Main advantages of ultrasound
- high reliability,
- versatility,
- painlessness,
- safety,
- wide availability,
- no side effects,
- possibility of repeated research,
- almost complete absence of contraindications.
- About the service
- Indications for use
- Preparation
About the service Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, kidneys and retroperitoneal space is a modern diagnostic method that helps identify tumors, cysts, polyps, stones (gallstones, kidney stones), inflammatory diseases, degenerative-dystrophic changes in organs, anatomical disorders, injuries or other pathologies with a high degree of reliability, information content of the data.
Ultrasound examinations at the Tibet Clinic are distinguished by the fact that they allow not only to diagnose diseases, but also to carry out their optimal treatment using oriental medicine methods - without side effects, pills, surgeries or hormones.
Diagnostics of the abdominal cavity, kidneys, retroperitoneal space in “Tibet” is a guarantee of high quality examination, the basis for successful treatment of diseases. Ultrasound in Moscow can be done in many places, but only in “Tibet” is it part of oriental medicine.
Prices for ultrasound
| Abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space | |
| Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs (comprehensive) | 2500 |
| Ultrasound examination of the liver | 1200 |
| Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder and ducts | 1000 |
| Ultrasound examination of the gallbladder with determination of its contractility | 1500 |
| Ultrasound examination of the pancreas | 1200 |
| Ultrasound examination of the spleen | 950 |
| Ultrasound examination of the bladder | 800 |
| Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and adrenal glands | 1200 |
* see all types of studies and prices
Which organs are being examined?
The examination allows you to determine the presence of the source of the problem.
Organs examined:
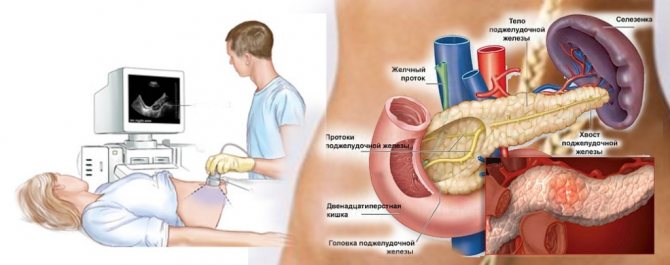
- Liver. This organ is examined first. Based on the results of the study, it is possible to diagnose hepatosis, cirrhosis, tumors and cysts;
- Gallbladder and ducts. The doctor evaluates the patency of the ducts, the presence of polyps, the condition of the walls of the organ, the presence of stones in the gall bladder;
- The stomach is examined only for the presence of neoplasms;
- Pancreas. If possible, all lobes are examined. It is possible to diagnose pancreatitis, tumor and pancreatic necrosis;
- Spleen. The doctor evaluates the structure, location and size of the organ, eliminating the possibility of neoplasms, cysts, and inflammatory processes;
- Intestines. Usually only the large intestine is examined. If formations or polyps can be detected, the patient is sent for additional examination;
- Kidneys. Their placement, relative position and size are assessed. Inflammations, tumors, cysts and conglomerates can be diagnosed;
- Bladder. The specialist looks at the shape, size, condition of the walls, as well as the contents of the organ;
- Vessels. It is mandatory to evaluate the abdominal aorta and large vessels feeding the organs. Blood flow and the condition of the vascular wall are also established;
- The lymph nodes. The doctor looks at their size. Enlargement of this organ is characteristic of oncological pathologies.
In women it looks like the uterus, in men it looks like the prostate gland. Despite the fact that these organs are located in the pelvis, they are still examined. Ultrasound can detect tumors or inflammation.
Indications for ultrasound
The main indications for an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity: flatulence (increased gas production), bitterness in the mouth, nausea, vomiting, pain in the right hypochondrium and abdominal area (epigastric region), jaundice (yellowing of the skin, sclera of the eyes).
It should be done in case of persistent indigestion, chronic constipation or diarrhea, loss of appetite, sudden change in body weight (increase or decrease). Ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed if there is a suspicion of oncological diseases (cancer of the liver, pancreas), metastases, benign neoplasms (tumors, cysts, adenomas), abscess, pancreatitis, hepatitis, hepatosis, cirrhosis of the liver, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, ascites, biliary dyskinesia paths (including bending, constriction of the gallbladder).
An abdominal ultrasound is usually performed in a child who complains of pain in the abdomen, lower back (lower back) or girdle pain.
Ultrasound of the retroperitoneal space is prescribed for girdle pain, the presence of blood in the urine, suspected urolithiasis, tumors, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, nephropathy, nephrosclerosis, diseases of the adrenal glands, pathology of blood vessels, lymph nodes.
Ultrasound of the retroperitoneal space allows you to see not only neoplasms, traumatic injuries or inflammatory processes, but also the condition of the blood vessels (the size of the lumen, the presence of atherosclerosis, blood clots, the location of the vessels), as well as an increase in regional lymph nodes.
Preparation
Research technique
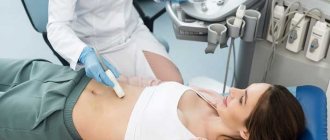
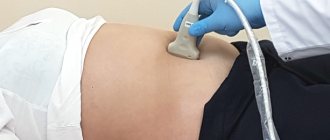
Before starting the ultrasound procedure, the examinee removes metal jewelry. He is placed on the couch in a supine position. During the process, the doctor will ask the patient to change position, turning over to the left or right side.
The examination is carried out abdominally, that is, through the anterior wall of the abdomen. A special conductive gel is applied to the abdomen, which improves the glide of the sensor over the body and helps reduce interference in the image.
The procedure is completely painless and takes no more than 20-30 minutes.
The examination algorithm involves performing an ultrasound of larger organs first. For example, a physician might start with the liver. It evaluates and records the size of the liver, its location and shape, structural features and ability to transmit ultrasonic waves, as well as the condition of the blood vessels.
Next, the doctor proceeds to examine the gallbladder and bile ducts:
- their forms;
- structure and condition of the walls;
- presence or absence of foreign inclusions;
- bile conditions.
The diagnostician checks the position of the pancreatic duct, the lumen of the biliary tract, the portal, inferior and splenic veins. Next, he evaluates the condition of the spleen, pancreas and kidneys according to a similar scheme. At the same time, the doctor must remember that examining the pancreas is often difficult due to the peculiarities of its anatomical location - it is partially overlapped by the intestines and stomach.
To visualize the spleen, the patient is placed on the right side. Access to it is also a little difficult, since it is surrounded by ribs and lungs.
In some cases, during an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, the bladder is also examined.
Preparing for an ultrasound
To maximize the reliability of survey data, it is important how to prepare for it.
There are several standard rules and recommendations for this. For three days before diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that cause increased gas formation, including brown bread, white yeast bread, baked goods, milk, legumes (beans, peas, beans), raw vegetables, fruits, and fatty meats. You should follow a regimen of fractional meals - 4-5 meals per day in small portions.
Before the examination, you can drink water up to 1.5-2 liters per day, but carbonated drinks, beer, fruit and vegetable juices should be excluded. Yeast bread should be replaced with yeast-free bread. You can eat low-fat cheese, soft-boiled eggs, as well as steamed, boiled or baked foods - lean poultry, fish, beef, buckwheat or oatmeal.
Preparation for an abdominal ultrasound may include taking enzymes (mezim, festal, etc.) to improve digestion, espumisan, enterosgel as prescribed by a doctor.
On the eve of the study, you should limit yourself to a light dinner. After 20 hours, eating is not advisable. If you are constipated, you should take a laxative. Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is performed on an empty stomach, so you should skip breakfast.
If the diagnosis is carried out after three o'clock in the afternoon, you should not eat food less than 8 hours before (a light breakfast is possible, but no later than 11 o'clock in the morning). Before the examination, you can only drink water, a little and at least 2 hours before. It is advisable to take 5-10 tablets of activated carbon two hours before the test. You should refrain from smoking, lollipops, and chewing gum.
In case of increased gas formation (flatulence), it is recommended to do a cleansing enema in the morning. The presence of air in the intestines interferes with obtaining reliable data, so colonoscopy and gastroscopy cannot be performed before the study.
If you plan to perform an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys to diagnose the bladder, you should drink up to 1 liter of water before the examination. This is necessary to keep the bladder full.
Go Take the test and get a BONUS - a discount on treatment in our clinic Take the test
Contraindications for MRI of the abdominal cavity
Despite the modernity and safety of the MR scanning technique, the procedure is not without contraindications.
Research is strictly prohibited for people:
- having a pacemaker;
- insulin pump;
- metal structures in the body;
- weight more than 130 kg;
- in the first trimester of pregnancy.
You should approach this with caution in the following cases:
- late stages of pregnancy.
The procedure is possible, but you should first consult with your doctor;
- claustrophobia.
The patient may take sedatives shortly before the examination to avoid fear of the confined space of the tomograph;
- the presence of implants in the body.
Most modern medical structures are made of metals that are insensitive to magnetic radiation. Their presence in the body does not interfere with the procedure.
Before conducting the study, the radiologist will definitely ask you about possible contraindications.
How is an ultrasound examination performed?
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space at the Tibet clinic does not take much time. Typically, the duration of the examination does not exceed 30-40 minutes. This is a completely painless, safe and completely comfortable procedure.
The examination is carried out in a lying position on a couch. The patient lies on his back, opening the abdominal area. The sensor is installed on the examination area (a special gel is first applied to the skin). During the scan, the doctor sees an image of the internal organs on the monitor. The sensor is moved manually over the surface of the body, and the patient may need to turn on his side or stomach. After the examination is completed, the gel is removed from the skin with napkins. Immediately after this, you can return to normal life.
The price of diagnostics at the Tibet clinic does not include any additional costs.
Abdominal ultrasound - what is it?
Abdominal ultrasound is a non-invasive examination of the patient’s organs and tissues using ultrasound waves. This procedure makes it possible to determine the size and structure of the organ being examined. The principle of operation is quite simple: ultrasound, when it passes through the boundaries of tissues of different densities, changes its characteristics, that is, it is reflected differently. The sensor detects these changes and converts them into a graphic image. This is very similar to how bats or dolphins use ultrasound.
By the way, it was thanks to bats that we learned about ultrasound. It was discovered at the end of the 18th century, but they tried to use it for medical diagnostics only in the 40s in Germany. It is from there that the ultrasound examination method begins its history. The ultrasound machine, also known as a sonograph, has been improved all the time, but the basic design principles remain unchanged. The basis of the device is a sensor, which acts as both a generator of sound waves and a receiver of echo signals. The received data is processed by a computer, then it is displayed on a monitor or printed on paper.
Ultrasound examination device
To carry out diagnostics, the Tibet clinic uses the latest device from Samsung Medison - the SonoAce R5 ultrasound scanner. The SonoAce R5 multifunctional scanner is an innovative development in the global production of medical equipment. Compared to the previous generation of ultrasound scanners, this device has a number of important advantages:
- advanced diagnostic capabilities,
- information content is 20% higher,
- higher data reliability,
- high resolution, increased clarity, detailed images.
Special options allow you to obtain higher quality images at any ultrasound penetration depth. Thanks to faster scanning speeds, ultrasound examinations take less time. The ability to combine ultrasonic information from different frequency bands minimizes the risk of false information and eliminates interference. The presence of color Doppler allows you to study in detail and reliably the nature of blood flow in the area of study.
SonoAce R5 allows you to conduct ultrasound examinations of all tissues, including hard-to-see tissues (tumors, etc.) and obtain contrast images of organs and tissues in people with normal or overweight.
The multifunctional ultrasound scanner SonoAce R5 is used for high-quality ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, pelvis, kidneys, mammary glands and other types of diagnostics. Thanks to technological innovation and design excellence, SonoAce R5 has proven itself exceptionally well in urology, gynecology, mammology, and abdominal studies.
How long does an abdominal MRI take?
The procedure for MRI diagnostics of the abdominal cavity will last about 40 minutes.
Radiologist at work
If the study is carried out using contrast, the duration of the procedure will be about 1 hour.
After completion of the procedure, the patient is given a disk with recorded images and a written conclusion from the doctor.
Who performs the ultrasound
At the Tibet clinic, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space is performed by a highly qualified ultrasound diagnostics doctor, Maria Aleksandrovna Vasilyeva. Her exceptional professionalism and extensive experience are a guarantee of the high quality of the examination, the reliability of the data obtained and the correctness of the diagnosis.
How to use class=”aligncenter” width=”992″ height=”247″[/img]
or call +7 Moscow
Free consultation Survey, examination, pulse diagnostics from 30 minutes
Diagnostics Ultrasound, MRI, Laboratory tests (as prescribed)
Treatment Individual plan
In what cases is abdominal ultrasound contraindicated?
The ultrasound examination procedure is absolutely safe for the body. It does not carry a radiation load and is not associated with exposure. Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity can be used even in pregnant women without harm to the fetus.
Ultrasound is a painless procedure that does not require intervention in the internal environment of the body. Therefore, after the manipulation there is no need for special rest or observation by medical staff. The patient, having received the conclusion, is sent to his attending physician.
Ultrasound is safe and does not affect the functioning of body systems. There is no convincing evidence of negative consequences of the examination. The study is carried out daily, once a week or every month, if required for health reasons.
After an abdominal ultrasound, testing is not contraindicated. Ultrasound examination does not affect the functioning of the body.
What organs are included in an abdominal examination?
Many patients are interested in which organs are included in this study. It is carried out to determine diseases of the liver, gall bladder and bile ducts, pancreas, kidneys, retroperitoneal region, spleen, abdominal aorta.
Thanks to an ultrasound of the liver, it is possible to determine its size, structure, and the presence of pathologies in it. The doctor, with a high degree of information, determines fatty degeneration of the liver, its inflammation, and the presence of tumors in it.
Abdominal ultrasound
When examining the pancreas, its condition, the presence of formations in it, etc. are assessed. However, the presence of gases in the stomach and intestines can hinder the progress of the study, as well as obtaining reliable clinical results. So the doctor recommends additional tests for patients undergoing such a study. The specialist can also see what changes have occurred in this organ as a result of the infectious process. This study is necessary to assess the activity of the organ in diabetes mellitus.
The study of the kidneys, adrenal glands and especially the retroperitoneal region is a difficult diagnostic task for a specialist. This is explained, first of all, by the anatomical features of their position and structure. Nevertheless, the doctor can evaluate the characteristics of the renal structures, determine the presence of pathologies, as well as neoplasms.
Examination of the stomach is necessarily assessed using gastroscopy data. The doctor evaluates the thickness of the walls of these organs.