Every month, a healthy woman of reproductive age undergoes dozens of processes associated with the possible conception and bearing of an unborn child. One of these processes is the formation of the corpus luteum, which is responsible for the synthesis of the pregnancy hormone (progesterone). In some cases, gynecologists send women for an ultrasound so that a screening specialist can identify the corpus luteum, describe its structure and take measurements for further interpretation of the analysis. Therefore, it is very important to know where the corpus luteum comes from and what functions of the female body it is responsible for.
Stages of development of the corpus luteum
The content of the article
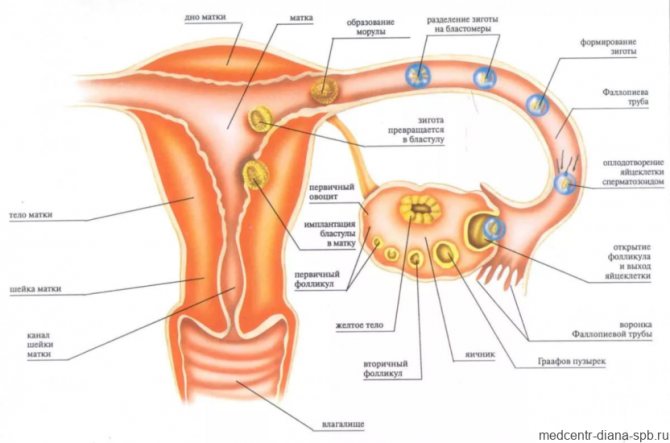
Although the VT appears instead of the follicle that released the egg into the fallopian tubes, its development begins long before the onset of the ovulation period. This complex process is controlled by the pituitary gland, ovaries and immune system.
- Initially, the follicle grows, increasing in size, and lutein accumulates inside it, a colored pigment that makes it yellow. The transformation process is called luteinization.
- After the release of the egg, vessels in the ruptured follicle begin to grow rapidly, penetrating into the luteal tissue. The corpus luteum gradually forms, the blood supply of which is higher than in other organs of the human body.
- The blooming stage of VT begins. During this period, iron is released up to 25 mg/day. progesterone. High doses of the hormone inhibit the development of other follicles, because the body adjusts to fertilization and pregnancy.
As a rule, there is only one corpus luteum, but when several eggs are released, two or three such structures are formed. If fertilization occurs during this menstrual cycle, twins or triplets will be born. These twins, called fraternal twins, do not look alike and may even have different sexes.
Progesterone not only inhibits new ovulation, but also prepares the uterus to “receive” the embryo. Even the work of the uterine muscles changes. Everything in the body is ready for pregnancy. If fertilization occurs, progesterone concentrations will increase until 16 weeks, until pregnancy maintenance functions are transferred to the developed placenta.
If conception does not occur, the corpus luteum will begin to sprout connective fibers, turning whitish. Gradually it will decrease in size and resolve. The concentration of progesterone drops, and new follicles begin to mature in the ovary.
But this “play with nature” does not pass without a trace. Ovulations that do not end in pregnancy lead to hormonal imbalances and gynecological pathologies. A burst follicle does not resolve, but begins to grow. Instead, a corpus luteum cyst is formed - a neoplasm that can exist for a long time.
It is better to turn off useless ovulation by taking hormonal pills that inhibit the development of eggs. The risk of developing a corpus luteum cyst in this case becomes zero.
When is an ultrasound performed?
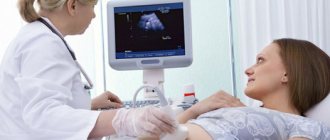
Changes in the endocrine gland require constant monitoring; diagnosis is carried out using ultrasound. We study how the size of the gland changes depending on the stages of the cycle.
Such diagnostics are necessary under the following conditions:
- Pregnancy planning. If the gland has formed in the middle of the menstrual cycle, ovulation has completed successfully and conception may occur in the near future.
- Early pregnancy. If the gland has dimensions that correspond to the norm, it means that the egg has attached to the uterus and development is proceeding normally. Pregnancy is at risk if there is no corpus luteum and, accordingly, progesterone levels are below normal. It is urgent to start treatment. An indicator of multiple pregnancy is the presence of two or more bodies.
- Infertility. If pregnancy does not occur during a normal menstrual cycle, the cause may be a violation or absence of ovulation. Also, the corpus luteum may be smaller in size than normal, in which case there is a lack of progesterone and pregnancy does not occur.
- Formation of a gland cyst.
Changes in the state of the corpus luteum using ultrasound are examined 2-3 times during the cycle. If a gland appears (from 30 to 40 mm), from the 7th to the 10th day of the cycle, the presence of a neoplasm will be confirmed.
Methods of conducting ultrasound examination:
- Transvaginal - a vaginal sensor is used. This type of examination does not require a full bladder.
- Transabdominal - a surface sensor is used that slides over the surface of the abdomen.
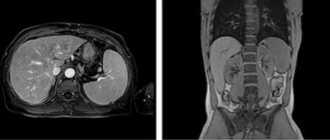
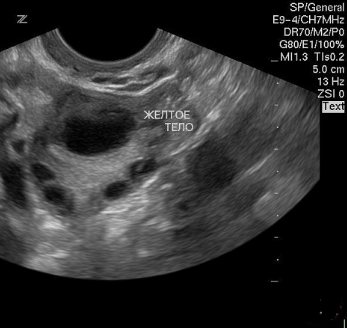
What is visible on ultrasound at different stages of development of the corpus luteum
During an ultrasound examination of the ovaries, the corpus luteum resembles a small sac located on the ovary. If it is not visible even after ovulation, it means that the woman has ovarian dysfunction. For example, during an anovulatory cycle, the egg is not released and the corpus luteum is not formed.
Sometimes it is not the ovaries that are to blame for the absence of the corpus luteum, but other organs - the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland. Such a woman needs to consult an endocrinologist and get tested.
The size of the VT depends on the day of the cycle:
- Before ovulation - on days 12-15 of the cycle, only the follicle is visible on ultrasound, but immediately after the release of the egg, the size of the corpus luteum can already be analyzed. Normally they are 12-20 mm. This is enough for the onset and maintenance of pregnancy. After this, the VT may “grow” a little more.
- The further picture of the ultrasound depends on whether fertilization has occurred. If the female cell is not fertilized, the size of the VT gradually decreases, and its color changes from yellow to purple. The formation visually rises above the ovary. Gradually it is replaced by connective tissue.
- If after this the VT does not disappear, but, on the contrary, begins to increase, this means that the woman is growing a cyst, which can reach 40 mm. Sometimes, for unknown reasons, on the eve of the next ovulation, the cyst disappears on its own.
Folliculometry
The size of the corpus luteum is of great importance, which is the main topic of the article. Why is it important? A deviation in the size of the gland from normal may indicate certain pathologies that will certainly play a negative role in the process of a woman’s pregnancy or completely eliminate the course of this process.
The measurement of the corpus luteum is called folliculometry. There are options for normal sizes of the corpus luteum: from 12 to 22 mm in various phases of the menstrual cycle and from 22 to 32 with successful fertilization.
Ultrasound of the corpus luteum during pregnancy
At 8 weeks. the size of this formation is 10-30 mm. Normally, it should disappear by about 16 weeks, when the placenta has formed in the uterus. But sometimes VT resolves earlier or even remains until delivery. Pregnancy proceeds absolutely normally.
The corpus luteum, which for some reason lasted longer than expected, disappears before childbirth at 35-38 weeks, when the overall level of progesterone decreases. Sometimes it resolves after the baby is born.
Scientists have not yet fully studied the cause of such anomalies, but even earlier disappearance of VT does not always lead to miscarriage. Sometimes its functions are taken over by the adrenal glands, which also produce progesterone, and the fetus continues to develop. Subsequently, the adrenal glands transfer hormonal functions to the placenta.
In the absence or insufficient size of VT, it is necessary to take tests for progesterone. Its decrease is a bad sign, indicating the possibility of miscarriage, fading pregnancy or uterine bleeding.
In this case, the woman is prescribed medications that replace the hormones that VT synthesizes. Unfortunately, sometimes hormonal deficiency persists until childbirth, so the woman will have to take medication for the entire nine months.
Why isn't it visualized?
What to do when the corpus luteum is not visualized on ultrasound? It depends on whether the woman is currently pregnant or not. Every woman periodically experiences anovulatory cycles, during which ovulation does not occur. There is no need to worry about this if there are no more than 5 such cycles per year. If there is frequent absence of ovulation, hormonal correction is required to allow you to become pregnant.
If a woman is pregnant, the absence of visualization of VT in the first trimester indicates problems with gestation. The expectant mother needs urgent treatment that will increase the level of progesterone in the body. Sometimes the absence of VT means that the pregnancy is frozen. In the second and third trimesters, the corpus luteum disappears - this is a normal process, so there is no need to worry.
Ovarian cyst
Diseases of the female reproductive organs can be asymptomatic. In this case, pathologies often become accidental diagnostic findings during a routine gynecological examination.
Sometimes diseases of the reproductive system are manifested by infertility, pain in the lower abdomen, menstruation disorders and other disorders. A gradually enlarging ovarian cyst can cause dangerous complications such as peritonitis.
This disease most often occurs due to hormonal disorders, so preventive measures are possible. If risk factors for ovarian cysts are detected, it is necessary to be regularly monitored by a gynecologist.
general information
An ovarian cyst is a benign structure filled with fluid. As the disease progresses, the cyst increases due to the constant secretory function of the organ.
A characteristic symptom of the disease is pain in the lower abdomen. In most cases, ovarian cysts are harmless. At the same time, large formations that gradually fill with liquid may rupture.
In this case, inflammation of the peritoneum occurs, characterized by severe symptoms.
In most cases, cysts are associated with the ovulation process. We are talking about follicular formations or cysts of the corpus luteum. Other common types of pathology include endometrial cell cysts and dermoid cysts.
Based on the symptoms, it is impossible to determine what kind of formation has arisen in the organ, so diagnosis is carried out using special examinations. In rare cases, cysts are precursors of malignant tumors.
In the medical literature, a cyst is a cavity containing fluid. Some cysts do not change in size, while others grow rapidly and rupture over time.
Such abnormal structures can form in the kidneys, liver, teeth, mammary glands and other organs. The cyst itself has nothing to do with cancer, but the contents of some formations may undergo malignant degeneration.
If a small cyst does not increase over time and does not cause concern, doctors resort to observation tactics.
Ovarian cysts are among the most common gynecological diseases. These abnormal structures are diagnosed in approximately 8% of women before menopause (up to 50-55 years).
After menopause, cysts are detected in 15-18% of women, and at this age the risk of malignant tissue degeneration increases.
Also, patients suffering from menstrual disorders are more likely to have cystic ovarian lesions.
Ultrasound and other diagnostic measures
Ultrasound examination is one of the main diagnostic methods that allows you to determine whether everything is in order with pregnancy, identify the presence of the corpus luteum and determine its size, and find out whether there are pathologies of the gland. Ultrasound of the ovaries is done transabdominally - in this case, the sensor is moved along the woman’s abdomen and pubis, or intravaginally - the sensor with a condom on it is inserted into the vagina.
Ultrasound is necessary in the following cases:
- suspicion of hypofunction of the corpus luteum;
- VT cyst;
- multiple pregnancy - in this case there will be two or more glands.
In addition to ultrasound diagnostics, a blood test for progesterone is done during pregnancy.
Diagnosis of persistent VT
How to treat persistence of the corpus luteum? Of course, you should first try to determine whether the bleeding could have another cause, such as an impending ectopic pregnancy. It should be remembered that the diagnosis of bleeding associated with the persistence of the corpus luteum is made on the basis of the characteristic ultrasound picture of the ovaries, changes in cycle duration, and high levels of progesterone. However, sometimes it is necessary to additionally perform the following tests and tests:
- general blood analysis;
- pregnancy testing using hCG determination. If the concentration of hCG exceeds the norm many times, this indicates that conception has occurred, and in this case, the corpus luteum will carry out its function during the first trimester until the placenta is formed;
- determination of the level of other hormones, for example, prolactin and TSH hormone.
- in addition to ultrasound of the ovaries “from the outside” and Doppler ultrasound, it is necessary to perform a transvaginal examination,
- as a last resort, according to indications, hysteroscopy with endometrial biopsy is performed, especially if the woman is “compromised” by the presence of endometrial hyperplasia, and it is necessary to find out what’s wrong;
- in any case, regardless of the reasons, the state of the blood coagulation system is examined - a coagulogram is performed;
- in case of prolonged and heavy bleeding, hospitalization is necessary.
Likewise, hospitalization may be required if you experience nagging pain in the lower abdomen, since the cystic formation in the ovary may rupture, causing bleeding, which may even be life-threatening. That is why you should know about the degree of risk, and if there is the slightest deviation from the normal course of the cycle, you should not guess, but urgently contact a gynecologist.
After all, it could be endometriosis, and even a neoplasm, fibroids, a manifestation of inflammation, that is, endometritis and adnexitis. This may be an abortion with the presence of remnants of the fertilized egg, or a spontaneous miscarriage in an undiagnosed pregnancy. Finally, the cause may be ulceration of a placental polyp (during pregnancy) or an endometrial polyp. You should also remember about the presence of extragenital diseases and hormonal system disorders.
But even at the initial appointment, the gynecologist can already use well-known methods to find out whether a woman is in the estrogen or progesterone phase at a given time. Let us recall that with very high estrogens, the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix will have a rich color, the symptom of the pupil and cervical mucus will be sharply positive, and the uterus will be enlarged, and vice versa.
In some cases, it will be necessary to examine serum ferritin, total iron-binding capacity, transferrin and iron concentration, hemoglobin, especially if there is a tendency to chronic bleeding.
In some cases, it is necessary to study the concentration of testosterone (in case of suspected polycystic ovary syndrome), the concentration of FSH in case of suspected ovarian failure, a Pap smear test and a test for human papillomavirus, which may be necessary when screening for cervical cancer.
Treatment
First of all, the most active position is required by the presence of ongoing bleeding of the type of menometrorrhagia. Although severe blood loss occurs relatively rarely with this type of habitual bleeding, it is necessary to prevent it in every possible way and not wait until it occurs. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and non-hormonal treatments such as tranexamic acid or plasminogen activator should be prescribed.
This leads to the elimination of dysmenorrhea, since NSAIDs inhibit the production of prostaglandins, and the presence of tranexamic acid in the treatment regimen can reduce blood loss by 50% or even more. If the persistence of the corpus luteum occurs in each cycle, then the “heavy artillery” comes into play: this is the use of hormones.
In each case, the appointment must be justified. With persistent corpus luteum, progesterone is already high, but if progestogens are prescribed, or intrauterine systems with prolonged release of progestins, it is still possible to achieve a more predictable bleeding pattern, suppress endometrial growth and reduce the severity of menstrual blood loss.
Various systems that release levonorgestrel are also used, and within 6 months of treatment, almost 100% of patients (up to 96%) get rid of dysmenorrhea, simultaneously providing the necessary level of contraception. In some severe cases, medications that suppress the production of hormones by the ovaries and induce drug castration can be used. However, persistence is almost always a functional disorder, and one can completely do without suppressing one’s own endocrine function.
When to scrape, or methods of surgical gynecology
Despite all the reluctance of women to go to the operating table, we must not forget that gynecology is a surgical specialty. In the event that there is no significant bleeding, the endometrium does not have pathology associated with hyperplasia, if this woman is of a relatively young age without proliferative diseases, then it is quite possible to treat such a pathology as persistence of the corpus luteum using conservative methods, for example, by prescribing combined oral contraceptives .
But if a woman is taken “in an ambulance,” with abdominal pain, prolonged bleeding, anemia and low hemoglobin, then, most likely, according to emergency indications, she will undergo diagnostic and therapeutic curettage, a biopsy, and hysteroscopy. Therefore, at present, in its pure form, such a functional diagnosis as persistence of the corpus luteum is rarely made, and there are several reasons for this. This is a craze for oral contraceptives, as well as a significant decrease in the health literacy of the population. Women try to cope with cycle disruption on their own. And if this condition is delayed, then there is a great chance of ending up on the operating table in order to avoid serious complications.
Hormonal support
To treat insufficiency of the temporary gland, gynecology prescribes hormonal drugs that stimulate its functioning. They must be taken if a woman is having difficulty conceiving, before IVF, or if she has been diagnosed with insufficiency during gestation.
| No. | Name | Active substance | Release form | Indications |
| 1 | Utrozhestan | Progesterone identical to that produced by VT | Capsules | Infertility due to luteal insufficiency. Threat of miscarriage due to progesterone deficiency, anovulation, hormone replacement therapy in pre-, peri- and postmenopause, prevention of premature birth, preparation for IVF. |
| 2 | Duphaston | Dydrogesterone, an analogue of natural progesterone | Pills | Indications are similar to Utrozhestan. |
The corpus luteum plays an important role in the reproductive function of the female body. It is thanks to him that it becomes possible to conceive and bear a child.