In this article we will answer the question of why this happens and how not to miss the first signs of pregnancy while breastfeeding.
Lactational amenorrhea and its mechanism
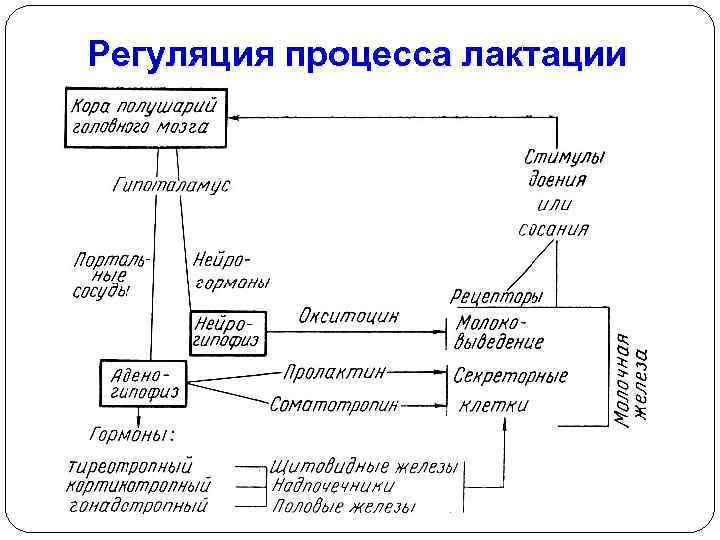
Prolactin, a hormone responsible for the secretion of milk, has an effect on a woman’s body that prevents her from becoming pregnant again. The production of this hormone occurs in waves, as a reaction to the feeding of the child and the subsequent emptying of the breast.
Therefore, in the first weeks after birth, prolactin levels are at their highest, but over time they decrease. If a woman does not breastfeed her baby often enough, then the next dose of the hormone may not be enough to block the structures of the reproductive system that are responsible for the maturation of the egg (ovaries and pituitary gland).
When additional drinks or food are introduced into the child's diet, prolactin levels decrease, as the child begins to latch on to the breast less often and for less time. The duration and frequency of sucking that effectively blocks the ability to conceive is determined individually.
However, there are general principles that can be used to delay ovulation and menstruation.
To effectively use lactational amenorrhea as a method of contraception, it is important to ensure that the following three conditions are met simultaneously:
- After giving birth, the woman never menstruated.
- The baby is fed exclusively breast milk on demand without supplementary feeding or formula feeding. The maximum interval between daytime feedings should be no more than 4 hours, and between nighttime feedings - no more than 6.
- No more than 6 months have passed since the birth of the child.
If all lactation conditions that support amenorrhea are met, the mother can count on the fact that a consistently high level of prolactin guarantees her 98% protection against unplanned pregnancy. Pregnancy during breastfeeding is possible even if the child is properly fed, since the individual characteristics of the body can contribute to fluctuations in hormone levels, which will contribute to the maturation of the egg and the onset of pregnancy.
If you do not want to get pregnant, then it is best to use a combination of LAM and other methods of contraception, which your doctor can select on an individual basis.
Is pregnancy dangerous during breastfeeding?
Breastfeeding during pregnancy is not considered dangerous, and many mothers successfully carry and give birth to babies of the same age. However, in each specific case, you need to consult a doctor who will assess the woman’s health condition and give recommendations.
There is an opinion among doctors that before deciding to become pregnant again, you should wean the child from the breast and plan to conceive no earlier than 1-2 years after birth. This is explained by the increased load on the body of a woman who has recently given birth and loses a lot of strength to produce breast milk. In addition, the baby's sucking movements stimulate the nipple and increase the tone of the uterus, which sometimes threatens miscarriage. After a cesarean section, the rest period increases to 2-4 years (the scar on the uterus may be weak and disperse during the growth and stretching of the organ).
What other complications may await a nursing woman if she becomes pregnant again:
- overload of the body associated with pregnancy and the need to produce milk;
- lack of nutrients – leads to vitamin deficiency and deterioration of a woman’s well-being;
- a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood is dangerous due to the formation of hypoxia in the fetus;
- increased uterine tone and the threat of miscarriage are a consequence of increased production of oxytocin, a hormone produced during lactation.
Such complications do not occur often, especially if a woman finds out about pregnancy in time and takes care of herself. During breastfeeding and pregnancy, you should eat heavily, take vitamins, provide the body with plenty of fluids and proper rest. Then conception during lactation will not cause problems, and pregnancy and childbirth will go smoothly.
Is it possible to continue breastfeeding during pregnancy and when should it be stopped?
Many women are concerned about the question of whether it is possible to continue to feed the baby with breast milk when pregnant with a second child. This is undoubtedly considered a risk due to the increased production of oxytocin and uterine contractions with regular nipple stimulation. But the physiological structure of the female body allows, in most cases, not to interrupt feeding and successfully carry the next child at the same time. The lining of the uterus changes, and hormonal levels regulate independently.
Doctors say that breastfeeding during pregnancy can be continued safely until the end of the second trimester. At this time, the amount of oxytocin is not so high, and uterine contractions are not pronounced. For many women, levels of the substance remain low until childbirth. If conception occurs 6 months after the first delivery, the amount of oxytocin is not so high as to cause dangerous “behavior” of the uterus.
Attention! The main indicator that breastfeeding should be stopped during pregnancy is a deterioration in the woman’s well-being. If, while putting your baby to the breast, you experience nagging pain in the lower abdomen, or scanty bloody discharge from the vagina appears, you should refuse breastfeeding.

Repeat pregnancy is not a reason to stop breastfeeding
Reliable signs of pregnancy during lactation
If a woman is breastfeeding, but her menstrual cycle has already improved, then the signs of pregnancy that occur during lactation will be familiar to her: delayed menstruation, general weakness, nausea and a sharp reaction to certain foods and smells. However, how can one understand that a woman is pregnant if she has not yet had menstruation after the birth of the child?
The most pronounced sign of a change in the functioning of the body is a change in the quantity and quality of breast milk due to hormonal changes. Most mothers notice that there is less milk, and based on the baby’s reaction they notice a change in his taste, as he begins to suck at the breast sluggishly - or even refuses to eat. The shape of the breast also visually changes, which usually noticeably enlarges and swells during milk flow.
A reliable sign of conceiving a child is a positive pregnancy test. Using this rapid method at home will help confirm an increase in hCG levels, regardless of the presence or absence of lactation.
In addition, a woman can visit a gynecologist, who will confirm the fact of pregnancy during an examination and ultrasound.
The first symptoms of pregnancy during breastfeeding
Determining the onset of pregnancy based on subjective sensations is quite difficult. The classic signs that arise after conceiving a child, as a rule, are rather weakly expressed, or go unnoticed by women, as they are attributed to recovery from the previous birth.
Indeed, the presence of insomnia, anxiety, excessive fatigue, nausea and lower back pain may be in favor of rehabilitation. And the most obvious sign of pregnancy—the absence of menstruation—is completely impossible.
Therefore, you should pay closer attention to the following symptoms:
- The appearance of general weakness and a constant desire to rest. This manifestation of pregnancy can be attributed to lack of sleep at night. However, if a woman notices that she is more tired than usual, and after a short rest she still feels exhausted, then it is best to use a pregnancy test.
- Increased urge to urinate. This may be due to one of the inflammatory diseases of the urinary system or pregnancy. As the fetus develops, the woman’s body responds to this process by increasing blood flow, which is aimed at providing the unborn baby with all the nutrients. This provokes an increase in the amount of urine. Therefore, it would be useful to visit a gynecologist.
- Pain in the mammary glands. The feeling of discomfort can be caused not only by stagnation of milk, but also by the onset of pregnancy. Changes in the level of progesterone and estrogen provoke the development of painful sensations in the mammary gland.
- Nausea in the morning. This symptom can occur due to a variety of reasons, and an increase in the concentration of hCG in a woman’s blood is one of them. The level of human chorionic gonadotropin increases with the onset of pregnancy. Therefore, using the test will be informative even during breastfeeding.
- The child refuses the breast. Changes in hormonal levels help thicken the consistency of milk and reduce its quantity. Therefore, in such a situation, it is best to consult a doctor to clarify the reason for changes in the child’s preferences.

What will indicate pregnancy when breastfeeding your first child?
It is quite difficult to think about the possibility of another pregnancy while breastfeeding, because a woman does not have classic symptoms such as toxicosis and sudden cessation of the menstrual cycle. But several factors still allow her and the doctor to identify the first signs of a new period of gestation without stopping feeding the first one.
Changes in the glands
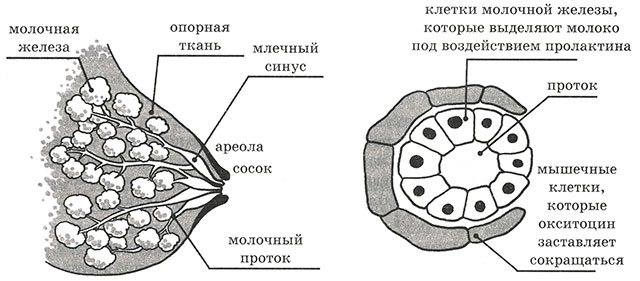
She may notice an increase in sensitivity in the nipples, and she feels this especially strongly when putting her firstborn to the breast. This is expressed in unusual pain, causing psycho-emotional stress and anxiety in a woman. If such a symptom appears, it is better for a nursing mother to immediately visit a doctor in order to reduce the duration of stress from unpleasant changes, because this can affect both the newborn and the beginning of a new pregnancy.
Quantitative composition of milk
If a nursing mother has a fertilized egg again, a reduced amount of milk quickly becomes noticeable. Her glands fill less, and because of this, the baby does not receive enough food, becomes capricious and gains weight worse.
The decrease in the amount of milk synthesized by the mother is due to the fact that during pregnancy more hormones are produced in the uterus, the concentration of estrogen and progesterone in the blood increases, which inhibits lactation.
Other signs
In addition to the two most common changes in a pregnant nursing mother, there are several other signs that the nursing mother again has a fertilized egg that is successfully developing:
- The firstborn shows less interest in nutrition or refuses it. This is due to the fact that hormonal changes in a pregnant woman are accompanied by changes in the taste of breast milk, often it becomes bitter.
- The way a woman feels uterine contractions changes during breastfeeding. After childbirth, the uterus gradually returns to its original shape and size, which is accompanied by peculiar contractions in the pelvis. A woman quickly gets used to them, since they do not cause discomfort, so the slightest changes in their frequency or character will become obvious to her.
- The menstrual cycle resumes and suddenly stops again. This symptom is rarely observed, but also requires attention.
A woman must report such changes, even if she herself induced them.
Pregnancy during lactation: the main pros and cons
The birth of another child is a joy for parents. However, every woman should be familiar with both the positive aspects of pregnancy during breastfeeding and the possible risks that it poses.
Raising children of the same age is much easier than raising children with a fairly large age difference, since they can follow a general daily routine. In addition, they can use the same toys and have common interests. Therefore, it will be much easier for parents to adapt.
Possible risks include:
- Insufficient restoration of the woman’s body, since this requires at least two years. The new fetus may not receive the necessary resources for full growth and development.
- Increased risk of fetal death and deterioration of the woman’s health.
- Continuing breastfeeding causes the uterus to contract, which can cause miscarriage.
Maintaining or terminating an unplanned pregnancy is the sole responsibility of the expectant parents. In addition, if the first pregnancy proceeded without complications, then the chances of carrying a second child without risk to your own health are quite real.