What worries the expectant mother at 36 weeks of pregnancy
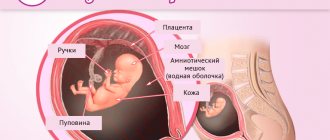
At 36 weeks of pregnancy, the expectant mother’s belly causes a lot of inconvenience due to its large size. Due to the load, a woman feels pain in the lower back and legs, suffers from swelling and has difficulty moving. At 36 weeks of pregnancy, the uterus continues to put pressure on the internal organs, causing shortness of breath and heartburn. Some women experience abdominal prolapse during this period: the baby slowly moves closer to the “exit”, occupying the pelvic floor with the presenting part (head or buttocks). By the way, a baby at 36 weeks of pregnancy is already the size of a large papaya, weighing approximately 2.5 kg.
Almost all women experience fear before childbirth, especially if it is their first time. At 36 weeks, expectant mothers become increasingly irritable, anxious and nervous. Meditation, relaxation, yoga for pregnant women, relaxing massage, listening to music, reading books, communicating with loved ones or a personal psychologist will be good helpers in the fight against fear.
Weight gain at 36 weeks of pregnancy ranges from 7.9 kg (with a BMI of more than 26) to 13.6 kg (with a BMI of less than 19.8). To calculate your individual weight gain at 36 weeks, use the pregnancy weight gain calculator.
What's happening
During this period, fatty tissue continues to accumulate in the tiny body, which is why the baby’s body becomes more and more rounded. Hair grows on the head, facial muscles develop, and eyebrows and eyelashes become even more noticeable. The auricles have also improved: the cartilages have hardened, and the grooves and curls are fully formed.
At the 36th week of pregnancy, the bones of the fetus are intensively strengthened, but the skull still remains flexible so that the head can easily pass through the birth canal. The heart is fully formed, although the hole between the right and left parts has not yet closed. Don't worry: it will disappear immediately after the baby is born. The lungs are also ready to work, but the baby will take his first breath only after birth.
Now you clearly feel the movements of your son or daughter. True, due to the fact that the uterus is very crowded, there is now less movement than before. On average, during this period there should be at least 10 movements in 12 hours. And by the end of pregnancy, when the fetus grows even more, their number will be halved.
Baby at 36 weeks of pregnancy
At 36 weeks, the baby is about the size of a pineapple.
At week 36, the Baby’s height is from 44 to 45 cm, and his weight is 2400-2500 g.
Your Baby at this time:
- begins to learn to breathe through his nose - until now he breathed through his mouth, since his nostrils were closed with mucus plugs. By inhaling and exhaling amniotic fluid, he trains to breathe air;
- able to distinguish shades of taste;
- begins to remember what he hears. Melodies or rhymes that are heard more than once cause a reaction of motor activity in the Baby.
Baby at 36 weeks of pregnancy
Normal growth rates for abdominal circumference during pregnancy
| Duration in weeks | Abdominal circumference in cm |
| 20 | 70-75 |
| 22 | 72-78 |
| 24 | 75-78 |
| 26 | 77-82 |
| 28 | 80-85 |
| 30 | 82-87 |
| 32 | 85-90 |
| 34 | 87-92 |
| 36 | 90-95 |
| 38 | 92-98 |
| 40 | 95-100 |
Circumference dimensions for multiple pregnancies
If a woman is expecting not one, but two, three or more babies at once, her belly will grow much faster. During examinations, the doctor will be able to palpate the uterus protruding above the pubis as early as 12 weeks, and the growth rates of the abdominal circumference will be ahead of the norm and by the end of the period will exceed 100 cm.
Doctors monitor the course of multiple pregnancies twice as closely and often prescribe ultrasounds to make sure that development proceeds without complications.
Helpful advice for a future dad
You are already accustomed to the fact that in this section we talk about mom - her well-being, emotions, useful and not so useful actions.
However, today this page is intended for future dads - please give it to your spouse to read or send him the link. So... Dear future dad! The baby has not only occupied your partner’s belly and is making his presence known more and more - he has “zombified” her brain and feelings! If conversations are only about the Baby, if feelings are only towards the Baby, it’s time to sort it out.
To do this, you need to form several undeniable attitudes:
- I am and will be the most important person in the life of my half, no matter how strong feelings for the Kid she may be overwhelmed at the moment;
- I allow my soul mate - the mother of my Baby - to talk about him and express her love for him, because I understand that this is how she shares these feelings with me and expects support from me. This helps me find common topics for conversation with her, and also be sure that a loving mother will give birth to a healthy and strong heir (heiress);
- I will not hesitate to ask you to express your love for me as much as for the Baby, but I will not abuse such a request;
- I will become more and more imbued with the idea that a new meaning has appeared in my life - a child who will be similar to me in many ways. And it depends on me what his life will be - joyful, happy or full of anxiety;
- only I can ensure the full safety of the mother and the Baby, and for the time being, their material well-being;
- I am the main representative among men for my Baby and soon I will be able to give him what his mother cannot. I will teach the Kid (be it a son or a daughter) to be strong and not be afraid to overcome obstacles, play football and fish, hold a hammer and drive a car;
- I will raise my son to be a real man, and for the time being I will talk about this through the wall of my mother’s belly;
- I’ll tell my daughter right now that she’s beautiful and that I’m looking forward to seeing her in a dress and bows.
Regardless of what your significant other says and feels in connection with the Baby, your Baby expects that he and you will develop his own unique friendly (and not competitive) relationship, into which the mother - for the sake of her own well-being - sometimes need not be initiated .
Mother. Changes in the psychological and physical state of the body at 36 weeks

From the 36th week of pregnancy, one of the most difficult periods of gestation begins. There are about 4 weeks left until the expected date of birth (EDD), and the expectant mother begins to feel that changes are happening to her body and psyche.
Hormonal levels change, the body trains and prepares for childbirth. As a result, the woman feels irritability, nervousness, and increased sensitivity (more than during the entire previous pregnancy). Relatives may note that she has become whiny, capricious, overly active or withdrawn. This is a normal phenomenon, a reaction to hormonal changes.
Interesting. From the 36th week, many women notice an increased desire to clean the house. This is popularly called “nesting syndrome.” The expectant mother always thinks that the environment is not clean enough for her future baby, and that everything urgently needs to be prepared. It is good if a woman follows safety precautions: does not overexert herself, does not move heavy objects, avoids working with her arms raised high, etc.
There is a growing feeling that my strength is becoming less and less every day. Walking becomes more difficult, periods of activity, when you really want to do something, are replaced by severe fatigue and a desire to get enough sleep.
Although there are often problems with sleep this week. The tummy has become even larger, the back constantly ache after a slight load, lying on the back one feels dizzy, and on the side the arms and legs become numb. These and other signs of the period prevent the expectant mother from resting normally. Many women begin to actively count down the days before giving birth, not realizing that this can happen earlier or later than the due date.
Is it worth counting the days until the PDR? Doctors do not recommend this; they advise continuing to monitor your well-being, noting and promptly informing the gynecologist about changes, and thinking that the baby should be born at the moment when he is most ready for it.
PDR is an estimated date, it means exactly 40 weeks from the beginning of the last menstruation, 38 embryonic weeks with a cycle of 28 days. Each woman is unique, and the moment of fertilization can occur on different days of the cycle (depending on many factors: nutrition, stress, hormonal levels, etc.), so the baby can be fully prepared for birth both at the 38th week and at the end of the 42nd.
At 36 weeks, the expectant mother may continue to be haunted by various fears. The most common ones are:
- not having time to pack things for the maternity hospital, not thinking through the details of discharge, etc. To get rid of this fear, it is worthwhile now to fully think through all organizational issues and discuss them with loved ones. Place the signed maternity hospital packages in a visible place, tell your husband or loved ones in detail what will need to be done while you are in the medical facility, what purchases to make;
- pain during childbirth. Childbirth is a natural process that many billions of women have gone through since the dawn of humanity. A pregnant woman's body and psyche have a full range of tools to get through this stage. You shouldn’t think about pain, or build up fears, so that at a crucial moment it does not hinder your actions, and allows you to listen carefully and follow the obstetricians’ commands.
Most women who have already given birth and have undergone psychological training claim that the pain during childbirth was significantly less than they expected.
- fear that something will go wrong during childbirth. At the 36th week, maternal instinct is fueled by hormones and begins to make assumptions about the future birth of the baby. A pregnant woman may try to project a variety of scary stories told by friends and on the Internet onto herself. As a result, fear intensifies, the woman loses herself in front of him. To prevent horror from taking over the mind of a pregnant woman, you should now avoid various stories and information containing negative experiences. The expectant mother should be determined that everything will be fine with her and her baby. This confidence can be supported by a timely visit to the gynecologist in case of questions, or immediate hospitalization when the labor process begins. The presence of a woman in labor in the maternity hospital makes the risk of complications during childbirth minimal; doctors have a variety of equipment at hand that they can use if necessary.
Psychological preparation for childbirth is an important element of a favorable birth of a baby. Free from fears, a mother can focus on the process, listen carefully and follow the obstetricians’ commands, and apply the necessary breathing techniques to reduce pain. At the 36th week, it is worth continuing to attend courses for expectant mothers in order to be perfectly prepared for childbirth.
Physical sensations
At the 36th week, something that they have been waiting for for so long will happen to some mothers: the stomach will gradually begin to drop, making room for the stomach and lungs. This change is a factor indicating that the body is preparing for the birth of a child. In primiparous women, the process of lowering the belly most often begins earlier than in multiparous women (several weeks before birth). Women expecting twins or having their second or third birth may notice this change in the lead-up to their due date. This is an individual indicator that does not clearly indicate the rapid onset of labor.
Inspired by the opportunity to breathe and eat without consequences (heartburn, heaviness), a woman should not relax. The uterus descends along with the abdomen and puts strong pressure on the intestines and bladder. The frequency of urination becomes more frequent, and sometimes you may feel like you want to urinate all the time. Often during this period, pregnant women complain that it is sometimes impossible to hold urine. This sign of due date is normal, but after giving birth (2 months), you need to visit a gynecologist to make sure that everything is back to normal.
Increasing pressure on the intestines is a potentially dangerous situation. During this period, it is very important to avoid constipation. They can provoke labor at a time when the baby is not yet ready. In order for everything to happen as nature intended, it is necessary to reconsider your diet. Increase the percentage of vegetables by 2 times, reduce to a minimum products containing animal proteins.
A drooping belly can also put a lot of pressure on the blood vessels that carry blood to the lower part of the body. As a result, a woman may experience increased swelling in the legs and pain. If these symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor for advice. If it is determined that what is happening is the result of uterine pressure, then wearing special clothing (compression stockings) will be recommended. Otherwise, swelling may indicate the development of gestosis, and this requires hospitalization and constant monitoring by doctors, in some cases urgent delivery.
Tests and studies during pregnancy
Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) - 35-36 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation.
The condition of the placenta, the height and weight of the child, its position in the uterus, and the quantity and quality of amniotic fluid are assessed. Blood test for AIDS (HIV), syphilis (RW) - 35-36 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation. These diseases can complicate pregnancy and childbirth.
Biochemical blood test - 35-36 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation. Gives an idea of the general health of the pregnant woman.
Vaginal smear - 35-36 weeks after the first day of the last menstrual period. Assessment of microbial flora before the baby passes through the birth canal.
Visiting a doctor monitoring pregnancy: once a week. Weighing, measuring blood pressure, measuring the height of the uterine fundus, listening to the fetal heartbeat.
General urine test - before each visit to the doctor. Indicates the quality of kidney function.
Dopplerography (a study that allows you to evaluate blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, placenta and main vessels of the child) - 33-34 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation, according to indications. The study allows you to find out whether the child is getting enough oxygen and nutrients.
Cardiotocography (CTG, synchronous recording of fetal heartbeats and uterine contractions) - 33-34 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation, according to indications. The child’s condition is assessed and intrauterine hypoxia is excluded.
Receive an exchange card with the results of tests and examinations - 30 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation. It is recommended that you always carry this document with you, which is required for admission to the maternity hospital.
Registration of maternity leave for workers - 30 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation.
Risk factors
Even at such a late stage, there is a danger of gestosis, so it is necessary to control weight gain and be sure to monitor the amount of fluid drunk and excreted.
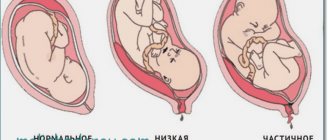
At 36 weeks of pregnancy there is a risk of placental abruption. This process can lead to large blood loss, and in some cases cause fetal death. There are three degrees of this condition:
- With the first, the child does not suffer. A detachment of less than 1/3 means a good chance of maintaining the pregnancy;
- The second degree is half-abruption of the placenta, which carries a high risk of hypoxia for the baby;
- The third degree is said to occur when the placenta has completely separated. In this case, the fetus almost always dies.
Symptoms of placental separation that an expectant mother may experience at 35–36 weeks of pregnancy are bleeding from the genital tract, aching pain in the abdomen (sometimes radiating to the thigh or perineum), and uterine hypertonicity. Among the reasons are problems with blood vessels, abdominal injuries, a sharp decrease in intrauterine pressure, as well as certain diseases (for example, nephritis).
At the 36th week of pregnancy, it is too early for the baby to be born, because his body is not yet quite ready for independent life. Therefore, the expectant mother needs to be extremely attentive to herself. Walk carefully so as not to fall, avoid crowded places - this way you will reduce the risk of contracting viral infections.
Good to know
Why does premature birth occur?
Which baby is considered premature?
How to test for amniotic fluid leakage at home
What is “oligohydramnios” during pregnancy?
Malpresentation of the fetus
How does childbirth occur with a breech presentation of the fetus?
All texts for pages about mother and baby were kindly provided by RAMA Publishing - these are chapters from the book by Svetlana Klaas “Your Favorite Little Man from Conception to Birth”, reviewer Irina Nikolaevna Kononova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Ural State Medical Academy (Ekaterinburg).
Deviation from the norm (what it can mean)
During an ultrasound examination of the cervix, two main points need to be clarified: how the placenta is located to the internal os, and if there is a threat of premature birth, it is necessary to carefully measure the length of the cervix. If it is less than 20 mm, labor develops prematurely in 70% of cases. If the cervical length is more than 30 mm, the likelihood of premature delivery is minimal. But in the third trimester, shortening of the cervix occurs naturally as labor approaches. During these periods, reducing its length is less important.
During an ultrasound examination of the placenta, the doctor will pay attention to hyperechoic areas, cavities, as well as cords of varying degrees of echo density. All these findings are very diverse, but none of them, taken separately, has a negative impact on the developing organism. Cavities are formed from accumulations of venous blood. Strands and areas of increased echogenicity are manifestations of calcification during degenerative changes that are natural for the third trimester.
However, areas of calcification before 34-35 weeks can cause some caution and pose a danger to the fetus. If calcification is severe, it may be associated with developmental delay or preeclampsia.
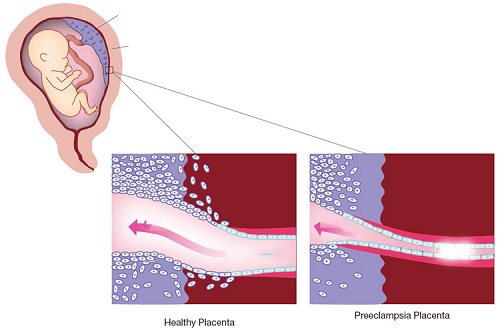
Preeclampsia
During an ultrasound examination, a significant change in the thickness of the placenta, thickening, or, conversely, a decrease in its thickness can be detected. A placenta that is reduced in thickness can lead to intrauterine growth retardation. Thickening of the placenta can be detected as a result of infectious diseases, their complications, anemia or triploidy (a rare chromosomal abnormality of the fetus), but there are often also other signs of intrauterine development disorders.
Bleeding in the last trimester
This is a fairly common case in obstetric practice. The main causes are premature detachment of even a normally located placenta, as well as placenta previa. Very often, the cause of bleeding cannot be identified; this pathology is associated with the consequences of ruptures of blood vessels along the edge of such an important organ as the placenta. In such cases, a pregnant woman is usually hospitalized in a hospital.
Determination of the quantity and quality of amniotic fluid
In the first and second trimester, the amount of amniotic fluid is determined by the function of the mother’s body, then the child himself influences more and more the amount of amniotic fluid. After 20 weeks, the main component of these waters is the baby’s urine.
The volume reaches its maximum value by the 3rd week and is 800 ml, then by birth it decreases to 600 ml. Amniotic fluid, especially closer to the period of childbirth, may contain suspension. This is vernix lubrication, sometimes meconium.
A specialist can identify oligohydramnios; its causes are varied:
- Shell rupture
- Various pathologies accompanied by a decrease in urine output (polycystic kidney disease, renal agenesis, urethral valve or urethral agenesis)
- Placental insufficiency, causing a decrease in kidney function (intrauterine growth retardation, postmaturity).
Polyhydramnios most often develops in the third trimester; its causes are also very numerous:
- macrosomia
- diabetes
- multiple pregnancy
- pathology of the fetus with swallowing disorders
- dropsy
- angioma of the placenta.
Average amniotic index values:
| Less than 5 cm | Low water |
| 5-10 cm | Reduced volume of amniotic fluid |
| 10-20 cm | Normal volume of amniotic fluid |
| 20-25 cm | Above average |
| More than 25 cm | Polyhydramnios |
Deviations from the norm of fetometry indicators
A discrepancy between head and abdominal measurements may indicate intrauterine growth restriction. There are two types of developmental delay - symmetrical and asymmetrical. Determination of the first type is possible when detected in the early stages of intrauterine development. The second option occurs much more often in later stages. Developmental delay is often accompanied by many defects in the development of organs and systems.
Detected deviations from normal values may indicate a malfunction of the internal organs of the developing organism or be a consequence of poor functioning of the placenta itself. In such cases, the expectant mother will be recommended to continue observation by specialists in the hospital, treatment will be prescribed, and daily monitoring of her condition and the development of the baby will be carried out.
Measuring abdominal circumference at home
The study will be more reliable if the abdominal circumference is measured by another person. Self-measurement has a large error; you should not trust it 100%.
A pregnant woman should take a lying position on a fairly hard surface with her stomach up, her arms should be extended along her body. The measuring tape should pass through the strongest curve of the spine at the back, and through the navel at the front. The expectant mother should first empty her bladder and not strain her abdominal muscles.
Increase in abdominal volume during pregnancy
Typically, a sharp increase in abdominal volume occurs at the 16th obstetric week; it is from this period that abdominal girth is measured during pregnancy.
An earlier examination does not make sense, since until this time the enlarged uterus does not push the anterior abdominal wall forward. On average, abdominal circumference during pregnancy increases by 2-3 centimeters every 2 weeks of gestation.
, respectively, by 1-1.5 centimeters in 7 days.
Normally, in the absence of excessively developed subcutaneous fat, when examined at 16 weeks, the abdominal girth is 70-75 centimeters. It follows from this that the abdominal circumference at 27 weeks of pregnancy should be 81-86 centimeters. Planned measurements of the volume of the abdomen and the height of the uterine fundus cannot be ignored, since changes in one direction or another make it possible to suspect pathology in time and prescribe additional examinations.
In normosthenic women, the abdominal circumference at 32 weeks of pregnancy should approach 90 centimeters, and by the time of birth it should reach 95-100 centimeters. However, the results of this measurement are quite subjective and depend on the figure and physique before the child is conceived. Therefore, it is considered more correct to track the dynamics of the increase in abdominal volume, which should grow evenly throughout the pregnancy.