MRI of the pelvis in women is a safe and effective method for diagnosing diseases of the female genitourinary system. This is an absolutely painless and safe procedure that does not use X-rays or other dangerous types of radiation. What does an MRI of the pelvis show in female patients?
The images obtained during the study are the result of computer processing of data on the complex interaction of magnetic fields and radio waves. The images show the structure of the pelvic organs and any possible pathological changes, based on the amount of water contained in the tissues.
Anatomy of the female pelvis
The small pelvis is the space bounded by the symphysis pubis in front and the promontory of the sacrum in the back. On the sides, the boundaries of the small pelvis run along arcuate lines separating the body of the ilium from the wings. The pelvic cavity in women serves as a container for the genital organs - the uterus and its appendages (ovaries, fallopian tubes). There are a large number of blood vessels, nerves and fiber. The pelvic cavity also contains the rectum and bladder.
What diseases can be diagnosed?
What does MRI of the pelvic organs show in women:
Diseases of the uterus, ovaries (benign, malignant tumors of the uterus)
Magnetic resonance imaging is an opportunity to see metastasis in the early stages and make treatment of the disease as effective as possible.
Bladder tumors
With such a detailed study, neoplasms can be recognized at the very beginning of their formation (even if the size does not exceed a few millimeters).
Damage to the pelvic lymph nodes
Metastases in the lymph nodes are secondary foci of growth of a malignant tumor already existing in the body. The development of metastases in the human body gives a signal about tumor progression.
Inflammatory diseases (abscesses)
Most often, this disease occurs as a complication of acute appendicitis, gynecological infections or medical invasive procedures. MRI can more accurately show the location of the abscess and indicate its cause.
Diseases of the pelvic organs in women
Main diseases of the female genitourinary system:
- Inflammatory diseases (salpingitis, oophoritis, endometritis, cervicitis, cystitis);
- Ovarian apoplexy;
- Polycystic disease;
- Torsion of the uterine appendages;
- Polyps, synechiae of the uterine cavity;
- Endometriosis, adenomyosis;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Endometrial hyperplasia;
- Bleeding;
- Infertility;
- Bladder polyposis;
- Benign and malignant neoplasms of the female genitourinary tract;
- Malformations of the female genitourinary system.
In addition, MRI is used to diagnose diseases of the rectum - Crohn's disease, polyps, perirectal abscesses, fistulas, and neoplasms.
Indications for MRI of the pelvic organs in female patients
The following symptoms may be the reason for a more in-depth examination with the appointment of magnetic resonance imaging:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the perineum, tailbone, lower back, lower limbs;
- Dyspareunia;
- Pathological discharge (blood, pus);
- Pathological impurities in the urine;
- Miscarriage, infertility.

Contraindications
The powerful magnetic field during an MRI exam can interfere with electronics and dislodge metallic foreign bodies. Therefore, MRI is contraindicated if the patient has:
- Electronic implants - hearing processors, defibrillators-cardioverters, artificial heart pacemakers, insulin pumps, neurostimulators;
- Ammunition fragments, shot, small particles of iron in the eyeballs (often found in metal workers), vascular stents, clips on the arteries of the brain made of surgical steel.
MRI of the pelvic organs is not recommended during pregnancy before 12 weeks due to the lack of experimental data on the effect of magnetic fields on the developing fetus. The study in children under 5 years of age is carried out only in a specialized clinic under the influence of sedatives that put young patients into medicated sleep.
A serious obstacle to the study is the patient’s weight more than 130 kg and torso girth more than 150 cm. The reason is that the working part of the MRI machine - tomograph - is a tunnel with a diameter of 60 cm, which is too small for obese patients.
Are there alternative diagnostic methods?
Currently, diagnosing the human body involves choosing one of the methods: ultrasound, computed tomography, x-ray or MRI. It is worth noting that magnetic resonance imaging has many advantages:
- The doctor gets the opportunity to study the required organ in as much detail as possible;
- The pictures have good clarity;
- The ability to notice even the slightest deviations in the structure of tissues and organs;
- Maximum information content regarding the diagnosis of cancer, etc.
Perhaps only hysteroscopy can compare with MRI, but its use requires penetration into the tissue through surgery. In comparison with hysteroscopy and other methods, Magnetic resonance imaging is a non-traumatic and absolutely safe procedure, which is carried out in a fairly short time and is popular all over the world.
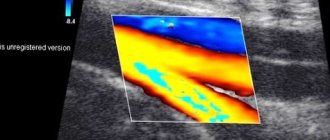
MRI of the pelvis in women with contrast
Contrast is a special solution for intravenous administration containing nanoparticles of gadolinium, an element of the periodic system that can accumulate in pathologically altered tissues. Contrast enhancement is an MRI technique that involves the administration of a contrast agent during the examination. Contrast helps detect some diseases of the pelvic organs, such as acute and chronic inflammatory processes, cysts, benign and malignant neoplasms. This technique is indispensable in controversial and complex cases, as it can increase the sensitivity and specificity of MR imaging.
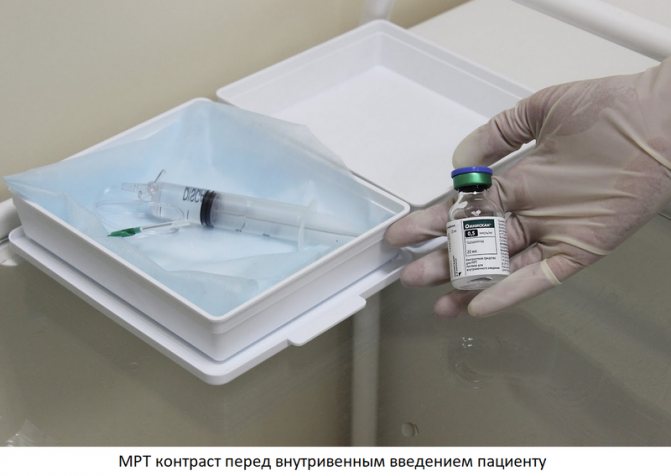

Contrast is injected midway through the pelvic MRI into the cubital vein using a routine intravenous injection. After administration of the drug, the study is repeated with contrast enhancement, which increases the duration of the procedure by 15 minutes. Contrast agents are safe, well tolerated by patients, and rarely cause allergic reactions.
General indications for pelvic MRI
After consultation, the doctor determines the need for examination using a tomograph. It is usually prescribed to:
- clarify the diagnosis if other diagnostic methods show conflicting results;
- find the cause of bleeding in urine and stool;
- determine the exact location of the pathology for surgery;
- diagnose urolithiasis;
- determine the causes of painful and difficult urination, sexual disorders;
- determine the cause of pain in the lumbosacral region;
- promptly identify the consequences of injuries to the lower abdomen and genital organs;
- identify foci of infection, inflammation and tumors.
This is an incomplete list of indications for MRI, which is prescribed by a urologist, gynecologist, proctologist and surgeon. But because the procedure is expensive, most patients agree to it only when all circumstances indicate the development of cancer. Although, in terms of information content, one MRI session can replace several types of diagnostics and significantly increase the chances of successful treatment.
Preparation for MRI of the pelvis in women
The study is carried out after preparation. The quality and clarity of the resulting images is greatly influenced by the intestines, the wall of which contracts rhythmically, moving the bolus of food. These movements, called peristalsis, are transmitted to the pelvic organs and can distort the image. In order to reduce the effect of peristalsis on the quality of images, 8-12 hours before the MRI examination you need to take an antispasmodic and carminative (no-shpu, espumizan, simethicone). No-spa will relax the intestinal wall, make peristalsis softer, and espumisan will reduce the formation of gases that irritate the intestines and increase its rhythmic contractions.
MRI diagnostics of the pelvic organs is best performed between the 5th and 12th day of the menstrual cycle. If menstruation is absent or has not yet begun, the test can be done on any day.
There are certain safety precautions that must be followed when preparing for an MRI scan. Due to the presence of powerful magnetic fields, it is prohibited to bring any metal objects (tools, cigarette cases) and electronic devices (smartphones, gadgets) into the study. Metal heats up in magnetic fields and can cause burns and damage electronics. For the same reason, it is necessary to carefully ensure that the patient’s body is free of piercings, jewelry, and metal fittings do not touch the skin. Violation of these rules may result in injury.
Types of MRI of the pelvis
Conventionally, several types of pelvic MRI can be distinguished:
- with contrast agent;
- without contrast agent;
- with anesthesia;
- for overweight people.
A contrast agent is used when there is a suspicion of the development of inflammatory processes or the presence of a low-quality tumor. The essence of its work is that the substance is concentrated in damaged tissues without changing their condition and structure. In this case, the area of pathology becomes clearly visible. For example, take metastasis. This is a secondary focus of pathology, which appears due to the movement of tumor cells. Early metastases modify tissues, but it is very difficult to notice them without contrast. If there is no suspicion of cancer, then a contrast agent is not needed.
Anesthesia and sedation are used in cases where for some reason the patient cannot lie still during the procedure. These reasons may be mental disorders, diseases of the spine, circulatory system, joints and increased excitability of the patient.
Since obese people are more often susceptible to diseases in the pelvic area and MRI is a necessity for them, open-type devices have been developed for patients weighing up to 120 kg.
How is an MRI of the pelvis performed in women?
The duration of the study is 40 minutes (55 when using contrast). Diagnostics begins with placing the patient in a tomograph - a cylindrical device with a tunnel in the center 60 centimeters long and wide. To accommodate the patient, the tunnel is equipped with a movable table. After laying the patient down, the medical professional will ask you to put on headphones - they are needed so that the noise from the tomograph does not interfere with the examination (as well as to communicate with the operator and listen to music, which helps to relax and reduce the wait). The patient is given a button on a wire - by squeezing it, you can contact the operator via intercom.
Please remain still throughout the entire examination. Follow all operator instructions - you may be asked to exhale or hold your breath. Try to relax and remain calm - the procedure is absolutely safe and will not cause harm.
After completing the procedure, you must wait 15-30 minutes until the results of your examination are deciphered. After this, you will receive a written report from the radiologist and images on a CD. For convenience, images can be ordered on film or on a flash drive - not all doctors have the opportunity to view CDs (you need to pay a little extra for this).
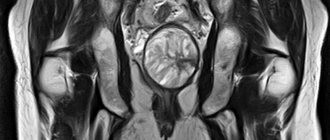
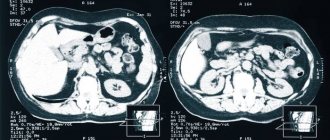
Deciphering the results of MRI of the pelvis in women - what the study shows
Interpreting the results of MRI of the pelvis is the job of real professionals. Each resulting image in the form of a 1-2 mm thick slice taken in several planes is the result of computer data processing, conveying the anatomy of the pelvis in great detail. During interpretation, the radiologist pays attention to the size, shape and position of the internal genital organs, bladder and rectum.
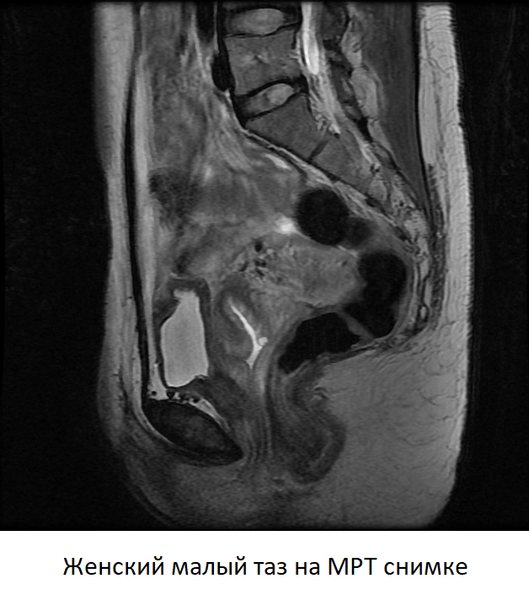
The anatomy of each organ is examined in detail, and deviations from the norm are searched for. The method allows you to “see” any space-occupying formation, be it a cyst or tumor, inflammatory processes, or anomalies in the structure of organs. When using contrast, attention is paid to the local accumulation of the drug, the dynamics of its absorption and release - these parameters make it possible to establish a diagnosis with almost 100% accuracy.
Indications for MRI screening
To undergo a tomography, you must obtain a referral from a specialist doctor. The reasons for prescribing an MRI of the pelvis may be the following:
- pain syndrome of unknown etiology;
- suspicion of the presence of a benign or malignant formation;
- reproductive dysfunction;
- trauma factor;
- planned surgical intervention;
- inflammatory pathologies of female or male internal genital organs;
- signs of hematuria (bleeding from the urinary tract);
- vaginal bleeding;
- metastasis check;
- congenital anatomical defects;
- diseases of the urinary system and lower intestine;
- the need to confirm or refute the results of other studies;
- in terms of differential diagnosis;
- as part of medical supervision after completion of treatment.
Medical, located in the Leventsovsky district of Rostov-on-Don, specializes in MRI diagnostics. Our specialists perform not only survey examinations of the pelvis, but also complex MRI procedures with dynamic contrast and using specialized protocols.
"DiMagnit" is equipped with high-field equipment: a PHILIPS INTERA tomograph (magnetic field strength is 1.5-T). This MRI scanner allows you to carry out the full range of necessary studies in the pelvic area.
In male and female versions of tomography, diagnosticians usually set different tasks and take into account the difference in anatomical structure by gender.
Among women
Organs and systems included in MRI screening:
- bladder;
- vagina;
- the cervix and the uterus itself;
- the fallopian tubes;
- ovaries;
- section of the rectum.
MRI scanning of the pelvis in women of reproductive age during menstruation is excluded and can only be performed for emergency indications. The optimal period for performing diagnostics is the first phase of the cycle, 5-12 days.
In men
Organs and systems included in the examination using the magnetic resonance method:
- bladder;
- prostate;
- seminal vesicles;
- inguinal lymph nodes;
- rectum.
Tomography is a safe procedure and excludes any violation of the integrity of the patient’s body. At the same time, doctors warn about existing contraindications to screening.