When there is a possibility of damage to the patient's body, a CT scan is considered the preferred clinical approach. The examination provides detailed and clear images that show the inflammatory lesions, their location, stage, type, shape and level of progression. Doctors have the opportunity to timely prescribe the correct course of medical therapy (operative or pharmacological) and predict tactics for eliminating possible complications.
The principle of operation of a tomograph is to emit x-rays that penetrate the patient’s body, are recorded by the device’s sensors and transmit the received information to a computer monitor. The dose of toxic radiation is given in a minimal amount, which will protect the patient from worsening the condition. Test results can be obtained within an hour and a half after the end of the session. Photos and information are provided in electronic or printed format.
Classification of computed tomography
Doctors divide clinical equipment depending on the nuances of the task and the design of the device. There are three types:
- Step-by-step research (classical technique) - during the test, the transforming table is moved inside the tunnel with slow movements, sensors record readings and simulate an image. To create a new cut, the couch must be in constant motion. The photo shows the desired section in section.
- Spiral analysis (SCT) - the workplace moves at a constant pace, and the X-ray emitter independently describes a trajectory in a circle of a certain area. The installed detectors will record vibrations that have penetrated into the anomalous area. The survey takes much less time compared to the first method and shows detailed and specific summary information.
- Multislice tomography (MSCT) is a multilayer assessment of the condition, which stands out from others due to the location of the clamps. They are placed in several lines.
The main advantages of liver CT with contrast
Computer research identifies the disease in the initial stages of development, which makes the technique in demand. Radiation diagnostics reveals functional disorders in the functioning of the organ as a result of the introduction of an additional amplifier in the form of a contrast agent. The doctor receives a sufficient amount of data to formulate a correct and accurate conclusion, determines a treatment regimen or changes the current tactics. If a disorder is detected at the first stage, the percentage of the patient’s ability to get rid of the disease without surgery increases. The main advantages of CT scan of the liver with contrast in Moscow include:
- Highly accurate diagnosis of abnormal phenomena of any origin.
- Ability to check several departments at once.
- Emergency examination without preparatory measures with rapid provision of results is allowed.
- The use of sensors with a reduced level of motion sensitivity, which improves the acquisition of detailed images.
- A computer program creates a 3D image to study the disease from different angles (the abnormal area can be viewed in its original position or enlarged).
- Reduced incidence of adverse reactions.
- Weak sensitivity of the device to metal structures built into the patient’s body.
- The session takes place without pain or discomfort.
Differential diagnosis of liver cancer
When analyzing CT data, you should always keep in mind that some liver lesions may resemble liver cancer. An inexperienced doctor may confuse different conditions and make an incorrect diagnosis. The pathology with which it is necessary to differentiate HCC is:
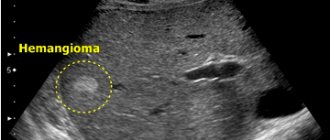
1) Liver hemangioma. To clarify the conclusion, delayed scanning (10-20 minutes after contrast administration) and visualization of vascular lacunae help.
2) Hepatocellular adenoma. Large adenomas may have the same structure as HCC and contain fat inclusions, necrosis, cystic cavities, and calcifications. However, adenomas are characterized by slow growth of the expansive type (without invasion) and the absence of intrahepatic metastases.
3) FNG. With focal nodular hyperplasia, the CT picture may be similar to that of liver cancer. Sometimes it is impossible to distinguish these diseases only from CT examination data - a biopsy is necessary.
4) Metastases. In some cases, the idea of secondary tumors may be suggested by the multiplicity of organ damage and the identification of the primary focus. However, an experienced radiologist with extensive experience in diagnosing liver disease can usually reliably distinguish between primary cancer and secondary metastatic lesions.
In what situations is a liver CT scan with contrast prescribed?
The main indications when doctors prescribe a computer scan include:
- The likelihood of the formation of a tumor, cyst or metastasis formed as a result of manual palpation of the organ, after laboratory or instrumental tests.
- Clarification of the nature, location and size of the tumor, which was identified during an ultrasound scan.
- Determination of the exact number, size and location of metastases before planned surgery.
- The presence of symptoms of a focal or diffuse disorder (pain in the right side of the abdominal cavity, regular belching, nausea reflex after eating, constant bloating, abnormal metallic taste in the mouth, etc.).
- Damage (search for hematomas, ruptures, finding foreign objects).
- Deviation from the norm in development.
- If the attending physician is unsure of the accuracy of the data after the ultrasound.
- Monitoring the effective impact of the treatment course.
- Periodic status checks if there is a violation.
- Study-controlled puncture appointment.
On the search service moskva-mrt.ru you will find out the prices of a liver CT scan with contrast in Moscow and can make an appointment at any medical center convenient for you online in a few clicks. When submitting an application through the portal, you will be able to take advantage of discounts and promotional offers.
What pathologies can a computed tomography scan of the liver detect?

The results of a CT scan of the liver are pictures and images, analyzing and studying which, a radiologist can identify the following diffuse changes in the liver:
- various neoplasms: cancer, hemangioma, adenoma, other types of tumors;
- liver abscess is a purulent inflammation that affects the tissues of the organ and leads to the formation of a purulent cavity in it;
- signs of liver cysts, the appearance of which may be associated with trauma (hematomas, seromas and liver bruises) of other types of cysts;
- presence and extent of spread of metastases;
- echinococcosis is a parasitic lesion of an organ caused by the proliferation of a parasitic infection in it;
- signs of liver cirrhosis;
- signs of infectious or viral lesions, such as hepatitis.
In addition to pathologies and disorders, CT scan of the liver also shows the functional characteristics of the organ, as well as the changes found in it - tissue density, size, location of tumors or metastases, their depth.
What does a liver CT scan with contrast show?
If a patient has symptoms of liver hemangioma, a CT scan with contrast is suitable to confirm the diagnosis. There are a number of anomalies that can be found using a diagnostic method. The main condition is to contact a medical professional in a timely manner to receive professional assistance. CT scan of the liver with contrast shows:
- Tumor formation.
- Formation of metastases.
- Mechanical injuries.
- Inflammatory processes.
- Damage to blood vessels or the presence of internal hemorrhage.
- Jaundice.
- Cirrhosis.
- Dystrophic disorders.
Contraindications for examination
It is prohibited to perform a CT scan of the liver in the following cases::
- pregnancy;
- The patient's weight exceeds 120 kg.
Carry out with caution and only if there are serious indications.:
- children under 12 years old;
- nursing women;
- patients with renal failure;
- with multiple myeloma.
Contraindications for the administration of a radiocontrast agent:
- pregnancy and lactation;
- renal and liver failure;
- diabetes;
- intolerance to iodine-containing contrast agents.
Restrictions
The study is considered safe due to the minimal dose of X-ray radiation. However, there are contraindications regarding the frequency of the procedure to prevent the progression of radiation sickness. Doctors identified the following as the main restrictive measures:
- Carrying a child (radiation has a significant impact on the development of the fetus and causes severe consequences).
- Age barrier up to 14 years (toxic radiation will have adverse effects on the development of internal organs, soft tissues and bone structures in children).
- Obesity (the design feature of the tomograph is that the permissible body weight is up to 150 kg).
During the diagnosis, the patient will be given an additional amplifier intravenously to improve image accuracy. There are restrictions for undergoing CT with contrast for liver hemangioma and other diseases:
- Chronic stages of kidney disease.
- Individual intolerance to the components of a pharmacological agent.
- Diabetes.
How does the CT scan process work?
The person being examined must remove all metal objects, accessories and jewelry and leave them along with all gadgets outside the door of the diagnostic room. He changes into special clothes - spacious, comfortable, made of cotton fabric and without metal parts, after which he is placed on the tomograph table and takes a comfortable, relaxed position.
For 15 minutes (in rare cases - up to half an hour) the patient is under the targeted influence of x-rays. All that is required of him is not to move, and strictly follow the doctor’s instructions when he asks him to hold his breath.
If the procedure involves the introduction of a contrast agent, then after the first scan the table with the patient is rolled out of the scanner, a catheter with the substance is placed in the cubital vein, and the patient is sent back to the tomograph for scanning. In this case, the contrast is introduced by the x-ray technician before the second scan begins.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
During the process, the device buzzes, crackles, and makes a characteristic noise. For patients for whom this fact causes discomfort, the x-ray technician has earplugs or headphones prepared.
The radiologist and x-ray technician are in the next room - from there they monitor the progress of the procedure and can communicate with the patient. If a person feels a sharp malaise, pain, or deterioration of health during the process, he immediately reports this to the doctor.
A series of images taken during the examination are recorded in computer media and processed by a special program that produces ready-made layer-by-layer images.
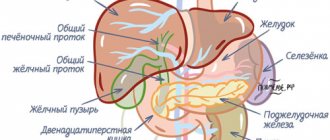
Tomographic scanning of the liver occurs in segments closely related to the duct system, of which there are five in the liver. This technique greatly simplifies the examination, further reading of the results and the radiologist’s conclusions.
Preparation for CT scan of the liver with contrast
A standard CT scan session does not require any preliminary preparations. An exception is examination with a contrast agent. Before use it is recommended:
- Avoid eating a few hours before the test.
- Take your past diagnostic results and outpatient card with you.
- Inform the technologist about the presence of diseases and phobias (for example, claustrophobia), pregnancy, and breastfeeding.
- Mentally tune in to a positive perception.
Preparation for a CT scan of the liver with contrast in case of increased anxiety levels involves administering a sedative. If a nauseating reaction to the additional enhancer occurs during preoral use, it can be added to tea or juice.
Is liver cancer curable?
Currently, several types of successful treatment for liver cancer are used. For small nodes (up to 2 cm), identified by CT or MRI, surgeons use radical tumor removal. For large nodes, as well as for multiple lesions, radiofrequency ablation is used - destruction of the tumor with special high-frequency waves, as well as liver transplantation. Liver transplantation for cancer is a complex operation that is increasingly being used successfully in Russia in large surgical centers. For large tumors, palliative treatment methods are used, such as transarterial chemoembolization (CEPA), as well as drug methods (Nexavar, sorafenib).
Stages of liver CT scan with contrast
Usually, when undergoing diagnostics, doctors initially scan using the classical method. The second step is the administration of a contrast reagent and a series of photographs is taken. It will show comparative information from two different examinations, which is an important step in studying the patient’s condition.
Iodine-based components are used to enhance the visibility of anomalous points. When administering a pharmacological substance, there is a possibility of feeling warmth or coldness in the body, a taste of iodine in the mouth, mild irritation of the skin, mild dizziness, nausea, gag reflexes, and an uncontrollable feeling to empty the bladder. Adverse reactions to an iodine-containing drug do not pose a danger to the patient’s health. It will go away on its own and the product will completely leave the body after 48 hours.
On the search portal moskva-mrt.ru you will find out the current prices for liver CT scans with contrast, the location of capital clinics in your area and throughout the city. On the website you can apply for an appointment with any doctor online. Simply fill out a short form and confirm your booked date.
Other malignant neoplasms of the liver
Fibrolamellar cancer (FLC) is usually detected in young men with complete well-being, in a cirrhotic liver, without concomitant hepatitis B or C. Computed tomography for fibrolamellar cancer is performed to assess the resectability of the formation and determine the TNM stage. In a native study, LPR looks like an intrahepatic lesion, large in size - 5 cm or more, and with clear edges. This lesion has a density lower than the density of normal hepatic parenchyma, a lobular structure and - a peculiarity - a central area of fibrosis of a “star-shaped” shape. During the arterial phase, the tumor slightly intensifies in the peripheral parts, while the central part does not change its density.
Cholangiocarcinoma (CAC) is a malignant neoplasm of the bile duct epithelium. With CT, you can see uneven thickening of the wall of the duct against the background of its significant expansion. The formation accumulates contrast and remains hyperdense for a long time - this is a hallmark of cholangiocarcinoma.
Example of cholangiocarcinoma on computed tomography. Arrows highlight areas of the tumor that accumulate contrast agent in the delayed phase.
Hepatoblastoma is most often detected in childhood (3-5 years). On CT examination, it appears as a large hypodense lesion, occupying most of the section area. Approximately 1/5 of all hepatoblastomas are characterized by the presence of multiple foci. The structure of hepatoblastoma is heterogeneous - it may include areas of necrosis, calcifications, and connective tissue. Differential diagnosis is carried out with HCC, LPR, metastases.
Angiosarcoma of the liver is a rare tumor of the walls of the hepatic vessels. Its potential for malignancy is extremely low. It occurs more often in young women under 40 years of age; on CT it appears in the form of multiple cystic foci with clear boundaries, prone to fusion and the formation of polymorphic pseudocysts. It manifests itself as a “target” symptom due to uneven accumulation of contrast in the presence of a zone devoid of blood vessels along the periphery.
Liver lymphoma is extremely rare as a primary tumor; it is usually detected in systemic diseases, for example, lymphogranulomatosis. The CT picture is generally nonspecific - hypodense or isodense nodes of various sizes can be identified, and enlargement of the nearest lymph nodes can also be determined.
Undifferentiated embryonic cell sarcoma of the liver is a malignant neoplasm of sarcomatous cells. It looks like a large cyst, in some cases containing septa. However, despite its low density, it is actually solid, soft tissue. It sharply increases with contrast (in the periphery), differential diagnosis with the cystic variant of HCC is extremely difficult.