Ultrasound at the 5th obstetric week of pregnancy
There are standard timings for performing ultrasound screening during pregnancy. For the first trimester it is 10-13 weeks, for the second – 20-24, for the third – 32-34 weeks. But in some cases, ultrasound diagnostics can be performed not only during these periods, but also earlier. Quite often, women are prescribed an ultrasound at 5 weeks of pregnancy. This is the period when the embryo can already be visualized and its heart begins to beat.
Why is an ultrasound performed at 5 weeks of pregnancy?
Ultrasound at the 5th obstetric week of pregnancy is performed for the purpose of:
- Confirm pregnancy. At 5 weeks, the pregnancy test should already show two lines, although rare errors do occur. To 100% confirm pregnancy, ultrasound screening can be performed.
- Confirm correct attachment of the fertilized egg. It must be fixed in the uterus, otherwise (for example, when the fertilized egg is fixed in the fallopian tube), an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed.
- Assess the vital activity of the embryo in the fertilized egg.
- Detect multiple pregnancies.
- To refute the possibility that the increased level of hCG to which the pregnancy test reacted is not a consequence of a pathology of the female reproductive system.
- Identify threats of miscarriage.
As a rule, at such an early stage, ultrasound is prescribed for those women who:
- Previously had a caesarean section. In this case, you need to look at how the chorion (which will later become the placenta) is attached. Close attachment to a uterine scar or attachment directly to a scar can become a serious threat of miscarriage.
- Previously suffered miscarriages.
- Previously had a frozen or ectopic pregnancy.
- We became pregnant through the IVF procedure.
When to sound the alarm
Pain is the main symptom of threatened miscarriage, regardless of the obstetric week. Sensations at the time of a dangerous condition can be very different: they are determined by the severity of the woman’s condition and the individual threshold of pain sensitivity. Mild nagging pain in the lower abdomen or severe attacks even with slight uterine tone - all this indicates an emerging pathology of pregnancy.
Note! Any pathological discharge in the early stages, from brown “spotting” spots to drops of scarlet blood, is a reason for an immediate visit to a gynecologist.
What to do if you have symptoms of a threatened miscarriage
In order to make a diagnosis, you need to do an ultrasound of the uterus. The examination will show the presence or absence of hypertonicity, the condition of the embryo, the appearance of hematomas or chorionic detachment. If an ultrasound examination does not reveal a pathology, in this case the woman is examined in a gynecological chair in order to identify the root cause of the bleeding (the presence of a polyp, erosion, etc.). Such an examination will help determine whether this is indeed uterine bleeding and whether there is a danger to the development of the fetus. If there is a significant threat of miscarriage, the woman is prescribed therapeutic therapy in a hospital.
What happens to the fetus in the fifth week?
During the first four weeks of pregnancy, the fetus developed at an incredible rate. In the fifth week, his heart begins to beat, his cardiovascular and nervous systems develop. The formation of the spine and spinal cord also occurs, and the fetal brain now consists of two lobes.
By the fifth week, the fruit becomes pear-shaped and reaches approximately 4 mm in length. Such dimensions can already be visualized by ultrasound scanning.
The rounded part of the embryo will in the future transform into the baby’s head, and the sharp part into the spine.
Also in the fifth week, the formation of the internal organs of the fetus occurs: liver, pancreas, larynx, trachea.
Pregnancy hormones
The fifth week of pregnancy is a time when large amounts of hormones are produced en masse - chemical signals that circulate through your body and work together to cause physical changes. These include estrogen, which keeps progesterone and hCG levels where they should be; progesterone, which supports the function of the placenta, prevents contraction of the smooth muscles of the uterus and stimulates the growth of breast tissue; and hCG, which support the corpus luteum until the placenta is approximately 10 weeks old and regulate the amount of progesterone needed.
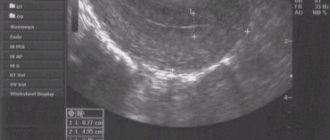
What will an ultrasound show at 5 weeks of pregnancy?
An ultrasound in the fifth week of pregnancy will show a fertilized egg with an embryo inside (with a normal, standard course of pregnancy). Also, based on the scan results, it will be possible to judge the attachment of the chorion and the location of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. If the fertilized egg has not reached the uterus and is fixed, for example, in the fallopian tube, an ultrasound will show this, and the woman will be diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy.
An ultrasound at the 5th week will show the baby’s heart and will allow you to evaluate the frequency of its beating. Already at such a short period of time, it will be possible to suspect possible pathologies of the fetal heart, although it is difficult to make an unambiguous conclusion about the presence/absence of a heart defect.
An ultrasound will show how actively the fetal neural tube, which will later become the baby’s bone marrow, is developing.
Embryo movements
To assess the viability of the fetus and its well-being in the womb, its heart rate is assessed.
Norms and decoding
There are several main parameters of fetal development that are taken into account when interpreting ultrasound results:
- embryo size – standard value is about 4 mm;
- yolk sac size – standard value 4-5 mm;
- the size of the fertilized egg - according to the norm, it should be approximately 1 cm;
- Heart rate is normal from 70 to 100 beats/min.
Ultrasound can also be used to estimate the weight of the embryo - it should be approximately 4 g.
Ultrasound results are not the only information that should be taken into account when making a diagnosis. It is also important to evaluate blood tests, urine tests, and the results of other additional studies.
What is early toxicosis
The fifth week of pregnancy can be characterized by the onset of early toxicosis for women. Expectant mothers expecting twins encounter this condition more often than others. Gynecologists associate early toxicosis with changes in hormonal levels and the functioning of the nervous system.
It mainly manifests itself in the form of nausea, vomiting, increased salivation, weakness and drowsiness. Toxicosis may be accompanied by increased irritability, depression and weight loss.
In some cases, it occurs in other forms:
- Dermatosis of pregnant women. It affects the skin. The disease may manifest as itching in the genital area or spread throughout the body.
- Tetany of pregnant women. Manifests itself in the form of cramps in the muscles of the limbs and face. This occurs when the parathyroid glands malfunction.
- Osteomalacia. It is associated with the occurrence of calcium and phosphorus deficiency in the body. Manifested by pain in the limbs and increased fatigue.
- Acute yellow atrophy of the liver. It occurs very rarely. The disease is characterized by a decrease in the size of the liver, jaundice and severe damage to the nervous system. The woman's condition worsens within 2-3 days and can be fatal. The only way out is to terminate the pregnancy.
Experts distinguish 3 degrees of severity of vomiting during pregnancy:
- 1st degree (mild). Vomiting can occur up to 5 times a day. This occurs after eating or when a woman smells an unpleasant odor. Loss of body weight no more than 2-3 kg. The woman's condition is satisfactory. All tests are normal.
- 2nd degree (moderate). Vomiting occurs 6-10 times a day. In 1 week, an expectant mother can lose 3 kg. There is a decrease in blood pressure. The woman experiences weakness, dizziness and constant fatigue. Urinalysis shows acetone.
- 3rd degree (severe). This condition is very rare in women. Vomiting can occur up to 25 times a day. The woman doesn't sleep at night because of her. Weight loss is 8-10 kg. The body becomes dehydrated, the skin becomes dry, and body temperature rises. Blood pressure decreases. Urinalysis shows acetone and protein.
If a woman experiences symptoms of toxicosis, she needs to visit a doctor.
If vomiting occurs several times a day, the expectant mother will be given recommendations and sent home. For grades 2 and 3, she will need hospital treatment.
A woman may be prescribed the following procedures:
- droppers that will replenish fluid loss in the body;
- antihistamines;
- vitamins B and C;
- drugs that protect against liver cell damage (hepatoprotectors);
- medications that can normalize metabolism, electrolyte balance and nervous system function.
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a doctor. If a woman's condition worsens despite treatment, the pregnancy must be terminated.
Sex in the 5th week of pregnancy
Having sex during this period is not prohibited if the woman does not have vaginal bleeding, pain or abdominal cramps. If intimacy causes her discomfort and there is a gynecologist’s prohibition, then it is best to refuse intimacy.
Some pregnant women have a complete lack of sexual desire at this time, which occurs due to increased fatigue and weakness.
If the embryo is not visible on ultrasound
If an ultrasound at the 5th obstetric week of pregnancy shows that there is a fertilized egg, but the embryo is not visible in it, this is not yet a reason for serious concern. Probably, the capabilities of the device are not great enough to see the embryo at such an early stage. To confirm pregnancy, you can undergo an ultrasound a little later - at 6-7 weeks.
A sadder prognosis is also possible. The absence of visualization of the embryo may indicate a frozen pregnancy or anembryony (that is, the embryo did not form or it died immediately after birth). In such cases, the attending physician must understand the reasons for the death of the embryo and prescribe certain examinations for the woman.
Nutrition

Dietary recommendations for week 5
A pregnant woman's diet should be based on the principles of healthy eating.
There is popular advice that pregnant women should eat for two. It should not be taken literally. You need to eat exactly as much as you want, without forcing the body to waste extra energy on digestion.
During your entire pregnancy, it is optimal to gain from 8 to 14 kg, no more. Lack of weight, like excess weight, in an expectant mother can harm both the baby and the woman.
Mandatory products for the expectant mother are:
- Vegetables and fruits, raw, boiled, stewed or steamed;
- Greens, nuts, dried fruits;
- Lean meat of various types (beef, veal, poultry);
- Dairy products of various types (boiled milk, cheese, cottage cheese, kefir, butter, etc.);
- Fish and seafood;
- Legumes;
- Cereal porridge;
- Coarse bread. Products made from premium wheat flour are best avoided.
You should try to steam or stew food, reducing the amount of fried foods to a minimum.
If meat causes vomiting, then try to eat more vegetables containing plant proteins - but it is better not raw, but boiled or baked. Raw vegetables increase toxicosis in many pregnant women.
The food temperature should be medium. You should not eat very cold or very hot.
Vitamins
Essential vitamins in the 5th week
In the 5th week of pregnancy, you should continue to take folic acid in the dosage prescribed by your doctor.
If desired, after consultation with a gynecologist, you can start taking special vitamin complexes for pregnant women, but you should not get carried away with them. It is optimal if you get essential minerals and healthy vitamins from food, and fortified complexes become a supplement.