Breastfeeding is the best thing that nature has invented for mother and child, because it is very useful for the baby and incredibly convenient for the mother; food is always at hand. It has long been known that there is no need to follow any diets while breastfeeding, it is only important to eat a balanced diet.
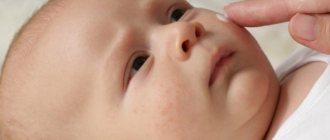
But it often happens that a month after birth a baby develops a rash on his cheeks. Pediatricians unanimously shout that this is an allergy, clarifying what the mother who was breastfeeding ate was eating. The first thing to do is to make sure that it is really an allergy and not newborn acne - a hormonal rash that does not bother the baby and goes away on its own within a month. If it really is an allergy, then it is important to identify which of the foods that the mother eats can cause a rash in the child.
Can you be allergic to breast milk?
In fact, babies should not have an allergy to breast milk.
After all, milk does not contain antigens with allergic properties. It is not the milk itself that can provoke a reaction, but its composition, which can change if the mother does not follow the diet. The allergen is often cow's milk protein, when inexperienced primiparous women begin to drink liters of tea with milk heavily, which does not have the best effect on the child's well-being, leading to digestive disorders, colic, the passage of foamy green stools, and the development of dermatitis. Allergies are insidious in that treatment can take a long time.
IMPORTANT! In principle, an allergy to breast milk cannot occur. Allergens can only enter the composition from the outside or due to improper nutrition of the mother. Moreover, the impact on the well-being of an allergic baby can be extremely unpleasant.
Causes of an allergic reaction
There are 2 main factors that can provoke allergies:
- lactase deficiency in the case of a lack of lactase production in a newborn, inadequate sensitivity of the body to foreign bodies of animal origin;
- protein intolerance to milk (sheep, goat, cow) in formula-fed children.
Important! Mothers are mistaken in thinking that milk enhances lactation. It is cow protein that is a frequent provocateur of extensive rashes on the baby’s skin and the passage of watery green stools.
To eliminate the problem means giving babies mixtures of exclusively plant origin (oatmeal, coconut, rice, soy).
The most common triggers of allergies in infants:
- tolerance of errors in food by a nursing mother;
- taking foods with potential allergens (eggs, dairy products, cottage cheese, citrus fruits, chocolate, strawberries);
- intake of gluten products - vegetable protein (semolina, rye, oats);
- abuse of preservatives, flavorings, dyes, potentially harmful and hazardous to health.
Mother's milk is healthy and nutritious, but only if the above-mentioned provoking elements are absent in the composition.
Composition of mother's milk
The composition is complex, multicomponent, although it contains the necessary microelements:
- proteins;
- fats;
- carbohydrates;
- vitamins;
- hormones.
If the mother neglects a special diet, then the composition of the milk becomes modified. The predominance of allergens in it leads to unpleasant manifestations of allergies in the baby.
Allergy to breast milk in children
Possible allergens in mother's diet
Inappropriate response to nutrition in newborns most often occurs in the first 2-3 months of life. The body is adapting to the introduction of unusual foods into the diet. An outbreak of food allergies is a common occurrence in children due to the nursing mother’s abuse of orange fruits, vegetables, nuts, eggs, fatty meat (fish), and citrus fruits.
If a newborn has an allergy, it is important for the mother to reconsider her diet. Even after eliminating the allergen from the diet, symptoms may remain for another 5-10 days. Much depends on the concentration of allergens that enter the child’s body along with milk and the reaction of the immune system to the amount of allergenic food eaten by the mother.
Cow's milk protein
The protein in milk is a strong allergen, so in the first months of a baby’s life, mothers should avoid drinking cow’s milk.
Of course, lactation will be accelerated for some time, and the process of producing milk for the baby will be easier if the nursing mother drinks a glass of fresh milk, but daily consumption can cause an inadequate reaction from the baby’s immune system to cow’s milk protein, leading to a large rash on the body, cooling spotty green stools. According to nutritionists, it is worth excluding dairy dishes and porridge with milk. Introduce complementary foods to newborns no earlier than 10 months. And if you have excessive sensitivity and allergies, do not neglect a gentle hypoallergenic diet.
An allergy to cow protein can manifest itself quite clearly in the form of unpleasant symptoms in a child.
Advice from pediatricians! Cow's milk contains more protein than breast milk. If a rash appears on the baby’s skin, then mothers should reconsider their diet and stop taking dairy products for 2-3 weeks.
This time will be enough for the child to go away the unpleasant signs of allergies. Of course, the body may experience a lack of potassium and calcium. But you can make up for it if you give your mother a vitamin complex and include foods with calcium in her diet: broccoli, spinach, liver.
Chemical additives
Preservatives, flavor enhancers, and chemical additives cause intestinal and stomach upset, severe intoxication in children, including developmental delays.
It is extremely important for mothers to exclude store-bought juices, semi-finished products, canned food, sauces, and mayonnaise from their diet. At least in the first months of life when the baby is breastfed.
Gluten
Gluten is a powerful allergen.
Contained in cereals: millet, semolina. Also dangerous products: bran, spaghetti, pasta, cereals, blue cheese, sausages, sausages, ice cream, crab sticks, canned food, fast food, chips, bouillon cubes. In the first months of lactation, women are advised to avoid taking such dishes. This allergen, no less than cow protein, will certainly lead to unpleasant consequences for the child. But here are products that do not contain gluten and are suitable for mom to eat: buckwheat, rice, corn, natural vegetables, eggs, peas, legumes, beans.
Medications
Many mothers know that many medications remain prohibited during pregnancy and lactation. There are known drugs that are absolutely incompatible with the period of natural feeding. For example, those containing theophylline, which must be abandoned until the child is 6 months old.
If a mother needs treatment, it is better to use inhalers that cannot pass into breast milk, sorbents, and activated carbon as a safer means.
Exotic food
Foreign substances in foods pass into breast milk and lead to insidious allergies in newborns. A provoking factor can be fruits and vegetables (red, orange), which also require careful consumption and gradual introduction into the diet.
A nursing mother should constantly monitor the baby’s reaction to certain exotic foods eaten.
Is it possible for a mother to be allergic to her own milk?
No, this is impossible, since an allergic reaction occurs only to foreign substances coming from outside. And breast milk is a woman’s own physiological fluid produced during lactation by a woman’s body.
Methods for treating allergies during breastfeeding
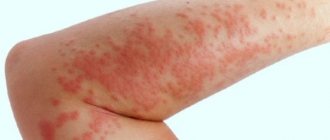
It is not always possible to recognize allergic dermatitis in a baby, because redness of the skin is not a sign of sensitivity. Before the age of 4 weeks, the baby’s skin begins to “bloom”—small rashes form on the face or other parts of the body, which go away on their own if hygiene is maintained. By the first month of life, children's hormonal balance normalizes. If the rash does not go away for a long time, and the rash becomes intense, comprehensive allergy treatment is required.
We recommend reading: Symptoms and treatment of ARVI in infants
The pediatrician prescribes tests and, if necessary, sends the patient to an allergist or dermatologist. The diagnosis is established based on a survey of parents, examination of the baby, test results for the presence of immunoglobulins, and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
A mother can keep a food diary for a week, observing the child's reaction to each product.
Therapy begins with a diet, eliminating allergenic foods (sugar, salt, meat broths, fried foods, dyes, preservatives). It is important to choose the right treatment tactics.
Age-appropriate antihistamines will help eliminate negative symptoms. For babies in the first year of life, Fenistil drops are prescribed, and after a year - Zyrtec, Zodak, Cetirizine. For external application, gels are effective - Fenistil, Bepanten. In case of serious disorders, suffocation, or suspicion of Quincke's edema, you must call an ambulance.
What should not be confused with an allergic reaction to breast milk?
Breast milk, containing proteins, carbohydrates, and enzymes, is quite complex in composition, but it protects the baby from the onslaught of infection. Allergens that get inside lead to atypical reactions in infants. The cause of milk intolerance can be lactase deficiency, when there is a lack of lactase in the milk contents, or galactosemia, when this enzyme is completely absent in milk.
Galactosemia is a congenital hereditary disease and not a reaction to breast milk. It is caused by a lack of an enzyme that can actively participate in the breakdown of galactose. As a rule, women in labor are examined in the form of a galactosemia test while still in the maternity hospital.
Lactase deficiency and allergy to breast milk in infants are two completely different diseases, although the symptoms are similar. In the first case, lactase activity is reduced, in the second, allergens in breast milk predominate. Nursing mothers should not confuse two different concepts.
Galactosemia
Galactosemia is a genetic disease in which carbohydrate metabolism is impaired and processes for converting galactose into glucose are absent. The main reason is a gene defect accompanied by a failure of galactose metabolism processes.
This disease is incurable. Women giving birth at home are required to take tests. If detected, undergo immediate treatment to avoid death in the baby. This is a genetic disease with the manifestation of watery diarrhea in a child from birth. Signs can be early or delayed with manifestation at 2-3 months in an allergic child: hepatomegaly, jaundice up to damage to the central nervous system.
In mild cases, galactosemia resembles lactose intolerance. But in the first case, additional adequate treatment is required. The basis is the complete abolition of food for newborns containing galactose. Breasts should be on a dairy-free diet.
On a note! Dairy foods can provoke the development of bacterial sepsis and liver cirrhosis in newborns.
If galactosemia is detected, a special dairy-free diet is prescribed: fruit puree, juices, porridge (rice, buckwheat). At 6 months – gradual introduction of meat. A strict diet is not prescribed if the manifestations of the pathology are minor. But children will have to undergo tests periodically to avoid adverse consequences.
Lactase deficiency
This is one of the common problems among young mothers, the reason for which is a deficiency of the enzyme lactase, without which the breakdown of milk sugar in the digestive system is impossible. In this case, the baby begins to lack important nutritional components, which can interfere with normal growth and development.
How to recognize and treat lactase deficiency
By type, lactase deficiency occurs:
- congenital due to genetic predisposition;
- acquired as an intestinal infection or allergy to cow protein;
- functional, passing.
Of course, the body in children produces lactase on its own. But its quantity is not enough if the percentage of carbohydrates predominates in breast milk. If an allergy to lactose occurs, mothers should avoid carbohydrate foods: sweets and baked goods, whole milk.
If you have an inadequate reaction to gluten, you should avoid oatmeal, semolina and wheat porridge, orange (red) fruits, cocoa, pork, and offal. It is important to reduce the fat content of milk or include fermented milk products with a low percentage of fat in the diet.
Cow's milk protein intolerance
Intolerance may occur to sheep, cow, or goat milk. If the baby is artificial, then it is recommended to feed dairy-free formulas using types of milk: vegetable, oat, coconut, rice, soy.
Paroxysmal manifestations in the form of belching, bloating, vomiting, and rashes on the body can occur after taking cottage cheese and sour cream.
Cow's milk contains a protein that is not specific to that found in breast milk. A mother who drinks 1 glass of milk a day runs the risk of developing rashes on her baby’s cheeks and the discharge of foamy green feces. A mother's intake of fresh milk in liters will certainly lead to problems for the baby, who is allergic.
REFERENCE! Cow protein is a strong allergen and you should avoid drinking whole milk. The advice of grandmothers that milk with tea enhances lactation is a real myth.
Protein intolerance is a common problem in bottle-fed infants. After all, many mixtures contain cow's milk, and this is the strongest allergen in the composition with b-lactoglobulin, globulin, casein.
Symptoms of allergy in infants to mother's milk
Signs of a reaction vary. The most important thing is to promptly recognize the pathology, identify the unfortunate allergen, and undergo treatment. Usually the digestive system and skin begin to react inadequately. If an allergy to breast milk is present, the symptoms are as follows:
- regurgitation after feedings;
- vomit;
- diarrhea, watery liquid greenish stools passed more than 5 times a day;
- nausea.
A baby with allergies begins to twist his legs and pull him towards his stomach, becomes whiny and restless.
Skin rashes such as urticaria, atopic dermatitis, and Quincke's edema appear in the form of pinkish-red papules with a chaotic location. Sometimes itching and diarrhea bother me. The signs of allergies are similar to other diseases, so it is extremely important for parents to be on alert, respond to the problem in a timely manner and see a pediatrician to get rid of the problem.
Folk remedies and recipes
Alternative medicine is relevant and safe for mild allergic signs, such as minor external rashes. To alleviate the child's condition, reduce itching of the skin, and relieve swelling, traditional methods help.
You can bathe your baby in a warm bath with chamomile or string infusion. And also apply these solutions with a cotton swab to the area of the rash.
Gauze swabs with chamomile infusion are applied to the swollen areas. If the affected areas are very itchy, strong tea leaves will help.
It is important to take into account the age of the baby and not self-medicate, because a minor rash may hide a serious illness.
How to distinguish an allergic reaction from lactase deficiency?
An allergy to cow protein is a response of the immune system, perceived as foreign by the digestive system.
In infants, the gastrointestinal tract is not able to break down molecules, and the body mistakes them for foreign antibodies. Lactase deficiency is a pathology that causes particular discomfort:
- frequent regurgitation;
- loss of appetite;
- moodiness;
- bloating;
- discharge of liquid feces with a sour smell, white undigested lumps of milk.
If persistent symptoms appear, you need to show your baby to a pediatrician.
Lactase deficiency can be either congenital or acquired. Intestinal diseases can cause: dysbacteriosis, giardiasis, toxocariasis. Protein allergy and lactase deficiency are two different pathologies. It is important to understand that lactase deficiency cannot be called an allergy, in which it is acceptable to eat dairy products, but gradually and carefully checking the child’s reaction to lactose intolerance. But allergies to cow protein in children are more common when symptoms appear immediately or with a delayed effect, after a few days in the form of rashes, itchy skin, swelling of the face, diarrhea, constipation, runny nose, eczema.
The symptoms of allergies and lactase deficiency are similar. Allergy is a response of the immune system to dairy products that are mistaken for “foreign”. Lactase deficiency is a response of the gastrointestinal tract to lactose entering it, indigestibility by the body due to a lack of enzyme for its processing.
How to maintain breastfeeding if you are allergic to breast milk?
It is important for mothers to fundamentally reconsider their diet, not overfeed their babies, and maintain a drinking regime. Of course, if an allergy to breast milk appears, then it seems better to transfer the baby to artificial feeding. This will only make the problem worse, since many formulas contain cow's milk protein. This is where mothers experience some difficulties when developing a dietary menu. The main thing is to make a balanced diet, include fruit drinks, compotes, green tea, vegetarian soups, green fruits, dairy products, lean turkey meat.
It’s worth making smaller meals and not forgetting to drink regular water up to 2 liters per day.
So it’s worth following the diet for 1 month. When the baby’s allergy to mother’s milk stops, new foods will need to be introduced into the mother’s diet gradually, monitoring the baby’s reaction.
Mom's nutrition
If lactase deficiency is detected in a baby, then mothers should refuse to take whole milk. If gluten is an allergen, then you should avoid baking, cereals (semolina, oatmeal, wheat), pasta, pork, cocoa, honey, and fish.
It is important to measure the fat content of milk and adhere to a strict diet once the baby reaches at least 3 months. Next, carefully include foods with a small amount of allergens, closely monitoring the reaction.
Hypoallergenic menu options
A hypoallergenic diet involves excluding highly allergenic foods from the diet: honey, coffee, vegetables, seafood, fruits, apples, pineapples, pickles, canned food, spices, carbonated drinks.
It is worth giving up dairy products, baked goods and salt. Include fermented milk dishes, cereal products, green vegetables, fruits, dried white bread, and boiled lean meat into your diet.
If the baby is bottle-fed or mixed-fed, then the mother needs to follow a strictly hypoallergenic diet and supplement with formulas based on split milk protein or hydrolyzate.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky
Komarovsky advises mothers to stop eating exotic fruits (vegetables) and find a conservative approach to the diet until the baby is 6 months old. Allergenic foods should be completely banned: honey, strawberries, chocolate, citrus fruits, smoked meats, nuts, raisins, sweets. Exception: marshmallows, marshmallows.
The diet should be as hypoallergenic as possible. Sample menu:
- for breakfast: cottage cheese, oatmeal cookies, fruit jam, green tea;
- for lunch: yogurt, apple, bread, chicken breast, vegetable salad, black tea with honey;
- afternoon snack: fruit salad (without citrus fruits);
- for dinner: steamed turkey, buckwheat porridge, baked vegetables.
Therapeutic diet
When an allergy occurs in a newborn while breastfeeding, what to do and how to help the baby? This question is often asked by inexperienced or first-time mothers who are faced with the problem.
If a food allergy is detected, the menu is reviewed, because everything depends on the diet of the nursing mother. Food products that are on the list of prohibited foods during lactation are excluded. Failure to comply with these measures will lead to relapses of allergies or transition to the chronic stage.
We recommend reading: Breast milk for a runny nose in infants
An allergist uses a blood test to determine the exact allergens that must be excluded.
List of prohibited or restricted products:
- Chocolate.
- Carrot.
- Bakery.
- Coffee, cocoa.
- Nuts.
- Honey.
- Seafood.
- Red apples.
- Milk.
- Eggs.
- Peanut.
- Smoked meats.
- Citrus fruit.
- Spices, spices.
- Raspberries.
If a woman follows a hypoallergenic diet, but the rash does not go away, you need to remove all suspicious foods from the menu. Every month they can be introduced in small portions.
Hypoallergenic products:
- Kefir, yogurt without additives.
- Turkey, rabbit meat.
- Zucchini, broccoli.
- Green apples.
The baby's nutrition depends entirely on the mother's diet. Pediatricians advise soaking potatoes and cereals before eating, cooking soups in vegetable broth, eliminating flour products and sweets. After excluding the pathogen, the rash disappears on its own.

If nutritional correction does not bring results, the doctor prescribes special medications.