Progesterone is a hormone from the group of steroids. Its production in small quantities occurs in the adrenal glands. However, it is mainly produced during pregnancy. During pregnancy, progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum, which is a temporary gland. Progesterone is called the “pregnancy hormone” because it plays a key role in bearing a child and preparing the body for childbirth. This hormone is an essential element of a woman’s reproductive health, both during pregnancy and during its planning. Its decrease can lead to miscarriage, which requires appropriate correction with medications.
Functions of progesterone during pregnancy
In the body of both women and men, progesterone performs many beneficial functions. However, its main task is to prepare a woman for pregnancy and childbirth, as well as to ensure adequate breastfeeding. Progesterone during pregnancy promotes proper implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity, ensuring thickening of the endometrium. At the same time, this hormone reduces the mother’s immunity so that the fertilized egg can easily penetrate the uterus and not be rejected. In addition, progesterone also affects the nervous system, rebuilding it for future childbirth. The hormone promotes relaxation of the uterine muscles, which reduces the likelihood of spontaneous abortion. Against the background of progesterone, the mammary glands grow and increase in size, which prepares them for the lactation period. This steroid prepares the pelvic joints for future childbirth. Progesterone affects not only the mother’s body, but also the child’s fetus, improving the production of steroid hormones in the embryo’s body.
Complexes with this research
Advanced women's anti-aging diagnostics Advanced monitoring of basic blood parameters in women aged 40+ 28,680 R Composition
Miscarriage Identification of the main causes of miscarriage 40,070 R Composition
IVF planning Examination for preliminary preparation of a woman for the IVF procedure RUR 12,990 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Entry into IVF RUB 23,020
- Female hormones. Luteal phase 1,160 R
- Female infertility RUB 16,210
- Women's anti-aging diagnostics RUB 12,070
Progesterone when planning pregnancy
Progesterone is important not only during pregnancy, but also at the planning stage. It must be in a woman’s body in a certain concentration in order to improve the quality of the fertilized egg and create conditions favorable for conception in the uterus. In addition, progesterone prevents the appearance of cystic and fibrous formations in the genitals, improves the nutrition of adipose tissue, optimizes the functioning of the coagulation system and ensures normal glucose levels. Therefore, when planning a pregnancy, any girl should be tested for progesterone levels in the blood. If it is outside the normal range, then you need to try to normalize its level by taking progesterone drugs.
Progesterone levels by trimester
There are norms for progesterone levels by trimester, indicating a normal pregnancy:
- 1st semester – from 9 to 468 mmol/l;
- 2nd semester – from 71.5 to 303 mmol/l;
- 3rd semester – from 88 to 771 mmol/l.
There is a direct relationship between progesterone levels and pregnancy loss or fetal death. When an embryo stops developing for some reason, a signal is sent to the hypothalamic-pituitary system to stop producing progesterone.
In response to a drop in progesterone levels, the uterus begins to contract, getting rid of the dead embryo. Bleeding begins, which cannot be stopped even by taking an artificial analogue of progesterone.
A blood test for progesterone does not give any predictions as to whether the pregnancy will continue or not, however, a decrease in the indicator accurately indicates the existing pathology. The cessation of pregnancy is indicated by the level of hCG - the concentration in the blood of a hormone produced by the membrane of the fertilized egg.
Test for progesterone during pregnancy
Determining progesterone levels during pregnancy is an important analysis that is included in the range of mandatory examinations. If a pregnant woman is at risk of miscarriage, has a history of miscarriages or chronic diseases, then she needs to determine the level of progesterone at the very beginning of the first trimester. If the expectant mother does not have health problems, it is enough to take the test in the second and third trimesters. The level of this hormone during this period of pregnancy will show the functional state of the placental tissue and the embryo’s body. In addition, progesterone during pregnancy is released in case of post-term pregnancy. The analysis should be taken strictly on an empty stomach. It is advisable not to expose yourself to stressful situations or overexert yourself physically the day before the test.
Reasons for deviations
Lack and excess of progesterone during pregnancy leads to complications. The violation can be detected using laboratory tests and during monitoring of the woman’s condition. Temporary deviations from the norm are caused by the following pathological conditions:
- drug therapy (including hormonal therapy);
- developmental disorders of the placenta;
- chronic form of adrenal hyperplasia;
- insufficient kidney activity.
Reduced
The appearance of nagging pain in the lower abdomen, bleeding (even minor) during pregnancy are symptoms of spontaneous abortion. One of the reasons for miscarriage is low progesterone concentration. The pathological condition is often associated with insufficiency of the corpus luteum.
In some cases, a sharp decrease in hormone levels occurs. Possible reasons for this phenomenon:
- frozen, ectopic pregnancy;
- threat of self-abortion;
- disorders of intrauterine development of a child.
Elevated
An increase in the amount of pregnancy hormone also poses a danger to the mother and fetus. Deviation from the norm is associated with the following pathological conditions:
- adrenal diseases;
- corpus luteum cyst;
- kidney dysfunction;
- dysfunction of the placenta.
Multiple pregnancy and progesterone levels
Up to 10 weeks, the concentration of the hormone during the development of several embryos at once remains the same as during normal pregnancy. At later stages, an increase in the level of the active substance is observed. There are cases when in women pregnant with twins, its content remains within the normal range.
Low progesterone levels during pregnancy
There are many reasons why progesterone levels in the blood may decrease during pregnancy. As a rule, a reduced level of this hormone indicates an increased risk of spontaneous miscarriage, the development of an ectopic pregnancy, or intrauterine growth retardation. A decrease in progesterone concentration can be observed with insufficiency of the fetoplacental system, postterm pregnancy and gestosis. Reduced levels of progesterone during pregnancy are manifested by symptoms such as unstable mood, sleep disturbances, depression, pain during sexual intercourse due to vaginal dryness, decreased skin elasticity, constipation, flatulence, dizziness and fainting. An important criterion for reducing the level of this hormone is temperature fluctuations. As progesterone levels decrease, there is a decrease in numbers when measuring basal temperature.
How is the level of pregnancy hormone determined, normal indicators
Determination of progesterone levels occurs through laboratory testing of a woman’s blood. In the absence of pregnancy pathologies and the risk of miscarriage, this test is on the list of mandatory ones only in the second trimester. But for medical reasons, an obstetrician-gynecologist can prescribe it both in the first trimester of pregnancy and in later stages of pregnancy.
When does a gynecologist prescribe a progesterone test?
If you suspect a pregnancy pathology or have obvious signs of it, as well as to prevent the development of various types of complications, your doctor may prescribe a blood test to determine progesterone levels.
When is it necessary to donate blood to determine hormone levels during pregnancy:
- threat of spontaneous miscarriage;
- placental abruption or other pathologies of its development;
- cysts or tumors on a woman’s genitals;
- after hormonal therapy to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Personally, I had to take a blood test to determine my progesterone levels at 8 weeks. This is due to the fact that during registration, a large number of deviations from the norm were identified, which means there was a high risk of spontaneous miscarriage. Moreover, even before conceiving a child, I constantly suffered from the problem of low progesterone levels. One day I came to see a gynecologist with a complaint of hellish pain in the first two days of my period, which, on top of everything else, was very scanty and lasted only 3 days. As expected, after an examination in the chair, the doctor prescribed a large number of tests, including progesterone. We didn't have to wait long for results. The next day after submitting the biomaterial, at my next appointment with the gynecologist, I found out that I had problems with the production of progesterone. Even after the prescribed treatment, a regular menstrual cycle was not established. It usually lasts at least 35 days. After the birth of the child, the situation did not change.
Progesterone preparations are prescribed to non-pregnant women:
- with numerous unsuccessful attempts to conceive a child;
- with an irregular menstrual cycle;
- women of reproductive age who lack menstruation;
- to stimulate ovulation when planning pregnancy.
A non-pregnant woman needs to take a test to determine the level of the hormone on the very day prescribed by the attending physician. If you take a menstrual cycle lasting 28 days, then the test must be taken on days 22 - 23, when progesterone levels reach their peak, namely in the luteal (second) phase.
Progesterone levels can be checked in the laboratory by taking a finger prick test on an empty stomach.
There is no need to try to decipher test results yourself if you do not have a medical education. It is not enough to know only the norms of hormones; it is important to consider them in conjunction with other components of the blood. While carrying a baby, I often had to undergo tests in private clinics, since the pregnancy was fraught with complications, and I did not always trust the state laboratory. Therefore, I received the test results in my hands before the doctor saw and deciphered them. Having found all the tables of norms that interested me on the Internet, I set about deciphering them. And as a rule, the picture was very deplorable. But at that moment I did not take into account all the conditions and the dependence of the blood components on each other. Therefore, I worked myself up even more, worried and imagined the not very successful outcome of the delivery. And unnecessary stress and anxiety during pregnancy is an additional burden on the body.
How to prepare for a progesterone test
The effectiveness and correctness of the results depends on many factors and requires preliminary preparation. The list of requirements is quite extensive and each of these points must be fulfilled:
- two days before the test, you must stop taking hormonal medications;
- The test is taken in the morning on an empty stomach. In emergency situations, it is possible to donate biomaterial after lunch, if the woman had a light meal for breakfast and at least 8 hours have passed;
- Before the analysis you should not drink carbonated drinks;
- Do not smoke 4 hours before the test. Although during pregnancy a woman is recommended to get rid of all bad habits, there are pregnant women who neglect this requirement;
- Avoid stressful situations and nervous overexcitation.
Normal progesterone levels during pregnancy
As noted above, progesterone plays an important role in maintaining pregnancy, so its amount varies depending on the trimester. The first three months are the most vulnerable in bearing a baby, so the risk of miscarriage increases significantly. This is due to the low production of the sex hormone in the initial stages. In the first trimester, progesterone is produced by the yellow and a small part - by the adrenal cortex, in the second and third - by the placenta. The second trimester of pregnancy is a relatively calm period, as the production of the hormone increases and its level grows every week. In the third trimester, the body begins to intensively prepare for childbirth and breastfeeding, and the level of the sex hormone reaches its peak.
A decrease in progesterone levels at the end of pregnancy may signal a post-term pregnancy.
Table: normal level of progesterone in the blood of a pregnant woman by week
| Week of pregnancy | Normal progesterone level in ngmol/ml | Normal progesterone level in nmol/l |
| 1 — 2 | 12 — 18,2 | 38,15 — 57,8 |
| 5 — 6 | 18,6 — 21,7 | 59,1 — 69 |
| 7 — 8 | 20,3 — 23,5 | 64,8 — 75 |
| 9 — 10 | 23 — 27,6 | 73,1 — 88,1 |
| 11 — 12 | 29 — 34,5 | 92,1 — 110 |
| 13 — 14 | 30,2 — 40 | 96 — 127,2 |
| 15 — 16 | 39 — 55,7 | 124 — 177,1 |
| 17 — 18 | 34,5 — 59,5 | 111 — 189 |
| 19 — 20 | 38,2 — 59,1 | 121,7 — 187,8 |
| 21 — 22 | 44,2 — 69,2 | 140,6 — 220 |
| 23 — 24 | 59,3 — 77,6 | 188,9 — 247,1 |
| 25 — 26 | 62 — 87,3 | 197,2 — 277,8 |
| 27 — 28 | 79 — 107,2 | 251,2 — 340,9 |
| 29 — 30 | 85 — 102,4 | 270,2 — 326 |
| 31 — 32 | 101,5 — 126,6 | 323,1 — 402,8 |
| 33 — 34 | 105,7 — 119,9 | 336,3 — 381,4 |
| 35 — 36 | 101,2 — 136,3 | 21,7 — 433,1 |
| 37 — 38 | 112 — 147,2 | 356,1 — 468,1 |
| 39 — 41 | 132,6 — 172 | 421 — 546 |
Permissible deviation from the norm is 10%. Error is possible due to the individual characteristics of each woman’s body. But if the difference between the test results and the table is more than 10%, then this must be regarded as the presence of a pregnancy pathology. Only a qualified specialist should interpret test results.
Treatment of progesterone deficiency
If infertility is caused by an insufficient amount of progesterone in the body, then the level of the hormone must be increased by taking appropriate medications. They can be prescribed either in tablets for oral administration or in injection form. With a high risk of miscarriage and reduced progesterone levels, these drugs allow you to carry the fetus to term and prepare the body for childbirth. There is no single regimen for prescribing these hormonal drugs, so the doctor must select an individual regimen for each woman. Treatment for progesterone deficiency begins before 16 weeks of pregnancy.
To prevent miscarriage, progestins that do not have virilizing characteristics are used. The most common drugs for the treatment of progesterone deficiency during pregnancy are utrogestan, duphaston and 17-OPK. These are synthesized analogues of this hormone, which are considered effective in cases of high risk of miscarriage. Progesterone preparations can reduce the excitability of the uterus and improve the function of its mucous membrane. In general, treatment of progesterone deficiency allows, in most cases, to normalize the course of pregnancy and significantly reduce the risk of spontaneous abortion. In addition, synthesized progesterone analogues can also be used in women who are not pregnant. These drugs are indicated for pathology of the menstrual cycle and endometriosis. They should also be taken for frequent uterine bleeding of various origins.
Treatment of progesterone deficiency during pregnancy
Progesterone deficiency is a pregnancy pathology that requires immediate treatment. You can compensate for the deficiency of this hormone with the help of medication, as well as by following a proper diet (including foods of animal origin in your diet). Moreover, vitamin therapy plays an important role in improving blood supply to endometrial tissue, which has a beneficial effect on the production of the pregnancy hormone. The most famous vitamin used in such cases is Ascorutin. The artificial introduction of hormonal drugs into the body of a pregnant woman in the first trimester of pregnancy can cause malformations of the unborn baby. Therefore, for the first three months, medications are taken only as prescribed by a doctor, if the potential benefits outweigh the possible risks. If there is a slight deviation from the norm, the use of hormonal drugs is possible at home; in emergency situations, a pregnant woman is admitted to a hospital. Treatment of pathology and taking medications should be strictly controlled by a doctor.
Table: drugs for the treatment of progesterone deficiency
| Drug name | Release forms | Active ingredients | Use during pregnancy | Contraindications | Possible side effects |
| Duphaston | Film-coated tablets for oral use. | Dydrogesterone. | The use of the drug is not contraindicated during pregnancy. |
| Breakthrough bleeding from the vagina (very rare). |
| Utrozhestan | Capsules for vaginal and oral use. | Progesterone micronized. | Contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy. Use in the second and third trimesters with caution if the expected benefit is significantly higher than the possible side effects. |
| For oral use:
For vaginal use:
|
| Progesterone | Injection solution for intramuscular administration. | Progesterone. | Use is allowed in all trimesters of pregnancy if the expected benefit is significantly higher than the possible side effects. |
|
|
| Crinon | Vaginal gel. | Progesterone. | Contraindicated during pregnancy, with the exception of the first trimester if the corpus luteum is not functioning properly. |
|
|
Progesterone injections are the most effective and common drug for treating pregnancy hormone deficiency. This is due to the rapid absorption of the drug into the blood. The maximum concentration of progesterone is achieved 5 - 6 hours after intramuscular injection.
While I was kept in the pregnancy pathology department for four weeks, I saw and heard a lot of sad stories associated with various kinds of pathologies. Unfortunately, even modern medications do not always cope with hormonal imbalance. Of course, if the problem occurs at the 36th week of pregnancy and at a later stage, then with properly prescribed treatment and adherence to the daily regimen prescribed by a qualified specialist, the woman has every chance of reaching the entire term. But next to me in the ward was a young woman, 23 years old. She was only 27 weeks pregnant, and she had hypertonicity of the uterus and dilatation of the cervix by two fingers. She was prescribed strict bed rest and intensive drug therapy. Among the prescribed medications was Utrozhestan. But in the end, the treatment did not bring the expected results and it was not possible to prevent the onset of premature labor.
Photo gallery: medications to treat progesterone deficiency during pregnancy
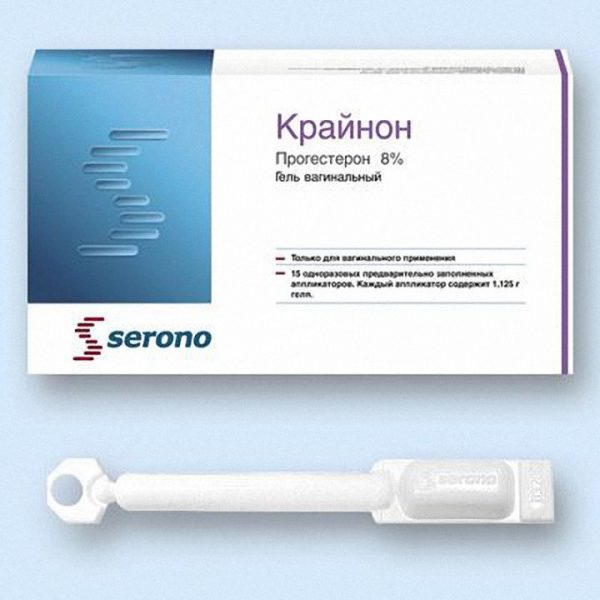
The use of the drug is possible only in the first trimester of pregnancy
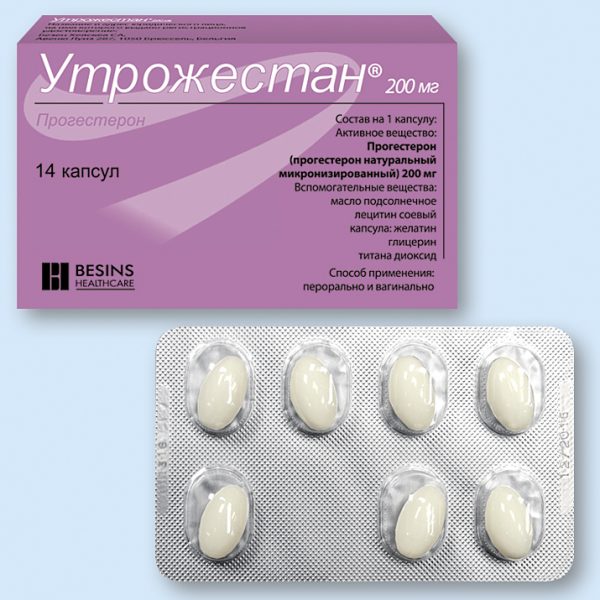
Utrozhestan can be used either orally or vaginally
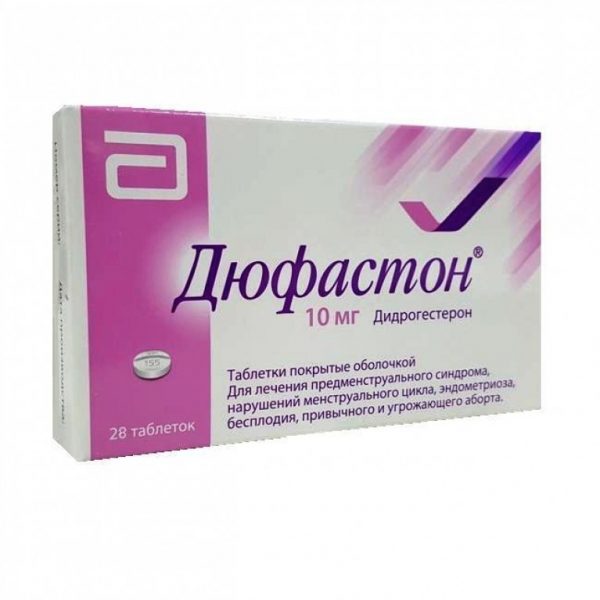
Duphaston is not contraindicated in the first trimester of pregnancy, but use should only be as prescribed by a doctor
The use of the drug is not practiced during pregnancy planning
Replenishment of the hormone progesterone should take place in complex treatment, aimed at eliminating the cause that caused this pathology.
Symptoms of hormone excess or deficiency
The following symptoms can be identified that indicate an excessive level of progesterone in the body:
- fast fatiguability;
- headache;
- vision problems;
- allergies (rashes and itching);
- decreased blood pressure;
- menstrual irregularities;
- depression;
- the appearance of pimples, often large and painful;
- increased body hair growth;
- bloating;
- emotional instability.

The main symptom of a lack of progesterone in the body is delayed ovulation, but there are other signs of this condition:
- painful menstruation;
- an increase or, conversely, a decrease in body temperature;
- increased gas formation;
- vaginal dryness;
- mood swings for no reason;
- excessive growth of body hair;
- increased activity of the sebaceous glands.
Treatment
The necessary treatment for high or low levels of progesterone in the body can only be prescribed by a doctor based on the collected medical history and studies performed. Under no circumstances should you prescribe medications on your own, because uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs will only worsen the situation.
Today, the main method of treating both high and low progesterone in the body is drug therapy with hormonal drugs. The hormone can be administered either in the form of tablets or through injections.
Another effective method of correcting progesterone levels is diet. To reduce hormone levels, you should give up dairy products, nuts and reduce your intake of protein foods.
To increase progesterone levels, you should include legumes, avocados, poultry, nuts, eggs, seeds, fatty cheeses and fish, and fish oil in both capsules and liquid form in your diet. Taking vitamins also helps raise hormone levels.