After a caesarean section, breastfeeding often does not begin immediately, but on days 4-5: the woman needs time to restore her body’s strength after the operation. In the first day after such a delivery, it is not recommended to put the baby to the breast, but lactation can be stimulated by pumping.
This procedure is also necessary in the future if the baby does not take the breast often enough. There can be a lot of reasons for this, related to both the body of the mother and the child; it is necessary to comprehensively assess the condition of both.
If the amount of milk is insufficient, this process can be stimulated with medications (Lactogon, Dezaminooxytocin, Mlekoin, etc.), nutritional supplements and physiotherapeutic procedures. To maintain lactation after cesarean section, prevention of complications, rational nutrition and rest of the mother are of great importance. Among the foods in the diet, there is a certain set that enhances lactation (porridge, juices, vegetables, fruits, etc.).
For the harmonious development of the child, it is rational to continue feeding for one or one and a half years.
When does milk come in after a caesarean section?
Usually milk comes after a cesarean section a little later, about 4-5 days after the operation. This depends on many factors:
- course and duration of labor;
- presence of complications;
- mother's age;
- state of the woman’s body;
- the amount of blood loss;
- time of putting the baby to the breast.
After the birth of a baby, a woman’s hormonal background changes and the hormone prolactin begins to be produced. This process is stimulated by putting the baby to the breast and irritating the areola, that is, the nipple, by his touch - the so-called “skin to skin” contact. After a cesarean section, such contact sometimes does not happen immediately, so the arrival of milk is delayed.
Often the mother is too weak after surgery to start breastfeeding, especially if the decision to deliver by cesarean came during a complication of natural childbirth. Normally, lactation after surgery begins from the third to the seventh day.
We recommend reading about how to care for a suture after a caesarean section. From the article you will learn about what a suture looks like after a cesarean section, the features of a cosmetic suture, how and how long it takes for a suture to heal, its treatment and care. And here is more information about how to remove the belly after a caesarean section.
The first days after childbirth: waiting for milk to appear
The most exciting moment is behind us, the baby is born! But maternal worries are now associated with the question “Where is the milk?” Even before giving birth, a woman may have noticed that a whitish liquid, colostrum, began to be released. This will be enough for the baby in the first time after birth.
Important: With regular feeding, after a few days the child will begin to receive complete natural nutrition.
But in reality it turns out that not everything is so simple. Often a newborn simply cannot make enough effort to “get” food from the breast. The situation becomes more complicated if in the maternity hospital the children are supplemented with formula from bottles; the formula flows much more easily from the bottle than the mother's formula.
Therefore, a child, having once tried the “easy” method, may refuse the not yet “developed” chest. But don't despair. In the maternity hospital, midwives often come to the aid of first-time mothers to stretch their swollen breasts and improve lactation.
Important: If you remain inactive and do not express milk, she will become stone-like, not far from mastitis.
A breast pump can also come to the rescue; it will develop the channels and stimulate the flow. But if your nipples become too hard and painful, you should immediately seek help from medical staff.
Characteristics of lactation after cesarean section
Lactation after a cesarean section differs little from breastfeeding after a natural birth. After surgery, a woman experiences significant stress, which affects the body. Strength is also needed to restore the postoperative wound, so the main difference is the time of milk arrival. During a natural birth, this happens in the first hours after birth, but after a cesarean birth it can happen a week later.
The intensity of lactation after surgery directly depends on the level of the hormone prolactin, as well as the presence and severity of postoperative complications. If the mother develops infectious or inflammatory processes in the body, the onset of lactation may be delayed.
The properties of breast milk do not differ from those during normal feeding: on the first day, thick colostrum with a high fat content is released, and then breast milk with an optimal ratio of fatty acids and milk proteins begins to form. It also contains maternal antibodies, enzymes for better absorption and a huge amount of micro- and macroelements.
All components of breast milk after cesarean section are present in it in normal proportions. The exception is infections in the reproductive organs or on the surface of the nipples: this can increase the secretion of the liquid part of the milk and reduce the concentration of beneficial elements.
Lactation after cesarean section is strongly dependent on the psycho-emotional background of the mother and contact with the child. It is the irritation of the areola that stimulates the process of milk separation. After a cesarean section, such stimulation is needed to a greater extent; the baby must be attached at will to maintain feeding. A woman should stop feeding on time to avoid loss of lactation after surgery.
Also, this process is significantly influenced after surgery by reasons such as:
- diet;
- support from loved ones;
- hygienic and sanitary feeding conditions;
- any diseases of internal organs during the recovery period;
- the course of wound scarring and its extent;
- the amount of blood loss during childbirth;
- during the last trimester of pregnancy.
Antibiotics and lactation after cesarean section
After a cesarean section, a woman is prescribed a course of antibiotics to prevent complications from developing. Read more about what complications there are after cesarean section→
In this regard, many mothers fear that drugs can penetrate through milk into the baby’s body and harm him. There is no clear opinion on this issue; it must be considered individually, in the context of the policy and equipment of the maternity hospital, as well as the condition of the mother. In any case, you need to consult your doctor and, if necessary, ask him to choose the safest medicine possible.
It would also be useful to consult with an anesthesiologist so that he can clarify whether anesthetics enter the bloodstream.
Don’t be embarrassed to ask questions or ask the maternity hospital staff for anything. You have every right to quality service and to have your opinion taken into account. However, do not rush to create scandals if you fail to achieve what you want, because this may turn against you. There are many peaceful ways to influence the nurse caring for your baby, from asking politely to stimulating her interest with a gift.
In return, you can get the opportunity to feed your baby on demand, and the guarantee that he will never be introduced to a pacifier. In any case, remember that only serious complications, which are extremely rare, and the mother’s disinterest in this issue can interfere with breastfeeding after a caesarean section. Don't worry, be consistent in your actions - and you will succeed!
Video: how to properly attach to the chest
We recommend reading: Complications after cesarean section: recognize and treat in time
Author
Editorial staff of the portal Mama66.ru
Share
Why doesn't milk come in after a caesarean section?
The lack of lactation after surgery can be alarming; milk does not come after a cesarean section for the following reasons:
- there was a large loss of blood during childbirth;
- disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome developed;
- the baby was not put to the breast;
- the woman is critically weakened;
- there is a deficiency of body weight;
- the woman in labor has a strong stress reaction;
- postpartum depression developed;
- pituitary tumor;
- endocrine pathologies that block the production of the hormone prolactin.
A week is considered the critical period. It is during this period that a woman’s body should normally begin to produce milk after surgery.
In any situation, a decrease or complete absence of milk may occur after a cesarean section. This phenomenon is even influenced by the state of the immune system and the nature of the diet.
The greatest influence on lactation after surgery is exerted by intra- and postoperative factors: inflammatory and infectious lesions. When the immune system reacts to a particular stimulus, the body “switches” to another mode of operation.
Milk production is an energy-consuming activity; it also requires a significant amount of nutrients and their processing, as a result of which prolactin production in such pathologies is compensatory reduced, giving the body the opportunity to recover.
The course of pregnancy also creates a certain pathological or physiological background in the body, influencing the development of typical accompanying problems of pregnancy:
- arterial hypertension;
- nephropathy;
- cystitis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypo- or hyperthyroidism;
- obesity.
All these diseases have a high chance of developing with the onset of pregnancy, which will aggravate the synthesis and secretion of milk after childbirth.
Watch this video about why there is no breast milk and what to do to get it:
Will there always be milk after surgery?
After the operation, milk will not always be available; more often, the mother is not allowed to breastfeed the baby right away, since the woman’s body has experienced enormous stress, and due to such a load, the milk will not arrive.
Another reason is the disruption of the normal hormonal changes in the body during childbirth: in the process of natural childbirth, a powerful production of various sex and related hormones of the pituitary gland occurs, which is an impetus for the implementation of the basic instinct - maternal, including breastfeeding.
After a cesarean section, mothers are deprived of such hormonal changes for some time, or they occur through other pathways. Therefore, milk may not come after surgery.
If there is no colostrum
If there is no colostrum after a cesarean section, this means that lactation has not yet begun. This also indicates a severe deficiency of nutrients in the body. Colostrum contains a large amount of protein, unlike breast milk, and many globulins. After a cesarean section, these substances are necessary for the mother herself to restore the body and protect against infection. They can go to heal the wound, so colostrum can linger and change its character.
Normally, the lactation process goes through the colostrum stage, after which human milk of normal composition begins to form. But if after cesarean there is no colostrum and milk for more than 10 days, then this is a good reason to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist first, and then a therapist.
If it was, but suddenly disappeared
If there was milk after a cesarean section, but then suddenly disappeared, then this indicates the development of a disease in the reproductive system or other internal organs, which can lead to:
- endometritis, adnexitis;
- viral or bacterial infection of the pulmonary system;
- hematometer or lochiometer;
- asthenic syndrome, malabsorption (impaired absorption of substances in the small intestine);
- body weight deficiency;
- diarrhea;
- development of endocrine pathologies (thyroid gland, pituitary gland);
- taking medications.
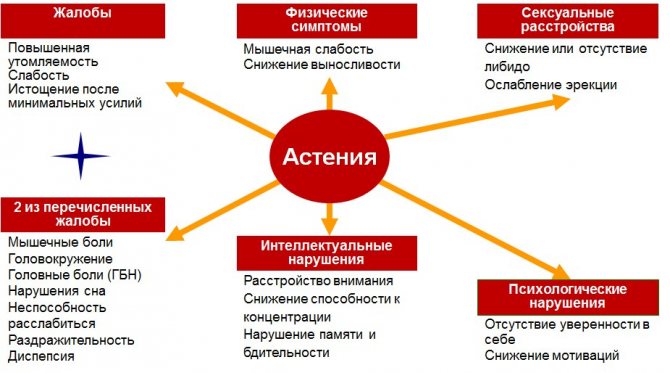
Ordinary nervous strain can also dramatically disrupt lactation. Women after cesarean section are at risk for postpartum depression, which is accompanied by lactation disorders, among other things. This can also be caused by a simple lack of sleep or conflicts with the mother’s relatives, since lactation is very sensitive to the effects of stress hormones.
If a woman suddenly begins to lose blood or nutrients (hidden bleeding, diarrhea, frequent and copious urination), then this also affects lactation: milk is less well formed due to the lack of its building elements.
Oxygen deficiency in the body also has an acute effect: the state of both ischemia and hypoxia negatively affects breastfeeding. This situation can develop with ordinary pneumonia, which has a pronounced effect on breathing and oxygen saturation in the blood.
Often the cause of a sudden cessation of lactation is the development of mastitis. This is facilitated by:
- violation of feeding technique;
- lack of pumping;
- decreased maternal immunity;
- the baby is not put to the breast;
- sources of infection in the body;
- violation of the mother’s personal hygiene in caring for the mammary glands.
Mastitis is the most common cause of cessation of milk supply after cesarean section.
Establishing milk production after surgical birth
Previously, babies were brought into the mother's room only for scheduled feeding; it is not surprising that many women in labor had to deal with the cessation of milk production. The first application occurred only on the second or third postoperative day, provided there were no complications.
Today, obstetrics is more developed, it approaches the problems of breastfeeding after surgical delivery much more intelligently; today, in most maternity hospitals, the baby is placed on the mother’s chest after being removed from the uterus.
This practice helps stimulate the nipples and triggers the active production of prolactin, the lactation hormone.
The type of anesthesia used for the operation is important. If a cesarean section is performed under spinal or epidural anesthesia, feeding the baby can begin a few hours after delivery.
It is also important to start the operation; if it is started even before delivery, then the likelihood of problems with breastfeeding is incredibly high.
Therefore, today even planned cesarean operations are carried out after the appearance of contractions, in the absence of which they are stimulated.
What other factors can affect breastfeeding after a caesarean section?
- Lack of attachment immediately after delivery.
- Staying after surgical delivery in an intensive care unit; usually mothers do not take babies there, so breastfeeding the baby on the first day will be problematic.
- Due to previous factors, lactation activity starts later, so lactation is activated only 4-9 days after the operation.
The bond between mother and newborn is enormous
On the first day, the newborn is separated from his mother and is fed formula from regular bottles. But sucking milk from them is much easier than from the mother’s nipple. Therefore, when a mother tries to establish breastfeeding, it is difficult for the baby to relearn.
- If a cesarean section was carried out as planned, then the body does not experience the same hormonal changes as during a traditional delivery, and therefore breastfeeding is much longer and more difficult to establish.
- After a cesarean section, a woman in labor is prescribed maintenance fluid therapy, which can cause breast swelling, causing the mammary glands to become hard and painful, making latching unbearable.
Even if a postpartum woman has encountered all of the above factors, it is quite possible to restore breastfeeding, you just need to make some efforts.
Difficulties with breastfeeding after cesarean surgery
It is better to know the enemy by sight, so patients who are about to undergo a planned cesarean section are advised to study in advance the likely difficulties that most often arise during the first attempts at breastfeeding. When a baby is born through the birth canal, in the process of overcoming it, he adapts to an unfamiliar and completely unusual environment.
But caesareans do not have this opportunity; surgical birth causes temporary disruptions in the genetic program, although the body of such children soon manages to adapt.
Immediately after extraction, the babies do not yet have sucking reflexes, they are sluggish and inactive, although soon, after a couple of hours, all reactions normalize, and they can already be breastfed.
First application
Every pregnant woman who is at risk for surgical childbirth needs to study in advance how to establish breastfeeding after a cesarean section.
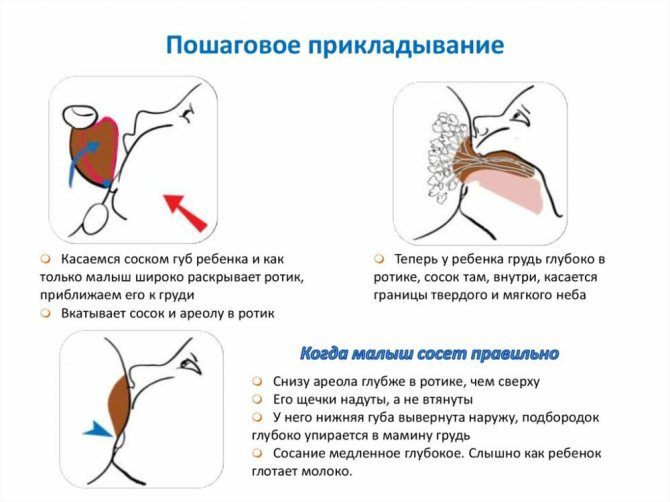
In order to avoid further difficulties with breastfeeding, it is necessary to correctly approach the issue of organizing the first attachment, which should be carried out in the first hour after the newborn is removed. In maternity hospitals, the practice of correct first attachment is by no means universal.
Full imprinting involves the first application of the baby to the breast during the period when the sucking reflexes are in a state of maximum activity, i.e. in the first half hour to an hour after birth.
With full imprinting, the newborn must first suckle on one breast for at least a quarter of an hour, and then on the other for the same amount of time. Such attachments actually happen in our maternity hospitals several hours, or even days after delivery, when the ideal time has already been missed.
As is known, in caesarean calves, sucking reflexes in the first hour of life are inhibited, or even completely absent. In this case, it is necessary to breastfeed every time the baby squeaks. Although maximum reflex activity is observed in the first hour, it remains at relatively high levels throughout the 6-hour period.
The important point is that the mother’s nipple becomes the first object that gets into the baby’s mouth, and not the rubber nipple. Therefore, it is necessary to avoid supplementary feeding or additional feeding. Mom should discuss this issue with the doctor in advance or ask loved ones to keep an eye on this.
Staying in the intensive care unit
After surgical delivery, the patient remains in the intensive care unit for approximately 1-3 days, which involves separation from the baby, even if the maternity hospital practices keeping the newborn and mother together.
The newborn feels very comfortable in the mother’s arms. This problem is associated exclusively with Russian maternity hospitals; in other countries this is not the case and the baby is always with the mother, even after a caesarean section. The only exceptions are cases when hardware support for respiratory functions is needed for a baby or a woman in labor.
- Of course, you can agree with the medical staff so that the baby is not fed anything during your stay in the intensive care unit. On the first day, the baby manages to suck out only 10 ml of colostrum, and on the second - 30 ml. Therefore, the lack of supplementary feeding does not in any way condemn the baby to hunger pangs.
- If the mother is assigned to a separate room, as happens during paid childbirth, then we can arrange for the grandmother to be nearby and take care of the baby while the mother recovers. As a last resort, if doctors require it, you can feed the baby from a spoon.
- If, nevertheless, the doctor is stuck on the instructions and does not allow any exceptions, then just relax and have a good rest. Be mentally prepared for the difficulties of retraining your baby. On the second day, you need to pump every couple of hours, rest 24:00-6:00. The duration of the procedure is approximately 5 minutes, regardless of the volume of fluid released.
With this approach, there will be no problems with feeding, even if the baby is not with the mother for the first 24 hours.
Insufficient milk production
One of the characteristic consequences of surgical childbirth is the delayed formation of lactation, which can begin only on the 9th day. In such situations, supplementary feeding is, of course, inevitable.
How to be? Firstly, such a late onset of milk production is quite rare, and secondly, physiologically in the first days the baby sucks out only small amounts of nutrition (colostrum).
Therefore, there is no need to panic, which can cause problems with milk production.
No milk after cesarean: what to do
If there is no milk after a cesarean section, then you do not need to immediately start doing examinations; you must first make sure that the young mother has sufficient rest and proper nutrition, and also pay attention to the course of the recovery period: any complications will delay lactation. If there is no history of such complications, then you need to:
- take general and biochemical blood tests;
- do a general urine test;
- take a vaginal smear;
- visit an obstetrician-gynecologist;
- do an ultrasound of the reproductive system;
- take an ECG;
- make a profile of sex hormones and prolactin levels;
- donate blood for thyroid hormones.
These examinations are prescribed depending on the suspected cause of lack of lactation, which the doctor will determine at the first appointment.
How to express colostrum yourself
There are certain rules for pumping:
- the first time is carried out manually;
- skin and hands should be clean;
- the container for colostrum is sterile;
- half an hour before the procedure, drink some liquid;
- Before pumping, gently massage your breasts;
- develop a rhythm of pumping at intervals of 2-3 hours;
- do the procedure according to schedule;
- empty your breasts until you feel relieved;
- Do not cause pain under any circumstances.
For manual expression you need:
- massage your breasts;
- grab the gland from above with your thumb, place the rest below the areola;
- separate the colostrum using pressing movements towards the nipple;
- hold the contents with your fingers.
The thumb should be 2-3 centimeters above the nipple. Do not injure the areola with sudden movements or sharp edges of the nails. Apply pressure until you feel empty and relieved.
How to express colostrum with a breast pump
You can express milk using a breast pump. But this tool is not recommended for women with their first child, or if they have not previously breastfed. In such cases, the colostrum does not pass well, the gland ducts are not yet wide enough, and the separation of colostrum under the influence of a vacuum can injure the structure of the mammary gland.
Longer massage and baby creams should be used to reduce the risk of injury or irritation when using a breast pump. It can be purchased at a pharmacy.
Normally, during breastfeeding and early attachment to the breast, there is no need to express colostrum, because the baby is immediately applied to the mother's breast. Colostrum ensures the transition of the baby's nutritional regime from hematotrophic, that is, through nutrients in the mother's blood to normal nutrition, so the baby must receive this stage of breastfeeding. In some cases, the mother cannot start breastfeeding after childbirth. This happens if:
- delivery was carried out by caesarean section;
- During childbirth, anesthesia was given, including epidural;
- the mother has severe postpartum complications;
- maternal cancer or infectious diseases;
- the child was born weakened or premature;
- Feeding a child requires special regimens for medical reasons.
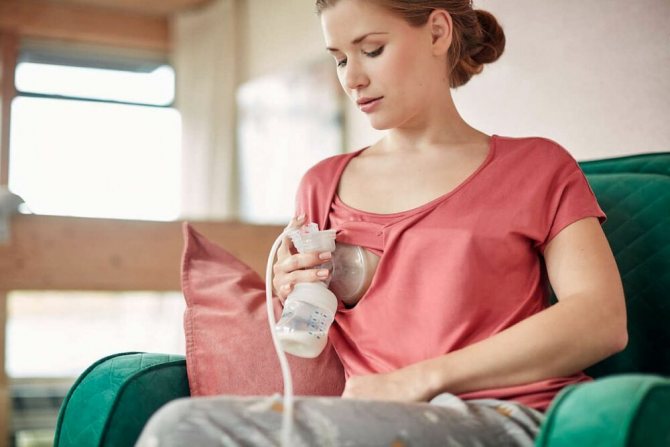

In all these situations, there is a need to express milk because it will help empty the breast. In a woman’s body, colostrum is formed under the influence of hormones, that is, with a certain rhythm. If feeding is not stimulated by skin contact with the baby, then it is necessary to express the colostrum so that the secretion does not stagnate in the gland and does not cause inflammation. Otherwise, the mother will quickly develop mastitis.
How to speed up the arrival of products
The following dishes and products increase lactation:
- broths and soups from lean meats and fish;
- vegetables and fruits;
- lettuce, dill and other greens;
- fermented milk products;
- cereal porridge;
- fruit juices;
- herbal decoctions, rose hips;
- carrot juice;
- whole wheat bread;
- garlic;
- apricots;
- fatty fish;
- watermelon.

There are herbal drinks that increase the intensity of milk production. Infuse tea from dill, cumin or anise: take a glass of boiling water for one teaspoon of raw material and infuse for half an hour. You need to drink one glass twice a day. A tea is brewed from lemon balm and oregano, which can be drunk 2-3 times a day; it also has an anti-inflammatory and sedative effect.
A mother should not consume cow's milk, which, according to a common misconception, supposedly increases lactation - this is not true, in addition, the child may develop an allergy if the mother has a lot of cow's milk in her diet.
You should not use:
- chocolate, citrus fruits;
- coffee;
- basil, parsley;
- sage, mint;
- hop cones, walnuts;
- lingonberries.
A woman must drink enough liquid - at least two liters per day, including all drinks and liquid food components.
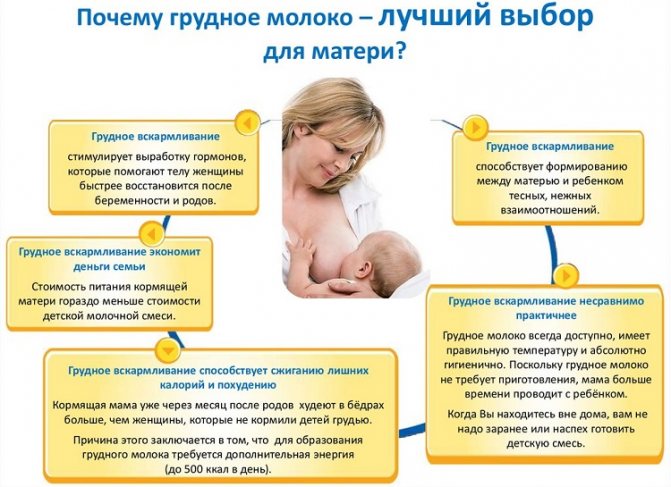
Nutrition plays a big role in the formation of lactation, especially after surgery. For normal breastfeeding, a woman should receive 500 kcal more in her diet per day than usual. These calories are divided as follows: proteins 40%, carbohydrates 30% and fats also 30%.
Watch this video on how to increase lactation:
Stimulation of lactation with drugs
If lactation does not occur, then it can be stimulated with drugs; for this, several groups of drugs are used:
- hormonal drugs;
- antispasmodics;
- sedatives;
- dietary supplements;
- vitamins and minerals.
Hormonal drugs include synthetic and natural analogues of oxytocin - Oxytocin and Desaminoxytocin. They act identically to their own hormones and restore the disturbed secretion rhythm. The prescription of these drugs is strictly controlled by an obstetrician-gynecologist and is more often used when there are problems with the production of the hormone in the pituitary gland or its delivery to the place of requirement.
Antispasmodics are necessary to eliminate excessive contraction of the smooth muscle elements of the ducts. After surgery, this condition occurs quite often. Such drugs as No-shpa or Drotaverine, Papaverine are suitable.
Often a woman who has given birth, especially after a cesarean section, is in a state of great stress, so sedatives are required. For this category of patients, herbal preparations are recommended: Novopassit, Persen, Valerian. Glycine and Glycine Forte also have a good effect.
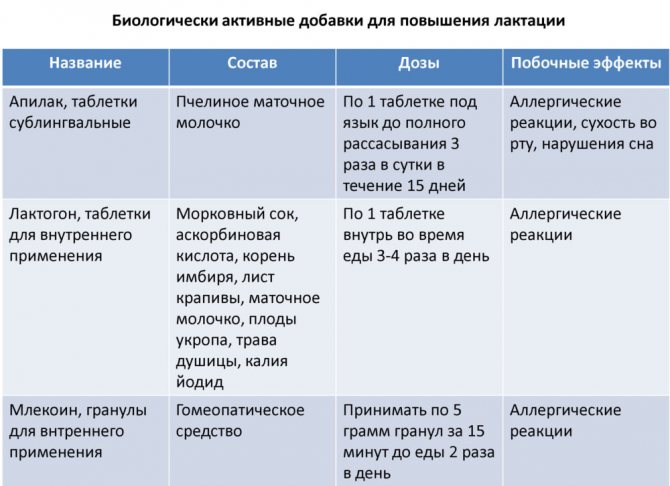
Dietary supplements for stimulating lactation contain complexes of plant herbs and natural elements and work as natural phyto-lactogens. Popular among them are:
- Lactogone;
- Femilak;
- Mlekoin;
- Apilak.
Lactogon Femilak Mlekoin Apilak
Vitamins and minerals in pharmacies are specially collected for nursing mothers. All drugs to stimulate lactation should be prescribed only after consultation with a gynecologist.
What to do if there is little milk after cesarean section
If there is little milk after a cesarean section, you need to:
- Monitor the condition of all organs and systems so as not to miss possible complications.
- Massage your chest with a stream of water from the shower and your hands 1-2 times a day.
- Eat nutritiously and properly, avoid foods undesirable for lactation.
- Use sedatives and vitamin supplements.
- Examine hormonal levels, prolactin levels.
- Try to put the baby to the breast as early as possible.
- If you are unable to breastfeed, express milk regularly.
- Use drugs to stimulate lactation if necessary.
- Do not squeeze the mammary gland with tight underwear made of synthetic materials.
- Follow a rest and exercise regime.
- Reduce stress exposure.

If after a week or two after all preventive measures the milk supply does not increase, you need to go to the obstetrician. To understand that there is not enough milk, you need to pay attention to the child’s condition:
- the baby sleeps poorly and is restless;
- apathetic or indifferent child at the end of the day;
- flaccid and dry baby skin;
- weight loss or insufficient weight gain;
- gastrointestinal disorders of the child;
- the baby quickly abandons the breast;
- scanty milk production when expressing.
A decrease in the amount of milk after a cesarean section occurs naturally in comparison with a normal natural birth. This is due to physiological stress in the body.
Features of the first application. When to latch on to your baby?
Breastfeeding after cesarean section has its own characteristics. It is worth noting that the first attachment plays a crucial role in this process, since it determines how the baby’s feeding will proceed in the future. It is worth noting that the mother may need nipple stimulation to make lactation more active.
Stimulating the nipples promotes the production of hormones that increase milk supply. And the mother’s emotions after she puts the baby to her breast for the first time trigger powerful processes to restore the body.
It is worth noting that when performing a caesarean section using regional anesthesia, the first breastfeeding after a caesarean section can be problematic. At the same time, some doctors practice applying to the mother's breast immediately after all the stitches have been applied. This option is the most optimal, because the baby will receive the milk he needs with beneficial microflora. This, of course, is a serious help for the formation of immunity. But if the surgical intervention was characterized by difficulties, then the woman will be able to wake up only after a few hours. There is no need to be upset about this, because if you did not put the baby to your breast immediately after the operation, this does not mean that further lactation and breastfeeding are impossible.
How to preserve milk after cesarean
To preserve milk after cesarean section, you need to strictly adhere to all the recommendations of doctors, first of all you need to:
- avoid physical and psychological stress;
- rest and try to get enough sleep;
- take medications only on the recommendation of a doctor according to indications;
- eat well;
- do not contact with patients with infectious diseases;
- See your doctor regularly to prevent complications.
You also need:
- put the baby to the breast as soon as possible;
- express milk if this is not possible;
- take vitamin and mineral supplements;
- do self-massage.
Watch this video on how to express milk correctly (manual method):
If the baby does not want to breastfeed
If the child does not want to breastfeed, you need to pay attention to the general condition of the baby. You may be concerned about:
- lethargy and apathy;
- pallor;
- sleep disturbance;
- bowel dysfunction;
- increase in body temperature.
The baby, as a rule, wakes up and asks for food, thereby initiating and stimulating lactation. If he feels unwell, one of the first symptoms is loss of appetite. This can also be affected by changes in the quality of milk: there may be some changes in the mother’s diet that the baby does not like, or the mother starts taking some medications. In any case, you need to pay attention to the female body.
Frequent use of artificial formula and bottles also contributes to the fact that the baby does not want to breastfeed. After all, to suck milk out of it, the baby needs to put in a lot of effort, but drinking from a bottle is much easier. Many mothers mistakenly assume the frequent use of soft nipples and bottles, while this has a bad effect on both the formation of the bite and the child’s desire to breastfeed.
Incorrect breastfeeding technique can lead to the baby not wanting to breastfeed over time. Excessive strain on the muscles of the mouth and pharynx will lead to fatigue in the baby, which will make him no longer want to resort to this method of feeding.
If the baby does not want to take the breast, you need to check:
- his state of health;
- maternal health status;
- maternal diet and nutritional supplements;
- technique and feeding regimen.
Watch this video about the mode and technique of breastfeeding: