Echo-CG, or echocardiography, is a simple and painless study, which, thanks to ultrasonic vibrations, allows you to obtain sufficiently voluminous information about the condition of the heart. Due to its non-invasiveness and the absence of absolute contraindications, the procedure is performed for both adults and children almost from the first days of life.
During a short diagnosis, the slightest disturbances in the structure and functioning of the heart muscle are revealed without much difficulty, confirming the doctor’s suspicions about the presence of pathology. At the same time, it is often possible to identify deviations that do not manifest themselves in any way, but are considered no less dangerous than the signs that worry the patient.
Description of the method
Echocardiography is a simple and painless medical procedure that shows possible problems in the functioning of the heart. The essence of echocardiography is the use of ultrasound - high-frequency waves that are not detected by our hearing organ.
Using a special sensor attached to the patient's body, the waves penetrate the tissue, as a result of which their main characteristics change - frequency and amplitude. These changes depend on the condition of the organs. Waves with changed characteristics return to the sensor, where they are converted into an electrical signal.
The next stage is processing with an echocardiograph. As a result, a complete picture of the study of the organ from all sides is formed. On the monitor, the doctor sees a flat or three-dimensional image, which, if necessary, can be transferred to a sheet of paper.
Ultrasound waves were first used to determine the condition of the heart by Swedish scientists in the 50s. last century. They created a special device with which it was possible to receive signals from the heart ventricle and one of the valves.
More than half a century has passed since the creation of the device. Since then, it has been modernized, and along with it, ultrasound diagnostics of the heart has improved.
Types of Echo CG and their differences
There are several types of cardiac ultrasound. Basically, methods are divided according to the method of access to the muscle organ.
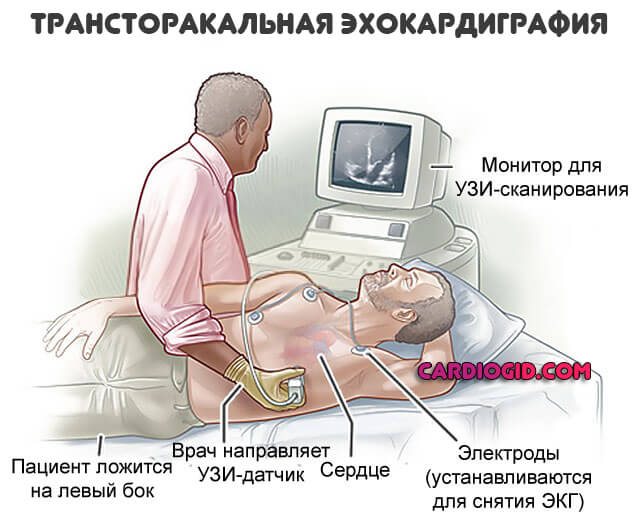
- Classic or transthoracic form, through the anterior wall of the sternum. This is the most common option. Gold standard for primary diagnosis. The ultrasound sensor is placed on the chest, after which the doctor changes its position. To visualize tissues in different projections and from several angles.
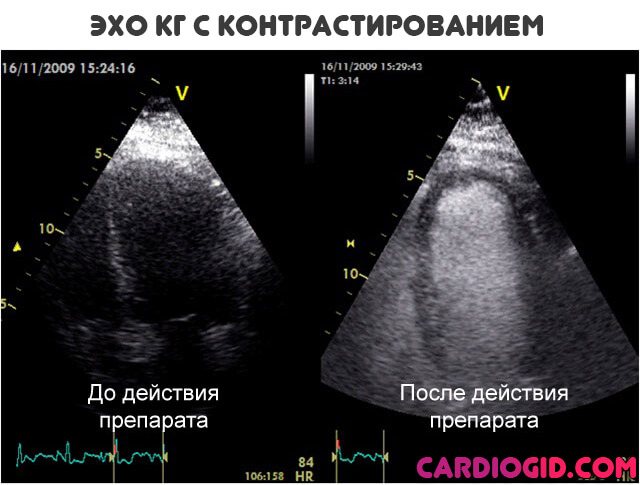
- The second option is an ECHO study with contrast enhancement. In essence, it’s the same transthoracic ultrasound. But this time special substances are injected intravenously. They accumulate in blood vessels, tissues and enhance the reflection of ultrasonic waves. Makes the picture clearer. In general, the method differs little from the previous one. From a technical point of view, everything is the same. But with contrast you can get much more information.
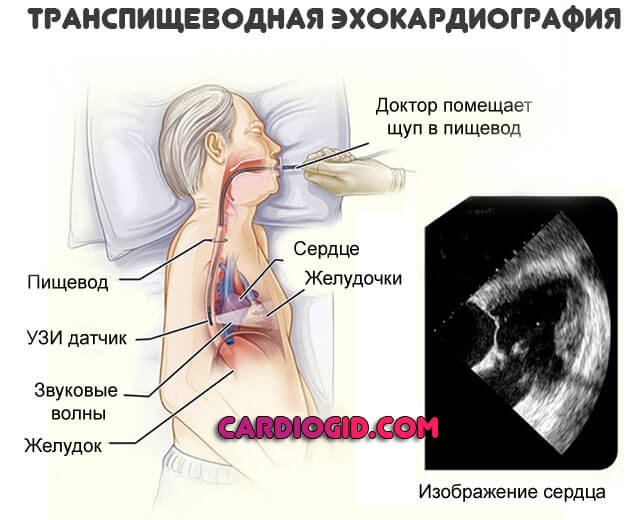
- Finally, transesophageal echocardiography. Invasive research. Due to its high complexity, it is performed only in a hospital setting. Moreover, problems and unforeseen disorders are possible afterwards. It is considered a particularly accurate method compared to others. The technique is used if previous modifications have not produced results.
Another way of classification is by the nature of the study.
- ECHO at rest. Occurs especially often. This is a typical cardiography.
- Assessment of cardiac condition after exercise. Appointed in controversial situations.
Classification
The procedure can be carried out using one of several methods. The main difference between them is the way the signal is reproduced. This can be 1 of 3 types of modes.
Each mode has a distinctive letter in its name:
| Mode | Description |
| A | The letter "A" indicates the relationship with amplitude. A-mode is the recording of signals in the form of peaks. The intensity of the signal is related to the amplitude. |
| M | In M mode you can see moving structures. This mode is based on movement. The letter M is English and stands for the word “motion”, which translates as “movement”. M-mode is most often used in diagnostics. Together with it, 2-dimensional echocardiography and Doppler echocardiography are performed. When an examination is carried out in M-mode, signals are sent along a single selected axis. As a result, an image of the heart is formed in the 1st plane. This regime can be used even for recently born children. When performing 2-dimensional echocardiography, an image is obtained in 2 planes. Therefore, the specialist conducting this examination has the opportunity to study the movement of the heart structures and analyze it. |
| IN | In this mode, the intensity of the signals is demonstrated by the brightness of the light. The mode got its name from the initial letter of the English word “brightness”, which translated into Russian means “brightness”. |
Doppler
Through a procedure called Doppler echocardiography, the speed of blood flow and its turbulence can be determined.
The method is based on the so-called Doppler effect. Its essence is as follows: the speed at which an object moves affects the frequency of the supplied signal.
Transesophageal
The examination methods named and described above are transthoracic echocardiography. It is not always possible to perform such a procedure. It cannot be carried out when there are sound barriers that do not allow the signal to pass through.
This barrier, for example, can be subcutaneous fat. In this case, another type of echocardiography is used, which is called transesophageal. The essence of this procedure is as follows: first the patient must swallow the sensor, then an examination is carried out.
This procedure can additionally be performed after conventional echocardiography. In this case, it will allow you to obtain additional data and clarify the diagnosis. This type of examination becomes especially relevant when it is necessary to obtain information about those parts of the heart that are located near the esophagus and at the same time remote from the surface of the body.
However, it is worth keeping in mind that this method of echocardiography is contraindicated for those who have problems with the esophagus.
Stress
This echocardiography is used to identify hidden pathologies that may appear during stress. In addition, this method allows you to identify problems that arise during heavy physical activity or under the influence of medications.
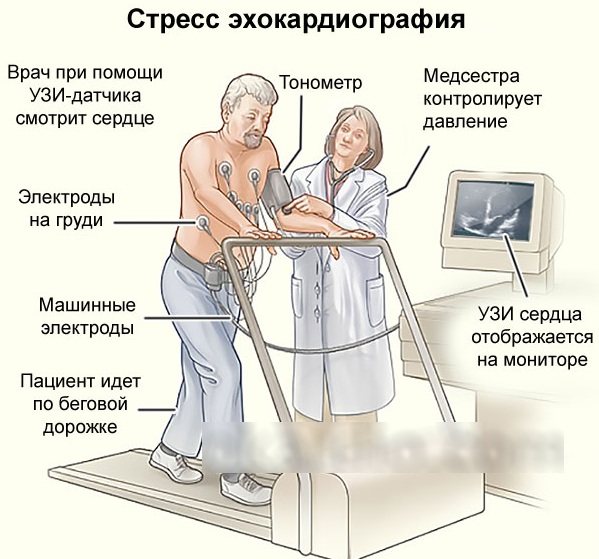
To perform stress echocardiography, you will need a minimum of 2-dimensional echocardiography. Also, a prerequisite for such an examination is the presence of several highly qualified specialists - 2 doctors and 1 nurse.
During the examination, various types of stress agents are used. These may be special pharmacological agents. The patient may also be asked to perform certain movements to increase physical activity. For example, you will need to pedal or run. When performing physical exercises, the load will increase and then the specialist will be able to monitor changes in pressure.
First, data from the heart is analyzed in a normal state, and then the functioning of the organ is studied at its maximum load.
Types of echocardiography
Thanks to continuous improvements in the diagnostic capabilities of ultrasound, echocardiography can now provide results in 2D, 3D and even 4D format. This choice allows the doctor to receive the highest quality information. Using two-dimensional echocardiography, the image of the heart is recreated in length and width, making it possible to analyze the movement of the organ’s components.
When performing 3D diagnostics, the doctor receives an image based on three parameters - width, length and thickness of tissue structures, which provides an order of magnitude more information. The 4D format implies all 3 of the above parameters, which are supplemented by a fourth - studying the organ in real time, that is, you can track the work of the heart at the current moment.
The diagnostic significance of Doppler Echo-CG is also very high, allowing one to assess the speed and turbulence of blood flow in the heart itself and nearby vessels. This method is based on the Doppler effect, the essence of which in relation to Echo-CG is to change the frequency of reflected ultrasonic waves, which directly depend on the speed of movement of the object under study.
Doppler echocardiography, in turn, can be pulsed wave, constant wave, color, tissue and energy. The speed of blood flow during the study can be measured both acoustically and optically. Such diagnostics are effective when it is necessary to study blood flow abnormalities, as well as to assess the degree of stenosis (narrowing) of the semilunar valves.
Color Doppler is an analogue of pulsed Doppler, in which the speed and direction of blood flow is mapped (depicted) in different colors. In this case, red shows the blood flow to the sensor, and blue, on the contrary, from it. As a result, the doctor is able to detect pathological flows near the septa and insufficient density of the atrioventricular valves.
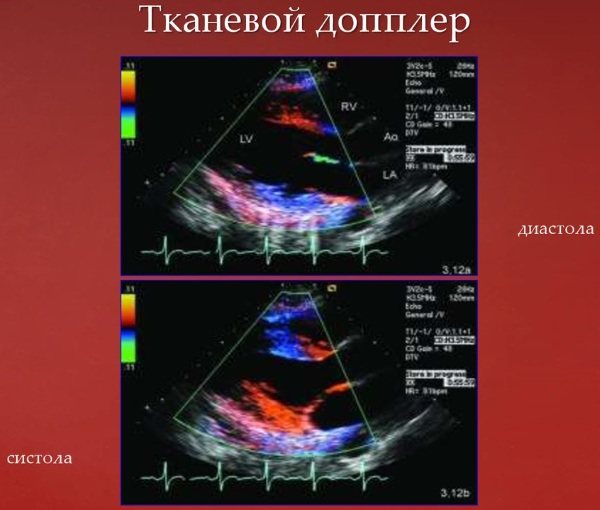
Tissue Doppler analysis is a procedure that allows you to visually track the movement of the heart muscle, valves and other structures, and in particular assess the performance of the right atrium. Through this diagnosis, the relaxation function (diastole) of the heart is studied.
All these types are performed according to the technique of transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), that is, non-invasively through the chest. If it is impossible to carry out the procedure this way, for example, there are acoustic barriers due to a large amount of subcutaneous fat in obesity or due to valve replacement, a cardiac echo is performed through the esophagus.
Indications
A cardiac echo shows possible problems and is prescribed for symptoms such as:
- feeling tired, lethargic;
- pain that is localized in the cardiac region;
- cold hands and feet;
- arrhythmia, including when drinking alcohol;
- frequent paleness of the skin;
- noises that are detected during auscultation;
- heart failure;
- high blood pressure;
- too slow weight gain in children;
- frequent headaches and loss of consciousness;
- high body temperature, accompanied by rapid heartbeat and shortness of breath. It is not associated with other diseases;
- cough.
This procedure may also be recommended when there is suspicion of fluid in the pericardial area. The most common reason for prescribing echocardiography is the need to identify heart defects.
An ultrasound of the heart may be prescribed for:
- ischemic heart diseases;
- problems associated with the membranes of the heart;
- myocardial infarction. In this case, echocardiography is usually performed for preventive purposes;
- changes in the size of the heart or blood vessels, as well as their position and shape, which were identified as a result of an x-ray examination.
When conducting echocardiography using modern devices, many indicators related to heart contractions can be identified. The specialist will be able to identify the pathology and prescribe the appropriate therapeutic course, including for the initial stage of contractile function.
Regular ultrasound examination of the heart is necessary for everyone who is professionally involved in sports.
As for children: cardiography is prescribed for them for the same reasons as for adults. In addition, every teenager over 14 years old should undergo examination, since at this age the body grows rapidly and there is a high probability of pathological changes in the heart.
According to the standards adopted in our country, all children 1 year have passed since their birth should consult a cardiologist, having previously undergone an echocardiogram.
An ECHO of the heart shows problems in the early stages, so the procedure is recommended for all expectant mothers, because during pregnancy the load on the heart and vascular system increases.
Execution techniques
As mentioned above, there are several methods for performing ultrasound of the heart, and when prescribing the doctor, he chooses the most optimal option for each specific patient. Sometimes, to obtain a complete picture of the condition of an organ, two different studies can be carried out at once in turn.
Transthoracic Echo-Kg
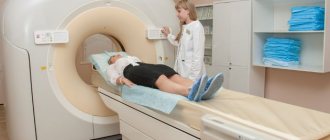
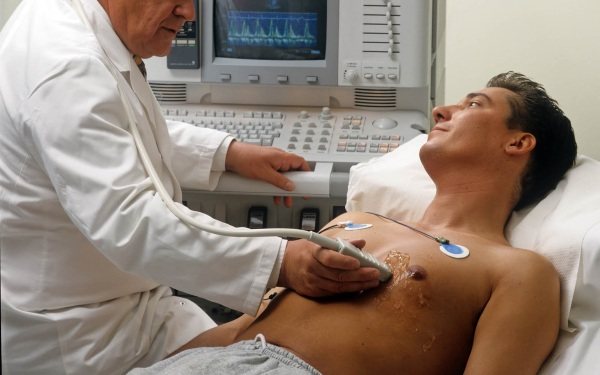
The procedure is simple and easy to perform for both the subject and the doctor. It does not require any preliminary preparation. The patient is placed on the couch, lying on his left side. Small sensors are attached to the chest and connected to an echocardiograph. The signals they generate travel to the heart through the intercostal spaces. Sound waves travel through tissues and are transformed, after which they return to the sensors.
The echocardiograph converts them into electrical signals and then processes them. As a result, an image is formed on the monitor. Sometimes an echocardiogram with a contrast agent may be required. It is administered intravenously, which makes it possible to obtain color images of various structures, measure holes in the septa (“oval window”), or determine the presence of blood clots in the myocardium.
Performing routine echocardiography
Stress echocardiography
This procedure is a kind of analogue of an electrocardiogram stress test, that is, the diagnosis is carried out not at rest, but when a load is placed on the heart.
Stress ECHO-KG with drug loading
This could be, for example, exercises on a stationary bicycle or climbing stairs. This method allows you to detect hidden deviations from the norm and evaluate their nature.
One of the types of stress echo-CG is a conventional TTE, before which the patient is given certain medications that can lead to an increase in heart rate, identical to physical activity.
Based on the echocardiography interpretation materials, the doctor will be able to assess the performance of the heart under load and identify changes in blood circulation in the coronary artery.
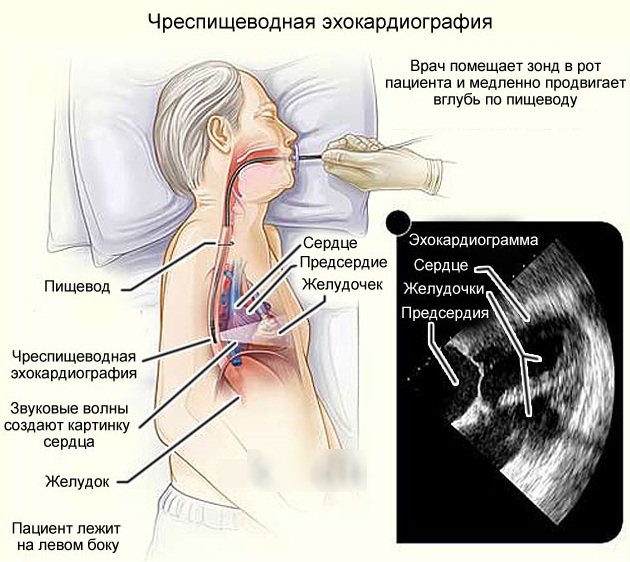
Transesophageal (TEE) Echo-CG
TEE, or transesophageal echocardiography, is performed by inserting a specially designed probe with a built-in ultrasound probe into the esophagus. This technique provides the highest quality visualization of most of the structures of the heart, since the esophagus is located in close proximity to the organ under study, and in particular the left atrium.
An echocardiogram (recording of heart activity), made as a result of TEE, can show concomitant pathologies of the heart and its developmental defects. In addition, the study makes it possible to find out the severity of the narrowing of the aortic valve, its condition, functionality, opening diameter, the presence of aortic enlargements, the condition of the ventricular walls and other characteristics.
Thanks to transesophageal echo-CG, it is highly likely to determine the presence of tiny blood clots and endocarditis (inflammation of the valve apparatus) in the heart. The procedure will also show the presence of congenital and acquired valve defects (stenosis, lack of function, etc.).
Reference! Transesophageal echocardiography is often used in the reconstruction of the valve apparatus using TAVI and MitraClip technologies, which involve the use of catheters.
Possible contraindications and restrictions
Considering that this procedure is safe, it can be performed on a person at any age. Thanks to this method, you can find out about the heart condition of an unborn child.
The procedure can be repeated many times, since it has no negative consequences. Contraindications apply to transesophageal examination. This procedure cannot be performed for those who have problems with the esophagus.
The following factors may also interfere with echocardiography:
- bronchial ac src=»https://healthperfect.ru/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/vinilin-balzam-shostakovskogo-3.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width=»600″ height=»321″[/ img]
- long-term smoking;
- severe deformation of the chest;
- large breast size.
What does it show?
Thanks to echocardiography, the doctor receives the necessary information about the patient’s heart.
The procedure allows you to:
- assess the functioning of the heart;
- see its dimensions and their possible deviations from the norm;
- determine how thick the heart walls are;
- measure the pressure not in the vessels, but directly in the heart itself;
- assess blood flow.
It must be remembered: timely echocardiography is an effective preventive measure against many diseases associated with blood vessels and the heart. An ECHO of the heart will allow you to accurately determine what treatment should be.
Preparation rules
Echocardiography does not require special preparation.
However, there are some conditions for carrying out that must be observed:
- The procedure can only be carried out when the patient is absolutely calm. Otherwise, he will have rapid breathing and an increased heart rate.
- It is important that the breathing and heart rate are not higher than the physiological norm. This means that you should refrain from physical activity before performing the procedure.
- The procedure cannot be performed in stressful conditions.
- Preparation for echocardiography also concerns nutrition. It is better to avoid foods that can affect the functioning of the heart. First of all, you need to pay attention not to food, but to drinks. It is advisable to refrain from coffee, tea and other invigorating drinks that contain a significant amount of caffeine.
If these conditions are met, then thanks to echocardiography, the doctor will be able to obtain the maximum necessary information about the organ being studied. If this is not possible, the patient must be sure to report what medications he is taking.
Transesophageal echocardiography requires special preparation. The patient must completely refuse food before such a procedure. Abstaining from food should last about 5 hours.
Stress echocardiography also has its own preparation features:
- 3 hours before the start of the examination, you should not exercise your body.
- You should not eat a lot before the procedure. Only a couple of hours before the start of the event you can have a light snack and drink a small amount of water.
- The patient should bring light clothing that will not hinder his movements.
Reasons for referral for transnutritive echocardiography:
identification of possible blood clots in the cavities of the heart (especially in the left atrial appendage), which can be a source of systemic embolism; mandatory examination before restoring sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation with a paroxysm duration of more than 48 hours);
assessment of the size, structure, degree of mobility and place of attachment of neoplasms (tumors) of the heart; identification of infective endocarditis and its complications; diagnosis of diseases of the thoracic aorta (dissecting aortic aneurysm, atherosclerotic lesions of the aorta and its complications); assessment of the valvular apparatus of the heart for acquired heart defects, including before the upcoming operation (condition of the leaflets, subvalvular structures, careful assessment of regurgitation); assessment of dysfunction of prosthetic heart valves (especially mitral prostheses); diagnosis of congenital heart defects, clarification of anatomical features before surgical treatment; monitoring during heart surgery; prolonged spruce fever of unknown origin.
Stages
Cardiac ECHO shows accurate results thanks to the use of the latest and most powerful equipment in modern clinics. This greatly simplifies making the correct diagnosis and determining the appropriate treatment method.
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis. According to the results of recent research by specialists, a properly performed echocardiography procedure does not pose a risk to the patient’s health. During the study, the patient does not experience any discomfort. For this reason, it can be carried out not only for adults, but also for children.
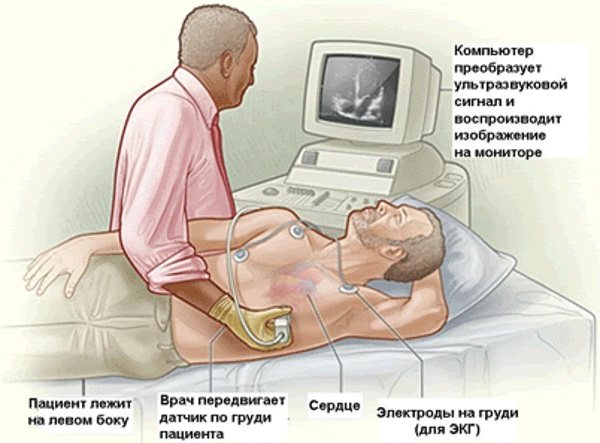
Its stages are as follows:
- The patient undresses to the waist. It is important to ensure that there are no jewelry or accessories on the body, especially metal ones.
- The patient, stripped to the waist, lies down and completely relaxes.
- A special composition in the form of a gel is applied to the chest.
- The specialist attaches sensors to certain points that must be connected to the equipment.
- On a special screen you can see the heart and monitor its functioning in real time. Thanks to this, it is possible to detect possible violations in the functioning of the organ.
The average duration of the procedure is 40 minutes. Sometimes it lasts about 20 minutes, and sometimes it can last up to 1 hour.
All information that will be obtained during echocardiography is stored electronically. The next stage is the interpretation of the data obtained. This is what the doctor does. Subsequently, he must form a conclusion.
Carrying out echocardiography
When conducting echocardiography, a specialist can determine indicators such as the size of the heart chambers, wall thickness, describe the valve apparatus, measure the speed of blood flow on the valves and large vessels, assess the contractile (systolic) function of the heart and the ability of the heart to relax (diastolic function).
From the first weeks of a child’s life, echocardiography makes it possible to diagnose congenital heart defects. The method is very informative in diagnosing complications of hypertension (hypertrophy of the heart muscle), acquired heart defects, cardiomyopathies, endocarditis and pericarditis, heart tumors, and is used in a comprehensive examination of patients with coronary artery disease (especially after myocardial infarction) and after heart valve replacement surgeries. Quite often, findings during echocardiography may include variants of heart development that are not defects (additional chords in the left ventricle) or do not require active treatment and observation (mitral valve prolapse without hemodynamic impairment, usually grades I and II).
In some cases, to clarify the results of a conventional (transthoracic) echocardiography, you may be referred to a transesophageal echocardiography (TEE), in which an ultrasound probe is inserted into the esophagus. This study is carried out on an empty stomach. You may feel discomfort and nausea when swallowing the probe, but the test is short-lived and usually well tolerated.
Decoding the results
After the examination is completed, you can see its results. Here, many patients mistakenly believe that the analysis and decoding that was received from the doctor is the finished result. Patients may think that along with the final result, they are also given a diagnosis and an identified problem related to the functioning of the heart. In reality this is not the case.
The results of the procedure are what was revealed during the study. It is indicated whether there are pathologies and whether the functions of the circulatory system are impaired. If everything is fine with the heart and blood vessels and no problems have been identified, nothing else will be needed. If there are even minor changes, you should definitely contact a cardiologist and consult with him.
The doctor will look at the results of the echocardiography, talk with the patient, and evaluate previous factors, diseases and possible causes. Then the correct diagnosis will be made. After this, the doctor is obliged to prescribe the correct therapy, which will help improve the condition by eliminating the problem.
After the examination, the analysis of the obtained data begins, the main of which are the parameters of the ventricles of the heart and the partitions separating them.
Heart ECHO shows:
| Right ventricular parameters | Left ventricular parameters |
|
|
What shows Correct analysis of the information received about the heart can only be done by a professional - a cardiologist. If the patient wants to decipher the data about his heart on his own, errors may occur that will entail serious consequences. After all, the data can be affected by age, as well as physical condition.