Pregnancy is a difficult period in the life of any woman, entailing a number of difficulties of both a physical and emotional nature. One of the important points in overcoming these difficulties is the timely implementation of a set of measures and procedures aimed at maintaining the health of the expectant mother.
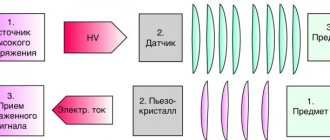
Echocardiography, or in other words, ultrasound of the heart, is an important study, which is an ultrasound scan of the heart muscle. This procedure allows you to identify not only the malfunction of the heart, but also analyze the condition of all its valves, as well as determine the average speed of blood circulation.
Such indicators are important components of the overall health of the mother and unborn child, and also help to analyze the degree of risk of developing heart disease. It is important to know that timely detection of cardiac abnormalities in a pregnant woman allows the appropriate treatment to be prescribed in a timely manner and makes it possible for the expectant mother to bear a healthy baby. For this reason, heart ultrasound for pregnant women in Moscow
is a fairly common procedure.
You can make an appointment with a cardiologist from our consultants by calling +7 (495) 125-49-50
Prices for cardiologist services Addresses of clinics Cardiac ECHO Cardiologist Pain in the heart Calling a cardiologist to your home
Ultrasound of the heart is an important procedure during pregnancy
Heart disease during pregnancy is extremely dangerous for the mother and her unborn child. It should be remembered that during pregnancy, the load on the heart of the pregnant mother increases due to increased body weight, which increases the risk of heart disease and jeopardizes the very process of safe childbirth. These factors clearly indicate that cardiac ultrasound for pregnant women
for women is a very important and recommended procedure.
Heart ultrasound is not included in the list of mandatory studies, but it is prescribed to pregnant women in the following cases:
- pain in the chest area;
- the presence of increased fatigue, lethargy or the appearance of severe shortness of breath;
- high blood pressure;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- sudden weight loss or gain;
- the occurrence of tachycardia attacks;
- detection of heart murmurs by listening and much more.
Evaluation parameters and norms
Interpretation of ultrasound of the heart
During the examination, the doctor determines the following indicators and their compliance with accepted standards:
- anatomical location of the heart (correct/incorrect);
- organ size (must be equal to 1/3 of the cross section);
- the angle of the heart axis in relation to the midline of the chest (ideally 45 degrees);
- chambers of the heart (relatively equal in size);
- purity of the sound of the fetal heartbeat (without pronounced acoustic phenomena in the form of creaking, whistling, etc.).
- interventricular and atrial septa (without deformations);
- organ tissue (without pathological changes);
- rhythmicity of cardiac work (clear, without interruptions).
Heart rate is determined according to the table, according to the perinatal period.
The permissible deviations of the fetal heart rate are shown in parentheses.
Preparing for the procedure and conducting the study
Heart ultrasound for pregnant women
women do not require advance preparation. The only necessary condition is to carry out a number of tests before echocardiography, namely:
- general blood test;
- general urinalysis;
- electrocardiograms with interpretation.
You must take the results of these tests with you to the cardiac ultrasound procedure. The procedure itself is carried out quickly and painlessly with the application of a special gel to the area being examined. The patient does not feel any discomfort during the ultrasound.
The results of the study are displayed on the device screen and reported immediately. Based on their results, a special conclusion is issued. If heart pathologies are detected, the pregnant woman is referred to a cardiologist for monitoring and appropriate treatment. Prices for ultrasound for pregnant women
quite affordable for the budget of a young family.
Timing of the examination
The doctor decides on an individual basis at what time to perform an ultrasound. For some patients, this procedure is prescribed repeatedly, as the child’s heart forms and develops. The device detects the first heartbeat at 4–5 weeks. This sign also determines the number of embryos in the uterus (multiple pregnancy), in this case the beating of two or more hearts will be heard. Heart rate is first determined around the seventh week.
Ultrasound will show the cardiac chambers (atria, ventricles) no earlier than at 14 weeks. Smaller vascular structures are visualized in the middle of the second trimester (starting at 18 weeks). The choice of how many weeks to undergo the examination depends on the information the doctor needs. The optimal period from which week to monitor the baby’s cardiac activity is considered to be 12–22.
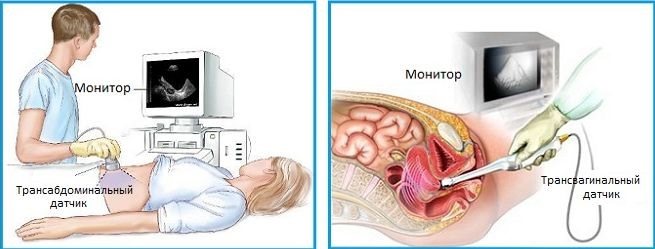
Ultrasound diagnostics externally and internally
Why should you have an echocardiogram?
Heart ultrasound for pregnant women
is an important procedure, the results of which determine the health of not only the mother, but also the child. This study does not take much time, but it makes it possible to feel confident about the healthy future of your baby.
A healthy child is the key and guarantee of a happy family life. Cost for heart ultrasound for pregnant women
women is an acceptable and necessary payment for safe childbirth and a healthy life for the unborn child.
This article does not constitute medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for consultation with a physician.
Modern echocardiography, heart murmurs, pregnant women and diving
Ultrasound scanner WS80
An ideal tool for prenatal research.
Unique image quality and a full range of diagnostic programs for an expert assessment of a woman’s health.
Experience in the diagnostic and treatment department allows us to divide patients who come for echocardiography into certain groups, depending on the reasons for their visit.
The first category will be pregnant women
, since an echocardiographic examination is considered mandatory and is included in the examination plan.
The second, numerous category will consist of young people
with cardialgia.
The third group will consist of patients with chronic heart pathology
who need dynamic monitoring (congenital and acquired defects, etc.) or clarification of the diagnosis.
The fourth group will consist of patients with new complaints of pain in the heart area
, shortness of breath, manifestations of heart failure.
This group of patients is the most serious, because among them one can find “acute” pathology (aneurysm of the thoracic ascending aorta, thromboembolism in the pulmonary artery system, development of aneurysm of the left ventricle, etc.). The fifth group will consist of patients with a heart murmur
. We will try to explain the capabilities of echocardiography in the diagnosis of heart pathology and differential diagnosis. To do this, we will try to analyze the above groups of patients.
Echocardiography during pregnancy
During pregnancy, a healthy woman can experience minor changes in the size of the heart cavities and changes in hemodynamics compared to the baseline. Systolic pressure in the pulmonary artery can increase to 40 mmHg. Art. The diameter of the aortic root, left atrium and left ventricle may increase by 2 - 3 mm. The heart rate increases by 25 - 30%, and already in the first trimester of pregnancy the minute volume of blood flow and stroke volume increase. Blood pressure does not change. The degree of valve regurgitation increases (on the tricuspid valve and pulmonary artery valve to degree 3, on the mitral valve to degree 2). In rare cases, a reaction of the pericardial layers can be observed - the presence of a small amount of fluid in the pericardium. The fluid disappears 1 to 3 months after birth in the absence of treatment.
One of the features in pregnant women is dynamic stenosis of the inferior vena cava. This phenomenon may be accompanied by an auscultatory picture - noise during auscultation and syncope that occurs when the body position in space changes. In some cases, during pregnancy, the oval window opens and a slight shunt of blood from left to right is noted. All of the above changes usually disappear after childbirth. Dynamics are best carried out 1 - 3 months after birth.
Causes of cardialgia - pain simulating pain in the heart
The most common cause of cardialgia in young people is overwork, stress and hypokalemia (potassium deficiency). Sometimes in this category of patients one can observe a slight prolapse of the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve into the cavity of the left atrium, which is a variant of the hole for young people and children (Fig. 1). This prolapse should not be confused with pathological prolapse when there are organic changes in the valves (for example, with myxomatous degeneration - Fig. 2).
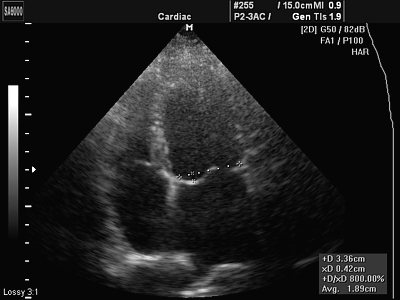
Rice. 1.
Minor prolapse of the anterior leaflet of the mitral valve (normal variant).
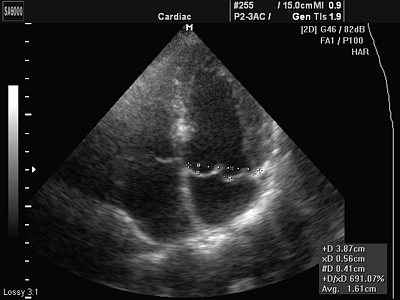
Rice. 2.
Myxomatous degeneration of the mitral valve leaflets.
A differential diagnosis can be made at an appointment with a cardiologist or therapist. As a rule, after a conversation with the patient and auscultation, the doctor prescribes an ECG and EchoCG examination. If an electrolyte imbalance is suspected, a biochemical blood test is recommended.
In patients with chronic heart disease
, for example, rheumatic heart disease, congenital heart disease, prosthetic heart valve, etc. Echocardiography is performed once a year or once every 2 years. Echocardiography allows you to assess the condition and structure of the heart valves, the degree of defect, the condition of the prosthesis, the systolic function of the ventricles of the heart, the condition of the aortic walls, the degree of pulmonary hypertension, the condition of the pleural cavities and pericardium, etc. (Fig. 3 and 4). In some cases, patients come to clarify the degree or nature of the defect.
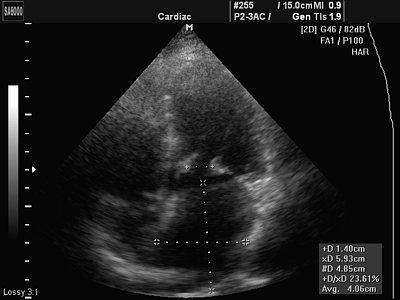
Rice. 3.
Rheumatic heart disease - mitral valve stenosis.
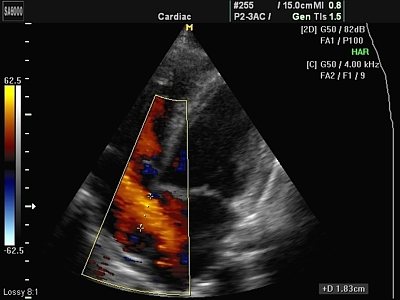
Rice. 4.
Congenital heart disease - atrial septal defect. Dilation of the right chambers of the heart, shunting blood through the defect in color Doppler mode.
Patients with new complaints of pain in the heart area and clinical manifestations of heart failure
are the most serious group of those examined and often require a more detailed examination (for example, coronary angiography) or consultation with a cardiac surgeon or vascular surgeon (Fig. 5).
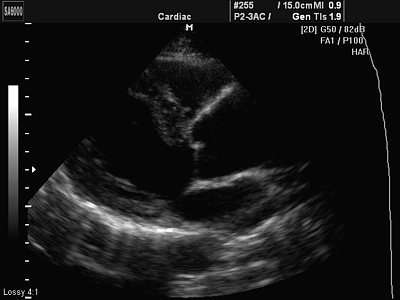
Rice. 5.
Aneurysm of the ascending aorta.
The causes of heart failure are varied. The echocardiography technique allows for closer verification of the diagnosis, and in some cases, an accurate diagnosis.
Heart murmurs
One of the most common reasons for referral to echocardiography is the presence of a heart murmur.
In the “pre-echocardiographic” era, it was in some cases difficult to distinguish normal functional murmur from pathological one. Let's try to list the causes of the most common normal functional murmurs in the heart area. They are especially good for children, teenagers and thin people.
Additional chord in the cavities of the ventricles (false chord or false chord)
- a filamentous structure located in the cavity of the left or right ventricle. Located between the interventricular septum (IVS) and the wall of the heart, the head of the papillary muscle and the wall, etc. The base of the accessory chord does not thicken during systole. The number of chords may vary. Occurs in 98% of cases (Fig. 6).
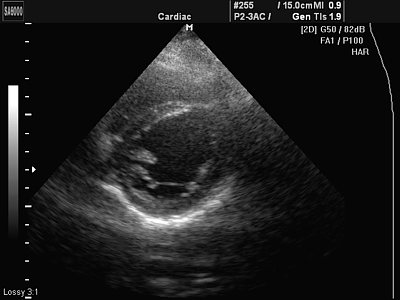
Rice. 6.
A minor developmental anomaly is an additional chord in the cavity of the left ventricle (normal variant).
Additional muscle trabecula in the ventricular cavity (false trabecula)
- a muscular structure located in the cavity of the left or right ventricle. Often located parallel to the interventricular septum or transversely between the walls of the ventricle. The base of the accessory muscle trabecula thickens during systole. Occurs in 85% of cases (Fig. 7).
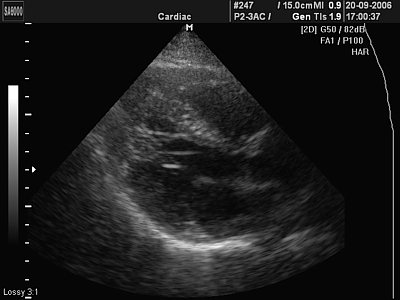
Rice. 7.
A minor developmental anomaly is an additional muscle trabecula in the cavity of the left ventricle and two additional chords (normal variant).
Eustachian valve of the inferior vena cava
- vestigial valve. Does not play any role in cardiac hemodynamics. Occurs in 20% of cases.
Hiari network
- rudiment, continuation of the Eustachian valve of the inferior vena cava into the coronary sinus. Occurs in 2% of cases.
Aneurysm of the interatrial septum
Atrial septal aneurysm (ASA)
- a congenital feature of the development of the interatrial septum. The membrane of the fossa oval is elongated and bulges to the side (Fig. 8). There are a number of types of atrial septal aneurysm:
- type L - bulging of the fossa ovale membrane towards the left atrium.
- type R - bulging towards the right atrium (Fig. 9).
- Type R - L - bulges to the right and then to the left.
- Type L - R - bulging to the left and then to the right - occurs in 5% of cases.
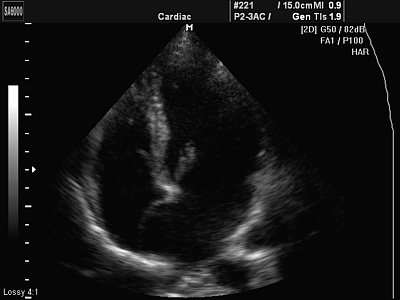
Rice. 8.
Aneurysm of the interatrial septum.
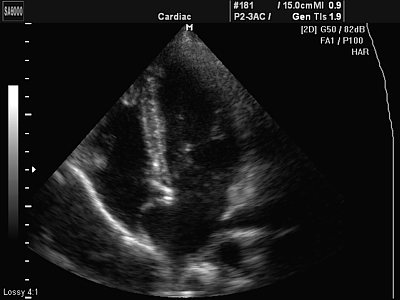
Rice. 9.
Aneurysm of the interatrial septum - type R.
If the aneurysm is very large and protrudes significantly into the atrium cavity, it can be regarded as a congenital defect of the interatrial septum (extremely rare). If there is an atrial septal defect in the area of the atrial septal aneurysm, the situation is regarded as a congenital heart defect.
Aneurysm of the membranous part of the interventricular septum
- rare (0.5 - 1% of cases).
Accessory heads of papillary muscles
- their number can be different and, according to anatomists, can reach 16, the sizes of the heads are also different. The more papillary muscles in the ventricular cavity, the more chordae extend from them.
Non-closure of the oval window
- a variant of the development of the membrane of the fossa oval, occurs in 25% of people. The valve of the fossa ovale membrane covers the oval window. There is no shunting of blood, but it can occur in a number of situations (for example, with a sharp increase in pressure in the cavity of the left or right atrium).
Patent foramen ovale
- occurs less frequently (1 - 2% of people).
Currently, in pediatric practice
there is an overdiagnosis of an open oval window. In this case, blood shunting occurs from left to right, is intermittent, and the volume of the shunt is small. There is no pulmonary hypertension or dilatation of the right chambers. Color Doppler allows you to clarify the presence or absence of an open oval window. These patients require observation once every 2-3 years.
Contraindications for diving
The only contraindication for people with a patent oval window is diving (scuba diving). In any case, whether you are going to Egypt or Thailand and want to plunge into the enchanting world of the seabed, or spend time in the city, do not be lazy to go to a cardiologist and undergo an echocardiographic examination. This will avoid tragic consequences.
Ultrasound scanner WS80
An ideal tool for prenatal research.
Unique image quality and a full range of diagnostic programs for an expert assessment of a woman’s health.