Why does a newborn have a white tongue?
Typically, a newborn's tongue is pink and velvety, without ulceration.
However, parents often notice a white coating on the tongue. Plaque on the tongue is often a symptom of many diseases. These include problems with the gastrointestinal tract, diseases of the nervous system, and damage to the body by viruses and bacteria. Therefore, many parents immediately begin to panic. There's no need to rush. First of all, you need to observe the baby. If his behavior has not changed, he eats well, sleeps, is calm and cheerful, then there is no reason for concern. In a newborn, a white coating on the tongue most often occurs when
- Residues of milk or formula on the tongue papillae;
- Damage to the oral mucosa by a fungus of the Candida family (thrush, candidiasis).
If the surface of the tongue is visible through the white spots that cover the tongue, they are easily washed off with water, then there is no reason to worry. This is milk resignation. If the spots are cheesy, do not wash off, and there are white spots on the gums and palate, then most likely it is thrush.
What is white plaque in the mouth?
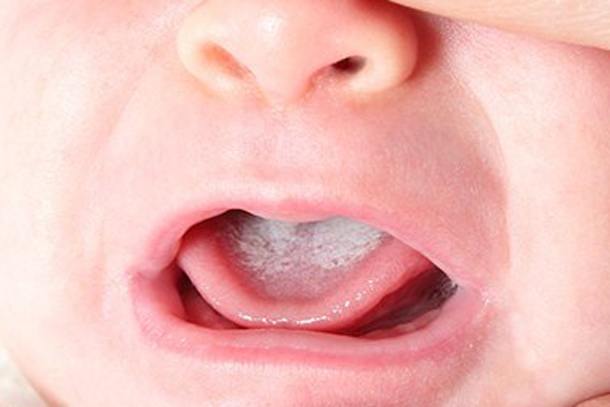
In a healthy baby, the tongue, gums, and palate have a delicate pink color, they are smooth to the touch, without wounds or roughness. Plaque that appears after eating and is easily wiped off with clean, damp gauze is not dangerous and should not alarm parents. Residues of milk settle in the oral cavity, forming a kind of white trace. If you give your baby a couple of spoons of water, the plaque will be easily washed off and will not pose any threat. The same can be said when food remains in the mouth after regurgitation, then the color of the tongue will have a yellow tint.
The formation of white plaque in the child’s mouth (on the tongue, lips, gums, palate, cheeks), the presence of wounds, ulcers, accompanied by the poor condition of the child indicate the development of certain diseases. These include thrush, herpes, stomatitis, and dysbacteriosis.
Why does plaque appear during breastfeeding?
If the child is breastfed, then the appearance of a white tongue after feeding is quite natural. Especially if the baby is attached to the breast quite often. In this case, after feeding, a little milk remains on the papillae of the tongue. After some time, the tongue is cleaned with saliva. You can give the baby a little water, then the milk will be washed off faster. However, after the next feeding it will appear again. The surface of the tongue is visible through a uniform white coating. Cheeks, palate and gums are clean. See photo.
Why does white plaque occur?
In order for the fight against pathological changes in the baby’s oral mucosa to be successful, the causes of the white coating on the tongue of a baby that appears during breastfeeding are identified. It is not always possible to determine them on your own; to do this, consult a doctor.
The doctor will determine what factors caused the accumulation of white plaque, and whether the condition is pathological and requires treatment. White tongue is observed both in newborns who are breastfed and in artificial babies.
Dysbacteriosis
Dysbacteriosis may be caused by poor nutrition
Signs of dysbacteriosis appear with poor nutrition, artificial formula, and failure to comply with hygiene rules during feeding. The gastrointestinal tract in newborns and babies up to six months is not fully formed, and the microflora is sensitive to negative changes. Therefore, in addition to covering the tongue with a white coating, dysbiosis is accompanied by bloating in the abdomen and colic, diarrhea, lethargy and tearfulness of the baby. It is not recommended to treat the disease yourself; only a doctor will determine the causes of dysbiosis and draw up the correct treatment regimen.
Digestive problems
Enterocolitis and gastritis are diseases that cause the appearance of a white coating on the tongue of a newborn during breastfeeding. Enterocolitis is an inflammatory process localized in the small and large intestines, manifested by a number of symptoms:
- abdominal pain and bloating;
- problems with stool - it becomes liquid, or, conversely, signs of constipation appear;
- inclusions of mucus and blood are visible in the stool mass;
- When the pathology worsens, the baby’s temperature rises.
With enterocolitis, the root of the tongue is covered with a white coating, and with gastritis, its central part is covered. Gastritis in young children is rare, but such a pathology cannot be ruled out. Inflammation of the gastric mucosa is characterized by the accumulation of a white-yellow layer on the tongue, the appearance of grooves and cracks on it, and the symptoms are similar to those inherent in enterocolitis.
Oral diseases
White plaque in the mouth of a breastfed baby may appear due to diseases affecting the oral cavity. These include herpes and stomatitis - the most common childhood pathologies.
A baby can become infected with stomatitis from a sick mother, or as a result of poor hygiene - when toys and pacifiers are not washed. Children with weak immune defenses are susceptible to pathology. Pathogenic flora multiplies inside the epithelium of the oral cavity, penetrating there through the delicate mucous tissue. The baby becomes lethargic and capricious, refuses to eat, sleeps poorly and cries constantly. The tongue, palate, surface of the cheeks and gums are covered with a whitish coating; grains are visible on the mucous membrane, which bleed when trying to remove them.
Herpes affects 90% of children from 6 months to 3 years of age who have a weakened immune system. Younger infants tolerate the disease much easier. The main symptoms are fever and malaise. In addition to the white coating, small bubbles appear on the oral mucosa, which burst on their own after a few days. The herpes virus must be treated with antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs.
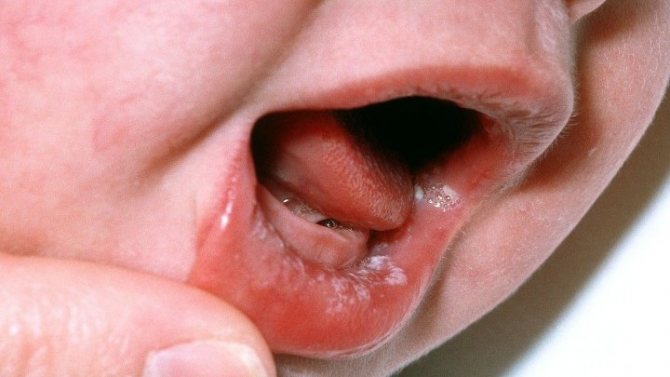
Stomatitis may be caused by poor hygiene
Thrush
An infectious disease caused by the yeast-like fungus Candida affects children under one year of age due to the weakness of the body's immune defense, who are often bottle-fed. To distinguish thrush from a white coating, which is not a pathology, is simple - try to remove the layer that has accumulated on the tongue. With candidiasis, this will be difficult to do, and red, bleeding spots will be visible on the cleaned surface.
Attention! Candidiasis is accompanied by vomiting, fever up to 37-38oC, lack of appetite, pain during feeding, sleep disturbance and lethargy of the baby. If such signs appear, you need to show the baby to the doctor.
Other reasons

Colds can also cause a white coating on the tongue.
In addition to the listed reasons for the white plaque covering the surface of the oral mucosa, the baby also develops other diseases with similar symptoms. Most often these are pathologies of the respiratory system:
- Acute respiratory infections and influenza - with a respiratory infection, the tongue is often covered with a white coating; it disappears on its own after recovery. If the surface of the palatine tonsils is covered with plaque, we are talking about the development of sore throat;
- bronchitis - when the lungs are affected, a white coating forms on the tip of the tongue. The chronic form of the disease is manifested by a foam-like coating, its compaction indicates the progression of the pathology, and the transition to pneumonia is characterized by blue discoloration of the oral mucosa;
- tonsillitis - the tongue and tonsils become coated, characterized by the appearance of pustules and problems with swallowing, fever;
- pharyngitis - the throat and papillae of the tongue turn red, the layer of plaque on the mucous membrane is dense and snow-white, the surface of the tongue becomes bumpy.
A viscous plaque localized on the tip of the tongue may indicate the development of bronchial asthma in a baby, so timely diagnosis is important. Consultation with a doctor is necessary even if the child behaves as usual and the symptoms do not look alarming.
The appearance of plaque during artificial feeding

When feeding a child with an adapted formula, the baby's white tongue may be due to the remainder of the formula. At the same time, some mixtures may leave a coating both on the tongue and on the cheeks, gums, and palate. You can easily check this by rinsing your mouth with the mixture yourself.
This plaque is also easily washed off with water. There are no changes in the mucous membrane underneath. Plaque can also appear during mixed feeding.
Diagnosis of the newborn's condition
The appearance of a white coating on the tongue of a newborn does not always indicate the development of any pathology. But despite this, it is recommended to carefully analyze changes in the child’s behavior.
If necessary, do not neglect a consultation with a pediatrician, where the cause of its appearance will be accurately determined and appropriate treatment will be selected.
The table will help us understand the reason for the appearance of a white coating on the tongue of a baby:
| When not to worry | Cause for concern |
| White spots | |
| The area of the spots is not large, evenly covering the back of the tongue. A thin layer is formed from the peeled horny scales, through which the papillae are visible. The spots are characterized by a whitish color and easy removal, after which no damage to the mucous membrane is observed. The child behaves well, is gaining weight steadily and is not capricious when feeding. | The area of the tongue is covered with spots of a dense and curd-like consistency, especially its back. The lateral areas of the tongue are covered with bubbles with transparent exudate. The child's behavior becomes capricious due to the appearance of pain when sucking the breast or pacifier. |
| White dots | |
| On the tongue, the points are located evenly over the entire area and are characterized by a thin layer. There is no cause for alarm if dots appear on the tongue immediately after your child consumes dairy products. | Focal arrangement of points on the surface of the tongue. The child refuses the breast, body temperature rises. Erosion may form at their localization sites. In the event that a child exhibits additional symptoms or concomitant diseases: glossitis, stomatitis, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, chronic vitamin deficiency, diphtheria, ARVI, scarlet fever. |
| White plaque on lips | |
| The mucous membrane of the oral cavity and the sponges themselves are light pink. If the white coating on the lips is a crust of callus that appears when sucking the breast. When natural atrophied epithelial cells accumulate on the lips, palate and gums, especially in the first days of life. | After feeding, the amount of plaque does not decrease, but constantly increases in size, affecting an increasingly larger area of the oral mucosa. The plaque layer is dense and continuous. The child's behavior deteriorates sharply for the worse. Refusal to feed, or the child abruptly throws the breast or bottle only after putting it in his mouth. |
Thrush or not?
As discussed above, an easily washed off smooth white coating on a baby’s tongue is a natural phenomenon and does not need to be treated. The baby does not show signs of anxiety and sucks well on the breast or bottle. Nothing worries him. Plaque appears after feeding, and after time it decreases and goes away.
If the coating is cheesy and spreads to the palate and gums, then we can talk about thrush. With thrush, plaque is difficult to remove. Underneath there is often a reddened mucous membrane, and there may be bleeding wounds. This disease is easy to treat and is not dangerous for the child. The main thing is to detect it in time and begin treatment.
Don't miss the symptoms of dangerous diseases. Find out what to do if your baby's eye is festering.
What can cause a white coating to appear?
The reasons for the appearance of white plaque in infants must be established so that the nursing mother begins treatment of the baby’s oral cavity as early as possible and prevents the development of any pathologies. It can be difficult to do this on your own, so it is best to consult your doctor.
The pediatrician will identify the reason why this layer formed, determine the degree of pathological changes and prescribe treatment, if necessary. After all, this phenomenon can happen to every baby one way or another, regardless of the type of feeding.
Dysbacteriosis
The development of dysbiosis is possible due to problems with nutrition, formula feeding, or lack of proper care for the mammary glands during breastfeeding. The digestive system in children under 6 months is not yet formed, and the sensitive microflora reacts sharply to any innovations. Therefore, the problem cannot be solved with plaque alone, but is complemented by increased gas formation, colic, bowel dysfunction, and general malaise in the child. It is the doctor who should be involved in the treatment, because it is necessary to identify the cause of dysbiosis, and only then begin therapy.
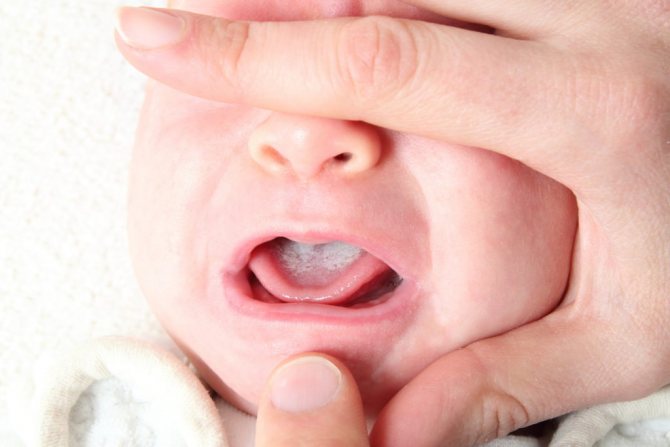
Some people deny dysbiosis as a disease, but white coating on the tongue caused by gastrointestinal problems is real.
Problems in the digestive system
When breastfeeding, a white coating on a child's tongue may form due to problems with the digestive system, more precisely due to diseases such as gastritis or enterocolitis. There are a number of signs that indicate the development of enterocolitis - inflammation in the intestines. This:
- Abdominal pain, bloating.
- Stool disorders - diarrhea or constipation.
- The stool contains mucus or blood clots.
- In an acute condition, the temperature may rise.
The plaque during the development of these diseases is different: with gastritis, it affects the central part of the baby’s tongue, and with enterocolitis, it affects the root of the tongue. Doctors rarely diagnose gastritis in infants, but the risk still remains. The inflammatory process on the gastrointestinal mucosa is expressed by a yellow-white coating, while cracks or small grooves form on the tongue, and symptoms similar to enterocolitis appear.
Diseases in the oral cavity
With natural feeding, a white coating in the baby’s mouth can be caused by diseases of the oral cavity. Perhaps it is herpes or stomatitis. Only these diseases are common in childhood.
A baby can catch stomatitis from his mother, or in the absence of proper care, as well as as a result of poor hygiene - dirty toys, bottles or pacifiers. Most often, such pathologies occur in children with weak immune systems.
Harmful bacteria, entering through the mucous membrane, spread throughout the oral cavity, affecting the epithelium. This worries the baby, he is capricious, his appetite and sleep deteriorate, lethargy and crying appear. The tongue or cheeks, as well as the palate and gums, may be covered with plaque, and the mucous membrane is affected by ulcers in the form of grains. If you try to remove them, bloody discharge may appear.
Herpes is usually detected in older children, not in newborns, but from six months to three years. Children overcome this disease much more smoothly. Symptoms of herpes include fever and a weakened state. This is accompanied by the appearance of small bubbles, which can burst on their own after a few days. To treat the disease, antiviral drugs and immunomodulating agents are prescribed.
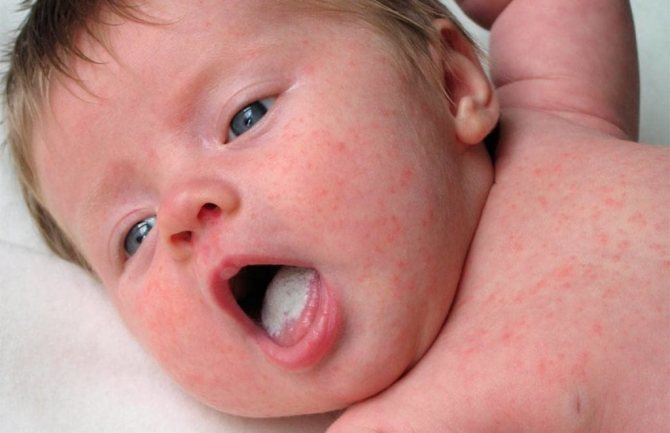
A white, cheesy coating in a child’s mouth is a thrush that requires appropriate treatment.
Fungal diseases (thrush)
Thrush often affects “brother-fed” babies, but infection is also possible in breastfed children. Candida fungus appears in children due to weak immunity. It is quite simple to distinguish the disease from ordinary food residues after feeding - they try to remove it. Pathological formations are cleaned off with great difficulty, and in their place the affected area remains in the form of red spots with bruises. In this case, a temperature may appear, but not more than 38 degrees, pain when swallowing, and loss of appetite. Babies sleep worse and generally look lethargic and depressed. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you should call a doctor.
How does a child become infected?
Infection of an infant with Candida fungus usually occurs in the following cases:
- When passing through the birth canal, the child can become infected with the fungus from the mother. This happens very often, since many women suffer from candidiasis during pregnancy;
- In the maternity ward. In case of insufficient sterility or if the health worker becomes ill;
- In everyday life at home, through things, toys, mother’s breasts, etc.
Fungal infection in itself does not pose a threat. The main thing is not to create conditions for the growth of microorganisms.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Well-known pediatrician E. Komarovsky says that a whitish coating on the tongue of a newborn or infant up to 1 year is a common and harmless phenomenon. If plaque collects in hard lumps that are difficult to remove, it is thrush. He explains the appearance of thrush by the fact that saliva loses its protective properties, and this happens due to drying out.
To cure or prevent thrush, it is necessary to restore the bactericidal properties of saliva. To do this, you need to walk a lot, humidify the air in the room by ventilating it, and after drinking milk, give the baby a few sips of water. It is good to treat your mouth with a 2% soda solution.
How to remove plaque
If plaque on an infant's tongue is caused by food debris, it can be washed off with water. It is necessary to give the baby something to drink.

If it is a fungus, then to remove plaque, use a swab or finger with a piece of gauze or bandage wrapped around it , soaked in a soda solution or honey solution (a teaspoon per glass of water). You should be careful with honey, as it can cause very strong allergic reactions; you should first consult your pediatrician.
How to remove white coating from a baby's tongue?
If a white film on the tongue of a newborn has formed due to feeding with breast milk or formula, then removing it will not be difficult for the mother.
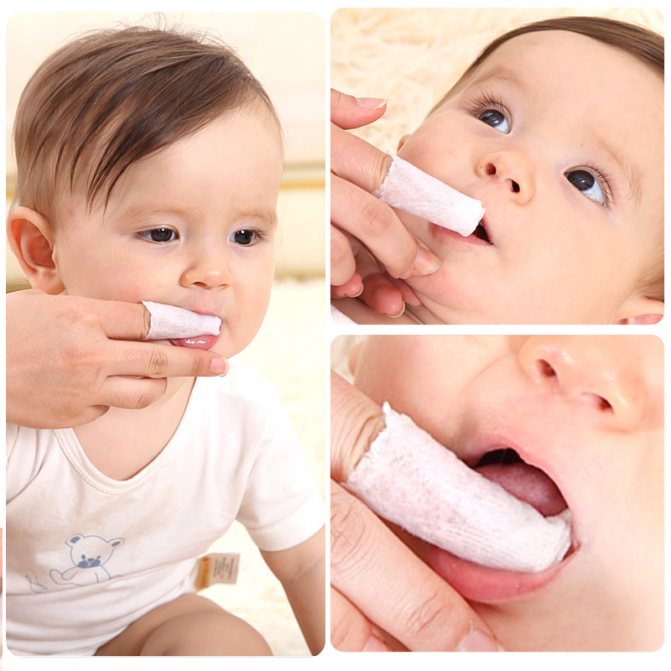
- For this purpose, ordinary baking soda , which is dissolved in a glass of boiled warm water. Then wash your hands with soap, wrap a piece of sterile gauze or bandage around your finger, moisten it in a soda solution and carefully clean the baby’s tongue.
- Some parents remove plaque with honey , which is mixed with a pinch of turmeric for a better antibacterial effect. But these products should be used with caution, because the baby may be allergic to honey.
- Another way to remove plaque from the tongue is lemon juice . But many pediatricians do not recommend cleaning a baby’s mouth with citrus juice, as it can not only cause allergies, but also burn the baby’s delicate mouth.
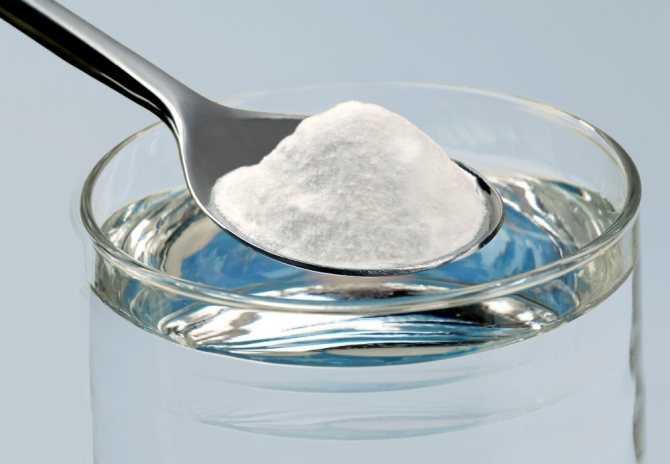

You can remove the white film on the tongue using soda.
When cleaning plaque, you should not rub a newborn’s tongue too hard or use a hard toothbrush for this purpose. This will damage the baby's delicate skin, causing wounds to form on the tongue that can become infected.
Dr. Komarovsky recommends
A well-known pediatrician advises parents not to panic at the sight of an incomprehensible coating on the baby’s tongue, but first to closely observe his behavior.
If the newborn behaves as usual, does not refuse favorite foods, does not cry and gains weight normally, then there is no reason to worry. Evgeniy Komarovsky does not recommend cleaning plaque with soda solution , as this product has a rather unpleasant taste. In his opinion, you can rid the tongue of plaque with water, giving the baby something to drink after each feeding.

If the newborn feels well and does not cry, then there is no reason to worry.
If the baby behaves restlessly, does not want to eat and often cries, and the plaque has a cheesy structure, then a reputable pediatrician strongly recommends going to the hospital to establish an accurate diagnosis and treatment of the problem .
Treatment
For successful treatment of thrush, it is important not only to clean the plaque, but also to take measures to moisturize the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose in order to increase the child’s local immunity. To do this, it is necessary to maintain the humidity in the nursery not lower than 50-60% and the temperature not higher than 22 degrees. In hot weather, give your baby a little water to drink after each feeding or between them.
If the disease is detected at an early stage, then treating the oral cavity with a weak soda solution 4-5 times a day will be sufficient.
Do this until the plaque disappears completely.
If the form is advanced, then the use of antifungal agents is necessary. Only a doctor can prescribe a medicine , because not every newborn can take it, and only a specialist can choose the right dosage. Most often, medications with nystatin or clotrimazole are prescribed for infants, for example, Candide solution.
In addition to thrush, the baby can become infected with other infections from the mother. Why it is necessary to do an analysis for Ureaplasma Parvum during pregnancy and how it can be dangerous, read the material at our link.
Treatment of white plaque on the tongue of a baby
The first thing to do when a white tongue appears in an infant is to ensure that the mucous membrane is moisturized. To do this, it is necessary to ensure room humidity (about 50-60%) and temperature conditions (no more than 20-22 degrees). When white spots begin to appear, they can be washed off with a weak solution of water and soda several times a day.
Important! The main thing is not to subject the mucous membrane to strong mechanical stress, so as not to disturb its structure and not cause infection.
If you are dealing with an infectious or fungal infection of the oral cavity, doctors prescribe special medications.
How to properly examine your tongue
The color of the tongue can tell about the child’s health and the presence of certain diseases. Therefore, it is recommended to check the condition of the oral mucosa (tongue, gums, inner cheeks, palate) from time to time. Inspection of the tongue should be carried out from above and below, examining the tip of the tongue and its root.
Important! An oral examination should be performed 2 hours after eating.
Drug treatment
If it is found that the change in the color of the tongue is not associated with food intake and does not disappear after rinsing, then treatment must be carried out with the help of medications. In the case of thrush, in addition to local effects on the mucous membrane, in advanced cases it is necessary to take a course of internal antifungal drugs. These are medicines that contain nystatin or clotrimazole (Candida solution). The dosage and duration of taking the drug are prescribed by the doctor based on the degree of complexity of the disease and the age of the child. For infectious diseases of the oral cavity, antibiotics are prescribed, and there are cases of treatment in a hospital setting. Physician supervision is especially necessary during chronic stomatitis.
How to treat thrush in a baby
If a doctor discovers thrush in a baby, then, depending on the stage of the disease, he can prescribe safe antifungal drugs and procedures for local action. For example, a weak solution of boiled water and soda helps fight thrush. Moisten sterile gauze with this mixture and wipe the tongue with light movements several times a day. It is important not to make strong efforts when cleaning the mucous membrane, so as not to damage it. Soda solution disinfects the mucous membrane well and relieves the symptoms of thrush in the oral cavity.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Pediatrician Komarovsky, regarding the white coating on the tongue of a baby, says that if this does not bother the child, then there is no need to worry. If the baby’s behavior has not changed and he does not feel discomfort, then this plaque is most likely the remainder of the milk. If, along with a change in the color of the tongue, there are other symptoms and the child feels unwell, you should definitely consult a doctor. He does not recommend using soda solution because of its unpleasant taste.
Traditional methods of treatment
At home, it is recommended to use honey or lemon juice in addition to soda to remove white plaque from a baby’s mouth. Honey is used along with turmeric for better effect. This combination has good antibacterial properties, but must be used with caution, as it can cause allergies. A popular method of combating plaque is also rinsing the mouth with lemon juice. But doctors do not recommend using this method as the main method of combating plaque. It is quite acidic and can burn the delicate skin of a child, and citrus fruits can also cause an allergic reaction.
Treatment with folk remedies

Traditional medicine methods can also be used to treat thrush in children. But you should be careful with such methods, they can cause allergies.
- Honey is an excellent natural antibiotic; it has an anti-inflammatory and antifungal effect, and improves immunity. Rubbing with honey diluted with water (1:2) will help rid the child of thrush. If the child does not allow the mouth to be wiped with a swab soaked in honey, then you can moisten the pacifier and let the baby suck.
- Lemon juice will help fight the fungus. Lemon also strengthens the immune system.
If the condition does not improve after several procedures, a rash or other changes appear, you should stop treatment and consult a doctor.
What to do?
What to do if a white coating appears on the tongue of a newborn or baby in the first months of life? It is often noticeable immediately after the child has eaten. There is nothing wrong with this and getting rid of milk deposits is easy.
It is enough to give the baby a little clean water or, wrapping a finger in gauze or a bandage, gently clean the tongue, palate and inner surface of the cheeks. You can also clean off plaque that appears after eating certain foods (then the plaque can be yellow, orange and even blue).
Treatment with soda
Treatment and preventive care with soda are safe for children of any age - newborns, one-year-olds, teenagers. Soda helps fight thrush and disinfects the oral mucosa during viral and infectious diseases.
Dissolve a small amount of baking soda in warm drinking water to create a weak solution. The oral cavity is treated with this solution 4-5 times a day until the plaque disappears.
The doctor's consultation
So, you took simple steps - gave the child water, tried to clean the tongue with gauze or soda to get rid of plaque. However, the tongue is still coated, and plaque and bad breath either soon reappear or are not removed at all and cause discomfort to the baby. What to do then?
Go to a specialist for help - describe in detail the symptoms you notice in your child. After the examination, the doctor will make a diagnosis and give recommendations, and, if necessary, write a referral for examination.
- for candidiasis and stomatitis, antifungal drugs are prescribed,
- for viral diseases (herpes, respiratory diseases, measles, etc.) - appropriate antiviral medications,
- for bacterial infections (scarlet fever, etc.) - antibiotics.
It is impossible to delay treatment, since in the case of dangerous diseases (scarlet fever, CMV, tonsillitis, etc.) there is a high probability of complications.
Diet of a breastfed mother
Since everything that a nursing mother consumes passes into the milk and into the baby, she needs to follow a diet, especially in the first months. Basic principles of nutrition during breastfeeding:
- the diet should be balanced and enriched with all useful substances,
- it is necessary to reduce to a minimum carbohydrate foods and products that cause gas formation,
- food should be natural and fresh,
- it is necessary to exclude products containing chemical additives, as well as hot and spicy spices,
- no alcohol.
With any atypical reaction of the child’s body, you need to quickly navigate. If necessary, you will have to temporarily exclude some foods from your diet.
Prevention
To prevent thrush in a newborn, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Follow hygiene standards: wash your hands thoroughly before examining the child, keep your breasts clean when breastfeeding, wash your baby’s hands, clean your mouth of food debris, boil bottles, pacifiers, and toys intended for the baby;
- Carry out wet cleaning in the nursery every day, change the child’s bed linen often, and iron it well.
- Do not kiss the baby on the lips, do not lick his pacifier, spoon, etc.
- Strengthen the baby's immunity.
Thus, if it is discovered that a baby has a white coating on the tongue, this is not a reason to panic. Most likely, treatment will not be needed. However, if after self-administered measures the condition does not improve, then it is better to show the baby to a pediatrician.
Prevention of white plaque
To prevent the accumulation of white plaque in a baby’s mouth, simple preventive measures should be followed:
- before picking up the baby, examine and treat the oral cavity, wash your hands thoroughly;
- boil bottle nipples, pacifiers and utensils before use;
- feed and water the child from separate dishes to reduce the risk of infection and thrush;
- do not lick pacifiers and spoons when feeding, do not kiss the baby on the lips;
- Before applying to the breast, you should wash the breast and treat the nipple with boiled water.
To prevent white plaque in a bottle-fed baby, you need to boil bottles and pacifiers more often. The mother of a baby who is exclusively breastfed must follow a diet to prevent the development of dysbiosis, thrush and infections in the baby.
If you notice a layer of plaque on your baby’s tongue, you shouldn’t immediately worry and run to the doctors. You should try to cope with the problem yourself, especially if the baby’s condition has not worsened and there are no dangerous symptoms (fever, bad breath). If the baby is capricious, refuses food, has a tummy ache, and the process is accompanied by hyperthermia, you should not wait, an urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary.