound is smaller than normal, we can talk about a phenomenon such as hypoplasia of the nasal bone in the fetus.
Hypoplasia of the nasal bone is a marker of chromosomal abnormalities and abnormal fetal development, but this is not yet a diagnosis. Hypoplasia itself does not make it possible to say with a high degree of accuracy about genetic disorders of the embryo, but it allows timely research to be more informative than ultrasound.
- Why do you need to know the length of the fetal nasal bone?
- Nasal bone hypoplasia and other indicators
- Fetal malformations - reliability of ultrasound
- Fetal nasal bone
- Normal fetal nasal bone by week
- Further diagnostics
- Additional diagnostic methods
- How is amniocentesis performed?
Prevention of pathology
There are no guaranteed and reliable methods for preventing hypoplasia or aplasia. However, doctors recommend a number of measures:
- Conceiving a child is carried out until the age of 39, this applies to both parents;
- undergo regular genetic testing, which is recommended to begin before pregnancy;
- maintain proper nutrition;
- spend most of the time outdoors;
- do not take medications unnecessarily or as prescribed by a doctor;
- start taking folic acid when planning pregnancy;
- try to avoid stressful situations;
- take special medications prescribed by a doctor after assessing the clinical picture.
A woman suffering from any abnormalities needs specialized medical therapy and prenatal screening. It is better for pregnant women to choose a multidisciplinary hospital where they can receive comprehensive care.
Hypoplasia of the nasal bone is not a reason for great concern. Don't give up, go through all the examinations. To be able to diagnose pathology in a timely manner, you need to undergo an ultrasound scan on time, follow all the doctor’s recommendations, and monitor your health and immunity.
When should the next screening be done?
If the results of previous tests give rise to concern, then the pregnant woman is referred for 2nd screening. In exceptional cases, if pregnancy is at risk.
Screening is done from the 16th to the 20th week.
At this stage, the structure of the baby’s skeleton is analyzed using ultrasound.
| Name | Deadlines in weeks | |||||
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | ||
| Femur Length(mm) | DBK | 13-23 | 16-28 | 18-32 | 21-35 | 23-38 |
| Humerus Length(mm) | DPK | 13-23 | 16-27 | 19-31 | 21-34 | 24-36 |
| Bipartite head size (mm) | BPR | 26-37 | 29-43 | 32-47 | 36-52 | 39-56 |
| Fronto-occipital size (mm) | LZR | 32-49 | 38-58 | 43-64 | 48-70 | 53-75 |
| Length of tibia or tibia bones (mm) | DKG or DBB | 11-21 | 14-25 | 16-28 | 19-31 | 21-34 |
| Length of forearm bones (mm) | PrEP | 12-28 | 15-21 | 17-23 | 20-26 | 22-29 |
| Nose bone length (mm) | 3,6-7,2 | 5,2-8 | 5,7-8,3 | |||
| Tummy circumference (cm) | coolant | 0,88-1,16 | 0,93-1,31 | 1,04-1,44 | 1,14-1,54 | 1,24-1,64 |
| Head circumference (cm) | OG | 1,12-136 | 1,21-149 | 1,31-161 | 1,42-174 | 1,54-186 |
| Brain structure | ||||||
| Cerebellum (mm) | 12-16 | 14-18 | 15-19 | 16-20 | 18-22 | |
| Large tank (mm) | No more than 10-11 | |||||
| Lateral ventricles (mm) |
Attention is also paid to the proper development and functioning of internal organs. If there are no visible pathologies, then the protocol will indicate
The position of the baby will be indicated, as well as characteristics of the level of amniotic fluid, umbilical cord and placenta.
The most favorable location for the placenta is the posterior wall of the uterus due to good blood circulation. The attachment can be indicated more specifically: on the right, on the left. Closer to the bottom there is also good blood circulation.
The anterior wall of the uterus stretches as the baby grows and its motor activity, making it unsuitable for attaching the placenta. Most often leads to placenta previa. But this situation is not considered a pathology. The doctor will adjust the care of the pregnant woman and choose the appropriate method of delivery. Until the 30th week of fetal development, the structure of the placenta should remain homogeneous.
MVP - expansion of the intervillous space and other deviations in the structure of the placenta complicate the supply of oxygen to the baby. With timely treatment, the child is born healthy.
AFI (amniotic fluid index) is an indicator of the amount of amniotic fluid.
| Duration in weeks | Norm, mm |
| 16 | 73-201 |
| 17 | 77-211 |
| 18 | 80-220 |
| 19 | 83-225 |
| 20 | 86-230 |
There is a concept of “moderate” and “pronounced”. If the deviation from these standards is insignificant, and the baby’s development indicators and the mother’s well-being are positive, then there are no threats. Doctors usually recommend appropriate diets, a minimum of physical activity, and may prescribe vitamins. For example, with moderate water deficiency, vitamin E must be taken. A significant deviation requires serious treatment.
The umbilical cord must have 3 vessels. The absence of one or two vessels significantly complicates the development of the baby. Such children are born with low birth weight. In the future, the child will often get sick. But in the absence of congenital anomalies, proper care and nutrition, after a year the weight improves.
The visualization should be designated as “satisfactory.” Possible causes of poor visibility:
- mobility or awkward position of the baby;
- swelling;
- Mommy’s excess weight - the cause of PZH will be indicated;
- hypertonicity of the uterus.
Nasal bone: table
Modern equipment can work wonders if the results of ultrasound examinations are correctly deciphered. As soon as the first indicators are included in the patient’s pregnancy monitoring chart, this serves as a starting point for comparison and further support in the development of the fetus.
If the anomaly is detected in the early stages, the result is not yet considered final; you must undergo a perinatal screening procedure to ensure the accuracy of the diagnosis. It happens that doctors make mistakes, so it is better to exclude the possibility of medical error with the help of modern embryo studies, which can track the growth and development of not only the nasal bone, but also the limbs, the shape and size of the head, the collar area, etc. The main task of accompanying pregnancy is to ensure that the fetus develops harmoniously, and the child is born to the joy of the parents, healthy and strong. To exclude Down's disease, Edwards' disease, Turner's disease, Patau's disease and various facial defects in the unborn child, specialists entered the results of anomalies into the table that we present below.
Further diagnostics
Detection of nasal bone pathology during pregnancy should be a reason for further examination of the woman. Repeated ultrasounds evaluate:
- Changing the size of the nose.
- Thickness of the collar area.
- Dimensions of development of the limbs and torso.
- The presence or absence of hydrocephalus.
- Physiology of the development of the cardiovascular system.
For a more accurate diagnosis, invasive techniques such as amniocentesis are used. During this procedure, the amniotic membranes are punctured and amniotic fluid is taken for examination. They may show signs of genetic diseases.
Having assessed all the data received, the doctor informs the woman of the diagnosis. If severe chromosomal abnormalities are detected during the diagnosis, the woman can make a timely decision about the possibility of prolonging the pregnancy.
Categories
AllergistAnesthesiologist-resuscitatorVenereologistGastroenterologistHematologistGeneticHepatologistGynecologistHomeopathDermatologistPediatric gastroenterologistPediatric gynecologistPediatric dermatologistPediatric infectious disease specialistPediatric cardiologistPediatric ENTPediatric neurologistPediatric nephrologistPediatric ophthalmologistPediatric psychologistPediatric pulmonologistPediatric rheumatologistChildren Chinese urologist Pediatric surgeon Pediatric endocrinologist Nutritionist Immunologist Infectious disease cardiologist Clinical psychologist Cosmetologist Speech therapist ENT and Mammologist Medical lawyer Narcologist Neuropathologist Neurosurgeon Nephrologist Nutritionist Oncologist Oncourologist Orthopedic traumatologist Ophthalmologist Parasitologist Pediatrician Plastic surgeon Proctologist Psychiatrist Psychologist Pulmonary OlogistRheumatologistRadiologistReproductologistSexologist-AndrologistDentistTherapistTrichologistUrologistPharmacistPhysiotherapistPhytotherapistPhlebologistPhythisiatristSurgeonEndocrinologist
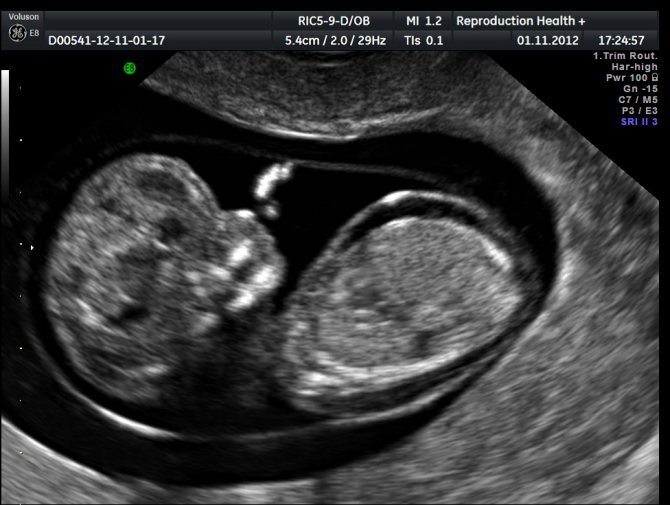
Fetal nasal bone
The timing of the first ultrasound screening is 11–14 weeks, it is at this time that the condition of the fetal nose can be visualized. It is detected during the procedure in the form of three lines:
- The skin is the uppermost and least echogenic.
- The bone is the thickest and most noticeable.
- The tip of the nose is located in front of the first line and slightly above it.
These lines are compared with each other. Normally, the bone part should be more echogenic than the skin and have a certain size corresponding to the gestational age.
Pathology is considered:
- Aplasia is a complete absence of bone tissue; the second line of the nose is not defined at all.
- Hypoplasia is underdevelopment of a portion of the facial skull, the length does not correspond to the period of pregnancy.
- Change in echogenicity - with the second line being less clear and bright than the first.
If pathological abnormalities are detected, the presence of chromosomal pathologies, in particular trisomy 13, 18 and 21, should be suspected. However, in 3 percent of cases at this stage of pregnancy, deviations in the development of bone tissue are observed in healthy children.
Standard ultrasound data during pregnancy
This section provides a summary table of fetometric parameters for each week of pregnancy. All data are for the 10th percentile. Only fetal nasal bone norms are given for the 5th.
*10th percentile means that lower values can be observed in only 10% of the subjects.
Recommendations for using the table
These data are not intended to clarify the duration of pregnancy - completely different tables are used for this. You can find them yourself on the Internet.
The purpose of this table is to roughly determine whether your ultrasound data corresponds to the norms of child development. Precisely “approximately” - because it is quite difficult to decipher your indicators on your own. This is the task of a professional doctor who will take into account a lot of other factors:
- your height;
- nationality;
- Lifestyle;
- data from previous ultrasounds and other tests;
- features of development from the beginning of observations.
In addition, it should be taken into account that the measurement results may differ slightly on different ultrasonic devices.
So, ultrasound usually measures:
- fetal nasal bone length;
- length of the femur, humerus, tibia, forearm;
- Head circumference;
- BDP (biparietal size - measured between the temporal bones);
- fronto-occipital size (LZ).
Additionally, to clarify the diagnosis of developmental delay, the following can be determined:
- tibia length;
- length of the radius and ulna;
- size of the collarbone and scapula;
- size and structure of hands and feet;
- connections of the bones of the skull, structure of the spine.
Comparison table:
| Gestational age | Nasal bone length | Head circumference | Biparietal size | Fronto-occipital size | Femur | Shin bone | Brachial bone | Bones of the forearms |
| less than 2 | 53 | 13 | 3.4 | |||||
| 58 | 18 | 4 | ||||||
| 2,9 | 73 | 20 | 7 | |||||
| 84 | 23 | 9 | ||||||
| 3.6 | 97 | 26 | 13 | |||||
| 112 | 31 | 41 | 17 | 15 | 15 | 12 | ||
| 5–5,2 | 121 | 34 | 46 | 20 | 17 | 17 | 15 | |
| 131 | 37 | 49 | 23 | 20 | 20 | 17 | ||
| 5,5–5,7 | 142 | 41 | 53 | 26 | 23 | 23 | 20 | |
| 154 | 43 | 56 | 29 | 26 | 26 | 22 | ||
| 5,8–6,1 | 166 | 46 | 60 | 32 | 29 | 29 | 24 | |
| 178 | 48 | 64 | 35 | 31 | 31 | 26 | ||
| 6,5–6,9 | 190 | 52 | 67 | 37 | 34 | 34 | 29 | |
| 201 | 55 | 71 | 40 | 36 | 36 | 31 | ||
| 7,2–7,6 | 214 | 58 | 73 | 42 | 37 | 39 | 33 | |
| 224 | 61 | 77 | 45 | 41 | 41 | 35 | ||
| 8,2–8,5 | 235 | 64 | 80 | 47 | 43 | 43 | 37 | |
| 245 | 67 | 83 | 49 | 45 | 45 | 39 | ||
| 8,6–8,7 | 255 | 70 | 86 | 50 | 47 | 47 | 40 | |
| 265 | 71 | 89 | 52 | 49 | 49 | 42 | ||
| 8,9 | 273 | 73 | 93 | 54 | 50 | 51 | 44 | |
| 283 | 75 | 85 | 56 | 51 | 52 | 45 | ||
| 9 | 289 | 77 | 89 | 58 | 53 | 54 | 46 | |
| 295 | 79 | 101 | 60 | 55 | 55 | 48 | ||
| 299 | 81 | 103 | 62 | 56 | 57 | 49 | ||
| 303 | 83 | 104 | 64 | 57 | 58 | 50 | ||
| 307 | 85 | 106 | 66 | 59 | 59 | 51 | ||
| 309 | 86 | 108 | 68 | 60 | 60 | 52 | ||
| 311 | 88 | 109 | 69 | 61 | 60 | 53 | ||
| 312 | 89 | 110 | 70 | 62 | 61 | 54 |
If your ultrasound results do not correspond to the standards given in this table, or after the examination you were diagnosed with “fetal growth retardation”, or even “Down syndrome” - this is not a reason to panic!
General questions about ultrasound during pregnancy
I had an ultrasound at 23 weeks of pregnancy and was told that the baby had severe intestinal echogenicity and needed an ultrasound at 28 weeks to look at the intestines again. After that, I went on my own to another specialist, where I was told that everything was fine with my intestines. At 29-30 weeks, the doctor sent me for an ultrasound at the antenatal clinic, where they again said that everything was fine with the intestines, but they said something that I simply didn’t know what to think. Middle cerebral artery S/D – 6.00 N. Single entanglement. Low in cephalic presentation. Low water with suspended matter, no frontal waters. Placenta l – 26 mm, with extension m in p, subgood. type. Um cord Ri – 0.75 (0.56 – 0.78) a ut sin Ri – 0.45 (0.34-0.64) a ut clex Ri – 0.69. The echogenicity of the intestine is not increased, peristalsis is +. Conclusion: Oligohydramnios, intrauterine infection, hemodynamic disturbances I – A st. Pregnancy 28 – 29 weeks. The doctor prescribed treatment with cocarboxylase, glucose, and ascorbic acid. How serious is it? What does intrauterine infection mean? The blood flow indicators you indicated are all within normal limits, except for the right uterine artery. Asymmetry of indicators of peripheral vascular resistance in the uterine arteries was regarded by doctors as a hemodynamic disorder of stage IA. However, such a situation requires clarification and observation in dynamics. Most likely the blood flow will be normal. The position of the fetus is normal and there are no problems. The entanglement of the umbilical cord and the frequency of entanglement can only be suspected based on ultrasound data with a certain degree of probability, but it is impossible to say so categorically. The thickness of the placenta 26 mm is somewhat small for 29-30 weeks, although it is acceptable. If there really is an identified I degree of placental maturity, then this indicates some placental insufficiency. The expansion of the intervillous space (IVS) usually does not pose a danger, since it is just a compensatory reaction. Oligohydramnios is a serious reason to be wary of placental insufficiency and nothing more. It is not very clear on what basis the conclusion about intrauterine infection was made? Such a conclusion is generally not made based on ultrasound data. One can only assume the possibility of this complication, which is that the placenta, membranes and fetus are affected by some kind of infection. However, this assumption requires serious clarification, primarily using microbiological research methods. Consequently, it is currently necessary to clarify the presence of placental insufficiency, clarify its origin (cause), and confirm (or exclude) intrauterine infection. To resolve these issues, qualified specialist consultation and a number of additional studies are required. You can get all the necessary consultations and examinations at the ART-MED Children's Center.
Summary
Remember that ultrasound results always depend on many factors - the specialist’s experience, the accuracy of the equipment, and even the position in which the fetus was during the examination. The doctor could have made a mistake or simply missed something. Wait for another ultrasound, other tests, contact a specialist in another clinic.
But even if the doctor was not mistaken, you should know that none of the ultrasound parameters indicate a disease with one hundred percent probability. We wish you and your child good health!
Gnomik.ru
Hypoplasia of the nasal bone in the fetus
In recent years, medicine has been rapidly developing as one of the types of natural sciences. And if previously a pregnant woman during the entire period of bearing a child took a small number of tests and underwent an ultrasound examination twice a year, today the development of the child in the womb is monitored by doctors much more carefully and various groups of specialists are concerned about his health.
You should not consider numerous examinations to be a whim of doctors. Modern medicine, with their help, makes it possible to identify various pathologies in an unborn child at an early stage, which can subsequently affect the general health of the baby, and even an adult.
Speaking about hypoplasia of the nasal bone in the fetus, it should be noted that during the formation of the child’s body, the length of the nasal bone is a significant indicator of its future development.
The size of the nasal bone in the fetus can be determined as early as 10-12 weeks of its development using ultrasound examination.
What is hypoplasia of the nasal bones in the fetus?
Any diagnosis of a pregnant woman using a modern and harmless ultrasound examination necessarily involves determining the length of the nasal bone in the unborn child. If the indicator of its length for a given period of pregnancy differs from the standard norm in the direction of decrease, then they say that there is hypoplasia of the nasal bone in the fetus.
Sometimes examination reveals a complete absence of nasal bones. In these cases, they talk about aplasia, that is, the absence of an organ.
Why is information about the length of the nasal bone necessary?
Starting from the 10-11th week of pregnancy, quadrangular bones - the nasal bones - are reflected in the ultrasound of the fetus.
If they do not meet the required parameters - hypoplasia, there is a well-founded and serious fear of the development of severe chromosomal abnormalities in the child.
This type of hypoplasia is a sign of the development of Down, Turner, Patau, Edwards diseases and other serious abnormalities in the unborn child.
During this period, the very presence of such bones is more important, and their size can only be determined from the 11th week of gestation
What is the normal size of the nasal bone during pregnancy?
Of course, each period has its own development dynamics.
At 12-13 weeks, the nasal bone is only 3 mm in length. By 21 weeks, its size can be approximately 5-5.7 mm, and at 35 weeks this figure normally increases to 9 mm.
It is very important to accurately determine the length of the bone during ultrasound examination. To do this, it is necessary for the specialist to be experienced and highly qualified.
In addition, the examination must be carried out using high-precision equipment. Otherwise, the diagnostic result may be called into question.
Nasal bone hypoplasia and other pathologies
Often, having learned about the alleged diagnosis, future parents experience panic and horror in anticipation of the final diagnosis.
But the fact is that based on the size of the nasal bone alone, it cannot be reliably stated that the child will be born with Down syndrome or another chromosomal abnormality.
In case of repeated diagnosis of underdevelopment of the nasal bones, it is recommended to examine the amniotic fluid for genetic analysis, that is, perform amniocentesis.
Fetal development anomalies and diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound
As already noted, to make a diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities, one cannot judge only by the underdeveloped size of the nasal bones identified on ultrasound.
All people are individual by nature and this can be observed even during observation of intrauterine development. Therefore, tabulated values of fetal development are not always a criterion for determining various pathologies. And the length of the nasal bone is no exception.
It is possible to reliably determine whether the unborn child has chromosomal pathologies only if hypoplasia of the nasal bones is accompanied by fetal hypoplasia, i.e. In addition to a shortened nasal bone, he was found to have reduced dimensions of his limbs or internal organs.
Considering all this, there is no need to panic ahead of time.
Even if the next ultrasound examination reveals that the size of the baby’s nasal bone is smaller than the table values, this is not yet a reason to diagnose a genetic anomaly.
It is very possible that your baby is completely healthy and will be born with an elegant small nose. The final diagnosis can only be made by a doctor after various examinations and long-term observations of fetal development.
Nasal bone hypoplasia and other indicators
Many parents, hearing from a doctor that the size of their unborn child’s nasal bone does not correspond to normal values, panic. In fact, it is too early to worry - it is simply impossible to accurately determine Down syndrome or any other chromosomal abnormality in a fetus just by the size of the nasal bones.
In order to confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis, a pregnant woman is recommended to undergo a second ultrasound - with a different specialist and on a different device.
If, upon repeated examination, it is determined that the size of the baby’s nasal bone does not correspond to those that should be at this stage of pregnancy, then the woman is usually recommended to undergo additional examination - amniocentesis, i.e., sampling a small amount of amniotic fluid for subsequent genetic testing. analysis.
Fetal nasal bone at 13 weeks: normal and hypoplasia
Advances in modern obstetric medicine make it possible to detect fetal pathology in the early stages and take timely measures to eliminate it.
A set of medical examinations - prenatal screening - includes the determination of an important parameter, the size of the fetal nasal bone
Prenatal screening
Studies of a pregnant woman’s body during pregnancy can reveal pathologies in the baby’s development. During prenatal screening, biochemical studies and ultrasound are performed.
Already in the first trimester, screening provides reliable information about the state of health of the fetus. During this time, an ultrasound examination can assess:
- The presence of pathology of the heart muscle and valves.
- Patency of the ductus venosus.
- The presence of some signs of congenital malformations.
- The thickness of the collar space is a sign of chromosomal abnormalities.
- Development of fetal nasal bones.
The last indicator is quite important, since already in the first months of pregnancy it allows one to suspect a number of developmental anomalies.
Fetal nasal bone
The timing of the first ultrasound screening is 11–14 weeks, it is at this time that the condition of the fetal nose can be visualized. It is detected during the procedure in the form of three lines:
- The skin is the uppermost and least echogenic.
- The bone is the thickest and most noticeable.
- The tip of the nose is located in front of the first line and slightly above it.
These lines are compared with each other. Normally, the bone part should be more echogenic than the skin and have a certain size corresponding to the gestational age.
Pathology is considered:
- Aplasia is a complete absence of bone tissue; the second line of the nose is not defined at all.
- Hypoplasia is underdevelopment of a portion of the facial skull, the length does not correspond to the period of pregnancy.
- Change in echogenicity - with the second line being less clear and bright than the first.
If pathological abnormalities are detected, the presence of chromosomal pathologies, in particular trisomy 13, 18 and 21, should be suspected. However, in 3 percent of cases at this stage of pregnancy, deviations in the development of bone tissue are observed in healthy children.
The indicator in question should be used solely as a preliminary marker, which requires additional diagnostics.
Norms
Experts have developed tables that include the approximate sizes of the nasal bones at various stages of pregnancy. For practical use, bone sizes in the second and third trimesters are not particularly important; the most valuable are the indicators for the first screening.
Fetal nasal bones by week, table:
In the second trimester, the bone reaches a size of about 6–8 mm, and in the third, about 9 mm. These dates were obtained during a mass examination of pregnant women and represent the average values of this indicator.
It should be understood that ultrasound examination is quite subjective. Even the detection of a deviation from the ideal norm does not allow us to accurately judge the presence of a pathological process.
Cause of pathology
The causes of nasal bone hypoplasia are quite diverse. They may be:
- Adverse effects of medications during pregnancy.
- Intoxication – smoking, alcohol, drug use.
- Hereditary predisposition to the development of chromosomal abnormalities.
- Severe injuries during gestation.
- Infectious pathology. Rubella and influenza viruses, toxoplasma.
- Poisoning with chemicals at work and at home.
- Exposure to radiation and radiation.
Eliminating exposure to adverse factors is very important for normal pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby. https://www.youtube.com/embed/LAI3XKQkx7M
Pregnancy should be planned, it is better that it is preceded by full preconception preparation.
Further diagnostics
Detection of nasal bone pathology during pregnancy should be a reason for further examination of the woman. Repeated ultrasounds evaluate:
- Changing the size of the nose.
- Thickness of the collar area.
- Dimensions of development of the limbs and torso.
- The presence or absence of hydrocephalus.
- Physiology of the development of the cardiovascular system.
For a more accurate diagnosis, invasive techniques such as amniocentesis are used. During this procedure, the amniotic membranes are punctured and amniotic fluid is taken for examination. They may show signs of genetic diseases.
Having assessed all the data received, the doctor informs the woman of the diagnosis. If severe chromosomal abnormalities are detected during the diagnosis, the woman can make a timely decision about the possibility of prolonging the pregnancy.
Normal fetal nasal bone by week
Experts have developed tables that include the approximate sizes of the nasal bones at various stages of pregnancy. For practical use, bone sizes in the second and third trimesters are not particularly important; the most valuable are the indicators for the first screening.
Fetal nasal bones by week, table:
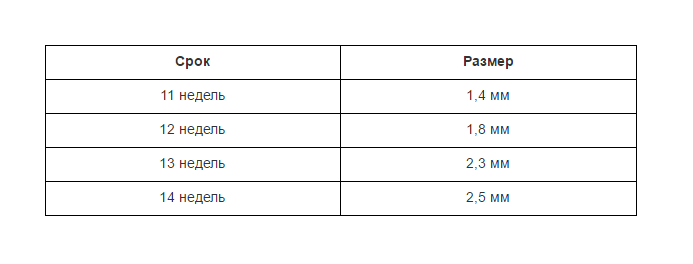
In the second trimester, the bone reaches a size of about 6–8 mm, and in the third, about 9 mm. These dates were obtained during a mass examination of pregnant women and represent the average values of this indicator.
It should be understood that ultrasound examination is quite subjective. Even the detection of a deviation from the ideal norm does not allow us to accurately judge the presence of a pathological process.
Cause of pathology
A chromosomal abnormality or exposure to unfavorable environmental factors can cause a deviation in the development of the nasal bone.
The causes of nasal bone hypoplasia are quite diverse. They may be:
- Adverse effects of medications during pregnancy.
- Intoxication – smoking, alcohol, drug use.
- Hereditary predisposition to the development of chromosomal abnormalities.
- Severe injuries during gestation.
- Infectious pathology. Rubella and influenza viruses, toxoplasma.
- Poisoning with chemicals at work and at home.
- Exposure to radiation and radiation.
Eliminating exposure to adverse factors is very important for normal pregnancy and the birth of a healthy baby.
Pregnancy should be planned, it is better that it is preceded by full preconception preparation.
When is it necessary to perform a fetal ultrasound?
If the pregnancy is not accompanied by pathologies, then 3 routine ultrasounds or perinatal screenings are performed. If there is a suspicion of abnormal fetal development, the doctor will prescribe additional examinations. Women at risk include:
- over 35 years old;
- having relatives with hereditary anomalies;
- those who survived a frozen pregnancy, gave birth to a stillborn child, or experienced spontaneous abortion (miscarriage);
- have had a viral or infectious disease in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- leading an unhealthy lifestyle (systematically using drugs and alcohol);
- forced to take medications on an ongoing basis (hormones, anticonvulsants).
The length of the nasal bone can be assessed already during the first examination. If the data obtained correspond to the table of nasal bone norms at 13-14 weeks, the risk of severe fetal development disorders is assessed as minimal.
At week 20, all the main bones and cartilage are already formed
The second ultrasound is performed at 20-24 weeks. The number of pathologies studied here is much greater, since anomalies are detected that were not identified during the first examination. The doctor may detect that the umbilical cord is entwined around the neck, but this is not an alarming signal, since the baby is constantly moving, which means the umbilical cord can return to its normal position. The condition of the cervix and internal os must be assessed. If the cervix is shortened and the pharynx is open, the woman is sutured to the cervix or a relieving pessary is inserted.
The third screening or ultrasound is carried out at 32-34 weeks, it is final. The specialist examines the size and degree of maturity of the placenta, assesses the presentation of the fetus and the pelvic position, determines the expected weight of the baby at birth, and excludes or confirms entanglement of the umbilical cord. He also gives recommendations on the management of labor tactics, especially if malformations are detected in the child, including suspected chromosomal defects.
Ultrasound at 12 weeks of pregnancy
Nowadays, monitoring the progress of pregnancy is difficult to imagine without ultrasound.
This method is safe, painless and universal in that the doctor has the opportunity to evaluate various parameters of fetal development and the functional characteristics of the placenta, uterus, and umbilical cord. According to the standards established by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, the first screening ultrasound
given to women at 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Why is an ultrasound performed at 12 weeks of pregnancy?
At the end of the first trimester, namely at 12 weeks (perhaps a little earlier or a little later), every pregnant woman should undergo an ultrasound screening. This procedure is carried out for the purpose of:
- Confirm pregnancy (because sometimes tests or blood tests for hCG can give ambiguous results).
- Confirm the correct location and attachment of the fertilized egg with the embryo. The pregnancy must be intrauterine. The ectopic location of the ovum is a serious pathology that requires immediate medical intervention.
- Identification of pathologies of the female reproductive system that can negatively affect the process of gestation. For example, at the first ultrasound, the length of the cervix is assessed. If it is insufficient (1-1.5 mm), this indicates the presence of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, which can lead to miscarriage.
- Determine the gestational age, that is, the length of pregnancy.
- Assess the level of development of the fetus and the preliminary result of the process of laying its main internal organs.
- Assess how correctly and completely the fetal heart muscle is formed.
- Identify primary markers of chromosomal or genetic disorders. Not all such pathologies can be detected at 12 weeks, but, for example, it is possible to suspect Down syndrome in an unborn child after the first screening.
An ultrasound at the 12th week of pregnancy (screening examination norms will be described below) is also the first opportunity for the expectant mother to see her baby, which, of course, causes a lot of positive, useful emotions.
What does the nasal bone tell you?
It is important to determine the presence or absence of a nasal bone, that is, visualization or visibility. Since active growth occurs in the second trimester
Although some experts insist on the importance of not only visualization, but also measuring bone length, regardless of the timing. It is believed that ossification of the nasal bone in children with Down syndrome occurs much later. In medicine, this deviation is called “hyperplasia”.
In addition to the nasal bone, the following should be clearly visible on the monitor:
- skull bones;
- spine;
- bones of the arms and legs;
- bladder;
- abdominal wall.
Given the controversial nature of the situation, this indicator is considered additional. Measuring the nasal bone is one of the most difficult for many specialists.
A small nasal bone may also indicate that the newborn baby will have a short, snub nose in the future.
How is 1st screening carried out, preparation
Ultrasound in the first trimester can be performed in two ways:
- transvaginally;
- abdominally.
In the first case, no preparation is needed. When performing an abdominal ultrasound, it is necessary that the woman’s bladder is full - for this purpose, it is recommended to drink 2 glasses of water half an hour before the procedure.
You need to donate blood for biochemical analysis on an empty stomach - you cannot eat at least 4 hours before the procedure. This is especially true for sweets, fatty foods, meat and seafood. Failure to comply with this diet may lead to errors in the analysis.
How is amniocentesis performed?
The study involves the collection of amniotic fluid from the embryonic membrane. It contains fetal cells, which act as material for analysis. Amniotic fluid
used for a number of analyses:
- hormonal;
- immunological;
- biochemical;
- clinical.
But to identify the pathology of embryo development, a cytological examination is performed.
- The fluid is withdrawn using a thin needle, the movements of which are controlled using an ultrasound sensor.
- As a rule, anesthesia is not required during the procedure, but if the pregnant patient wishes, the doctor can numb the area where the needle is inserted.
- The amniocentesis process lasts no more than one and a half minutes, after which the patient is asked to spend a couple of hours in the ward under the supervision of medical personnel.
The study is considered safe, but before conducting it, it is necessary to collect the patient’s medical history to exclude complications, for example, bleeding due to decreased blood clotting.
Every woman needs examinations during pregnancy. Hypoplasia of the nasal bone cannot be treated, but it indicates the risk of pathologies, which are best known about as early as possible in order to have time to take the measures that the doctor will suggest to the patient.
https://uzikab.ru/prenatalnaya/nosovaya-kost-u-ploda-na-uzi.html https://flovit.ru/beremennost/diagnostika/nosovaya-kost-ploda-v-13-nedel-norma.html https://www.gnomik.ru/articles/art-gipoplaziya-nosovoy-kosti-u-ploda/
Experts can judge how healthy a child will be born long before he is born. Using ultrasound, doctors carefully study the proportions of the little man to understand whether the size of the embryo corresponds to the norm for obstetric weeks. Are his limbs and organs developing correctly? Are there any obvious markers of chromosomal abnormalities?
The first ultrasound of the expectant mother is prescribed at 10–14 weeks of pregnancy. Already at this time, doctors draw the first conclusions from their observations. Doctors are especially interested in the size of the child’s nasal bones. This parameter allows you to draw some conclusions about the general health of the baby.

12–13 obstetric weeks is the most appropriate time to try for the first time to visualize the proportions of the baby’s face using ultrasound. It is at this stage that children are usually diagnosed with hypoplasia of the nasal bones - one of the clearest markers of genetically determined fetal malformations.
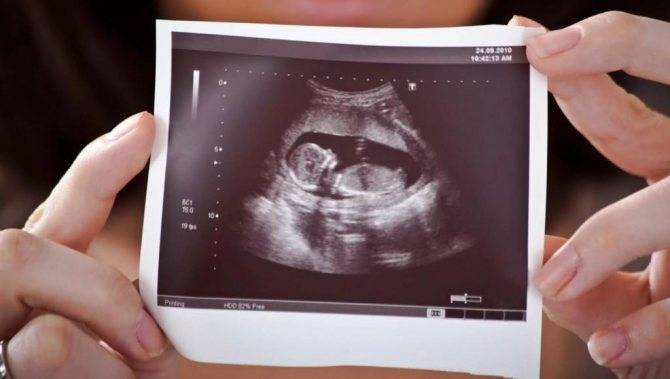
What it is?
Hypoplasia (underdevelopment) of the nasal bones is a clear discrepancy between their length and acceptable parameters (shortness). In most cases, the presence of this pathology indicates serious chromosomal abnormalities and an abnormal karyotype of the fetus. This is often a symptom of Down, Turner and Edwards syndromes in a child.
An ultrasound specialist can detect the first signs of fetal nasal bone hypoplasia as early as 12–13 obstetric weeks of pregnancy. However, it is too early to talk about 100% accuracy of diagnosis at this time. Unlike aplasia (the complete absence of nasal bones), hypoplasia may turn out to be false, and by the 20th week of gestation the baby’s indicators will reach normal sizes and proportions.
What are the causes of pathology?
Like any genetic disorder, hypoplasia can be triggered by many factors of different nature and nature. Those children whose mothers are included in the “risk group” are most susceptible to developing pathology:
- They are regularly exposed to toxic effects. They smoke, drink, use drugs. They take potent medications on an ongoing basis. They do not pay attention to the quality and freshness of the food they eat (they often become victims of food poisoning). They live in a region with an unfavorable environmental situation and can receive doses of toxins from the outside.
- The illness that occurred during the first trimester of pregnancy was difficult to endure. Infections (rubella, influenza) pose a particular danger in this regard, but ordinary ARVI can also have a negative impact.
- Were exposed to adverse external influences in the first weeks of pregnancy. For example, they received severe injuries, abdominal bruises, overheated in the sun or were exposed to other types of radiation, etc.
- They have bad heredity. During gestation, one of the woman’s closest blood relatives was diagnosed with fetal hypoplasia.
Standards for screening 1:
The indicators of 1 screening screening may vary - during this period, intensive growth of bones and internal organs of the fetus begins, so a difference in the period at which an ultrasound is performed, even a couple of days, can lead to differences in measurements.
During the first screening, the following indicators must be measured:
- thickness of the collar area;
- nasal bone size;
- coccyx-parietal size;
- heart rate;
- biparietal size of the head (the distance between the outer and inner contours of both parietal bones).
These values differ greatly depending on the period: for example, the width of the baby’s head at 10 weeks should be approximately 14 mm, at 12 - from 20 mm, and at 13 exceed 26 mm.
There is no need to try to decipher the results of ultrasound screening on your own - a competent specialist will do this and explain to the expectant mother what all these mysterious numbers mean. In our clinic you will be able to get comprehensive answers after passing the screening - our specialists will tell you about the baby’s condition and his health.
Clinic "ABIA" - caring for the baby from the first days!
The importance of the first ultrasound screening should not be underestimated, because it allows early assessment of the fetal health status and possible risks of pathologies. The ABIA clinic offers a wide range of services for expectant mothers: from complete pregnancy management to individual procedures. With us you can undergo ultrasound and biochemical examination at 11-13 weeks of pregnancy. The clinic’s modern equipment allows us to determine with maximum accuracy how healthy the baby will be born and what possible risks exist. You will receive recommendations from an experienced doctor that will help keep your baby as healthy as possible, as well as the first photos and videos from the ultrasound. Feel the joy of motherhood and start taking care of your baby long before he is born!
Nasal bone on ultrasound: normal at 12 weeks and fetal NK hypoplasia (small nose)
Advances in modern medicine make it possible to carefully monitor pregnant women and identify those who are at risk for possible chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus. Thus, ultrasound examination of the fetal nasal bone (NB) is an important diagnostic tool for identifying possible anomalies.
Why is it necessary to measure the fetal nasal bone?
The length of the nasal bone is an indicator of the normal development of the fetus. There are two pathological conditions – hypoplasia and aplasia. Hypoplasia is a decrease in its length, and aplasia is the absence of this bone.
Both of these conditions indicate the presence of pathologies in the fetus associated with chromosomal abnormalities. This indicator is detected through ultrasound.
Its normal values indicate intrauterine development without deviations.
If it is clear that the indicators are small, i.e. If there are deviations in the direction of decrease, then this condition is a sign of hypoplasia. An obvious pathology and deviation is the absence of bones, which indicates the absolute underdevelopment of this organ and a gross anomaly. This happens rarely, in exceptional cases.
The nasal bone is visualized by ultrasound already at 10-11 weeks. Deviations in this indicator are considered a sign of certain diseases caused by chromosomal abnormalities. These are conditions such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome, etc.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the presence of this bone in the fetus is important, and measurement of its size for diagnostic purposes should be made no earlier than 12-13 weeks.
With hyperplasia or aplasia detected on ultrasound, one can suspect not only abnormal intrauterine development, but also Down syndrome.
In this case, it is necessary to conduct an additional examination after 2 weeks to monitor the situation.
When deciphering, it should be remembered that, first of all, the fact that the fetus has a nasal bone is important, and measurement indicators at this stage are not so informative, since chromosomal abnormalities for this marker appear somewhat later.
However, we should not forget that the conclusion about chromosomal abnormalities leading to the birth of a child with serious illnesses is a serious diagnosis that requires careful verification and detailed analysis.
Diagnosis of hypoplasia
At 10 weeks of pregnancy, ultrasound can be performed to measure various parameters of the fetus that characterize its development. The discrepancy between their indicators and the norm is the basis for making assumptions about possible developmental deviations.
The study will provide objective data on intrauterine development and assess the degree of chromosomal abnormalities. However, even if the ultrasound showed a small nose that does not correspond to the norm, you should not despair ahead of time.
This parameter alone is not always enough to issue a conclusion about the presence of a disease and severe pathology.
Despite the fact that the first screening indicators have important diagnostic value, it is necessary to conduct a more in-depth examination and wait for its results. When diagnosing pathologies, we must not forget about the individuality of any organism, which is characteristic even at the level of intrauterine development
When diagnosing pathologies, we must not forget about the individuality of any organism, which is characteristic even at the level of intrauterine development.
Due to such features, when measuring important indicators, in this case the nasal bone, they may differ slightly from the given standard values.
Therefore, it is advisable to say with a high degree of confidence that there are chromosomal abnormalities only in the presence of general fetal hypoplasia.
In this case, reduced sizes of all limbs and organs are noted. All this suggests that the difference between indicators and the accepted norm is not always a sign of one or another developmental defect. This can only be an individual characteristic of the unborn child, and he will be born a completely healthy baby. Only a doctor is able to correctly decipher the examination results and make a diagnosis.
Interpretation of ultrasound results at 12-13 weeks
The pregnancy period is a very important period for a pregnant woman and for the unborn child. The process of embryo growth and development is very dynamic, especially during the first trimester of pregnancy. An ultrasound scan during pregnancy helps:
- evaluate fetometric indicators, determine the correspondence of parameters to the gestational age according to menstruation and diagnose intrauterine growth retardation or prerequisites for its development
- evaluate the anatomical structures of the fetus, detect anomalies and malformations at the intrauterine stage
- detect echographic markers of chromosomal diseases and, based on this, create a risk group among pregnant women for more careful monitoring
- study the condition of the placenta, amniotic fluid, umbilical vessels, which provides additional information about the course of pregnancy.
Taking this into account, ultrasound examination should be carried out as quickly as possible.
However, disputes about the number of studies and timing are still relevant to this day. Programs differ from country to country, but most countries have adopted the “10-20-30” scheme, according to which ultrasound is performed for pregnant women three times at 10-14 weeks, 20-24 and 30-34 weeks.
During the first trimester, the best time for ultrasound screening is 12-13 weeks. Diagnostics during this period makes it possible to assess the gestational age and the correspondence of fetal development to this period.
Also, the results of the first ultrasound help to form risk groups and set the date for the next sonography.
Average internal diameter of the ovum
Average internal diameter of the fertilized egg (SVD)
The error in determining the gestational age according to the SVD is up to 10 days, which reduces its significance in the present period. However, this indicator is included in the protocol for screening ultrasound examination at 10-14 weeks.
The error in determining the gestational age according to the SVD is up to 10 days, which reduces its significance in the present period. However, this indicator is included in the protocol for screening ultrasound examination at 10-14 weeks.
| Gestation period (weeks) | Average diameter of fertilized egg (mm) |
| 12 | 53 |
| 13 | 60 |
By the end of the 12-13th week, the fertilized egg is destroyed and this parameter cannot be assessed. Coccygeal-parietal size of the fetus.
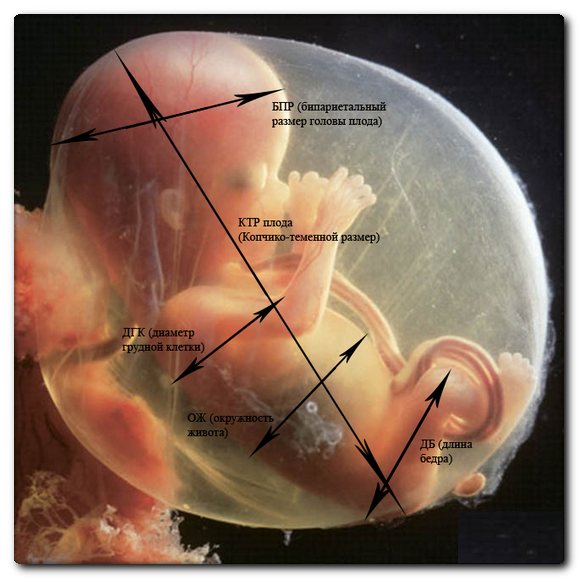
Fetometry indicators on ultrasound
KTR is the maximum length of the fetus, which is measured from the outer edge of the head end to the tailbone. The measurement is carried out several times at maximum fetal extension during longitudinal scanning, the smaller of the obtained values is taken as true.
CTE values at 12-13 weeks.
| Gestation period (weeks) | Coccygeal-parietal size (mm), percentile values | ||
| 5th | 50th | 95th | |
| 12 | 42 | 51 | 59 |
| 13 | 51 | 62 | 75 |
The coccygeal-parietal size is used to determine the duration of pregnancy (since it does not depend on the personal characteristics of the woman), as well as as a marker of pathology on the part of the expectant mother or child.
An increase in CTE above the 95th percentile can be caused by a Rh conflict between the mother and the unborn child, or by the presence of diabetes mellitus in the mother. A decrease in CTE below the 5th percentile can occur as a result of: non-developing pregnancy, infectious diseases in the mother, hormonal imbalance of the woman, genetic diseases of the fetus.
Collar thickness
The nuchal translucency thickness (TNT) is considered to be the size measured from the inner edge of the skin to the outer contour of the soft tissues in the area of the cervical vertebrae. Assessment of this indicator is mandatory in the first trimester and requires compliance with a number of conditions:
- gestation period 10-14 weeks
- CTE of the fetus in the range of 45-84 mm
- The maximum size obtained during scanning in a strictly sagittal plane is considered true.
Standard values of TVP
| Gestation period (weeks) | Neck thickness (mm), percentile values | ||
| 5th | 50th | 95th | |
| 12 | 0,8 | 1,7 | 2,6 |
| 13 | 0,8 | 1,8 | 2,8 |
An excess of the TVP value above the 95th percentile is considered pathological . Exceeding the normative values of the nuchal translucency is associated with the formation of heart defects in the unborn child or chromosomal diseases (usually trisomy 21). However, deciphering the increase in TVP should be carried out in combination with other highly informative research methods (amniocentesis, chorionic villus biopsy, fetal karyotyping).
Heart rate
Determination of fetal heart rate is mandatory for ultrasound examination in each trimester. The heartbeat is detected from the 5th week of intrauterine development (with transvaginal examination it is also possible at the 3-4th week).
| Gestation period (weeks) | Heart rate (bpm) |
| 12 | 151-175 |
| 13 | 146-170 |
A decrease in heart rate (less than 120 beats/min) can be caused by intrauterine hypoxia and an abnormality of the umbilical vessels. An increase in heart rate may be caused by hypoxia and stress factors. If the heartbeat of a fetus older than 5 weeks or in an embryo longer than 8 mm cannot be detected, this is a sign of a non-developing pregnancy. Fetal heart rate, together with other indicators, is used to determine the risk group for heart disease.