The fourth blood type is Rh negative - this is the rarest blood type among all. It occurs in only eight percent of the world's population. This fact seriously complicates the search for suitable donors for recipients. At transfusion stations, such material is frozen and subsequently used for its intended purpose. It is known that each blood group has its own characteristics regarding compatibility, pregnancy planning, nutrition and human character. Let's take a closer look at the characteristics of negative blood group 4.
Why do you need to know the group?
Every person needs to know their own blood parameters - this will help protect themselves in the event of a serious injury, heavy bleeding, and when unscheduled surgical intervention may be necessary. To make up for the shortage with donor biomaterial, you must know your group and Rh factor. If the blood does not meet the specified parameters, serious complications will develop. It is important to know which blood group is suitable for 4 negative.
The Rh group and Rh factor are also determined during family planning so that everything goes smoothly. If a pregnant woman has a negative Rh factor, and her fetus has a “+” sign, this provokes a Rh conflict when specific substances are synthesized in the female body - antibodies that reject the fetus. From this, the child receives serious pathologies and may even die in the womb.
Positive Rh in the mother
If the mother has a positive Rh factor, then the negative Rh factor of the man does not affect the development of the fetus.
When a child inherits Rh negative, a conflict does not arise, because there is no protein in the child’s blood that would be unfamiliar to the woman’s immune system. Rhesus compatibility:
- If the mother is Rh positive and the father is Rh positive, the child inherits Rh positive. There will be no complications.
- Positive mother and positive father, the child inherits negative. There will be no complications; the mother’s body does not react to the elements of the child’s blood.
- Positive mother and negative father, the child inherits positive. The protein in the mother’s blood is “familiar” to the immune system, so the protein in the child’s blood is not perceived as foreign.
- Positive mother and negative father, the child inherits the negative one. There is no protein in the child’s blood, no reaction occurs.
In all cases, the child’s body will not contain elements that are unfamiliar to the mother’s immune system.

The fourth blood group is Rh negative: features of transfusion
The fourth group has its pros and cons. First of all, the positive point is that a person with such blood with a positive Rh is permissible for an emergency infusion of any other blood.
And if a person has a negative blood group: which one can be transfused? When Rh is “-”, then the donor blood must have a negative factor, and any group will do.
But people with group 4 are especially valued as donors; special donation records are kept for them. Therefore, answering the question of how much blood of group 4 negative costs, we can say that it is the most expensive.
Another positive factor is that carriers of the fourth group have high resistance to allergies and autoimmune pathologies.
Regarding the negative Rh factor of group 4, it is worth noting that with a donor transfusion, the Rh factors must necessarily match.
4th negative blood group and character
Russia, Europe, America are horoscopes: “What is your sign?” Japan, Korea, China - “ketsu-eki-gata” - the dependence of a person’s character on his blood type.
Blood AB R is by definition a “Mystery.” Its bearers are always pronounced extroverts . For a comfortable existence, they need an environment, they need an audience. They are very good at public speaking. When choosing a partner, they are most often guided not by the heart, not by emotions, but by logic and calculation.
And despite all this, people with this blood type are indecisive, often doubt their abilities, and cannot imagine their life alone, without the support of others. Behind the external self-confidence lies a vulnerable and touchy person.
AB blood carriers are more often endowed with psychic and healing abilities than others, their IQ is much higher than average. And according to the testimony of modern magicians (how reliable?), the 4th negative is “pure and strong blood.” The “black” sorcerer will never stand in the way of its owner.
Fourth negative blood: characteristics of people
The influence of the fourth group is especially noticeable in terms of the behavior, temperament and health of its carriers. Owners of group 4 have strong immunity, but at the same time they have weak digestion. For this reason, people often become ill with infectious, viral pathologies that enter the body through the respiratory system or esophagus.
It is characteristic that the fourth blood group combines all the negative features of the first and second. It is known that this type is the youngest and not fully examined. It is worth noting that this blood has a remarkable ability to adapt to changes in diet. It was acquired during the process of human evolution. This trait makes it easy to lose weight and adapt to new diets.

Blood type 4 is Rh negative: this characteristic describes the difference between such people in their perception of the world. Carriers of this group have creative thinking, developed intellectual abilities, and a sharp mind.
Although AB (IV) carriers have a strong character, they are sometimes touchy, emotional, and whiny. This mainly depends on the people around you, parents, friends, and the team at work. When choosing a profession, such people give preference to the creative field of activity and art. They love games, intellectual pursuits, and pay attention to self-development.
Such people strive to be different from others, try to do something special, unusual.
However, the disadvantage of the character of the carriers of group 4 is considered to be emotional instability and vulnerability to insults. These people are sensitive to their defeats and bullying, so they are capable of falling into drug or alcohol addiction and even committing suicide.
Blood type (AB0)
Determines belonging to a certain blood group according to the ABO system.
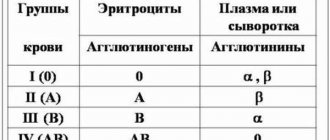
Functions. Blood groups are genetically inherited characteristics that do not change during life under natural conditions. A blood group is a specific combination of surface antigens of erythrocytes (agglutinogens) of the ABO system. Determination of group membership is widely used in clinical practice during transfusion of blood and its components, in gynecology and obstetrics when planning and managing pregnancy. The AB0 blood group system is the main system that determines the compatibility and incompatibility of transfused blood, because its constituent antigens are the most immunogenic. A feature of the AB0 system is that in the plasma of non-immune people there are natural antibodies to an antigen that is absent on red blood cells. The AB0 blood group system consists of two group erythrocyte agglutinogens (A and B) and two corresponding antibodies - plasma agglutinins alpha (anti-A) and beta (anti-B). Various combinations of antigens and antibodies form 4 blood groups:
- Group 0 (I) - there are no group agglutinogens on red blood cells, alpha and beta agglutinins are present in the plasma.
- Group A (II) - red blood cells contain only agglutinogen A, agglutinin beta is present in the plasma;
- Group B (III) - red blood cells contain only agglutinogen B, plasma contains agglutinin alpha;
- Group AB (IV) - antigens A and B are present on red blood cells, plasma does not contain agglutinins.
Determination of blood groups is carried out by identifying specific antigens and antibodies (double method, or cross reaction).
Blood incompatibility is observed if the red blood cells of one blood carry agglutinogens (A or B), and the plasma of another blood contains the corresponding agglutinins (alpha or beta), and an agglutination reaction occurs.
Transfusion of red blood cells, plasma and especially whole blood from a donor to a recipient must be strictly observed in group compatibility. To avoid incompatibility between the blood of the donor and the recipient, it is necessary to accurately determine their blood groups using laboratory methods. It is best to transfuse blood, red blood cells and plasma of the same group as determined for the recipient. In emergency cases, group 0 red blood cells (but not whole blood!) can be transfused into recipients with other blood groups; Group A red blood cells can be transfused into recipients with blood group A and AB, and red blood cells from a group B donor can be transfused into group B and AB recipients.
Blood group compatibility cards (agglutination is indicated by a + sign):
| Donor blood | Recipient's blood | |||
| 0 (I) | A (II) | B (III) | AB (IV) | |
| 0(I) | — | + | + | + |
| A(II) | + | — | + | + |
| B(III) | + | + | — | + |
| AB (IV) | + | + | + | — |
| Donor's red blood cells | Recipient's blood | |||
| 0 (I) | A (II) | B (III) | AB (IV) | |
| 0(I) | — | — | — | — |
| A(II) | + | — | + | — |
| B(III) | + | + | — | — |
| AB (IV) | + | + | + | — |
Group agglutinogens are found in the stroma and membrane of erythrocytes. Antigens of the ABO system are detected not only on red blood cells, but also on cells of other tissues or can even be dissolved in saliva and other body fluids. They develop in the early stages of intrauterine development, and are already present in significant quantities in the newborn. The blood of newborn children has age-related characteristics - characteristic group agglutinins may not yet be present in the plasma, which begin to be produced later (constantly detected after 10 months) and the determination of the blood group in newborns in this case is carried out only by the presence of antigens of the ABO system.
In addition to situations involving the need for blood transfusion, determination of blood type, Rh factor, and the presence of alloimmune anti-erythrocyte antibodies should be carried out during planning or during pregnancy to identify the likelihood of an immunological conflict between mother and child, which can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn.
Hemolytic disease of the newborn
Hemolytic jaundice of newborns, caused by an immunological conflict between mother and fetus due to incompatibility of erythrocyte antigens. The disease is caused by incompatibility of the fetus and mother for D-Rhesus or ABO antigens, less often there is incompatibility for other Rhesus (C, E, c, d, e) or M-, M-, Kell-, Duffy-, Kidd- antigens. Any of these antigens (usually D-Rh antigen), penetrating into the blood of a Rh-negative mother, causes the formation of specific antibodies in her body. The latter enter the fetal blood through the placenta, where they destroy the corresponding antigen-containing red blood cells. Predispose to the development of hemolytic disease of the newborn by impaired placental permeability, repeated pregnancies and blood transfusions to a woman without taking into account the Rh factor, etc. With early manifestations of the disease, an immunological conflict can cause premature birth or miscarriages.
There are varieties (weak variants) of antigen A (to a greater extent) and less frequently of antigen B. As for antigen A, there are options: “strong” A1 (more than 80%), weak A2 (less than 20%), and even weaker ones (A3 , A4, Ah - rarely). This theoretical concept is important for blood transfusion and can cause accidents when assigning donor A2 (II) to group 0 (I) or donor A2B (IV) to group B (III), since the weak form of antigen A sometimes causes errors in the determination blood groups of the ABO system. Correct identification of weak A antigen variants may require repeated testing with specific reagents.
A decrease or complete absence of natural agglutinins alpha and beta is sometimes noted in immunodeficiency states:
- neoplasms and blood diseases - Hodgkin's disease, multiple myeloma, chronic lymphatic leukemia;
- congenital hypo- and agammaglobulinemia;
- in young children and the elderly;
- immunosuppressive therapy;
- severe infections.
Difficulties in determining the blood group due to suppression of the hemagglutination reaction also arise after the introduction of plasma substitutes, blood transfusion, transplantation, septicemia, etc.
Inheritance of blood groups
The laws of inheritance of blood groups are based on the following concepts. At the ABO gene locus, there are three possible variants (alleles) - 0, A and B, which are expressed in an autosomal codominant manner. This means that individuals who have inherited genes A and B express the products of both of these genes, resulting in the AB (IV) phenotype. Phenotype A (II) can be present in a person who has inherited from parents either two genes A, or genes A and 0. Accordingly, phenotype B (III) - when inheriting either two genes B, or B and 0. Phenotype 0 (I) appears when inheritance of two genes 0. Thus, if both parents have blood group II (genotypes AA or A0), one of their children may have the first group (genotype 00). If one of the parents has blood type A(II) with a possible genotype AA and A0, and the other has B(III) with a possible genotype BB or B0, children can have blood groups 0(I), A(II), B(III) ) or AB (!V).
Indications for the purpose of analysis:
- Determination of transfusion compatibility;
- Hemolytic disease of newborns (detection of incompatibility between the blood of mother and fetus according to the AB0 system);
- Preoperative preparation;
- Pregnancy (preparation and follow-up of pregnant women with negative Rh factor)
Preparation for the study: not required
Material for the study: whole blood (with EDTA)
Determination method: Filtration of blood samples through a gel impregnated with monoclonal reagents - agglutination + gel filtration (cards, crossover method).
If necessary (detection of the A2 subtype), additional testing is carried out using specific reagents.
Execution time: 1 day
Research result:
- 0 (I) - first group,
- A (II) - second group,
- B (III) - third group,
- AB (IV) - fourth blood group.
When subtypes (weak variants) of group antigens are identified, the result is given with an appropriate comment, for example, “a weakened variant A2 has been identified, individual selection of blood is required.”
Rh factor Rh
The main surface erythrocyte antigen of the Rh system, by which a person’s Rh status is assessed.
Functions. Rh antigen is one of the erythrocyte antigens of the Rh system, located on the surface of erythrocytes. There are 5 main antigens in the Rh system. The main (most immunogenic) antigen is Rh (D), which is usually referred to as the Rh factor. The red blood cells of approximately 85% of people carry this protein, so they are classified as Rh positive (positive). 15% of people do not have it and are Rh negative (Rh negative). The presence of the Rh factor does not depend on group membership according to the AB0 system, does not change throughout life, and does not depend on external reasons. It appears in the early stages of intrauterine development, and is already found in a significant amount in the newborn. Determination of Rh blood is used in general clinical practice during transfusion of blood and its components, as well as in gynecology and obstetrics when planning and managing pregnancy.
Incompatibility of blood according to the Rh factor (Rh conflict) during blood transfusion is observed if the donor's red blood cells carry Rh agglutinogen, and the recipient is Rh negative. In this case, the Rh-negative recipient begins to produce antibodies directed against the Rh antigen, leading to the destruction of red blood cells. Transfusions of red blood cells, plasma, and especially whole blood from a donor to a recipient must strictly observe compatibility not only by blood type, but also by Rh factor. The presence and titer of antibodies to the Rh factor and other alloimmune antibodies already present in the blood can be determined by specifying the “anti-Rh (titer)” test.
Determination of blood type, Rh factor, and the presence of alloimmune anti-erythrocyte antibodies should be carried out when planning or during pregnancy to identify the likelihood of an immunological conflict between mother and child, which can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn. The occurrence of Rh conflict and the development of hemolytic disease of newborns is possible if the pregnant woman is Rh negative and the fetus is Rh positive. If the mother is Rh + and the fetus is Rh negative, there is no danger of hemolytic disease for the fetus.
Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborns is hemolytic jaundice of newborns, caused by an immunological conflict between mother and fetus due to incompatibility of erythrocyte antigens. The disease can be caused by incompatibility of the fetus and mother for D-Rhesus or ABO antigens, less often there is incompatibility for other Rhesus (C, E, c, d, e) or M-, N-, Kell-, Duffy-, Kidd antigens (according to statistics, 98% of cases of hemolytic disease of newborns are associated with D - Rh antigen). Any of these antigens, penetrating the blood of a Rh-negative mother, causes the formation of specific antibodies in her body. The latter enter the fetal blood through the placenta, where they destroy the corresponding antigen-containing red blood cells. Predisposition to the development of hemolytic disease of newborns is impaired placental permeability, repeated pregnancies and blood transfusions to a woman without taking into account the Rh factor, etc. With early manifestations of the disease, an immunological conflict can cause premature birth or repeated miscarriages.
Currently, there is a possibility of medical prevention of the development of Rh conflict and hemolytic disease of newborns. All Rh-negative women during pregnancy should be under medical supervision. It is also necessary to monitor the level of Rh antibodies over time.
There is a small category of Rh-positive individuals who are able to form anti-Rh antibodies. These are individuals whose red blood cells are characterized by significantly reduced expression of the normal Rh antigen on the membrane (“weak” D, Dweak) or expression of an altered Rh antigen (partial D, Dpartial). In laboratory practice, these weak variants of the D antigen are combined into the Du group, the frequency of which is about 1%.
Recipients containing Du antigen should be classified as Rh-negative and should be transfused only with Rh-negative blood, since normal D antigen can cause an immune response in such individuals. Donors with the Du antigen qualify as Rh-positive donors, since transfusion of their blood can cause an immune response in Rh-negative recipients, and in the case of previous sensitization to the D antigen, severe transfusion reactions.
Inheritance of the Rh blood factor.
The laws of inheritance are based on the following concepts. The gene encoding the Rh factor D (Rh) is dominant, the allelic gene d is recessive (Rh-positive people can have the DD or Dd genotype, Rh-negative people can only have the dd genotype). A person receives 1 gene from each parent - D or d, and thus has 3 genotype options - DD, Dd or dd. In the first two cases (DD and Dd), a blood test for Rh factor will give a positive result. Only with the dd genotype will a person have Rh negative blood.
Let's consider some variants of the combination of genes that determine the presence of the Rh factor in parents and children
- 1) The father is Rh positive (homozygote, genotype DD), the mother is Rh negative (genotype dd). In this case, all children will be Rh positive (100% probability).
- 2) Father is Rh positive (heterozygote, genotype Dd), mother is Rh negative (genotype dd). In this case, the probability of having a child with negative or positive Rh is the same and equal to 50%.
- 3) The father and mother are heterozygotes for this gene (Dd), both are Rh positive. In this case, it is possible (with a probability of about 25%) to give birth to a child with negative Rh.
Indications for the purpose of analysis:
- Determination of transfusion compatibility;
- Hemolytic disease of newborns (detection of incompatibility between the blood of mother and fetus according to the Rh factor);
- Preoperative preparation;
- Pregnancy (prevention of Rh conflict).
Preparation for the study: not required. Material for research: whole blood (with EDTA)
Determination method: Filtration of blood samples through a gel impregnated with monoclonal reagents - agglutination + gel filtration (cards, crossover method).
Execution time: 1 day
Interpretation of results:
The result is given in the form: Rh + positive Rh - negative When weak subtypes of antigen D (Du) are detected, a comment is given: “a weak Rh antigen (Du) has been detected, it is recommended to transfuse Rh-negative blood if necessary.”
Anti-Rh (alloimmune antibodies to the Rh factor and other erythrocyte antigens)
Antibodies to the clinically most important erythrocyte antigens, primarily the Rh factor, indicating the body's sensitization to these antigens.
Functions. Rh antibodies belong to the so-called alloimmune antibodies. Alloimmune anti-erythrocyte antibodies (to the Rh factor or other erythrocyte antigens) appear in the blood under special conditions - after a transfusion of immunologically incompatible donor blood or during pregnancy, when fetal red blood cells carrying paternal antigens that are immunologically foreign to the mother penetrate through the placenta into the woman’s blood. Non-immune Rh-negative people do not have antibodies to the Rh factor. In the Rh system, there are 5 main antigens, the main (most immunogenic) is antigen D (Rh), which is usually referred to as the Rh factor. In addition to the Rh system antigens, there are a number of clinically important erythrocyte antigens to which sensitization can occur, causing complications during blood transfusion. The method of screening blood for the presence of alloimmune anti-erythrocyte antibodies, used in INVITRO, allows, in addition to antibodies to the Rh factor RH1(D), to detect alloimmune antibodies to other erythrocyte antigens in the test serum.
The gene encoding the Rh factor D (Rh) is dominant, the allelic gene d is recessive (Rh-positive people can have the DD or Dd genotype, Rh-negative people can only have the dd genotype). During pregnancy of a Rh-negative woman with a Rh-positive fetus, the development of an immunological conflict between mother and fetus due to the Rh factor is possible. Rh conflict can lead to miscarriage or the development of hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborns. Therefore, determination of blood type, Rh factor, as well as the presence of alloimmune anti-erythrocyte antibodies should be carried out when planning or during pregnancy to identify the likelihood of an immunological conflict between mother and child. The occurrence of Rh conflict and the development of hemolytic disease of newborns is possible if the pregnant woman is Rh negative and the fetus is Rh positive. If the mother has a positive Rh antigen and the fetus is negative, a conflict regarding the Rh factor does not develop. The incidence of Rh incompatibility is 1 case in 200-250 births.
Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborns is hemolytic jaundice of newborns, caused by an immunological conflict between mother and fetus due to incompatibility of erythrocyte antigens. The disease is caused by incompatibility of the fetus and mother for D-Rhesus or ABO (group) antigens, less often there is incompatibility for other Rhesus (C, E, c, d, e) or M-, M-, Kell-, Duffy- , Kidd antigens. Any of these antigens (usually D-Rh antigen), penetrating into the blood of a Rh-negative mother, causes the formation of specific antibodies in her body. The penetration of antigens into the maternal bloodstream is facilitated by infectious factors that increase the permeability of the placenta, minor injuries, hemorrhages and other damage to the placenta. The latter enter the fetal blood through the placenta, where they destroy the corresponding antigen-containing red blood cells. Predisposition to the development of hemolytic disease of newborns is impaired placental permeability, repeated pregnancies and blood transfusions to a woman without taking into account the Rh factor, etc. With early manifestations of the disease, an immunological conflict can cause premature birth or miscarriages.
During the first pregnancy with an Rh-positive fetus, a pregnant woman with Rh “-” has a 10-15% risk of developing an Rh conflict. The first meeting of the mother's body with a foreign antigen occurs, the accumulation of antibodies occurs gradually, starting from approximately 7-8 weeks of pregnancy. The risk of incompatibility increases with each subsequent pregnancy with a Rh-positive fetus, regardless of how it ended (induced abortion, miscarriage or childbirth, surgery for an ectopic pregnancy), with bleeding during the first pregnancy, with manual separation of the placenta, and also if childbirth is carried out by caesarean section or accompanied by significant blood loss. with transfusions of Rh-positive blood (if they were carried out even in childhood). If a subsequent pregnancy develops with an Rh-negative fetus, incompatibility does not develop.
All pregnant women with Rh “-” are placed on special registration in the antenatal clinic and dynamic monitoring of the level of Rh antibodies is carried out. For the first time, an antibody test must be taken from the 8th to the 20th week of pregnancy, and then periodically check the antibody titer: once a month until the 30th week of pregnancy, twice a month until the 36th week and once a week until the 36th week. Termination of pregnancy at less than 6-7 weeks may not lead to the formation of Rh antibodies in the mother. In this case, during a subsequent pregnancy, if the fetus has a positive Rh factor, the probability of developing immunological incompatibility will again be 10-15%.
Testing for alloimmune anti-erythrocyte antibodies is also important in general preoperative preparation, especially for people who have previously received blood transfusions.
Indications for the purpose of analysis:
- Pregnancy (prevention of Rh conflict);
- Monitoring of pregnant women with negative Rh factor;
- Miscarriage;
- Hemolytic disease of newborns;
- Preparation for blood transfusion.
Preparation for the study: not required. Material for research: whole blood (with EDTA) Determination method: agglutination + gel filtration method (cards). Incubation of standard typed erythrocytes with the test serum and filtration by centrifugation of the mixture through a gel impregnated with a polyspecific antiglobilin reagent. Agglutinated red blood cells are detected on the surface of the gel or in its thickness.
The method uses suspensions of erythrocytes from group 0(1) donors, typed according to erythrocyte antigens RH1(D), RH2(C), RH8(Cw), RH3(E), RH4(c), RH5(e), KEL1( K), KEL2(k), FY1(Fy a) FY2(Fy b), JK (Jk a), JK2(Jk b), LU1 (Lu a), LU2 (LU b), LE1 (LE a), LE2 (LE b), MNS1(M), MNS2 (N), MNS3 (S), MNS4(s), P1 (P).
Execution time: 1 day
When alloimmune anti-erythrocyte antibodies are detected, their semi-quantitative determination is carried out. The result is given in titers (the maximum dilution of the serum at which a positive result is still detected).
Units of measurement and conversion factors: U/ml
Reference values: negative.
Positive result: Sensitization to Rh antigen or other erythrocyte antigens.
Description of suitable nutrition
Since people with group IV and a negative Rh factor have a disappointing health profile and are at risk of developing anemia, they should take care of a properly balanced diet and intake of vitamins.
Thanks to numerous scientific studies, important foods have been identified, the consumption of which leads to the normalization of weight, mineral and vitamin balance in the body. It is recommended to include in the menu exactly those foods that help speed up metabolism and lose weight. In this case, it is first necessary to determine the compatibility of food with the blood type, so as not to cause harm to the body.
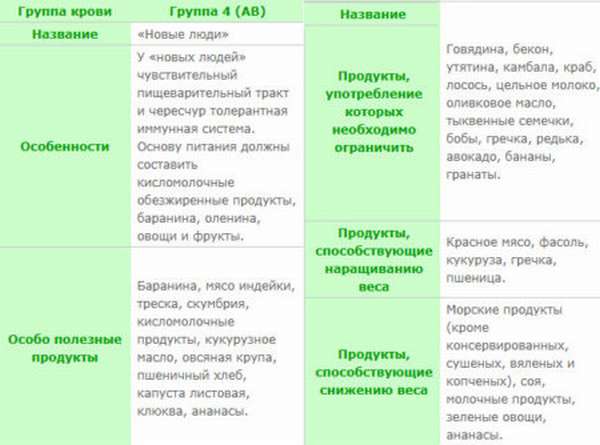
For those with AB(IV) blood who are Rh negative, it is recommended to limit recipes to dishes from the following list:
- Liver and other offal,
- Red beef meat,
- Beans in any form
- Corn and porridge made from it.
Regarding seafood and fish, it is worth saying that this item of the diet requires a lot of attention. Ideal for carriers of the fourth group are mackerel and river fish: carp or perch. But you will have to forget about all types of red fish and smoked seafood forever.
Nutrition
Representatives of the fourth group are usually unpretentious in food, often limit themselves to snacking on fast food, but at the same time they are very fond of complex and delicious dishes, and prefer to constantly consume dairy products and vegetables. There is a tendency to gain weight. Therefore, foods rich in animal fats and carbohydrates should be excluded from the diet or limited as much as possible: pork, lard, brisket, fatty chicken, bacon. Due to the tendency to joint diseases, you should limit seafood - crustaceans, mussels with a high content of protein and salts, and limit dishes made from beans and peas. It is also advisable to exclude canned food and spicy seasonings or limit them as much as possible. Consumption of black tea and coffee should be limited.
The following products are recommended for regular consumption:
- lean meat - beef, rabbit, turkey, beef liver;
- sea and river fish;
- low-fat dairy products, preferably fermented milk products;
- porridge from oatmeal and buckwheat, rice, preferably unpolished;
- a sufficient amount of vegetables and fruits, with the exception of high-calorie vegetables - potatoes, eggplants, bananas, persimmons;
- fruit and vegetable juices and purees;
- herbal drinks from linden, chamomile, lemon balm, St. John's wort, rosehip decoction.
With normalization of nutrition and a proper lifestyle, representatives of the 4th group can easily do without serious health problems.
We also recommend studying this topic:
What are the types of blood types and how are they determined?
Is pregnancy possible?
Blood type 4 with a negative factor and pregnancy are quite compatible things, contrary to popular belief. However, in medicine there are known cases of incompatibility with a spouse or with one’s own child. If there is incompatibility with dad, then this is not too terrible a phenomenon compared to intrauterine conflict.
When a problem of incompatibility between parents arises, the doctor asks for additional tests and prescribes special examinations that make it possible to prevent future problems.
For a baby, a situation with a Rh mismatch is more dangerous. At 28 weeks of gestation, the doctor must inject the mother with immunoglobulin in order to overcome the antibodies and prevent them from entering the newborn’s blood. Otherwise, a Rhesus conflict will develop. A child whose blood contains maternal fluid that does not correspond to Rh will develop severe anemia and jaundice, and may fall into a coma inside the womb.

It is worth saying that the first pregnancy in women with such incompatibility occurs with the lowest risks. And if a woman becomes pregnant again or after an abortion, then the risk of developing a Rhesus conflict increases significantly, which negatively affects the child. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend that couples where the woman has a fourth negative blood group give birth to only one child from the first conception.
If the first pregnancy was successful, this does not mean that the next one will end the same. After all, a child does not inherit maternal negative blood in every case. He can also receive his father's Rh positive genes.
Health by blood type
The majority of the world's population, who have the third positive group, do not have any health problems in their lives. A minority of residents may encounter problems in the endocrine system. These people may develop diabetes or multiple sclerosis.
K. Landsteiner's discovery suggests that 85% of group 3 carriers have a positive Rh factor. The remaining 15% are Rh negative. Therefore, when blood is transfused from one person to another, the compatibility of the Rhesus of the donor and recipient is considered a prerequisite.
It is compatibility that all doctors pay attention to when they need 3 positive blood. If compatibility is low, then a precipitate may appear, leading to the destruction of blood cells - red blood cells
One of the worst cases of low compatibility can be the death of the patient.
It is important to note that the third Rh-positive group is compatible both with its own group and with other groups. Compatibility with other groups can be characterized as follows:
- the positive third group can be combined with groups 1 and 3 with negative and positive rhesus;
- compatibility with groups 3 and 4 (Rh positive in both cases);
- the third c can be combined with groups 1 and 3 (Rh negative in both cases).
Compatibility of men and women
Since those with the fourth blood type are considered universal and at the same time unique, the perception of their intimate life is significantly different from other people. The fact is that girls and guys in this category love to receive great attention to themselves. Their chosen ones will also have to be different from other people in order to satisfy their “halves” and build a happy marriage.

It is worth noting that marital unions with people of the fourth type are often long-lasting. The carriers of this group are always attentive, caring, faithful and reliable, even if they marry the owners of the first or third groups. Due to such character qualities, strong and long-term families can be formed, especially among those couples who manage to give birth to healthy offspring.
What are the compatibility characteristics of blood group 1 positive?
What are the compatibility characteristics of blood type 1 positive? Let's talk about this further
Pay special attention to the following list of foods that are both beneficial and harmful to the functioning of the human body. The diet is based mainly on the content of (protein) protein products
The fact is that this can include various meat products: different types of fish and meat; if there are no meat products in a person’s diet, he will begin to feel hungry. You must watch your diet and should not be lazy about exerting yourself physically.
Let me give you a small example: drinks include green tea, coffee, natural juices, beer, dry wines, and herbal teas from sage, chamomile, ginseng, strawberry leaves and echinacea are especially useful. Products include greens, non-acidic vegetables, lamb, liver, iodized salt, buckwheat, legumes
This also includes vitamins: special attention should be paid to vitamins such as groups B and K. The mineral composition should be enriched with iodine, manganese, calcium
People with this blood type are characterized by a slow metabolism and will have to fight this by giving up the following foods: wheat, lentils, corn products. Because of them, metabolic processes slow down, which interferes with the production of insulin. The right diet will keep the body in good shape until old age. But do not forget to listen to your own body, because our body is our own laboratory in which we conduct experiments, through trial and error, we will learn to make our body work like a clock and have the health of a young man.
People with the first group cannot but be noticed by the following signs and qualities such as leadership, optimism, independence, determination, representing a person with the character of a hunter. They are always in a good and cheerful mood, which they can boast about and raise it to the people around them. With cheerfulness and good spirits, they more easily achieve their goals at work, in their personal lives and self-realization. Particularly noteworthy are marital relationships or the choice of your partner when planning a pregnancy. Such people can be called deficit.
Everyone should know this. Do not forget that people with the first positive blood group are prone to diseases such as arthritis, poor blood clotting, development of a predisposition to allergies and deterioration of the thyroid gland. Don't forget that the diet should be high in protein and low in carbohydrates, so check the expiration date of foods. People with this blood type are quite active, but there are also less active ones who need to do aerobics, weight lifting and running or cycling. This will help you lose excess weight and be 100% toned.
What is the probability of conception
Most men and women know that nothing else affects pregnancy like blood type, especially when it comes to the rarest of them being Rh negative.
Quite often there is a phenomenon called lack of compatibility, which can happen to either the father or the child. It should be noted that incompatibility with the father is not such a terrible phenomenon that can affect health, like, for example, its presence with the fetus in the womb. But with proper support from experienced specialists, the period of bearing a child will pass without complications. If problems during pregnancy are related to the compatibility of future parents, then a number of diagnostic measures are mandatory, thanks to which problems can be avoided . But if there is incompatibility between mother and child due to the Rh factor, then things are much worse, and you simply cannot do without a vaccine, which is given at the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy - it is needed in order to destroy antibodies that are not suitable for the baby. In this regard, the rare type AB blood with a negative Rh factor conceals a certain kind of danger, since only the first pregnancy can pass without deviations. That is why experts strongly recommend that couples, one of whose parents has a quarter blood type, not take risks and give birth to only one child.
People with the fourth blood group and a negative Rh factor can give birth to healthy babies; you just need to follow all the instructions of specialists, do not miss scheduled examinations and listen to your body. If you feel any discomfort, do not hesitate to tell your doctor about it, because not only your health, but also the life of your unborn child depends on it.
Healthy food
It is important that blood type AB with a negative Rh factor is most susceptible to diseases such as anemia. To prevent the development of this disease from making itself felt, it is necessary to adhere to proper nutrition, not forgetting to take vitamins and dietary supplements. Numerous studies have identified a number of products, the use of which can lead to the gradual loss of extra pounds and normalization of weight.

So, products that increase the metabolic process in the body of both men and women:
- Lean meats such as turkey and chicken. In this case, single servings should not exceed one hundred and fifty grams.
- As for fish, people with a negative Rh factor and blood type IV should eat it no more than five times a week, in exactly the same portions as meat, excluding halibut and haddock.
- Fermented milk products such as yogurt, kefir, natural yogurt or cottage cheese. Cheese is also allowed.
- Fresh fruits and nuts, but citrus fruits should be excluded from your daily diet.
- You are allowed to consume no more than four eggs per week.
- Vegetables are allowed to be consumed in large quantities, with the exception of avocados, radishes, olives and beans.
- If you are a big fan of mushrooms, then you are in luck, since if you follow a diet, you are allowed to eat them, although no more than four times a week.
- Flaxseeds or flour obtained from them.
There are also foods that need to be excluded, as they can contribute to rapid weight gain. In this case we are talking about fatty meat, flour, corn, wheat and buckwheat. While following such a diet, both women and men should not forget that the consumption of seafood and various spicy dishes is strictly prohibited. It may seem that you cannot create a normal diet from what you are allowed to eat, but this is far from the case.
If you are unable to choose the right products for yourself and cannot create a daily menu, then it is best to seek help from a qualified nutritionist with experience who will take into account all the characteristics and your preferences.
Regardless of what you eat on such a diet, some foods still need to be consumed, but in limited quantities, since they are sources of vitamins and amino acids that are vital for the body. We are talking about liver, red meat, legumes and various cereals. This prescription must be taken into account by a nutritionist when preparing a diet. Even with such a rare blood type, you can live a full and vibrant life.
Rh negative and positive, how to find out?
In fact, Rh is a property of blood and can be analyzed using a zolicone. To do this, your blood is taken, mixed with a special serum and observed. Red blood cells stick together - the blood is positive, if not - negative. It is impossible to make mistakes in such a study. The blades have new technical equipment, which means the clarity of the experiment is guaranteed. But it happened that the biomaterial lost its properties or inexperienced trainees confused the plugs. Also, patients with kidney and liver diseases have elevated protein levels, and this contributes to distorting the results.
In any case, having a positive Rh is much nicer and safer than having negative blood counts.
Compatibility with other groups
If we talk about the owner of the fourth plasma group, as a recipient or donor, then there is a special character in terms of compatibility. When a person becomes a donor, his special blood is highly valued. Because it is quite rare.
Recipients with positive blood fluid type IV can be said to be lucky. Since their blood is compatible with all other types. The peculiarity lies only in the situation of negative Rh. In case of Rh-, blood of the same Rh factor can be injected into the blood vessels.
A person who has such rare blood is able to help other people by becoming a donor. Of course, for this you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and have the desire. But in absolutely any donor center, clients with IV Rh- blood are the most valuable.
How to eat healthy
A person with this type of blood is not suitable for any special diet. There will be no particular difficulties with choosing food and establishing the correct diet. This blood type makes it possible to easily digest both foods of plant and animal origin. This aspect will allow you to follow either one diet or a completely different one.
You should know that there are also foods prohibited for consumption (wheat, peanuts, buckwheat). It is better for a person with positive group 3 to include in their diet: low-fat kefir or yogurt, beef liver, carrots, red fish, bananas and grapes, green tea. There is also an extensive list of foods that should not be consumed. These include: alcohol, coffee and black tea, tomatoes and tomato juice, ketchups and mayonnaise, pork, chicken and wheat bread, ice cream and other sweets
Knowing your blood type, it is important to properly monitor your health, eat and plan your pregnancy.
Separation of men and women by blood groups
was first produced by the Englishman K. Landsteiner. The scientist was able to identify two components in the blood of people, which represent special antigens - groups A and B. Among them there is a third positive group, in which there are no antigens at all. All the rest belong to the carriers of the fourth - it has both components.
Complexes with this research
Expanded hospital complex Expanded infectious screening for prevention and hospitalization RUB 5,030 Composition
Pregnancy planning. Clinical indicators 4,310 R Composition
Future dad Comprehensive examination to prepare a couple for conception RUB 5,820 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Entry into IVF 16,850 RUR
- Preparation for IVF for a man RUR 4,450
- Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 11,790 RUR