X-ray examination for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract allows you to diagnose pathologies in the early stages - when treatment brings maximum effect. X-ray of the esophagus and stomach is the simplest and most informative way to establish an accurate diagnosis. Using this method, functional disorders, such as gastric ulcers, are diagnosed, and tumor processes are detected.
X-ray of the stomach
Despite the fact that the stomach is a hollow organ, the density of its walls is identical to the density of other organs of the peritoneal cavity; it will be practically indistinguishable on a standard x-ray. Therefore, preliminary contrasting is necessary - filling the stomach with a radiopaque substance. A standard x-ray is a less informative method, since it only involves obtaining a static image.
Benefits for diagnosis, benefits for the patient
X-ray examination of the esophagus and stomach with barium, which most often acts as a contrast agent, is not performed so often, since it involves irradiation of the patient, and is prescribed if the following pathologies are suspected:
- stenosis of the esophagus, diverticula and neoplasms in it;
- malformations and erosions of the esophagus;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- tumors;
- inflammatory bowel diseases, disorders of its motility.
There are few contraindications for this research method, and the absolute one is pregnancy - ionizing radiation is unacceptable at any stage. Such a diagnosis is not carried out even if there is continuous bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
It is fluoroscopy that becomes the optimal way to identify existing problems with the digestive organs - the doctor receives a “live” image of the stomach and can assess the dynamics of the distribution of the contrast agent in the gastrointestinal tract.
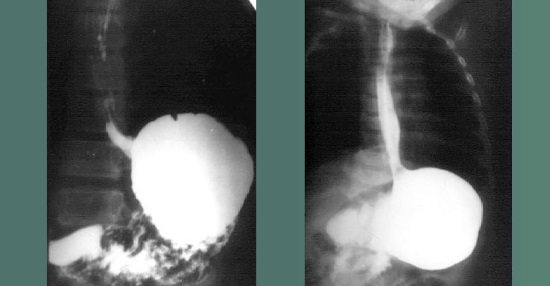
X-ray of the esophagus
Advantages of polypositional radiography/fluoroscopy of the esophagus and stomach at the Rassvet clinic
At the Rassvet clinic, radiography and fluoroscopy of the esophagus and stomach are performed. Our radiology department is equipped with an X-ray machine with an active worktable and digital fluoroscopy. Modern equipment allows Dawn's radiologists to conduct highly accurate and informative examinations necessary to establish the correct diagnosis and surgical interventions.
We care about our patients, therefore we guarantee high speed and simplicity of the study, high-quality assessment of the result and accurate diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases.
Source
Preparing for fluoroscopy
In order to do the study correctly, a little preparation of the patient is necessary. Fluoroscopy is performed on an empty stomach, so the last meal is allowed at least seven hours before the procedure. Not only food is prohibited, you cannot drink, take medications, or smoke.
Important! Even at the stage of preparation for the procedure, the attending physician must be warned about manifestations of allergies - even if the reactions have been noted for a long time and were not very intense. Any jewelry from the body must be removed before the examination.
All patients with severe digestive disorders, as well as elderly people, require a special diet for 2-3 days before fluoroscopy, from which the following are completely excluded:
- baking;
- cabbage;
- carbonated drinks;
- overly sweet foods;
- milk and dairy products.

The doctor explains to the patient how to prepare for fluoroscopy of the stomach
These days, the diet should contain grain porridge with water, lean meat and fish, eggs are allowed. It must be remembered that failure to follow the preparation rules may lead to the results being incorrect. Fluoroscopy is not an x-ray; repeating it is highly undesirable, since the radiation dose will be too high. The patient takes the barium liquid while he is behind the X-ray machine screen. If it is necessary to examine the large intestine, contrast is administered through an enema.
Preparation for X-ray examinations
X-ray examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum
Brief description of the study: under the supervision of a doctor, during fluoroscopy, the patient drinks 200 ml of barium suspension. After which the study is carried out in multiple positions: in horizontal and vertical positions, on the right and left side, on the back and stomach. For a detailed study of the esophagus, the patient swallows a creamy barium suspension.
Indications for the procedure are the following symptoms:
difficulty swallowing, pain and feeling of fullness in the chest and abdominal cavity, nausea, vomiting, additional examination before and after surgical interventions on the chest and abdominal organs; as well as diseases associated with impaired motility of the gastrointestinal tract, cancer, diverticula, deformities, fistulas of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
Contraindications to the study can be determined only after consultation with one of the specialists: gastroenterologist, therapist, surgeon, neurologist, endocrinologist.
How to prepare for research. No special preparation is required. The study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach (it is not recommended to drink, take food or take medications). The last meal should be the evening before the study at 20:00.
Duration of the study:
On average, the study, including the preparation of the protocol and conclusion, lasts about 30 minutes. But can be continued for up to 24 hours (if necessary or if delayed radiographs are obtained)
How long will the recovery period be after the procedure?
After the study, the patient can lead a full life.
Irrigoscopy and irrigography
Brief description of the study: the study is carried out in two stages (two stages) on an X-ray machine stand. A contrast barium suspension is administered with the patient in the left lateral position on an X-ray machine stand, under minimal fluoroscopy control using a Bobrov apparatus or a special device of a similar design. About 300 ml of contrast suspension is injected into the colon. As soon as the contrast mass reaches the splenic flexure, the patient turns onto his back and, by switching the nozzle valve, air insufflation begins. The amount of introduced air is monitored during fluoroscopy. Once the entire colon is filled, the tip is removed from the anus. Next, the patient is examined polypositionally in horizontal and vertical positions. After this, the patient empties the colon in the toilet, after which radiographs are taken in vertical and horizontal positions;
Contraindications to the study can only be determined after consultation with one of the specialists: gastroenterologist, therapist, surgeon, neurologist, coloproctologist.
How to prepare for the study: a slag-free diet is required 2 days before the scheduled date of the study. Products that increase the formation of feces and increased gas formation are excluded.
Such food products include:
Performing fluoroscopy
After the patient is fully prepared for the study, he drinks barium, the amount of which in the standard procedure is 250 ml. Gradually washing the gastrointestinal tract, contrast gives the radiologist the opportunity to examine the condition of the mucous membranes, identify their defects by the degree of filling with contrast, and find out the time required for the onset of the absolute filling phase.
After this, the phase of “tight” filling begins. At this time, the doctor receives the following information:
- stomach size;
- form;
- location of all digestive organs;
- displacement and structure;
- extensibility and contractility.
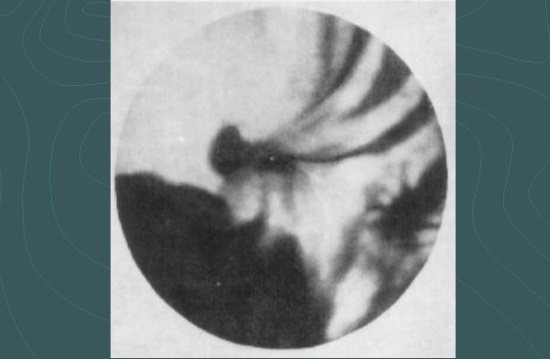
Ulcer niche
Here you can determine the specific location where the ulcer or tumor is located. If there is a suspicion of a tumor, additional examination will be required, since X-ray methods do not allow determining the type of tumor - whether it is benign or malignant. Standard fluoroscopy may not detect some pathologies.
To obtain more information, fluoroscopy of the esophagus and stomach in the Trendelenburg position may be prescribed. The patient fixes the pelvis in an elevated state of 45 degrees - this position allows you to clearly diagnose a hiatal hernia. In addition, the doctor often asks the person to lie on his side, or take a different position, depending on the characteristics of the suspected disease.
Immediately before fluoroscopy, consultations are held with the participation of specialists:
- attending physician;
- radiologist;
- gastroenterologist.
If necessary, doctors of other specialties also take part in the preliminary examination.
Double contrast in the study of the stomach and intestines
The gastrointestinal tract can suffer from many pathologies, and standard fluoroscopy methods cannot always give a complete picture of what is happening. In some cases, the doctor may see the need for double contrast fluoroscopy. It is carried out with the same barium suspension, but the patient needs to drink it through a special perforated tube, which allows air to enter the stomach.
Massaging the anterior abdominal wall promotes better distribution of barium along the walls of the stomach, and the air entering it ensures the straightening of the folds. If it is necessary to study the large intestine, a contrast agent is injected into it through an enema. Special preparation is required before the study. Prescribing a diet during fluoroscopy of the large intestine is also desirable, as when examining other parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Other methods
X-ray examination is not the only procedure prescribed for diagnosing diseases of the stomach and duodenum. If there are contraindications, it is advisable to use other diagnostic methods that have their own advantages and disadvantages.
| Procedure name | pros | Minuses |
| Radiography |
|
|
| FGDS |
|
|
| Ultrasound |
|
|
|
| |
| Capsule endoscopy |
|
|
Along with X-ray, the leader in the reliability of the results obtained is FGDS. Our article will help you choose one of these two studies, where we identify the pros and cons of both methods.
Advantages over other types of diagnostics

Fluoroscopy has a number of advantages over other research methods
There are many advantages to this research method, such as fluoroscopy, and the following stand out among them:
- speed of obtaining results - the doctor sees a picture of what is happening in real time, there is practically no need to confirm what he saw using other methods;
- painless examination that does not require the use of anesthesia - important for elderly patients;
- affordable cost and simplicity - fluoroscopy equipment is installed in every municipal clinic;
- a minimum number of restrictions, excellent tolerability and easy preparation for the study, which is available to every person, regardless of age and financial situation.
Consequences of fluoroscopy
Any type of X-ray examination is quite safe and does not cause negative consequences, including those associated with ionizing radiation. This is due to strict consideration of the amount of all exposures; unless absolutely necessary, a person is not subjected to additional research using such methods. Contrast fluoroscopy, for some patients, causes dyspeptic disorders:
- moderate pain in the epigastrium;
- nausea and heaviness in the stomach;
- stool disorders - constipation predominates.

Unpleasant sensations in the epigastric region
If such symptoms persist for more than three days, you should seek medical help. Such symptoms are associated with barium, which often leads to constipation and mild digestive disorders. To speed up the elimination of this substance after the procedure, you can drink 1.5-2 liters of clean water, or take a mild laxative. There is no need to carry out any other activities.