Briefly: Do an ultrasound of the liver once a year to notice possible abnormalities in time. Do not eat anything for 8 hours before the procedure. And three days before the ultrasound, give up alcohol, fatty foods and foods that increase gas formation.
- Structure of the liver
- When is an ultrasound performed?
- Liver size on ultrasound in an adult
- What is the normal size of the liver in women according to ultrasound?
- Is it possible for the liver to change in size during pregnancy?
- What diseases does a change in liver size indicate?
This article was checked and edited by Candidate of Medical Sciences, toxicologist Stanislav Radchenko.
The liver is located in the abdominal cavity under the ribs on the right side and has a rather complex irregular shape. Therefore, to understand what measurements are made during an ultrasound, it is necessary to briefly dwell on the structure of the liver.
Structure of the liver
Anatomically, this organ is divided into two areas:
- Left lobe.
- The right lobe, which consists of the quadrate lobe and the caudate lobe.
Segmentally, the organ can be divided into 8 parts. Each part appears as a pyramidal-shaped area of hepatic parenchyma. The segments are supplied with blood and innervated separately. Each section of the segment contains nerve endings that ensure interaction between the liver and the central nervous system.
The structure of the liver and its location in the body.
Lobular parenchyma includes:
- hepatic plates, which consist of radial rows of hepatocytes;
- intralobular blood capillaries,
- capillaries of the biliary tract.
In the stromal part of the liver there are:
- outer connective tissue capsule,
- loose fibrous tissue of interlobular layers,
- blood vessels
- and nerve endings.
Clinical case
A 23-year-old unmarried woman was admitted for nonspecific pain in the epigastric region. An ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs was performed, the results of which are presented in Fig. 1.
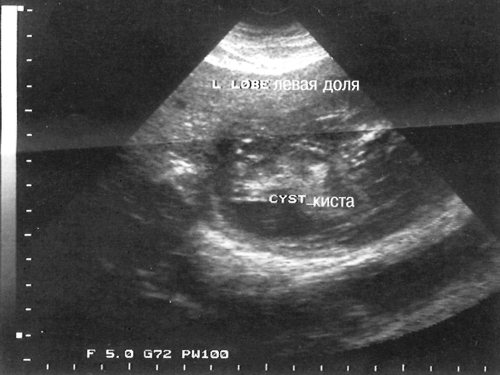
Rice. 1.
Ultrasound examination reveals the presence of a large hypoechoic lesion with irregular hyperechoic edges, which obscures and replaces the gallbladder wall and causes inward depression.
a)
Posterior segment of the right lobe of the liver.
b)
Lateral segment of the left lobe of the liver.
What is the patient's diagnosis?
Interpretation:
Two hypoechoic foci are identified, the first in the posterior segment of the right lobe and the second in the lateral segment of the left lobe. Both lesions, followed by dorsal enhancement of sound, have clear contours, multiple internal septations, and hyperechoic contents.
Diagnosis:
hydatid cyst.
Hydatid echinococcosis
The most common cause of hydatid disease in humans is infestation of the parasite Echinococcus granulosus, which is common in countries where sheep or cattle farming is developed, primarily in the Middle East, Australia and the Mediterranean. After the intermediate host ingests the eggs of E. granulosus (a 3-6 mm long tapeworm that usually lives in the intestines of dogs), the embryo implants through the mucous membrane of the duodenum and through the portal vein system reaches the liver, where it is retained, although the lungs may be affected. kidneys, spleen.
Signs of the disease on echography:
simple cyst without internal echoes (Fig. 2), cyst with daughter cysts, cyst with separated endocyst, calcified formations.
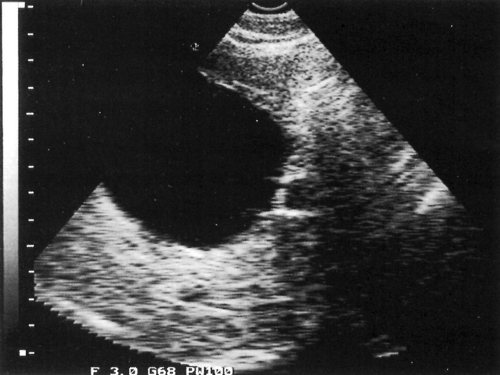
Rice. 2.
A simple cyst without internal echoes.
Signs of the disease on computed tomography.
The disease is manifested by the presence of cysts with clear contours, which can be multi- or single-chamber, with a thin or thick wall and an appropriate level of attenuation (usually 15-25). Small daughter cysts can sometimes be visible inside a large cyst. Central or peripheral calcification may occur. Strengthening is observed only in the cyst wall.
Differential diagnosis for liver cysts:
congenital liver cyst, liver abscess, common bile duct cyst, cystic metastases, pseudopancreatic cyst in the liver.
When is an ultrasound performed?
Ultrasound examination of the liver is included in the general examination of the abdominal cavity. For preventive purposes, it is recommended to do an ultrasound at least once a year. Liver ultrasound for clinical indications in adults and children is prescribed in the following cases:
- Frequent pain in the intercostal area on the right side.
- Change in skin color, yellowness, itching.
- Skin rashes of unknown origin.
- The appearance of a vascular network and internal subcutaneous hematomas.
- Change in color of stool.
- White coating or crimson color of the tongue.
Ultrasound is safe and suitable for initial screening.
How should you prepare for a liver ultrasound? To obtain correct research results:
- Three days before the test, completely eliminate fatty foods, alcohol, and foods that promote gas formation.
- If the pancreas is also supposed to be examined, then do an enema 2–3 hours before and take activated charcoal (6–8 tablets).
- Do not eat anything for the last 8 hours before your procedure.
Preparation for the liver ultrasound procedure
Before performing an ultrasound of the liver, it is not advisable to eat food for at least five hours (it is better to wait eight). Therefore, if you have a study scheduled in the morning, do not have breakfast under any circumstances. If the ultrasound is scheduled for the day or evening, a light breakfast is acceptable, but during the day preceding the examination, you should not eat foods that are excessively rich in fat. It is also recommended a few days before the ultrasound to control fiber intake (it increases gas formation, which, in turn, negatively affects the results of the study), not to drink carbonated drinks and, of course, to refrain from drinking any types of alcoholic beverages. If you suffer from excess weight in the obesity stage, you will need an enema about a day before the procedure itself, which will contribute to more accurate ultrasound results.
Liver size on ultrasound in an adult
The specialist will accurately determine the size of the organ and find any deviations. The main indicators during the study are:
- liver size,
- tissue structure,
- boundaries of the liver.
The normal size of a healthy liver in adults is determined for the left and right lobes separately.
- Normal sizes of the right lobe:
- thickness no more than 11 cm for women and 13 cm for men;
- KVR (oblique vertical dimension) no more than 15 cm;
- length for women - 11 cm, for men - 15 cm.
- Normal dimensions of the left lobe:
- thickness about 7 cm;
- CCR (craniocaudal size) - no more than 10 cm.
The total length of a healthy adult liver is from 14 to 18 cm. The width should not exceed 22.5 cm. In the sagittal (passing from the spine to the anterior midline) plane, its size should be between 9 cm and 12 cm.
For children, the norms differ and depend on age. For example, in the liver of a one-year-old child, the length of the right lobe is 6 cm, and the left lobe is 4 cm. In a 15-year-old teenager, the size of the right lobe is up to 10 cm, and the left lobe is up to 5 cm.
A case from the practice of an expert on the website Pokhmelye.rf, gastroenterologist Daniela Purgina.
A mother and her 15-year-old son came to the appointment. An abdominal ultrasound revealed hepatomegaly. All possible examinations were carried out to look for liver diseases, but no pathology was identified. It turned out that the ultrasound diagnostic doctor did not take into account the fact that the boy at 15 years old was much taller and larger than his peers. She compared the size of his liver with the average size that is typical for childhood and adolescence - and according to these data, the boy’s liver was larger than normal. However, when we compared its size with the normal size of an adult male liver, all parameters turned out to be normal. That is why, when assessing the size of an organ, it is necessary to pay attention to the constitutional characteristics of the patient.
The contours of the liver normally have clear outlines, the tissue structure is homogeneous. The liver has a significant ability to regenerate, and even with 25% healthy tissue, new cells begin to grow. However, this ability to regenerate turns out to be harmful in the situation of existing structural damage. With cirrhosis, nodes of pathological regeneration are formed, the growth of which impairs the blood supply to other parts of the organ. In general, this leads to deformation of the contours and surface of the liver, which can be detected not only by ultrasound, but also by palpation.
Estimated price for liver testing
CVR of the liver (the norm in adults is slightly different from that in children) is carried out in many medical centers and outpatient clinics.
Cost of the procedure:
- Ultrasound of the liver with color circulation: from 2 thousand rubles.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (pancreas, gall bladder, liver): from 2 thousand 300 rubles.
- Ultrasound, which evaluates the intrahepatic bile ducts, the structure of the organ, its contours: from 1 thousand 200 rubles.
- Comprehensive ultrasound of the abdominal organs: from 1 thousand 200 rubles.
The price of a diagnostic procedure depends on the scale of the study and the prestige of the medical institution.
For prevention and control of normal indicators, adult patients should undergo a complete examination of the abdominal organs annually. In this case, doctors will determine the size of the liver using the diagnostic methods of CVR, CCR, determine the condition of the gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, and detect pathologies, if any, at an early stage.
What is the normal size of the liver in women according to ultrasound?
The normal liver sizes in women are:
- vertical size of the right lobe - 126 mm;
- anteroposterior size of the right lobe - 113 mm;
- vertical size of the left lobe - 109 mm;
- the anteroposterior size of the left lobe is 82 mm.
Hepatomegaly is considered to be an increase in the oblique vertical size: then it is more than 155 mm.
Is it possible for the liver to change in size during pregnancy?
No, the liver does not undergo changes in structure during pregnancy, with the exception of acute conditions such as acute fatty liver degeneration, when fat accumulates in the liver parenchyma. Normally, the fat content in the liver does not exceed 5%, and with the development of acute fatty liver degeneration, the fat content increases to 13–19%.
The liver, as the main chemical laboratory of our body, performs a double load during pregnancy, providing the mother and fetus with the necessary substances:
- There is a decrease in the amount of glycogen in the liver, which is due to the intensive transfer of glucose from the mother’s body to the fetus, but this does not lead to an increase in blood sugar levels.
- The intensity of lipid metabolism changes, which is manifested by an increased content of cholesterol in the blood and its esters, which indicates an increase in the synthetic function of the liver.
- The protein-forming function of the liver also changes. This change becomes significantly pronounced from the second half of pregnancy, when the concentration of total protein in the blood decreases. At the same time, there is a decrease in the concentration of albumin and an increase in the level of globulins. Activation of protein metabolism is aimed at providing the growing fetus with amino acids, which are the source of the synthesis of its own proteins.
- An increased level of alkaline phosphatase can be detected in the blood due to the synthesis of this enzyme by the placenta.
- The processes of inactivation of estrogens and other steroid hormones synthesized by the placenta also intensify. The detoxification function of the liver is slightly reduced.
And despite all these intensive processes, the size of the liver does not change during pregnancy.
Indications for the study
The doctor recommends doing an ultrasound of the liver in the following cases:
- in the presence of laboratory and clinical data indicating liver dysfunction;
- to clarify and confirm the diagnosis detected using other examination methods;
- if there is a suspicion of malignant degeneration of organ tissue;
- to clarify the location and number of metastatic foci;
- if necessary, interventional (catheter-based) intervention, which requires ultrasonography;
- presence of abdominal trauma (road accident, fall from height);
- tracking the dynamics of treatment of liver diseases;
- presence of human complaints of heaviness, pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting, malaise, loss of appetite;
- icteric tint of the skin, mucous membranes;
- darkening of urine, discoloration of stool;
- changes recorded in biochemical blood tests that reflect liver function (increased transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, total protein);
- the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity (ascites);
- the presence of symptoms of malignant tumors that can metastasize to the liver;
If a malignant disease is suspected, an ultrasound of the liver and kidneys may be prescribed to assess the extent of the process. Additionally, a computed tomography or MRI is performed.
- increase in organ size. When visiting a doctor, a physical examination is performed, which involves palpation (palpation) of the abdomen. During the study, the size of the liver is determined in children and adult patients.
What diseases does a change in liver size indicate?
This may indicate any pathological processes in the liver. For example, the size of the liver may change due to:
- alcoholic liver disease;
- viral hepatitis;
- non-alcoholic fatty liver disease;
- drug-induced hepatitis;
- liver cirrhosis;
- autoimmune hepatitis;
- primary biliary cirrhosis;
- hemochromatosis;
- Wilson-Konovalov disease.
An expert on the website Pokhmelye.rf, gastroenterologist Daniela Purgina, dispels a typical misconception among patients.
Is your liver healthy? Take the free test!
Many patients, having learned that according to the results of an ultrasound examination they have an enlarged liver, immediately begin to panic: they think that they have cirrhosis of the liver. Actually this is not true. Hepatomegaly is not the same as cirrhosis of the liver. If this condition is detected, you must contact a gastroenterologist to find the cause.
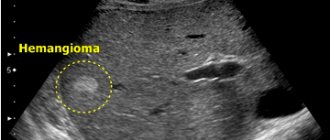
The size of the liver may increase unevenly due to the presence of formations: cysts, hemangiomas, nodular hyperplasias, metastases.
You can contact the hepatologist in the comments. Don't hesitate to ask!
Article published: 2019-01-01
This article was last updated: 06/17/2019
Didn't find what you were looking for?
Try using search
doctor or administrator.
Read the dictionary of terms.
Progress of the procedure
The patient is located on the couch, takes a horizontal position: lies on his back or on his side. The area being examined is treated with a special gel to facilitate the sliding of the device's sensor. The doctor examines the image of the organ on the screen. If visibility needs to be improved, the patient is asked to change position. The duration of the ultrasound is about 15 minutes. The procedure is completely painless for the patient.
An ultrasound diagnostic specialist deciphers the result, records it in a conclusion, and passes it on to the patient. After this, you can immediately return home and do your usual activities.