Objectives of ultrasound examination during pregnancy
The content of the article
Ultrasound examination is the most accurate and effective assessment of the condition of the pregnant woman and the fetus at different gestational stages. A woman undergoes it for the first time after learning about pregnancy, and then several more times during pregnancy.
A pregnant woman must undergo at least three routine screening ultrasounds without fail: during the period 10-14, 20-24, 32-34 weeks.
An ultrasound may also be required at an earlier stage or immediately before birth - an unscheduled examination is prescribed if the diagnosis is questionable or if there is an increased risk of pregnancy complications.
Observing the course of pregnancy week by week, the doctor pursues the following goals:
- confirmation of pregnancy;
- monitoring the development of the fetus, its size and weight;
- assessment of fetal viability;
- detection of pathologies at all stages of pregnancy;
- determining the sex of the child;
- assessment of maturity parameters, size and place of attachment of the placenta;
- calculation of amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) values.
Ultrasound by week of pregnancy is the most important examination during pregnancy.
Do's and don'ts
We advise you not to forget about physical activity even after the appearance of an impressive tummy. Thanks to sports and movement, tissues are better saturated with oxygen, which means the baby will not suffer from hypoxia. Strong muscles will help you endure the difficulties of pregnancy and childbirth more easily. Among the many sports, we especially recommend swimming, yoga, Pilates, walking, and fitball exercises.
If you feel well, do not deny yourself intimacy. You will not be able to harm the baby, but your positive emotions and endorphins will definitely be transferred to him.
Is it possible to fly while 6 months pregnant?
The second trimester is the optimal time for traveling by plane. However, before traveling, consult your gynecologist to see if you have any contraindications. Usually, if gestation proceeds calmly, there are no restrictions. Just don't forget to bring your exchange card.
What a fetal ultrasound can and cannot reveal
1st trimester
: Ultrasound reveals the following pathologies:
- defects of the central nervous system (for example, anencephaly - absence of the brain);
- absence of the peritoneal wall (severe pathology - gastroschisis);
- spinal abnormalities - absence, hump, etc.;
- Down syndrome;
- umbilical hernia (diagnosis of omphalocele);
- absence of limbs.
2nd trimester
: all visible abnormalities can be identified, since all organs of the fetus are almost formed by this time.
3rd trimester
: defects previously identified by blood tests, chorionic villus biopsy and other methods are confirmed or refuted.
It is impossible to diagnose using ultrasound:
- blindness and deafness - ultrasound cannot show the quality of transmission of nerve impulses to visual and auditory receptors
- mental retardation, since these are properties of the brain, not its structure;
- minor disorders of organ development (for example, obstruction of the liver ducts or defects of the cardiac septum);
- some genetic diseases (for example, Duchenne myopathy, phenylketonuria, cystic fibrosis are not diagnosed);
- chromosomal abnormalities themselves (Edwards, Patau, Turner syndromes), the doctor can only observe the result of their development.
Having studied the list of problems that are not detected on fetal ultrasound, you should not worry - these pathologies will not go unnoticed. Many fetal malformations are detected by blood tests for fetal pathology and other special methods.
How is an ultrasound performed by week of pregnancy?
The doctor chooses from 2 methods:
- Transabdominal
– the examination is carried out using an external sensor through a small layer of a special gel applied to the woman’s abdomen. The main condition for the procedure is a full bladder. 30-60 minutes before the ultrasound, a woman should drink 1-1.5 liters of non-carbonated liquid and not urinate; - Transvaginal
– examination takes place using a vaginal sensor – transducer, inserted into the vagina. This type of ultrasound does not require special preparation. You just need to empty your bladder immediately before the procedure.
Basically, the examination is carried out using the abdominal method. It happens that in the early stages the fetus is poorly visualized, so they proceed to examination through the vagina. Read here which method to choose.
Why do we do an examination at 6 weeks of pregnancy?
The doctor determines the presence of an embryo, measures its size, and determines whether the size of the embryo (CTE) corresponds to the period of pregnancy according to menstruation. The size of the fertilized egg is also important, whether its size corresponds to the size of the embryo.
From the side of the ovum, the following parameters are assessed: its shape, size, the presence of pathological inclusions, as well as the presence of detachment of the ovum. If the patient ovulates in the middle of the cycle on the fourteenth to fifteenth day, accordingly, by this time the embryo should have a heartbeat. If the doctor does not detect a fetal heartbeat - in this case, a control ultrasound is necessary after a week - it is very important to determine whether the pregnancy is progressing.
Signs of progressive intrauterine pregnancy:
- the size of the fertilized egg (fetal CTE) and yolk sac corresponds to the gestational age;
- there are no signs of a threat of miscarriage;
- presence of fetal heartbeat.
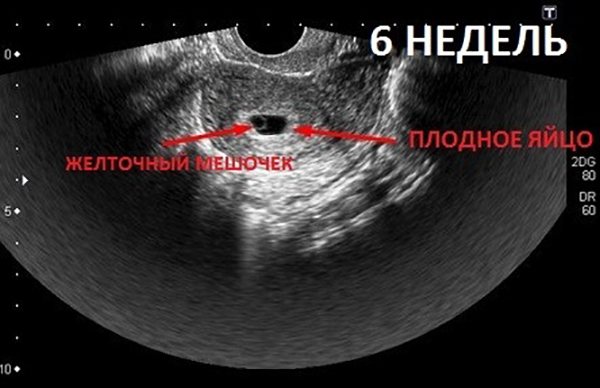
Ultrasound at 6 weeks of pregnancy
Very often we can hear the expression “uterine tone”, what does this mean? The uterus is a muscular organ, which in the early stages of gestation may have local tone (muscle fiber tension in certain areas of the uterus); such changes are typical for the early stages of pregnancy, and this does not constitute a threat of termination of pregnancy. In this case, sedation and rest are prescribed.
An indirect sign of a threatened miscarriage is the presence of a hematoma. This is a blood clot located between the uterus and the fertilized egg. This clot results from the rupture of the spiral arteries, which are located between the uterus and the fertilized egg. This is a condition that deserves dynamic monitoring and correction of the condition with the help of certain medications.
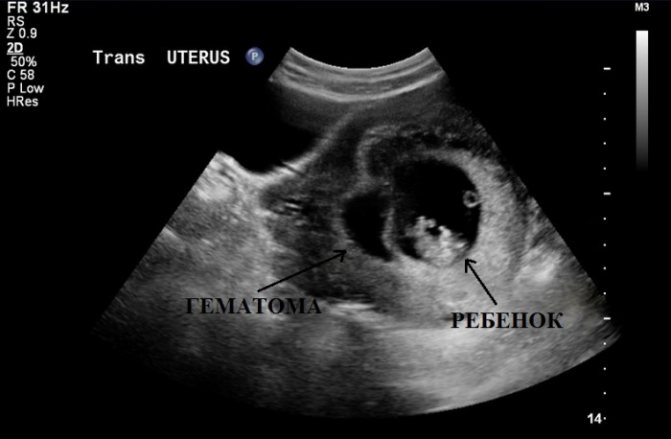
Ultrasound image of a hematoma
What are spiral arteries? These are vessels that are located between the uterus and the fertilized egg. They connect and accordingly nourish the fertilized egg. This is the implanted fertilized egg. In the early stages, spiral arteries grow into the endometrium. The endometrium is the functional layer in the uterus. In the absence of pregnancy or implantation defect, it is this layer that is flattened, and the patient begins menstruation.
Ultrasound at 3 weeks of pregnancy
An ultrasound examination during this period is necessary to confirm pregnancy. Now the processes of embryogenesis are just beginning, but on ultrasound you can already see the fertilized egg attached to the wall of the uterus.
At week 3, a study may be prescribed in certain cases:
- diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy;
- Hydatidiform mole is a rare pathology of the ovum, characterized by the absence of an embryo in the presence of all the symptoms of pregnancy. The reason is that the structure necessary for the attachment of the fertilized egg in the uterus (trophoblast) degenerates into a huge number of small bubbles;
- doubts about pregnancy - signs of pregnancy are unclear.
Ultrasound at 5 weeks of pregnancy
Often expectant mothers undergo their first examination at this time. A woman experiences a delay in menstruation (by about 3 weeks), so she, suspecting pregnancy, boldly goes to the gynecologist.
At the 5th week of gestation, it is still impossible to identify pathologies, assess the condition of the fetus, or determine the sex. However, during this period, ultrasound allows:
- hear the heartbeat of the embryo;
- diagnose normal and ectopic pregnancy;
- determine the duration of pregnancy;
- identify the cause of delayed menstruation if there is no pregnancy.
Feelings of the expectant mother
The height of the fundus of the uterus is 24-28 cm. This is 5-6 cm above the level of the navel. Due to the pressure that the uterus exerts on neighboring organs, a woman feels a frequent urge to urinate, heartburn, and possible constipation. Nausea in the 6th month of pregnancy can be associated with overeating and excess pressure of the uterus on the stomach. But if it is accompanied by severe swelling and increased blood pressure, consult a gynecologist immediately. These are symptoms of gestosis in pregnant women.
Due to a growing belly and a shift in the center of gravity, back pain is inevitable, especially after prolonged standing, sitting or walking. Try to take breaks and rest throughout the day. If possible, do not deny yourself the opportunity to lie down for 15-20 minutes with your legs elevated. This improves blood flow and helps prevent varicose veins.
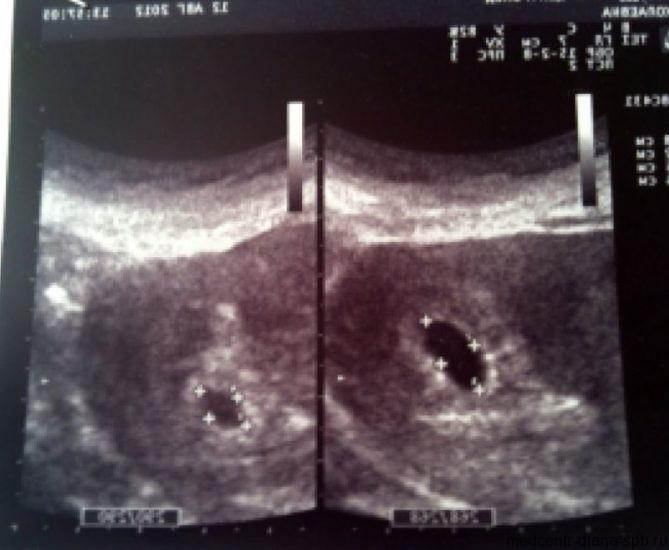
First ultrasound: at 10-14 weeks (planned, screening)
Typically, 1 scheduled examination is scheduled for the 12th week of pregnancy. Already at this stage, the woman’s condition and how the pregnancy is progressing in general are easily assessed. Moreover, ultrasound reveals pathological changes in the fetus. This is important because if abnormalities are detected, termination of pregnancy may be necessary, and in the first trimester the doctor will prescribe a medical abortion, which is not dangerous to the woman’s health.
The main tasks of the first planned ultrasound:
- Determination of a special parameter - the thickness of the collar zone (the area between the soft tissues covering the spine and the inner surface of the skin, filled with fluid). Measuring this indicator allows us to identify the development of chromosomal pathologies - Down syndrome, etc.;
- Measuring the coccygeal-parietal size. The indicator determines the size of the fetus and the exact gestational age;
- Diagnosis of fetal cardiac activity is the main indicator of viability;
- Detection of multiple births;
- Assessment of the presence and development of the child’s organs;
- Determining the expected date of birth;
- Establishing the correspondence of fetal size to gestational age.
Also, the first examination allows you to assess the location of the placenta and determine the condition and tone of the uterus. Often, the first scheduled ultrasound is a significant event for a couple, since they can see their unborn child for the first time.
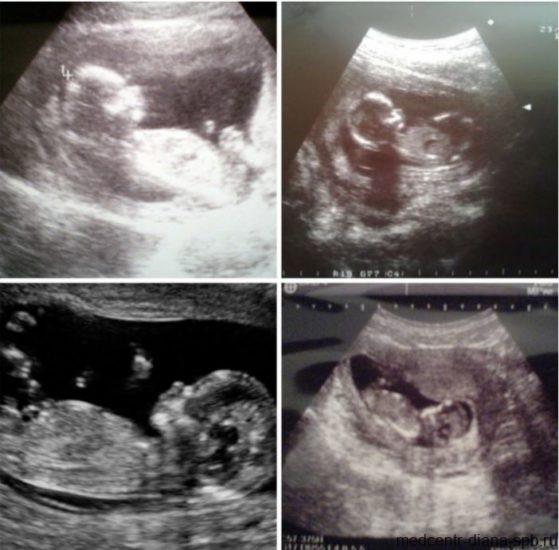
Second planned ultrasound: at 20-24 weeks
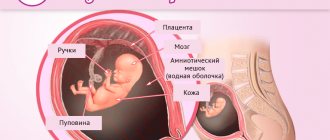
Examination in the second trimester is an extremely important event. By the 22nd week of pregnancy, all the internal systems and organs of the child are practically formed and active motor activity is observed, so you can assess the child’s condition and examine it in detail from all sides. In addition, this is when future parents can find out the sex of the child.
The main objectives of the second study:
- carrying out fetometry - determination of biometric indicators (length of tubular bones, circumference of the head, abdomen, biparietal and fronto-occipital size). Based on the data obtained, the child’s weight is calculated;
- identification of possible pathologies of fetal development;
- assessment of the size, maturity, structure and location of the placenta;
- conducting Doppler measurements - studies of uteroplacental circulation and blood flow in the aorta and middle cerebral artery of the fetus;
- assessment of the umbilical cord - it is possible to detect entanglement around the fetal neck, but at this stage it is not dangerous, since the child is actively moving and the situation can resolve itself;
- cervical assessment. The normal size is at least 3 cm. As labor approaches, it shortens and smoothes out. The internal opening must be completely closed. Violation of these parameters indicates isthmic-cervical insufficiency, requiring suturing of the cervix or insertion of an obstetric pessary.
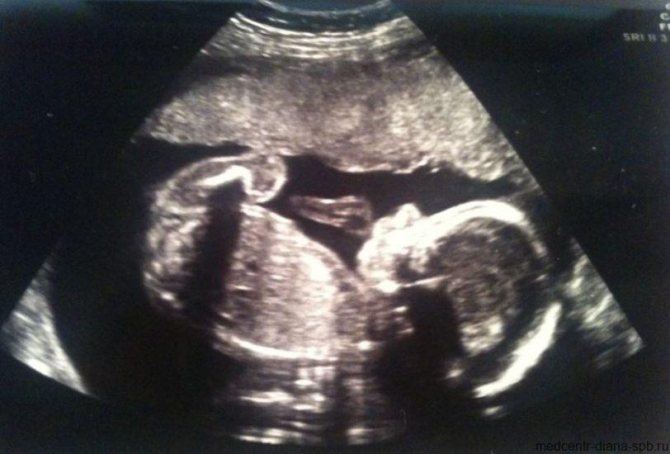
Third planned ultrasound: at 32-34 weeks
An ultrasound in the third trimester is also extremely important, as the doctor determines how the delivery will proceed. In addition, it pursues the following goals:
- determination of the position and presentation of the fetus. The position in which the baby will be will not change until birth. The method of delivery will depend on it and on the presentation. So, with a longitudinal position and a normal cephalic presentation, this is a natural birth; with a transverse or oblique position and a pelvic presentation, this is a cesarean section;
- assessment of the size and weight of the fetus;
- assessment of the size, maturity and location of the placenta;
- assessment of the quantity and quality of amniotic fluid.
Terminology
Accurate interpretation of ultrasound findings in the first trimester requires the use of appropriate and consistent terminology, as outlined in Doubilet et al. (2013). The criteria for viable and non-viable MBs are simple. However, MB of unknown viability is a broad category and can lead to confusion. To be precise, MB of unknown viability can apply to normal pre-embryo development situations with cardiac activity, including empty PU (PM with a yolk sac but no embryo), and PU with a yolk sac and an embryo smaller than 4 mm but without cardiac activity. activities. The second category of unknown viability is used when there is evidence of miscarriage (signs of poor prognosis). The authors of the publication found that using the term MB of unknown viability is more appropriate in this case because it conveys a sense of alertness. Alternatively, for small uterine ulcers, it is preferable to use the term “early intrauterine uterine ulcer at __ gestational age” instead of urinary tract of unknown viability, with a recommendation for follow-up ultrasound to confirm normal pregnancy development.
Pregnancy in an unknown location has several scenarios, and the authors encountered these scenarios while applying this terminology to their patient population. If the results of pelvic ultrasound are almost normal, a differential diagnosis of “very early MB”, “non-visualized ectopic pregnancy” or “complete spontaneous abortion” is provided. When vaginal bleeding and thickening of the heterogeneous endometrium occur, the authors used the term “pregnancy in an unknown location, the most likely scenario is spontaneous termination of pregnancy.” Detection of an area of low-resistance arterial trophoblastic flow may be useful to confirm the site of intrauterine implantation in these situations. However, spectral Doppler ultrasound should not be used in the first trimester if normal viable MB is likely (*And I keep hearing that these recommendations are often ignored...). The third scenario is vague intrauterine fluid accumulation. While intrauterine PO and early MB may be most likely, the differential diagnosis also includes a decidual cyst and localized intrauterine fluid. Thus, in these situations, it is recommended to monitor beta-hCG levels and control endovaginal (*transvaginal) ultrasound after 7-10 days.
Unscheduled ultrasounds are prescribed as necessary and at the request of the patient
In some cases, a pregnant woman is prescribed an unscheduled ultrasound. It may be needed to assess the woman’s condition and prevent possible complications if pathologies or alarming symptoms occur:
- abnormal fetal development;
- discrepancy between the size of the uterus and the gestational age;
- abdominal pain;
- bloody issues;
- pathologies of placental maturation;
- absence of movements and other signs of the fetus;
- intrauterine developmental delay of the child.
Additional studies can be prescribed by a specialist at any period of gestation until birth.
How the tummy grows
At the 6th month, the skin on the abdomen stretches and may begin to itch. In addition, as pregnancy progresses, the likelihood of developing stretch marks on the abdomen, chest and thighs also increases.
- Exercise, a special maternity bra, a bandage that supports the abdomen from below, and a moisturizer (or better yet, a special stretch mark cream for pregnant women) can somewhat reduce the likelihood or severity of this phenomenon. While waiting for a baby, stretch marks sometimes have a darker color than the skin in neighboring areas. After birth, they will begin to lighten and over time will differ in color from darker, unaffected skin.
- In the second and especially in the third trimesters, you may experience pain in the lower abdomen. The abdominal muscles and ligaments that support the growing uterus stretch and pull apart as it grows. This cannot but cause sensations ranging from tingling to nagging pain on the sides of the abdomen. They can occur and intensify when changing body position, sudden movements and physical activity. With such pain, changing posture, switching to another type of activity, rest and a warm bath help well.
- Although this doesn't happen to all women, you may also notice an unusual sensation in your lower abdomen where it becomes "rocky" for a few seconds. These are false contractions, or Braxton-Hicks training contractions, - irregular contractions of the muscles of the uterus and cervix preparing for childbirth. Spasms can occur up to 4 times an hour and last from 15 to 30 seconds, but in some mothers they can be longer - up to 2 minutes.
- It is important to remember that training contractions should not be painful, although - and this depends on the woman’s pain sensitivity - they can cause some discomfort. Another important difference between false contractions and labor is the lack of dynamics in the frequency and duration of muscle contractions.
- During Braxton Hicks contractions, doctors recommend sitting up, placing your feet on an elevated platform, and drinking a glass of water. Such recommendations are due to the fact that, according to observations, training contractions intensify in mothers who lead a very active lifestyle, as well as in those whose bodies experience mild dehydration.
The norm of indicators determined by ultrasound. Tables by week of pregnancy
Fetal size by week of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Weight, g | Length, cm |
| 8 | 1 | 1,6 |
| 9 | 2 | 2,3 |
| 10 | 4 | 3,1 |
| 11 | 7 | 4,1 |
| 12 | 14 | 5,4 |
| 13 | 23 | 7,4 |
| 14 | 43 | 8,7 |
| 15 | 70 | 10,1 |
| 16 | 100 | 11,6 |
| 17 | 140 | 13 |
| 18 | 190 | 14,2 |
| 19 | 240 | 15,3 |
| 20 | 300 | 16,4 |
| 21 | 360 | 26,7 |
| 22 | 430 | 27,8 |
| 23 | 501 | 28,9 |
| 24 | 600 | 30 |
| 25 | 660 | 34,6 |
| 26 | 760 | 35,6 |
| 27 | 875 | 36,6 |
| 28 | 1005 | 37,6 |
| 29 | 1153 | 38,6 |
| 30 | 1319 | 39,9 |
| 31 | 1502 | 41,1 |
| 32 | 1702 | 42,4 |
| 33 | 1918 | 43,7 |
| 34 | 2146 | 45 |
| 35 | 2383 | 46,2 |
| 36 | 2622 | 47,4 |
| 37 | 2859 | 48,6 |
| 38 | 3083 | 49,8 |
| 39 | 3288 | 50,7 |
| 40 | 3462 | 51,2 |
| 41 | 3597 | 51,7 |
| 42 | 3685 | 51,5 |
Deviation of indicators in a smaller direction is a sign of intrauterine growth retardation; changes in a larger direction are a sign of a large fetus, which will complicate natural childbirth. In such cases, doctors prefer caesarean section.
Head sizes by week of pregnancy
| Gestation period, weeks. | Fronto-occipital size (LZR), mm | Biparietal size (BPR), mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 11 | 17 | 13-21 | ||
| 12 | 21 | 18-24 | ||
| 13 | 24 | 20-28 | ||
| 14 | 27 | 23-31 | ||
| 15 | 31 | 27-35 | ||
| 16 | 45 | 41-49 | 34 | 31-37 |
| 17 | 50 | 46-54 | 38 | 34-42 |
| 18 | 54 | 49-59 | 42 | 37-47 |
| 19 | 58 | 53-63 | 45 | 41-49 |
| 20 | 62 | 56-68 | 48 | 43-53 |
| 21 | 66 | 60-72 | 51 | 46-56 |
| 22 | 70 | 64-76 | 54 | 48-60 |
| 23 | 74 | 67-81 | 58 | 52-64 |
| 24 | 78 | 71-85 | 61 | 55-67 |
| 25 | 81 | 73-89 | 64 | 58-70 |
| 26 | 85 | 77-93 | 67 | 61-73 |
| 27 | 88 | 80-96 | 70 | 64-76 |
| 28 | 91 | 83-99 | 73 | 67-79 |
| 29 | 94 | 86-102 | 76 | 70-82 |
| 30 | 97 | 89-105 | 78 | 71-85 |
| 31 | 101 | 93-109 | 80 | 73-87 |
| 32 | 104 | 95-113 | 82 | 75-89 |
| 33 | 107 | 98-116 | 84 | 77-91 |
| 34 | 110 | 101-119 | 86 | 79-93 |
| 35 | 112 | 103-121 | 88 | 81-95 |
| 36 | 114 | 104-124 | 90 | 83-97 |
| 37 | 116 | 106-126 | 92 | 85-98 |
| 38 | 118 | 108-128 | 94 | 86-100 |
| 39 | 119 | 109-129 | 95 | 88-102 |
| 40 | 120 | 110-120 | 96 | 89-103 |
An increased size of the fetal head is a sign of hydrocephalus - an increase in the amount of fluid in the brain. To make such a diagnosis, the ventricles must also be enlarged. Sometimes the pathology is accompanied by other developmental disorders, so additional thorough research is necessary.
Abdominal circumference, fetal head
| Gestation period (weeks) | Abdominal circumference, mm | Head circumference, mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 11 | 51 | 40-62 | 63 | 53-73 |
| 12 | 61 | 50-72 | 71 | 58-84 |
| 13 | 69 | 58-80 | 84 | 73-96 |
| 14 | 78 | 66-90 | 97 | 84-110 |
| 15 | 90 | 110 | ||
| 16 | 102 | 88-116 | 124 | 112-136 |
| 17 | 112 | 93-131 | 135 | 121-149 |
| 18 | 124 | 104-144 | 146 | 131-161 |
| 19 | 134 | 114-154 | 158 | 142-174 |
| 20 | 144 | 124-164 | 170 | 154-186 |
| 21 | 157 | 137-177 | 183 | 166-200 |
| 22 | 169 | 148-190 | 195 | 178-212 |
| 23 | 181 | 160-202 | 207 | 190-224 |
| 24 | 193 | 172-224 | 219 | 201-237 |
| 25 | 206 | 183-229 | 232 | 214-250 |
| 26 | 217 | 194-217 | 243 | 224-262 |
| 27 | 229 | 205-229 | 254 | 235-273 |
| 28 | 241 | 217-241 | 265 | 245-285 |
| 29 | 253 | 228-278 | 275 | 255-295 |
| 30 | 264 | 238-290 | 285 | 265-305 |
| 31 | 274 | 247-301 | 294 | 273-315 |
| 32 | 286 | 258-314 | 304 | 283-325 |
| 33 | 296 | 267-325 | 311 | 289-333 |
| 34 | 306 | 276-336 | 317 | 295-339 |
| 35 | 315 | 285-345 | 322 | 299-345 |
| 36 | 323 | 292-354 | 326 | 303-349 |
| 37 | 330 | 299-361 | 330 | 307-353 |
| 38 | 336 | 304-368 | 333 | 309-357 |
| 39 | 342 | 310-374 | 335 | 311-359 |
| 40 | 347 | 313-347 | 337 | 312-362 |
Length of shin bones, femur femur
| Gestation period (weeks) | Abdominal circumference, mm | Head circumference, mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 11 | 5,6 | 3,4-7,8 | ||
| 12 | 7,3 | 4-10,8 | ||
| 13 | 9,4 | 7-11,8 | ||
| 14 | 12,4 | 9-15,8 | ||
| 15 | 16,2 | |||
| 16 | 18 | 15-21 | 20 | 17-23 |
| 17 | 21 | 17-25 | 24 | 20-28 |
| 18 | 24 | 20-28 | 27 | 23-31 |
| 19 | 27 | 23-31 | 30 | 26-34 |
| 20 | 30 | 26-34 | 33 | 29-37 |
| 21 | 33 | 29-37 | 36 | 32-40 |
| 22 | 35 | 31-39 | 39 | 35-43 |
| 23 | 38 | 34-42 | 41 | 37-45 |
| 24 | 40 | 36-44 | 44 | 40-48 |
| 25 | 42 | 38-46 | 46 | 42-50 |
| 26 | 45 | 41-49 | 49 | 45-53 |
| 27 | 47 | 43-51 | 51 | 47-55 |
| 28 | 49 | 45-53 | 53 | 49-57 |
| 29 | 51 | 48-55 | 55 | 50-60 |
| 30 | 53 | 49-57 | 57 | 52-62 |
| 31 | 55 | 50-60 | 59 | 54-64 |
| 32 | 56 | 51-61 | 61 | 56-66 |
| 33 | 58 | 53-63 | 63 | 58-68 |
| 34 | 60 | 55-65 | 65 | 60-70 |
| 35 | 61 | 56-66 | 67 | 62-72 |
| 36 | 62 | 57-67 | 69 | 64-74 |
| 37 | 64 | 59-69 | 71 | 66-76 |
| 38 | 65 | 60-70 | 73 | 68-78 |
| 39 | 66 | 61-71 | 74 | 69-80 |
| 40 | 67 | 62-72 | 75 | 70-80 |
Length of the humerus, fetal forearm bones
| Gestation period (weeks) | Abdominal circumference, mm | Head circumference, mm | ||
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 16 | 15 | 12-18 | 18 | 15-21 |
| 17 | 18 | 15-21 | 21 | 17-25 |
| 18 | 20 | 17-23 | 24 | 20-28 |
| 19 | 23 | 20-26 | 27 | 23-31 |
| 20 | 26 | 22-29 | 30 | 26-34 |
| 21 | 28 | 24-32 | 33 | 29-37 |
| 22 | 30 | 26-34 | 35 | 31-39 |
| 23 | 33 | 29-37 | 38 | 34-42 |
| 24 | 35 | 31-39 | 40 | 36-44 |
| 25 | 37 | 33-41 | 43 | 39-47 |
| 26 | 39 | 35-43 | 45 | 41-49 |
| 27 | 41 | 37-45 | 47 | 43-51 |
| 28 | 43 | 39-47 | 49 | 45-53 |
| 29 | 44 | 40-48 | 51 | 47-55 |
| 30 | 46 | 42-50 | 53 | 49-57 |
| 31 | 48 | 44-52 | 55 | 51-59 |
| 32 | 49 | 45-53 | 55 | 52-59 |
| 33 | 50 | 46-54 | 58 | 54-62 |
| 34 | 52 | 48-56 | 59 | 55-63 |
| 35 | 53 | 49-57 | 61 | 57-65 |
| 36 | 54 | 50-58 | 62 | 58-66 |
| 37 | 55 | 51-59 | 63 | 59-67 |
| 38 | 56 | 52-60 | 64 | 60-68 |
| 39 | 57 | 53-61 | 65 | 60-70 |
| 40 | 58 | 54-62 | 66 | 61-71 |
Nuchal translucency (NVP) values in the first trimester of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Thickness of collar space, mm | |
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 10 weeks 0 days – 10 weeks 6 days | 1,5 | 0,8-2,2 |
| 11 weeks 0 days – 11 weeks 6 days | 1,6 | 0,8-2,2 |
| 12 weeks 0 days – 12 weeks 6 days | 1,6 | 0,7-2,5 |
| 13 weeks 0 days – 13 weeks 6 days | 1,7 | 0,7-2,7 |
If the nuchal translucency indicators are too high, the woman should consult a geneticist and undergo additional examinations as prescribed by a specialist:
- blood test for alpha fetoprotein, human chorionic gonadotropin;
- amniocentesis - study of amniotic fluid;
- placentocentesis - study of placental cells;
- cordocentesis is the study of blood taken from the fetal umbilical cord.
Coccygeal-parietal size values 1st trimester of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Coccyx-parietal size, mm | |
| Average | Permissible fluctuations | |
| 10 weeks | 31 | 24-38 |
| 10 weeks 1 days | 33 | 25-41 |
| 10 weeks 2 days | 34 | 26-42 |
| 10 weeks 3 days | 35 | 27-43 |
| 10 weeks 4 days | 37 | 29-45 |
| 10 weeks 5 days | 39 | 31-47 |
| 10 weeks 6 days | 41 | 33-49 |
| 11 weeks | 42 | 34-50 |
| 11 weeks 1 days | 43 | 35-51 |
| 11 weeks 2 days | 44 | 36-52 |
| 11 weeks 3 days | 45 | 37-54 |
| 11 weeks 4 days | 47 | 38-56 |
| 11 weeks 5 days | 48 | 39-57 |
| 11 weeks 6 days | 49 | 40-58 |
| 12 weeks | 51 | 42-59 |
| 12 weeks 1 days | 53 | 44-62 |
| 12 weeks 2 days | 55 | 45-65 |
| 12 weeks 3 days | 57 | 47-67 |
| 12 weeks 4 days | 59 | 49-69 |
| 12 weeks 5 days | 61 | 50-72 |
| 12 weeks 6 days | 62 | 51-73 |
| 13 weeks | 63 | 51-75 |
| 13 weeks 1 days | 65 | 53-77 |
| 13 weeks 2 days | 66 | 54-78 |
| 13 weeks 3 days | 68 | 56-80 |
| 13 weeks 4 days | 70 | 58-82 |
| 13 weeks 5 days | 72 | 59-85 |
| 13 weeks 6 days | 74 | 61-87 |
| 14 weeks | 76 | 63-89 |
Normal heart rate by stage of pregnancy
| Gestation period (weeks) | Heart rate, beats. |
| 10 | 161-179 |
| 11 | 153-177 |
| 12 | 150-174 |
| 13 | 147-171 |
| 14 | 146-168 |
A child's normal heartbeat is rhythmic, occurring at regular intervals, clear and distinct. Irregular heartbeats may indicate a congenital heart defect or fetal hypoxia, and a dull sound may indicate intrauterine oxygen deficiency.
If the heart rate exceeds the norm, a diagnosis of tachycardia is possible; if it decreases to 120 or less, a diagnosis of bradycardia is possible. A heart rate that goes beyond normal limits often occurs as a result of a reaction to a decrease in oxygen in the blood - fetal hypoxia. In this case, the woman is prescribed inpatient treatment aimed at improving uteroplacental blood flow and intracellular metabolism.
Normal values for placental thickness per week
| Gestation period (weeks) | Average, mm | Allowable fluctuations, mm |
| 20 | 21,96 | 16,7-28,6 |
| 21 | 22,81 | 17,4-29,7 |
| 22 | 23,66 | 18,1-30,7 |
| 23 | 24,55 | 18,8-31,8 |
| 24 | 25,37 | 19,6-32,9 |
| 25 | 26,22 | 20,3-34 |
| 26 | 27,07 | 21-35,1 |
| 27 | 27,92 | 21,7-36,2 |
| 28 | 28,78 | 22,4-37,3 |
| 29 | 29,63 | 23,2-38,4 |
| 30 | 30,48 | 23,9-39,5 |
| 31 | 31,33 | 24,6-40,6 |
| 32 | 32,18 | 25,3-41,6 |
| 33 | 33,04 | 24,6-40,6 |
| 34 | 33,89 | 25,3-41,6 |
| 35 | 34,74 | 26-42,7 |
| 36 | 35,59 | 28,2-46 |
| 37 | 34,35 | 27,8-45,8 |
| 38 | 34,07 | 27,5-45,5 |
| 39 | 33,78 | 27,1-45,3 |
| 40 | 33,5 | 26,7-45 |
If the thickness of the placenta exceeds the permissible normal values, this may indicate inflammation of the placenta (placentitis).
Normally, the placenta should be attached to the posterior wall of the uterus (rarely to the anterior or fundus). It should be 6 cm or more from the internal os of the cervix. Low attachment, marginal or central presentation with overlap of the internal os is a dangerous pathology that threatens the life and health of both mother and child. It often occurs in women who have given birth repeatedly, terminated pregnancies, or have inflammation or uterine fibroids. In this case, the woman needs careful hospital monitoring or at home with complete rest. With complete placenta previa, the birth of a child is possible only by caesarean section. If it is low, natural birth is possible, but there is a high risk of bleeding.
Degree of maturity of the placenta
| Gestation period (weeks) | Maturity level |
| up to 30 | 0 |
| 30-34 | 1 |
| 35-39 | 2 |
| after 39 | 3 |
The reason for late maturation of the placenta may be smoking by a pregnant woman or the presence of chronic diseases, and premature maturation may be due to gestosis, intrauterine infections, endocrine pathologies, termination of a previous pregnancy, and also smoking.
If such a deviation is detected in a woman, she needs to undergo a Doppler ultrasound and be tested for infections. After which a course of therapy is prescribed aimed at treating fetal hypoxia, vitamin supplementation, reducing uterine tone and getting rid of infection (if necessary).
Amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) index
| Gestation period (weeks) | Average, mm | Allowable fluctuations, mm |
| 16 | 121 | 73-201 |
| 17 | 127 | 77-211 |
| 18 | 133 | 80-220 |
| 19 | 137 | 83-225 |
| 20 | 141 | 86-230 |
| 21 | 143 | 88-233 |
| 22 | 145 | 89-235 |
| 23 | 146 | 90-237 |
| 24 | 147 | 90-238 |
| 25 | 147 | 89-240 |
| 26 | 147 | 89-242 |
| 27 | 146 | 85-245 |
| 28 | 146 | 86-249 |
| 29 | 145 | 84-254 |
| 30 | 145 | 82-258 |
| 31 | 144 | 79-263 |
| 32 | 144 | 77-269 |
| 33 | 143 | 74-274 |
| 34 | 142 | 72-278 |
| 35 | 140 | 70-279 |
| 36 | 138 | 68-279 |
| 37 | 135 | 66-275 |
| 38 | 132 | 65-269 |
| 39 | 127 | 64-255 |
| 40 | 123 | 63-240 |
Deviation of indicators towards a smaller or larger direction indicates oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, respectively. In case of polyhydramnios, a woman is prescribed mandatory treatment with antibiotics and drugs to improve uteroplacental blood flow. Oligohydramnios indicates a severe fetal malformation - the complete absence of kidneys. In this case, appropriate therapy is carried out to support the child.
An important indicator is the quality of the amniotic fluid. Normally, it should be transparent, without turbidity, mucus, or flakes. Otherwise, this may be a sign of the development of an infectious process.