This study allows you to determine the condition of the testicles, epididymis, and spermatic cords. Using ultrasound of the scrotum, deviations in the tissue structure, inflammatory foci, hernias and neoplasms are detected.
PRIMARY CONSULTATION WITH A UROLOGIST—RUB 1,000. ACCEPTANCE BASED ON ANALYSIS RESULTS – 500 rubles. Ultrasound of the kidneys - 1000 rubles. CLICK TO BOOK AN ULTRASOUND, TEST OR DOCTOR CONSULTATION
Let's try to figure out what an ultrasound procedure for men is, in what cases it is worth resorting to this diagnostic method, and what are its advantages or disadvantages over other research methods. You will also learn how often you should resort to the procedure, whether it is worth preparing for it, and what diseases can be detected.
Why do men need to have their genitals examined by ultrasound?
The content of the article
Early diagnosis of diseases of the genitourinary system makes it possible to detect pathology in tissue structure and examine blood circulation in the organ, making it possible to cure many diseases at an early stage.
Diagnostic methods for detecting diseases associated with the male reproductive system include ultrasound. With its help, you can painlessly examine the scrotum and appendages. Given the location of the male genitourinary system, many diagnostic examinations are difficult to implement, so the indispensability of ultrasound examination becomes obvious.
Ultrasound examination of the male pelvic organs is a non-invasive diagnostic method, therefore, it is a completely painless procedure. As the name suggests, scanning is performed using an ultrasonic wave, which penetrates the tissue, is reflected from it, and with the help of a sensor in the device, the information is deciphered and transmitted to the doctor’s screen.
Despite all the advantages, this method has disadvantages:
- It is not always possible to detect a neoplasm.
- It is impossible to determine the benignity or malignancy of an existing tumor.
In this regard, ultrasound is one of the primary diagnostic methods for the condition of the male genitourinary system. Based on this, the doctor may prescribe an additional examination of the patient.
Preparation for the examination and conduct
An adult man will not need any special preparation, but a child will need to take the time to explain the need for the upcoming actions or even persuade him to undergo the procedure. The only thing that will need to be done if the examination is scheduled is to toilet the external genitalia. To conduct the study, the patient is asked to sit comfortably on the couch, having first taken off his underwear, because they are doing an ultrasound of the scrotum on the naked body.
The penis is fixed on the stomach or the patient holds it with his hand so that there is no interference with the movement of the sensor.
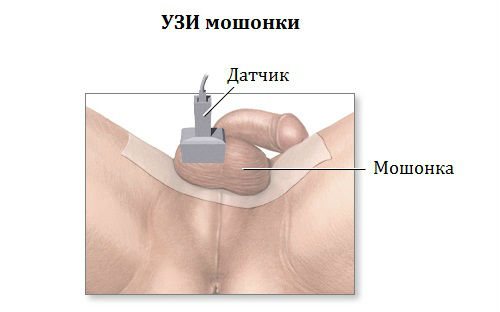
Ultrasound of the scrotum
In some cases, when performing an ultrasound with Doppler, when it is necessary to evaluate the functioning of the blood vessels of an organ, the procedure can be performed in a standing position. Then the doctor applies a special water-based gel, which promotes denser, higher-quality and painless contact with the surface of the patient’s skin. During the study, the scrotum is examined in the longitudinal, transverse and oblique plane, which allows you to carefully examine all its constituent structures and identify pathological elements. The procedure does not take much time - in most cases it lasts no more than 15–20 minutes, and only in controversial situations can it drag on a little.
Indications and contraindications
Doctors refer you for an ultrasound of the scrotum: a surgeon, urologist or andrologist. The reason for such a diagnosis may be:
Sonography should be used in the following cases:
- For preventive purposes, to clarify the diagnosis, after surgery for control;
- Pain or swelling in the scrotum and groin area;
- To scan the lymph nodes, which may indicate diseases of the reproductive system.
- In adolescence with early development or lagging behind;
- If you suspect dilated veins (varicocele), orchitis, orchiepididymitis, epididymitis;
- In case of infertility, unclear spermogram results;
- For various injuries, foreign objects, changes in the size of the scrotum, to study seals;
- When hematomas and inflammation of the scrotum appear, to search for neoplasms, to monitor tumors, cysts and other formations;
- In case of an inguinal hernia, in the absence of two or one testicle in the patient, to determine the reason for the failure of the testicles to descend;
- With partial or complete dysfunction of the reproductive system (impotence), pain during sexual intercourse;
- With poor functioning of the endocrine system.
There are no contraindications to ultrasound diagnostics of the scrotal organs; the examination can be carried out an unlimited number of times. Ultrasound is not an x-ray, so men’s fears for their “dignity” are groundless.
Preparation for the procedure
The study is carried out at any time of the day, regardless of food intake and bladder emptying. Simply wash the area with soap and warm (not hot) water. It is important to prepare yourself mentally—there is nothing scary, much less shameful, about this examination. When conducting research on children or adolescents, it is necessary to explain to them the essence and importance of the procedure.
Who is prescribed an ultrasound of the scrotum? Symptoms for undergoing an ultrasound of the scrotum?
Regardless of the symptoms, first of all you need to see a doctor, and only after an initial examination, a urologist, if necessary, will prescribe you an ultrasound of the scrotal organs if he recognizes the following symptoms or diseases:
- Infertility
- Injuries
- Foreign body
- To clarify or refute the diagnosis
- Pain or discomfort of unknown origin
- Changing the size and shape of an organ
Make an appointment with a urologist
Make an appointment
How to do an ultrasound of the scrotum
Conducting a diagnostic study should be entrusted to a qualified doctor. The level of the device is also important - antediluvian ultrasound machines provide incomplete information. For diagnostics, 10 MHz sensors are used, but if necessary, convex devices with a power of 5 MHz are used. They are used for large sizes of the study area.
The ultrasound procedure itself takes about 10-15 minutes. During this procedure, the patient lies on his back or side. A gel is applied to the scrotum so that the device glides over the skin with ease, and the diagnosis is more reliable - the gel transmits ultrasound perfectly. The examination is carried out using a special sensor.
On the screen, the doctor sees the condition of the organs and makes a conclusion about the presence or absence of pathologies. The structure of the scrotum is displayed in detail on the screen. If the doctor has questions about the examination results, the patient will be referred to a urologist for additional examinations and treatment.
Ultrasound results of the scrotum
The initial interpretation of the study results is carried out by an ultrasound specialist. He can make a preliminary diagnosis on the spot. A more detailed and refined diagnosis can only be made by a urologist based on additional examinations.
When scanning the scrotum, the structure of the internal tissues, their density, and the presence of foci of inflammation or neoplasms are studied. A healthy scrotum consists of echogenic tissue, which consists of layers of varying thickness and density.
Next, the patient's testicles are examined. Their shape and size are assessed. Their homogeneity is also taken into account. In children up to adolescence, the density of testicular tissue is significantly lower than in a mature man.
Then everything else is examined: lymph nodes, spermatic cord, veins and arteries, vas deferens, nerve endings.
Anatomical features of the scrotal organs
The testicles of an adult male normally measure 3–5 cm in length, 2–3 cm in thickness and width. The scrotum itself is a kind of case for the testicles, and it is formed by connective and muscle tissue approximately 8 mm wide. A seam runs down the middle, dividing it into two parts. Normally, there may be a small amount of fluid (1–2 ml) between the scrotal wall and the testicle.
How is a pelvic ultrasound done in men?
In the upper-lateral edge of the testicle there is an appendage consisting of a head, body and tail. The tail gradually passes into the vas deferens, and as part of the spermatic cord, bypassing the inguinal canal, it enters the abdominal cavity.
Connecting with the seminal ducts, it passes through the prostate and opens at the urethra. Normally, during an ultrasound examination, the structure of the testicle, the head of the epididymis (the body and tail are not visualized in the absence of pathologies) and the spermatic cord are clearly visible. When deciphering, the right and left testicles, as well as the thickness of the scrotal wall, must be compared.
The testicle in a normal state has a uniform consistency with a clearly defined segment of dense tissue located towards its posterior outer part - the mediastinum. With Doppler ultrasound, you can see the arteries that supply the organs of the scrotum and the venous network of the spermatic cord.
Diseases diagnosed by ultrasound
The examination reveals:
- inflammation and fibrous (hardened) tissue changes;
- echostructure and circulatory structure of male genital organs;
- the condition of the tissues around the testes and appendages;
- fluid, lymph, blood or pus in the interthecal space;
- neoplasms and traumatic injuries;
- atrophy and failure of the testicles (cryptorchidism);
- “entry” into the scrotum of an inguinal hernia
Ultrasound of the scrotum does not always provide complete information. For example, it is difficult to determine the malignancy of tumors or diagnose testicular torsion using ultrasound. In this case, ultrasound is supplemented with Doppler ultrasound.
After the procedure, the following pathologies and diseases can be diagnosed:
- Infertility. If there is a cyst in the testicles and epididymis, which can compress the spermatic cord.
- A hydrocele is an accumulation of fluid between the testicles.
- Lymphocele is a collection of lymph.
- Hematocele is an accumulation of blood between the membranes of the testicle.
- Testicular tumor, epididymal cyst, epididymal abscess.
- Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis and orchiepididymitis is inflammation of the testicle and epididymis.
- Closed injury.
- Hopoganadism. Diagnosed in young boys. Caused by reduced androgen content and lack of gametogenesis.
- The presence of calcifications is an accumulation of calcium (sometimes a sign of cancer).
- Cryptorchidism is the absence of descended testicles.
- Other developmental pathologies.
Free consultation with a urologist
What is an ultrasound examination of the scrotum (ultrasound of the scrotum)?
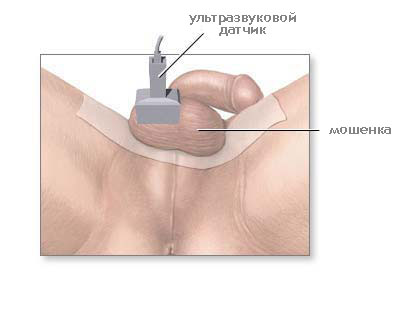
Scrotal ultrasound (scrotal ultrasound) , or sonography, is an examination of a part of the body using high-frequency sound waves to see the internal structure. Ultrasound does not use radiation sources (as with x-ray). Because ultrasound is performed in real time, it can show the movement patterns of internal organs, as well as the blood flowing through the blood vessels.
Ultrasound (ultrasound) is a non-invasive medical test that helps the doctor make a diagnosis. An ultrasound examination of the scrotum (ultrasound of the scrotum) can provide an image of the testicle.
What is the procedure for prescribing the procedure?
Ultrasound examination of the scrotal organs (ultrasound of the scrotal organs) is used as the primary diagnostic method for testicular pathology.
Ultrasound examination of the scrotal organs is used to determine:
- whether the formation detected in the scrotum is cystic or solid
- consequences of trauma in the scrotum area
- causes of testicular pain, inflammation, torsion
- the cause of infertility, for example varicocele, is determined
- determine the location of the testicle with cryptorchidism
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound of the scrotum) provides valuable information about the epididymis - the tube that collects seminal fluid, which is formed in the testicles and prostate gland.
Sudden pain in the scrotum can have quite serious causes. The most common cause is epididymitis, inflammation of the appendage.
This disease is treated with antibiotics. If left untreated, an abscess may form or blood flow to the testicles may be impaired.
An ultrasound examination (ultrasound of the scrotum) can also detect an undescended (cryptorchid) testicle. In rare cases, the testicle does not develop at all. Most often, patients have an undescended testicle. It is believed that approximately three percent of full-term boys have an undescended testicle. Diagnosis of an undescended testicle is very important because... there is a high probability of malignancy if left untreated.
An ultrasound examination (ultrasound of the scrotum) can detect testicular torsion, in which the vessels carrying blood into the scrotum are twisted. This condition occurs due to abnormal embryonic development, usually manifests itself in adolescence and is a rather painful condition.
Surgical treatment is necessary to avoid permanent damage to the testicles.
You can also determine the location and depth of tumor tissue in the scrotum. Most scrotal tumors are located outside the testicles. Most tumors found outside the testicle are benign; those found inside the testicle are mostly malignant.
Fluid accumulations and changes in blood vessels can also be analyzed.
What preparation is needed for an ultrasound of the scrotum?
You should wear comfortable, loose clothing. You may need to remove all clothing and jewelry in the area where the test will be performed.
No other preparation is required.
What does the equipment for ultrasound of the scrotum look like?
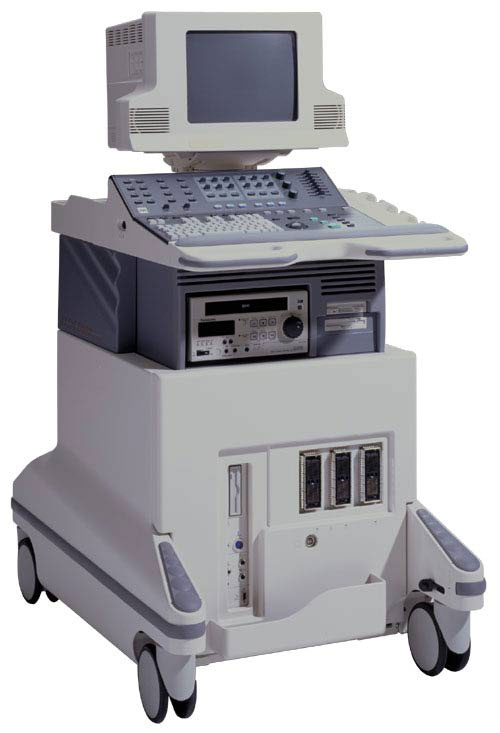

Ultrasound scanners consist of a main part, represented by a computer and electronics, a screen, and a sensor. The sensor is a small mobile device, similar to a microphone, connected to a cord. The sensor sends high-frequency sound waves into the body and then picks up the signal returned from the tissue. This principle is similar to the sonar used by submarines and submarines.
The ultrasound image is visible on a nearby screen, which resembles a computer or television monitor. The image is based on the amplitude, frequency and time it takes for the audio signal to return back to the transducer. Usually, a regular small probe is used for ultrasound of the scrotum.
Principle of operation?
Ultrasonic imaging is based on the same principles as bat, submarine and fish sonar. When a sound wave is reflected, an echo is formed. By measuring echo waves, you can determine how far away an object is and its size, shape, solid or liquid.
In medicine, ultrasound is used to detect changes in the structure of organs and tissues to detect new growths such as tumors.
In an ultrasound scan, a transducer sends out sound waves and picks up returning signals. When the sensor is pressed against the skin, it sends out a pulse of inaudible, high-frequency ultrasound waves. When the pulse is reflected from fluids and tissues, the sensor detects subtle changes in the signal fluctuation. These waves are reflected in the computer indicators, which create a picture on the monitor.
How is the scrotal ultrasound procedure performed?
During most ultrasound examinations, the patient is positioned lying on the table, perhaps he should be on his side or in a certain position.
A special gel is applied to the skin, which helps establish safe contact between the sensor and the skin. The ultrasonographer or radiologist who performs the procedure presses the sensor on the skin in the area of interest.
When the examination is completed, the patient can be asked to get dressed and wait while the images are analyzed.
The test usually takes less than 30 minutes.
How does the patient feel during and after the scrotal ultrasound procedure?
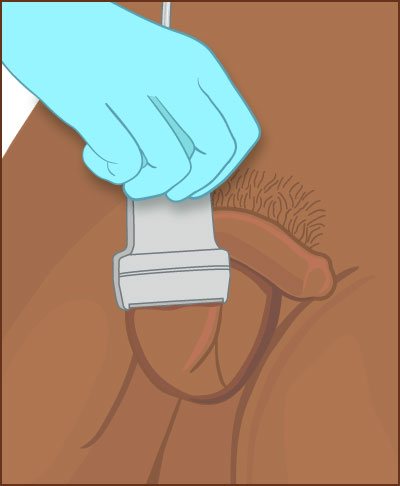
Most ultrasound examinations are painless, quick and easy.
After you lie down on the examination table, the ultrasonographer will apply a warm, watery gel to your skin and position the transducer in the area of interest.
If the test is performed in an area with delicate skin, you may feel pressure or slight soreness. After the examination is completed, the gel will be removed from your skin.
After the study, you will be able to return to your normal activities.
How are ultrasound results interpreted and how do you get them?
A doctor who specializes in analyzing ultrasound results - an ultrasonographer or radiologist - will analyze your data and refer it to your primary doctor, who will tell you about the results. In some cases, he may discuss the results with you at the end of the study.
What is the benefit to risk ratio?
- Most ultrasound examinations are non-invasive (no needles are inserted) and are painless.
- Ultrasound is widely available, easy to use, and cheaper than other research methods.
- Ultrasound examinations do not use radiation sources
- Ultrasound clearly visualizes soft tissues that are difficult to see with x-rays.
- Ultrasound examinations do not cause negative health effects and can be repeated as often as necessary.
- Ultrasound provides real-time imaging, allowing it to be used for needle biopsy and needle aspiration.
Risks of scrotal ultrasound
There are no harmful effects on people's health with standard ultrasound examinations.
Limitations when using scrotal ultrasound?
With this study, it is not always possible to distinguish between benign and malignant neoplasms.
The article is for informational purposes only.
For any health problems, do not self-diagnose and consult a doctor! Author:
V.A. Shaderkina is a urologist, oncologist, scientific editor of Uroweb.ru. Chairman of the Association of Medical Journalists.
Is it harmful for men to have an ultrasound?
To date, it has been proven that this study is absolutely safe and does not affect male function. Moreover, compared to X-ray examinations, ultrasound is a much more gentle scanning method. And if you compare ultrasound of the scrotum with biopsy and other invasive techniques, it becomes obvious that this is the only method that does not cause discomfort or harm to health.
Today, ultrasound is one of the most accessible, reliable and harmless studies available to a man. The absence of pain, fairly high accuracy and information content of the examination makes the method very popular. Thanks to ultrasound diagnostics, many men have overcome their problems and, after treatment with a urologist, were able to improve the potency and functions of the reproductive system.
Contraindications
Ultrasound scanning has no contraindications. There is no radiation exposure to the body; adults and children with prostheses, metal implants, pacemakers, etc. can undergo examination.
A mental or neurological abnormality may make the examination difficult, in which the patient is unable to remain still and control his actions. In this case, the doctor discusses with the patient’s relatives the possibility of using sedatives, which are included in the cost of ultrasound of the testicles.