Ultrasound MRI tests > MRI > Abdominal MRI > Barium passage through the intestines: preparation and procedure
When examining the intestines, an X-ray of the intestine with barium plays an important role. This is a very informative and modern procedure that allows you to detect disturbances in the intestines, find the cause of the disturbances and make a correct diagnosis.
Because X-rays show mostly dense tissue, the hollow intestine appears blurry on the images. To increase the information content, the patient is prescribed a passage with barium, which acts as a contrast agent.
Passage of barium through the intestines: preparation, implementation
A barium pass is an x-ray of the small intestine. The study helps to assess the general condition of the organ, its motor and evacuation function. All data is recorded in photographs.
The small intestine has many bends and narrowings, which the barium passage helps to examine. The study is mainly carried out for tumors in the organ, obstruction or narrowing of the intestine.
Information! On this page read about chest x-rays
Features of the technique
Barium passage is not carried out for preventive purposes. Diagnostics is used only for obvious disorders of the intestines, and if it is not possible to examine the organ by other methods. Barium passage is a highly informative technique, without which it is sometimes difficult to make a diagnosis.
The advantages of the study include less pain compared to colonoscopy (and this diagnosis applies only to the large intestine). With the help of a barium passage, the entire gastrointestinal tract, including the small intestine, is assessed. The method is inexpensive, but takes a long time.
Indications and contraindications for barium passage
Mandatory indications for barium passage include the appearance of blood streaks in the stool and black stools. Diagnostics is also prescribed for:
- Sudden causeless diarrhea, especially if it is persistent, despite a healthy diet and a healthy lifestyle.
- Chronic abdominal pain, which is accompanied by other negative symptoms. This signals bowel cancer. However, if the pain is severe at the time of the examination, then barium passage is not performed.
- Unexplained weight loss when eating normally.
- Congenital anomalies of the intestinal structure.
- Barium passage is contraindicated during pregnancy (there is a threat to the fetus), severe pain.
- The procedure is not performed for biopsy (this can cause inflammation of the mucous membrane) and intestinal perforation (there is a risk of peritonitis).
Preparation for the procedure
Before barium passage, preparation is necessary. Within 3-4 days a person should begin to adhere to a diet. Carbonated drinks, sweets and fatty foods are excluded from the diet. You cannot eat fresh vegetables and fruits. They can cause increased gas formation, which will distort the results of the study.
The day before the procedure, a person can only have breakfast. Then the intestines are cleansed with Fortrans. The drug is dissolved in 1 liter of water and drunk within an hour. Use 4 sachets during the day. After taking the drug, painful diarrhea will begin. When only clean water begins to flow out instead of feces, the intestines are considered cleansed. You are not allowed to eat until the examination is completed.
Features of an X-ray examination of the intestine
Carrying out an X-ray of the intestines requires preliminary preparation, compliance with certain rules of behavior directly during the procedure and after its completion.
Important! If the patient is taking medications or has an allergy to any substance (including barium), then he must tell the doctor about it. Some drugs can slow intestinal motility.
Preparatory stage
The diagnosis will take place without complications and discomfort, and the results of an X-ray of the intestine will be more reliable if the organ is thoroughly cleansed. To do this, it is recommended to follow a diet, as well as cleanse the intestines using enemas or special pharmacological preparations.

Fruits and grains
Dietary nutrition should be followed 2-3 days before the scheduled examination. To do this you will need:
- remove from the diet foods that contribute to the formation of a large amount of gases or take a very long time to digest (dairy, legumes, fatty foods, carbonated drinks, nuts, several types of vegetables and others);
- Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking (if you can’t give up cigarettes completely, then reduce their quantity);
- one day before the X-ray examination, remove all solid food (you can drink broth, juices, decoctions);
- During the diet you need to drink plenty of fluids.
Advice! If you forget to monitor the amount of liquid you drink, then in the morning pour 2 liters of water into a jar and place it in a visible place. As soon as you see it, immediately drink in large sips as much as you can (even if you are not thirsty). It should be empty by evening.
A day before the procedure, you need to start giving cleansing enemas. You can add magnesia or castor oil to the water. If you plan to use pharmacological drugs, it is better to first discuss this issue with your doctor. He will tell you how to cleanse your intestines before an x-ray using medications, and which one is best for you. Fortrans is usually used for this purpose.
On the day of the x-ray, you should not eat or drink anything, starting at midnight. It is advisable to do a control enema early in the morning; the water should be absolutely clear.
Progress of the procedure
If a patient encounters this diagnostic method for the first time, then, of course, he is concerned with the question of how to do an X-ray of the intestine. First you need to remove metal objects from yourself and change into a special shirt. If diagnostics is also required for the thin section, then you will need to drink a barium solution (about half a liter); if only the thick section needs to be examined, then the person is laid on a couch and the solution is injected through the anus.
Liquid is introduced slowly into the rectum, achieving its uniform distribution in the intestinal lumen by periodically turning the patient from one side to the other.
Important! Proper deep breathing will help eliminate unpleasant pressure sensations.
Air is introduced after the liquid. During the procedure, photographs are taken and/or the process is observed on a monitor. You will need to hold your breath while the image is being taken.
What to do after the procedure
After the intestinal x-ray is completed, the patient changes clothes and goes home. In some cases, a specialist does the decoding and hands over the results.
Within 2-3 days after diagnosis, the stool will have a light shade (up to white). At this time, you need to drink plenty of water, as barium provokes constipation. Some may need to take additional laxatives.
Be sure to continue to follow a diet in the first days after the x-ray. Exposure of the cleansed intestinal walls to fatty, spicy and hard foods can lead to serious gastrointestinal problems. Therefore, the transition to the usual diet should be gradual. If you experience abdominal pain, severe gas formation, or difficulty defecating for several days, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Conducting a survey
If only the large intestine is examined, barium is infused directly into the organ rectally. The man lies down on the couch with his legs tucked under him. A small tube is inserted into the anus. The barium solution is poured through it.

In this case, the patient feels internal distension. After the solution, a little air is introduced. Then pictures are taken in different positions. At the same time, make sure that the solution does not flow out of the anus. After the procedure is completed, the person has a bowel movement. The stool becomes white and liquid.
When the small intestine is examined, the person first drinks 0.5 liters of solution 5-6 hours before the procedure. It looks like milk and tastes like lime. After 5-6 hours, as soon as the barium reaches the small intestine, the doctor takes pictures, eight of them are needed. Pictures are stopped when the solution reaches the cecum.
Decoding the results
The doctor who performed the examination deciphers the results. The conclusion is given to the patient immediately or pasted into the medical record. If white flakes are visible on the pictures, it means that intestinal absorption is impaired. The images also show tumors, elongation of certain areas, and diverticula (irregularities, protrusions). If the solution spreads in steps, this indicates intestinal obstruction.
Barium passage is not a painful procedure, but it is unpleasant. After the study, no side effects occur, but if they do appear, they go away on their own in a short time. To remove barium solution from the body, laxatives are prescribed.
Results of an X-ray examination of the intestines
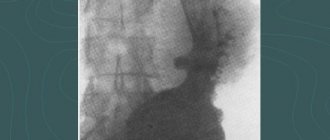
What does a barium x-ray show? Thanks to the contrast and air, the doctor can see the relief and structure of the organ, its contours in the resulting images. Based on this, he makes a conclusion about the degree of its extensibility and elasticity, and the ability for peristaltic contraction. By studying the lumen, a specialist evaluates the patency of the intestine, the presence of fecal accumulations and formations in it.
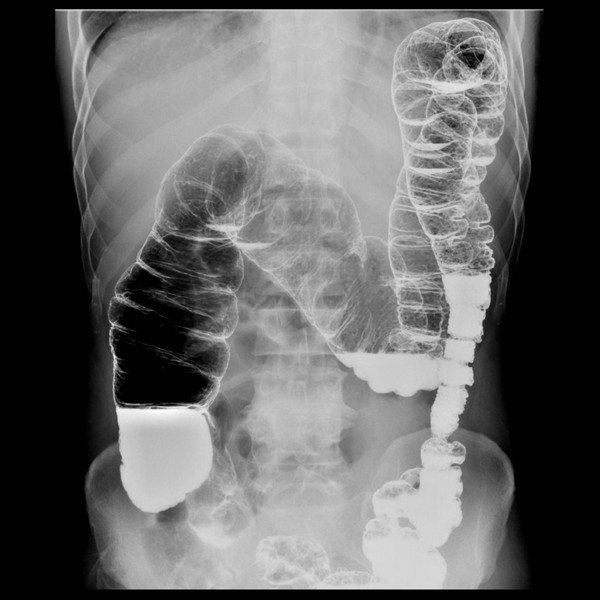
X-ray of the intestines with barium
An X-ray of the intestine can detect the following pathologies.
- Intussusception. In this condition, a section of the intestine twists in such a way that the lumen becomes completely blocked. This leads to its obstruction. This pathology manifests itself very sharply and painfully. The patient should be immediately sent to the hospital.
- Malignant formations. When examining the intestine, they appear as a narrowed area and can also lead to closure of the lumen, but this occurs already at a late stage of cancer development.
- Intestinal obstruction. This disorder manifests itself in the form of vomiting and severe abdominal pain, since peristalsis is severely impaired. During an X-ray examination, the pathology manifests itself in the form of a lack of movement of contrast and air into other parts of the organ, different levels of accumulation of substances.
- Polyps. Despite the fact that these formations on the intestinal wall do not harm the body, they must be removed, as they can lead to a malignant process.
- Diverticula. These are protrusions of the intestinal wall. As a rule, the cause of their formation is high pressure in the intestines. Diverticula can get fecal matter, causing inflammation.
What is barium passage
Barium passage (barium passage x-ray) is an x-ray examination of the small intestine, which allows you to see the general condition and motor-evacuation function of the small intestine using x-rays. This part of the abdominal cavity (small intestine) has many anatomical formations, bends, anatomical narrowings, areas of impaired motility and secretory activity, which can be visualized with this study. Most often used to identify pathologies such as intestinal narrowing, obstruction or tumors.
Important!
The reliability of the results depends on the correct preparation for the procedure. To ensure a comprehensive examination, the digestive tract is cleared of large volumes of feces, strictly following the prescribed diet.
You should follow a slag-free diet for two days before the test. Fatty and fried foods, coffee, fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as foods that promote gas formation (rye bread, legumes, baked goods, pearl barley and oatmeal porridge, milk, etc.) are excluded from the diet. Instead of fresh bread, you can eat Lenten cookies and crackers made from wheat buns.
It is recommended to drink plenty of fluids (up to 2 liters per day, in the absence of contraindications). Drinks such as fermented milk drinks, dried fruit compote, and weak green or herbal tea are allowed.
The day before the test, breakfast and lunch should be light. The last meal is the day before at 19:00, after which you are allowed to drink weak tea and water.
Radiography of the barium passage must be carried out! on an empty stomach, in the morning before the procedure it is forbidden to have breakfast.
To conduct a study, the doctor must first study existing information about your disease.
We ask you to bring your medical history or outpatient card with you to the study.
If there is no data on the course of the disease in the medical history or outpatient card, this information can be provided in any form - in extracts, research forms, copies of medical documents. The more the doctor knows about the patient's situation, the more effective the diagnosis will be.
You must also bring with you dry and wet wipes (for hygiene after bowel movements) and a clean sheet. You can ask for a sheet in advance from the nurses in the department where you are being treated.
X-ray with contrast for children
Most often, an X-ray with CE is performed on a child if there is a suspicion of abnormal development of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, atresia - the absence of a section of the esophagus. For children in the first months of life, fat-soluble (idiopol) or water-soluble (gastrografin) drugs are used, and at a later age barium sulfate is used. Due to radiation exposure and difficulties in preparing for the procedure, they try to prescribe radiography for children only in emergency cases. For example, when swallowing a foreign object or to clarify the location of fragments in fractures.
How the research works
We ask you to come to the radiology department (9th floor) 10-15 minutes before the scheduled start time of the study and, having contacted the office, inform the staff of your arrival. Given the possibility of emergency research, there is a possibility of waiting for the procedure for some time.
Experienced doctors and x-ray technicians will do everything to make you feel comfortable and safe throughout the entire examination. Immediately before the procedure begins, you will be asked to remove all metal objects from yourself if they could fall into the radiation zone. Before the examination, a survey x-ray of the abdominal cavity is taken.
The x-ray technician will prepare a special contrast mixture (approximately 300-500 ml), and you will be asked to drink the required portion of the prepared solution at certain time intervals.
The taste of the barium drink is quite neutral, and looks like a milkshake. 40-45 minutes after taking the first part of the solution, your first x-ray will be taken. The x-ray is performed on a special table in a supine position, and the radiologist will place the apparatus itself over the area of the abdomen that needs to be “visualized.” After you are seated on the table, the radiologist goes to the “command post” and gives the command “inhale and do not breathe”, after which he takes the picture.
As the contrast moves through the small intestine, targeted radiographs are taken at intervals of 30–60 minutes. A series of sequential images will allow the doctor to observe the gradual passage of barium through the intestines and determine possible inflammation, stenosis and obstruction. As a rule, the study of the passage of barium through the small intestine takes from two to three hours, but since we are talking about the gradual movement of barium through the small intestine, the study time is individual for each patient and can reach 24 hours.
The images and the conclusion of the radiation diagnostics doctor must be shown to your attending physician - a coloproctologist.
After the procedure After the procedure, you can return to your normal diet and daily activities unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
After the procedure, drinking plenty of fluids is recommended. Due to residual barium in the intestines, the stool may be stained for several days after testing.
How to carry out a barium passage
- 4 minutes to read

The passage of barium through the intestines is the most modern method of x-ray examination, thanks to which disturbances in the functioning of the anatomical structure and the factors provoking them are identified. Since X-rays in most cases can only show dense tissue, the hollow intestine is often not clearly visible. It is to increase the information content of the study that this procedure is carried out, in which the main role is played by the contrast agent.
Content
How to prepare for an X-ray of the intestine
To perform fluoroscopy of the stomach and duodenum, as well as the small and large intestines, careful preparation is required. It is necessary for high-quality cleaning of the intestines before x-rays from undigested food and feces that interfere with vision. In addition, the measures help normalize peristalsis. Proper preparation for an X-ray of the intestine allows you to obtain clear and informative images and, consequently, make the correct diagnosis.
Important! Preparatory manipulations play a special role when, to make a diagnosis, the doctor plans to monitor the passage of barium through the intestines - the progress of the contrast solution over time.
Standard preparation for an x-ray examination requires compliance with a number of conditions:
- changing your diet a few days before the procedure for better and easier bowel movements;
- taking medications that will help prevent the occurrence of gas formation, increased or slowed peristalsis, which interfere with X-rays of the gastrointestinal tract with barium;
- active cleansing, for which the doctor prescribes laxatives or enemas (depending on which section of the gastrointestinal tract will be examined) - before an x-ray of the large intestine, it is recommended to take laxatives in combination with a cleansing enema, while for x-rays of the small intestine it is enough to follow a diet and take laxatives.
This is interesting: Modern research methods for helminthiases. Blood test for worms: when and to whom is it prescribed? What does a blood test for helminths show?
Indications
Passage of barium through the small intestine is used in several situations. First of all, it is prescribed in case of causeless diarrhea. If a person leads a healthy lifestyle and eats right, but has constant diarrhea, then this study is necessary to identify the cause of the disorder. In addition, such a symptom may indicate the development of a more serious pathological process.
The procedure is also necessary when blood impurities are found in the stool. However, in this condition, the study must be carried out with extreme caution, since incorrectly performed actions can provoke even more severe bleeding.
An indication for the passage is pain in the abdominal area. An X-ray with a contrast agent is performed if the pain syndrome is accompanied by other symptoms. However, it must be remembered that if the pain is pronounced, then this type of examination cannot be prescribed.
On this topic
Differences between sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 9, 2021
A specialist can refer you for a barium passage even if you are rapidly losing weight. This is explained by the fact that unreasonable weight loss along with proper nutrition may indicate the appearance of cancer.
The procedure is also used for congenital anomalies. Thanks to x-rays, it is possible to identify the abnormal structure of the intestines, as well as determine how it affects the digestive process.
In what cases is the procedure prescribed?
An X-ray of the intestines with barium is performed to clarify the diagnosis and evaluate the therapeutic measures taken for the following conditions and diseases:
- long-term defecation disorders (diarrhea, constipation);
- suspicion of intestinal obstruction;
- fistulas, diverticula;
- if it is impossible to carry out diagnostics using instrumental methods in the presence of disorders in the intestines (for example, due to anal fissures, hemorrhoids and other conditions);
- suspicion of the development of tumor processes;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- sudden changes in body weight downward (possibly malabsorption of nutritional compounds);
- chronic colitis;
- presence of a foreign body;
- the presence of impurities (mucous, blood) in the stool, changes in their color and odor.
An X-ray may also be prescribed after the operation to ensure the patency of the organ, as well as to promptly detect adhesions and scars.
Contraindications
Despite the fact that this technique is effective and informative, there are certain limitations to its implementation. Experts identify a number of conditions and situations when examination cannot be carried out.
Pregnancy
Doctors do not recommend the procedure during pregnancy. This is explained by the fact that when the intestines are full, there is pressure on the uterine body. In addition, barium can negatively affect fetal development.
X-ray radiation also poses a danger to children. An examination can be carried out only when there is an emergency need, and the use of other diagnostic techniques is not possible for some reason.
Biopsy
This study involves taking a small piece of biological tissue for further study. If barium is present in this area of the mucosa, irritation or an inflammatory process may begin.
Severe pain
During the procedure, the patient must remain motionless. Severe pain usually disrupts this process. In addition, when exposed to a contrast agent, the pain can only intensify until loss of consciousness.
Intestinal perforation
If this pathology is suspected, the method is also not used, or the contrast is replaced with a water-soluble one. In case of perforation during the use of barium, the risk of developing peritonitis increases several times.
Contraindications to irrigography
Despite the information content and painlessness, contrast radiography, like any medical procedure, has a number of contraindications:
- Pregnancy.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system (recent heart attack, heart failure).
- Current infectious and viral diseases, accompanied by fever, chills and poor health.
- Pathological enlargement of the large intestine along the entire length or in a separate area (toxic megacolon).
- Perforation of the intestinal wall.
In the presence of the above pathologies, the doctor may be faced with the task of choosing alternative diagnostic methods, the implementation of which will not affect the patient’s health.

Pregnancy is a contraindication to contrast radiography
Important. If nothing interferes with performing an X-ray examination with contrast, the patient should be familiarized in detail with the preparatory measures. The reliability of the results directly depends on the quality of intestinal cleansing.
Preparation
Despite the fact that the examination is a painless procedure, during the procedure the patient may experience discomfort. To keep their manifestation to a minimum, it is necessary to follow some preparatory rules.
About four days before the appointed date, it is recommended to follow a slag-free diet. It is necessary to exclude fatty, fried, sweet foods, carbonated drinks, fresh vegetables and fruits from the diet, as they can cause increased gas formation.
The day before the examination, you are only allowed to have breakfast. After this, the patient cleanses the intestines using Fortrans. This medication is the only one that allows cleansing procedures to be carried out simultaneously for the large and small intestines.
Preparations for irrigography
The colon is a hollow organ, so without preliminary preparation the irriogram will not show anything. But if the intestines are cleared of feces in advance and filled with contrast liquid, you can visually assess its condition.
Preparations for the event should begin several days before the scheduled date. It is advisable to change your diet by removing cabbage, legumes, black bread, fried and spicy foods, alcohol and carbonated drinks from your diet. You should increase your water consumption to 2 liters per day.
In addition to the diet, the doctor may prescribe medications according to indications: activated charcoal, Espumisan, or laxatives based on macrogol.
The evening before irrigography, it is necessary to thoroughly cleanse the intestines. This can be done in two ways, choosing the most suitable one for yourself.
Using an enema
If the patient is in a hospital, the nurse will take all necessary actions. At home, for cleansing you will need an Esmarch mug and 1–1.5 liters of water.
In a hospital setting, preparation for the procedure is performed by a nurse
Important. Colon lavage should be repeated several times until the water coming out is perfectly clear. The main thing in this method is not the number of manipulations performed, but the transparency of the water.
The next morning before the procedure, it is recommended to repeat the enema as many times as necessary until clean water appears.
Using Fortrans
This is a medical drug that can be freely purchased at a pharmacy. The product will help you quickly and gently get rid of feces. The medicine is well tolerated and does not cause discomfort, pain or flatulence.
For the cleansing procedure, you should dissolve the contents of individual sachets in a glass of liquid, stir well and drink. The next morning before irrigography, the procedure should be repeated.
Fortrans cleansing is not advisable for people with disorders of the cardiovascular system.
Advice. Despite the fact that using Fortrans is more hygienic, doctors recommend that women and the elderly use an enema. This kind of test will help determine whether the patient can “hold” a barium solution, which is much heavier than water.
Practice shows that older people and women after childbirth do not cope well with the contrast solution and the X-ray room has to be closed for disinfection for some time. It is the enema that will help the patient understand whether he can undergo irrigography at all.
Purpose and advantages of the method
Most often, barium passage through the intestines is carried out if intestinal obstruction is suspected.
X-ray examination of the intestine with barium is not prescribed for preventive purposes. This is a serious procedure that is performed only if there are obvious problems with the large or small intestine and no other examination is possible.
The passage of barium through the intestines significantly increases the information content of the procedure. Without it, it will be difficult to make a diagnosis. The advantage of this method is that the likelihood of pain with it is lower than with a colonoscopy, which allows you to examine only the large intestine. Using X-rays, you can assess the condition of the entire gastrointestinal tract, including the small intestine.
X-ray of the intestine is not the most expensive examination method, but it takes a long time, ideally about a day, if we are talking about the small intestine. For the large intestine, the procedure lasts much less.
X-rays of the lower gastrointestinal tract are prescribed in the following cases:
- Causeless diarrhea. Constant diarrhea, as well as severe constipation with a healthy diet and healthy lifestyle, require examination. Both are disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and can be a symptom of a serious illness.
- The appearance of blood in the stool. If blood streaks appear in the stool or black stool, an examination of the intestines is mandatory, but carried out with caution, as the bleeding may increase.
- Stomach ache. For chronic abdominal pain accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, a colonoscopy or barium X-ray is prescribed. Pain syndrome accompanies many diseases, including colon cancer. However, if the pain is intense, the examination is not carried out.
- Weight loss. Unexplained weight loss with a normal diet can be a sign of serious disorders of the gastrointestinal tract or cancer.
- Congenital anomalies. Using X-rays, you can identify congenital abnormalities of the intestinal structure and determine their effect on the digestive process.
Irrigography. The essence of the study
Let's take a closer look at such a diagnostic method as irrigography - what kind of event it is, the subtleties of terminology and the features of its implementation.
At its core, irrigography is an X-ray examination of the colon. During the procedure, segments of the lower gastrointestinal tract are filled with a contrast solution of barium sulfate through the anus.
Attention. People who are far from medicine often confuse irrigography with the passage of barium through the intestines. It should be noted that these are completely different diagnostic methods.
In addition, when talking about irrigography, one should take into account its difference from irrigoscopy. Both procedures are a special case of radiography, but in the first stage, radiation is given in small doses no more than 5 times per session. This significantly reduces the load on the body and makes it possible to conduct research on young children and weakened patients.
Irrigography is a special case of radiography
During irrigoscopy, irradiation is carried out continuously, which significantly increases radiation exposure. The procedure is suitable only for adults without contraindications. During fluoroscopy, regardless of the research method, confirmatory images (irriograms) are always taken.
The results obtained allow us to more reliably assume the presence or absence of pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract. In case of doubt or the image is not clear enough, use the double contrast technique.
What does an x-ray show?
Irrigoscopy allows you to visually assess the condition of the mucous membrane and internal cavities of the colon. During the procedure you can examine:
- the process of contraction of the walls of an organ, its motor activity (motility);
- external contours of the intestine, lumen diameter;
- integrity of the mucosa, presence of fistulas, ulcers, polyps, wounds and microcracks;
- development of neoplasms.
Contrast fluoroscopy allows you to diagnose:
- congenital anomalies of the gastrointestinal tract (dolichosigma, dolichocolon);
- Crohn's disease;
- motor impairment;
- intestinal obstruction;
- ulcerative colitis;
- cancer alertness;
- the presence of foreign objects in the organ cavity.
To clarify the results obtained, a therapist, surgeon or gastroenterologist may resort to additional diagnostic methods: colonoscopy, ultrasound, CT or MRI.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
Irrigography is the most informative research method. The diagnosis does not cause the patient any particular discomfort or discomfort, while allowing the most accurate result to be obtained.
However, X-ray diagnostics also has its drawbacks. For example, irrigography does not allow you to take tissue samples for biochemistry at the time of examination. We should not forget about the negative effects of X-ray radiation on the body. Therefore, for some diseases this diagnostic method is contraindicated.