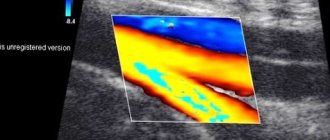
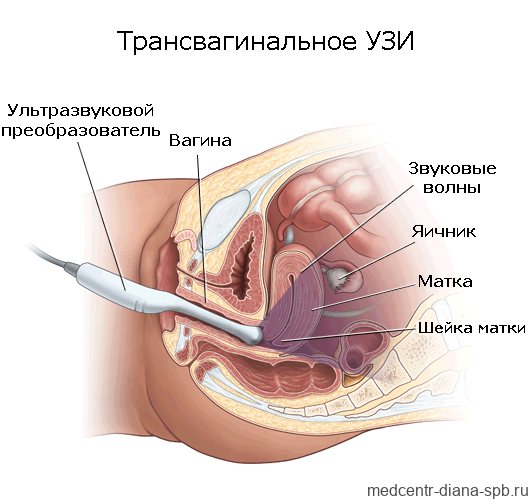
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) is performed to diagnose the condition of the pelvic organs in women. The study is prescribed to identify urological and gynecological diseases, monitor their course and treatment results, as well as to determine the duration of pregnancy and exclude pathologies in the first trimester. TVUS today is the most accurate and informative method for examining the pelvic organs in women.
CLICK TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
COST OF TRANSVAGINAL ULTRASOUND 1000 RUB. CONSULTATION WITH A GYNECOLOGIST ON THE RESULTS OF AN ULTRASOUND OR ANALYSIS - 500 rubles
This type of examination has a minimum of contraindications, is absolutely painless and inexpensive.
Features of the diagnostic technique
The content of the article
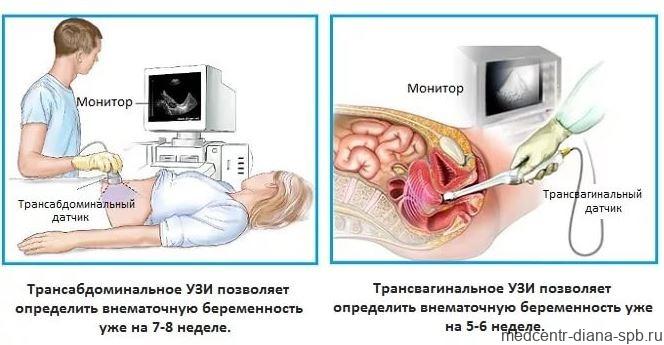
Transvaginal examination differs from transabdominal examination only in that in the first case, ultrasound waves are supplied through a sensor that is located in close proximity to the organs being examined or the fertilized egg: they are separated only by a thin vaginal wall. With transabdominal ultrasound, the sensor is moved along the lower abdomen, but this technique does not provide a clear overview if the patient is obese or suffers from increased gas formation in the intestines.
The intracavitary sensor (transducer) looks like a rod 12 cm long, and its diameter does not exceed 3 cm, so its penetration during the study does not cause unpleasant sensations. The sensor has an oblique view relative to its axis, which is necessary for better visualization of the uterus, taking into account its anatomical location. At the end there is a channel with a needle, which may be needed in case of tissue biopsy.
Intravaginal ultrasound examination is absolutely safe, so it can be done multiple times. Sometimes TVUS is prescribed several times during one menstrual cycle.
WE DO ALL TYPES OF ULTRASOUNDS 2D, 3D, 4D with DOPPLER / We do all kinds of ultrasound - 2D, 3D, 4D diagnostics with Doppler
We use one of the best ultrasound scanners with Doppler SonoAce X8 from SAMSUNG MEDISON. This device combines a maximum range of functions and a wide range of diagnostic capabilities - it includes all types of sensitive Doppler, it has an excellent degree of visualization, the ability to panoramic scanning of organs and constructing images in real time in 2D, 3D and 4D formats. The kit contains all the sensors necessary for performing any type of ultrasound - transavaginal, transabdominal and transrectal. We use one of the best ultrasound scanners with the SonoAce X8 doppler from the company SAMSUNG MEDISON. The device for the diagnostic combines the maximum set of functions and a wide range of diagnostic capabilities. SonoAce represents all kinds of sensitive Doppler, has an excellent degree of visualization, the possibility of panoramic scanning and the construction of images in real time in 2D, 3D and 4D formats. The kit includes all necessary ultrasound sensors of any type – transvaginal, transabdominal and transrectal.
ATTENTION! IN THE CLINIC IS A DOCTOR SPEAKING IN ENGLISH LANGUAGE!
Modern ultrasound 3D, 4D with Doppler from Samsung Medison
Advantages of the transvaginal method
| Higher information content than the transabdominal method | The ultrasound sensor is separated from the organs being examined only by the vaginal wall, which is much thinner than the abdominal wall. |
| Accuracy and reliability of the results obtained | The vaginal sensor, due to its shape and size, is able to get as close as possible to anatomical structures, allowing you to examine them in detail, which greatly simplifies the diagnosis. |
| Ability to bypass ultrasound obstacles | There is no need to resort to manipulations designed to remove swollen intestinal loops from view. |
| A good alternative to more expensive and painful research methods | Transvaginal ultrasound is the optimal method for examining the female reproductive system, which can be done as often as needed and, if necessary, multiple times. |
Indications for TVUS
Transvaginal ultrasound examination is prescribed for suspected diseases of the pelvic organs, emergency conditions, and also to assess the results of treatment. Indications for this diagnostic technique are:
- Severe pain during menstruation.
- Lack of menstruation or irregularity.
- Suspicion of hormonal imbalance in the body.
- The appearance of bleeding outside the menstrual cycle.
- Presence of symptoms of inflammation of the uterus or ovaries.
- Pathological changes in the endometrium: hyperplasia, polyps, chronic endometritis, submucosal nodes.
- Diagnosis of endometriosis of the uterus or adjacent organs.
- Determination of the presence of pathological fluids in the fallopian tubes.
- Suspicions of underdevelopment of the pelvic organs.
- Identification of neoplasms suspected during a gynecological examination.
- Diagnosis of neoplasms and tumor processes of the uterus and bladder.
- Detection of ovarian tumors and cysts.
- Suspicion of ruptured ovarian cysts.
- Infectious diseases of the urinary tract.
- Suspicion of uterine fibroids.
- Diagnosis of the causes of urological diseases, urinary incontinence and other urinary disorders.
- Determining the location of the intrauterine device.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
- Monitoring the condition of the endometrium with an intrauterine device installed or taking hormonal drugs.
- Inability to conceive for six months.
- Preparation for IVF and support of the procedure.
Transvaginal ultrasound allows a woman to know when she is ready to conceive a child. To do this, during a TVUS, a special substance is injected into the fallopian tubes, which, as a contrast, shows the patency of the tubes on the day of the study.
No other method, except TVUS, is capable of recording the baby’s heartbeat as early as the 5th obstetric week of pregnancy. Therefore, transvaginal ultrasound in early pregnancy can confirm the fact of successful conception.
TVUS during pregnancy
Since the intravaginal examination procedure is associated with a certain irritation of the walls of the vagina and pelvic organs (including the uterus), it is allowed only in the first trimester - up to 13 weeks of pregnancy. TVUS makes it possible to detect the very fact of pregnancy and determine its exact date. But there are other indications for conducting such a study:
- monitoring the fetus and its development over time;
- determination of intrauterine and ectopic pregnancy;
- early diagnosis of fetal and pregnancy pathologies;
- identification of threats of miscarriage;
- suspicion of detachment of the ovum;
- distinguishing the fertilized egg from a pathological formation in the uterus;
- assessment of the condition of the scar that remained on the uterus after a previous cesarean section;
- selection of the method of delivery based on the data obtained;
- complete and partial hydatidiform mole;
- determination of the position of the fetal egg in the uterus, the state of its attachment (presentation, low location).
TVUS during pregnancy allows you to determine the number of fetuses in the uterus, heart rate, and possible malformations. This type of study accurately determines the gender of the unborn child.
During pregnancy, transvaginal ultrasound can be done on demand as many times as needed. The sensor and ultrasound radiation are not able to affect the condition of the fetus and the pregnant woman herself.
What diseases are diagnosed using pelvic ultrasound
Thanks to ultrasound diagnostics, it is possible to accurately diagnose numerous inflammatory processes, the formation of tumors of various natures, changes in the location of the pelvic organs, their deformations, the presence of pathological inclusions and other changes. Therefore, based on the results of the study, the following can be diagnosed:
- malformations and deviations in the structure of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, vagina, in particular bicornuate, childish, saddle-shaped uterus, doubled, the formation of septa in the body of the uterus, etc.;
- cysts in the uterus and ovaries, including polycystic disease, fibroids of various types, cystomas, rupture and torsion of the pedicle of the cyst, fibroids, cystadenomas, teratomas;
- malignant tumors of the reproductive organs, polyps;
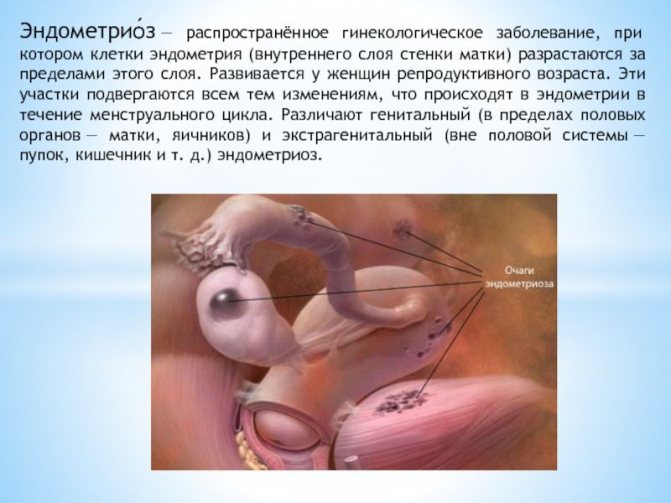
- endometriosis;
- inflammatory diseases, including adnexitis, cervicitis, endometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis, myometritis, parametritis, etc.;
- pathological changes in the fallopian tubes, including hydro- and pyosalpinx, obstruction;
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency, etc.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs is widely used to diagnose pregnancy, determine its duration, as well as the location of the fetus, i.e., detect an ectopic pregnancy that is dangerous for a woman. Subsequently, 3 screenings are required to promptly detect possible pathologies of intrauterine development and take measures appropriate to the situation. Also, performing an ultrasound during pregnancy allows you to diagnose pathologies of the placenta, premature shortening of the cervix and other disorders fraught with termination of pregnancy or the development of complications.
The method is used to monitor pregnancy when using ICSI, IVF, etc.
The study is widely used to assess the functionality of a woman’s reproductive system, namely:
- the nature of follicle growth and the onset of ovulation, which is important if there are problems with conception;
- size and condition of the corpus luteum after ovulation;
- correct installation of the intrauterine device.
It is also used to monitor a woman’s condition after diagnostic invasive interventions, abortions, and various surgical interventions, including after treatment of cervical erosion. In addition, the procedure can be carried out for preventive purposes even in the absence of complaints about the condition of the genitourinary system. It is worth undergoing it once a year as part of a routine examination.
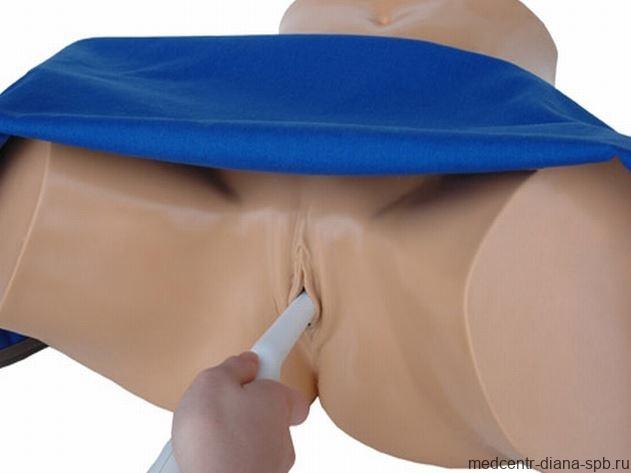
How is a transvaginal examination done?
To undergo an intravaginal examination, the patient needs to undress from the waist down and lie down on the couch, spreading her legs slightly to the sides. The diagnostician usually asks why the woman was sent for an ultrasound and what complaints she has. This information is necessary in order to pay special attention and examine the most interesting pelvic organs at multiple magnification. In this case, the examination involves a complete and thorough examination of the condition of the patient’s entire genitourinary system.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
1. The doctor places a medical condom on the ultrasound sensor and lubricates it with a special gel, which facilitates its penetration into the vagina and eliminates the air space between the transducer and the organs being examined.
2. The doctor performs all movements slowly and carefully, so there is no discomfort during the procedure. A woman can feel pain only if there is an inflammatory focus in the area being examined. If any discomfort occurs, you should immediately report this to your diagnostician.
3. An exact image of the organs being examined is visualized on the monitor of the ultrasound machine; the doctor can enlarge the resulting image many times and view the elements of interest in great detail.
4. Having recorded all the necessary data, the doctor removes the sensor from the vagina. The woman can get dressed and pick up the ultrasound results, which are later deciphered by the doctor who referred for the study.
How is an ultrasound of the uterus and appendages performed?
Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages does not cause pain or inconvenience to the patient, since the examination is done in most cases through the anterior abdominal wall. Before the procedure, the patient undresses to the waist or frees access to the abdominal area. During an abdominal ultrasound of the uterus and appendages, the woman lies on her back, the doctor applies a gel to her stomach and moves a sensor over it.
With other forms of examination, the position of the patient, as well as the location of the sensor, may vary. In some cases, the sensor is inserted into the rectum or vagina.
It is important to note that the decision about when and in what form is best to do an ultrasound of the uterus is made by a specialist based on a number of symptoms or pathologies of the reproductive system noticed during examination.
Preparation for TVUS
Intravaginal ultrasound is distinguished not only by its ease of implementation with high information content, but also by the lack of preparation for this examination. There is no need to drink water to fill the bladder; the transvaginal sensor clearly visualizes the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, ligaments and adjacent organs without additional manipulation.
Only patients suffering from severe flatulence need specific preparation:
1. 2 days before the test, you should limit the consumption of foods that increase gas formation in the intestines: baked goods, fresh vegetables and fruits, dairy products.2. On the day of the TVUS, the doctor may prescribe you to take Enzistal, Espumisan, activated charcoal or Smecta. The drug is selected by the doctor based on the patient’s tolerance to the active ingredients of the drug and cannot be chosen at his own discretion. Transvaginal ultrasound examination for pregnant women is recommended to be carried out on a moderately full bladder, so for such patients a preliminary visit to the toilet is not required.
What preparation is needed?
When planning a transvaginal ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, you need to consider several points:
| 1. The study is carried out on an empty bladder. | It is worth refraining from drinking an hour before the procedure and visiting the toilet before it. |
| 2. There should be no excess gases in the intestines. | To do this, you need to stop eating foods that cause gas the day before and, if necessary, take appropriate medications an hour before the ultrasound. |
| 3. Don't forget about hygiene. | The presence of vaginal discharge is not an obstacle to the procedure, but unless there are special indications, it is not performed during menstruation. |
On what day of the menstrual cycle is TVUS performed?
Women often ask whether it is possible to do a transvaginal ultrasound during menstruation. For the most accurate assessment of the condition of the female genitourinary system (outside the period of pregnancy), it is worth adhering to a certain dependence of TVUS on the day of the menstrual cycle:
1. A planned transvaginal ultrasound should be done on the 5th, 6th or 7th day of the cycle, while the endometrium of the uterus is not yet in the secretory phase. If you ignore this recommendation, the doctor may incorrectly interpret the results of ultrasound diagnostics.2. To determine the presence of a fertilized egg in the uterus and the exact duration of pregnancy, a woman needs to come for a transvaginal ultrasound diagnosis no earlier than the 10th day of the delay.3. If a patient is suspected of having endometriosis, then the study should be planned after ovulation - no earlier than the 14th day of the cycle.4. If uterine fibroids are suspected, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed on days 18-24 of the cycle5. To monitor the patient’s reproductive function, monitor the ovulation process, or determine the cause of hormonal imbalance in the body, transvaginal ultrasound is recommended to be performed on the 10th day of the cycle, and then every 3 days until its end.
However, there are situations when an emergency procedure is necessary, regardless of the day of the cycle:
- sudden disruption of menstrual function: the next menstruation turned out to be more abundant and with clots, longer (longer than 7 days) or did not occur at all within 1 month;
- spotting that the patient does not associate with the onset of menstruation, i.e. they can appear before, after the next menstruation or in the middle of the cycle;
- discharge with blood in pregnant women;
- discharge mixed with blood during or after sexual intercourse;
- the appearance of bleeding in a woman during the menopausal period;
- pain in the lower abdomen.
The appearance of such symptoms should prompt a woman of any age to contact a gynecologist and further undergo a TVUS scan.
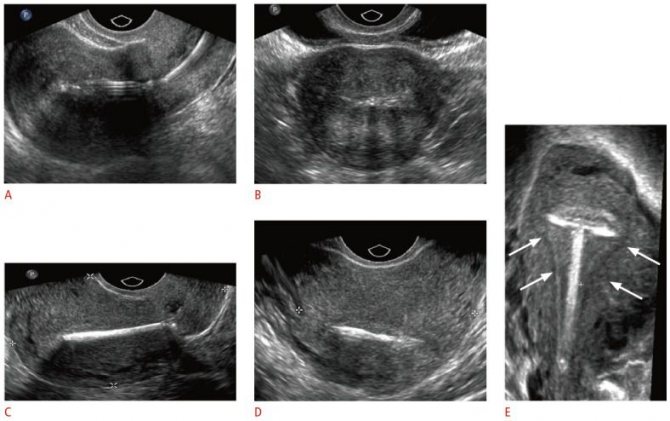
Transvaginal ultrasound: photo
Transvaginal ultrasound
Pelvic ultrasound in St. Petersburg
transvaginal ultrasound during pregnancy
transvaginal ultrasound
transvaginal ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasound at the Diana clinic
How often should a transvaginal ultrasound be done?
You need to contact a gynecologist and undergo a transvaginal ultrasound examination every time a woman develops the symptoms and conditions described above in the indications for the procedure. A gynecologist or urologist may prescribe this type of examination if the development of a disease of the genitourinary system is suspected.
If there are no complaints and the woman assesses her condition as satisfactory, she needs to undergo TVUS for preventive purposes at the following frequency:
1. For women with the onset of sexual activity – once every 2 years.2. Women over 40 years old – annually.
If endometriosis is suspected, the procedure is performed in the second half of the cycle. If bleeding occurs in the middle of the cycle, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed urgently to determine the cause of this phenomenon.
Evaluation of TVUS results
Having transvaginal ultrasound data in hand, an experienced specialist can accurately diagnose and select the appropriate treatment for the identified pathology. The results are interpreted by a gynecologist.
About consultation with a gynecologist / Consultation of a gynecologist
Our clinic employs gynecologists of the highest and first certification categories. All doctors have certificates confirming their qualifications, issued in St. Petersburg and Moscow. The cost of an initial appointment with a gynecologist is 1000 rubles, a consultation based on test results or ultrasound is 500 rubles. Appointment with a gynecologist You can make an appointment with a gynecologist without an insurance policy, registration in St. Petersburg and Russian citizenship. We have gynecologists and ultrasound specialists who speak English. You can apply to us without having an insurance policy, registration in St. Petersburg and Russian citizenship. ATTENTION! IN THE CLINIC IS A DOCTOR SPEAKING IN ENGLISH LANGUAGE! Sign up for an appointment with the doctor
During a TVUS, the diagnostician evaluates the following indicators:
Uterus size and position
The size of the organ depends on the individual characteristics of the anatomical structure, the number of pregnancies, childbirths and some other factors. In women who have given birth, the dimensions of this organ are approximately 70 x 60 x 50 mm. If these sizes are much larger than acceptable, the doctor looks for the cause of this pathology.
When performing a transvaginal ultrasound, the position of the uterus is also taken into account. If it is slightly tilted forward, this is considered normal. If its position is shifted back, they speak of a pathological location of the organ.
Echogenicity of the uterus
Here, the structure of the walls and cavity of the organ itself is important; the clarity of the boundaries of the uterus also determines. The presence of hyperechoic areas in the picture may indicate the presence of neoplasms in the uterus.
Endometrial thickness, cervix and endocervix
The inner layer of the uterus changes its thickness depending on the day of the menstrual cycle: at the beginning the endometrium has a thickness of about 3 mm, and at the end it can reach 2 cm. The data obtained on the thickness of the endometrium is compared with the day of the patient’s cycle: if there are discrepancies with the norm, inflammatory process.
Cervix and endocervix . What matters is the structure of the cervix and its size, which normally should correspond to 40 x 30 mm. The cervical canal should have a diameter of less than 3 mm and be filled with mucus.
Sizes and contours of the ovaries
Transvaginal ultrasound perfectly shows the size of the right and left ovaries. At the same time, they may differ slightly, but their total volume should not exceed 10 cubic cm. If this indicator is exceeded, polycystic syndrome or an inflammatory process may be suspected. Their contours can be either smooth or irregular due to the formation of follicles.
Presence of free fluid in the pelvis
A small amount of it can normally be seen in this area, but only immediately after ovulation, which is associated with rupture of the follicle. Otherwise, the fluid may be a sign of ovarian inflammation resulting from an infectious lesion.
Fallopian tubes
They are usually visualized in the presence of an ectopic pregnancy or an inflammatory process in them. To diagnose tubal patency, a contrast agent is used. Already at the stage of ultrasound diagnostics - transvaginal ultrasound, the doctor can determine the following pathological conditions:
- inflammation of the fallopian tubes, ovaries or endometrium of the uterus;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- ovarian cyst;
- endometriosis of the uterus and nearby organs;
- polyps or uterine fibroids;
- cancer of the ovary, uterus or cervix.
Appointment of vaginal ultrasound
An ultrasound with a vaginal probe is performed to obtain information about the condition of the woman’s pelvic organs. Such a study allows us to determine even the slightest deviations from the norm and determine treatment tactics that are adequate to the patient’s condition. A gynecologist or surgeon can refer a patient for examination if pain occurs, delays in the onset of regular menstruation, abnormal discharge, in the absence of a planned pregnancy, and in many other cases.
What is transvaginal ultrasound?
In itself, vaginal ultrasound is a completely safe diagnostic method. This research is based on ultrasonic waves, which are reflected differently from tissues, depending on their structure. Based on exactly how the waves were reflected from certain organs and their parts, the doctor draws up a conclusion about the patient’s state of health. Features of the transvaginal research method
is that during the procedure it is necessary to insert a sensor into the woman’s vagina, and not just examine the organs through the abdominal wall.
Interpretation of transvaginal ultrasound: table of indicators and diseases
| Genitals | Normal indicators | Deviations |
| Uterus | Anteflexio (anterior tilt); The contours of the uterus are smooth and clear; Dimensions of the uterus: length - 7 cm, width - 6 cm, diameter - about 4 cm; Homogeneous echogenicity of the walls; Homogeneous structure; Crisp and smooth edges | Retroflexio is a variant of the norm that prevents conception; Uneven contours indicate inflammation in the uterus and tissues or tumors of various origins; Heterogeneous echogenicity is a sign of a tumor; Hyperechoic formations (polyps, tumors, myomatous nodes); Heterogeneous structure: a sign of endometritis |
| Cervix | Dimensions: anteroposterior size - 2-3 mm, length - 3-4 cm. Diameter of the cervical canal: 2-3 mm. Homogeneous echostructure. Mucus of homogeneous echostructure. | Increased size of the cervix and cervical canal Heterogeneous structure |
| Free liquid | Normally, its amount is several mm. | A large amount of fluid is a sign of infection |
| Ovaries | Dimensions: width - 2.5 cm, length - 3 cm, thickness - 1.5 cm. Normal volume: 2-8 cm³; Fuzzy, lumpy contours. Homogeneous structure, small areas of fibrosis; In the middle of the cycle, follicles 4-6 mm in size and one dominant follicle up to 2 cm in size are formed | Increase in size (inflammation, polycystic disease) Large fibrous foci (inflammatory process). The size of the dominant follicle is greater than 2.5 cm (follicular cyst) |
| The fallopian tubes | Almost invisible | Clearly visualized (a sign of ectopic pregnancy or inflammation) |
Echo signs of uterine pathologies
| Pathology | Features |
| Uterine cancer | Changes in the contours of the uterus, swelling |
| Myoma | Increased size of the uterine body, altered contours, “hyperechoic zone” (nodule in the muscle) |
| Polyps | Fuzzy contours of the uterus, space-occupying formations in the uterus |
| Endometriosis | “Bubbles” on the cervix, in the tubes and in the uterus itself |
| Adnexit | Thickening of the fallopian tubes, enlarged ovaries, unclear and blurry contours |
| Ovarian cancer | Increase in size with deformation of contours |
| Ovarian cyst | Accumulation of fluid with a diameter greater than 25 mm |
| Endometritis | Swelling of the endometrial layer, increased size of the uterus, thickening of the walls |
| Cervical tumor | Deformation and enlargement of the cervix |
Timely diagnosis and identification of pathological processes in the genitourinary system allows, in most cases, to manage only with drug therapy. Only in rare cases are identified problems solved exclusively by surgery. This speaks to the importance of an annual preventive examination by a gynecologist and undergoing a transvaginal ultrasound by a good specialist.
CLICK TO MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Decoding the results
After an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs, the woman is given a conclusion that describes the condition of the uterus, endometrium, left and right ovaries, cervix, fallopian tubes, retrouterine space and veins. If pathological changes are detected during the examination, the doctor must indicate their nature, location, nature of the structure and other features. He can also suggest the cause of such changes, but the final diagnosis is made only by the attending gynecologist. At the same time, he takes into account not only the results of ultrasound, but also the features of the clinical picture, as well as the results of other studies.
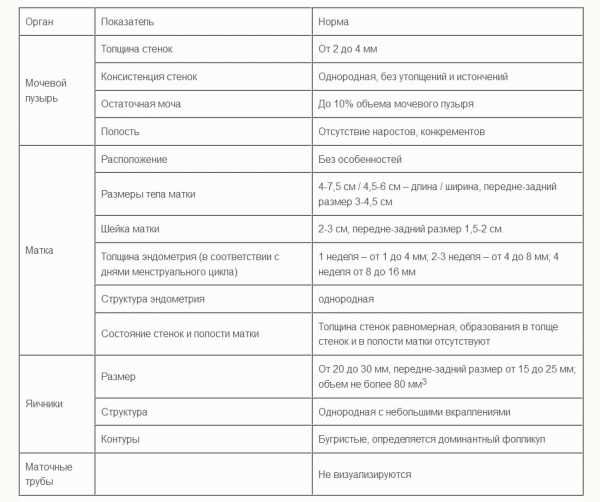
Normally, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs does not visualize the fallopian tubes, Douglas and retrouterine spaces. The uterus has a pear-shaped shape, a uniform structure and smooth, clear contours. The endometrium is visualized as a clear line with a homogeneous hyperechoic structure. The cervix normally has a homogeneous structure, has a length of 35-40 mm, and the diameter of the cervical canal does not exceed 3 mm. The condition of the ovaries depends on the phase of the cycle. In any case, normally they should have a uniform structure, clear, bumpy contours. Healthy pelvic veins are not dilated and do not show signs of tortuosity.
Thus, ultrasound of the pelvic organs is a very informative diagnostic procedure that allows one to detect almost any deviation from the norm in the condition of the female genital organs. And the simplicity of its implementation, accessibility and absolute safety make the method widely in demand.