Tests for tumor markers for women are a set of indicators that are evidence of malignant neoplasms in gynecology: ovarian, cervical, endometrial cancer, trophoblastic tumors, and breast cancer. Regular monitoring of the level of tumor markers in the blood is one of the ways to detect the development of a tumor in the body at a stage when other examination methods are ineffective. Their increased concentration may indicate the presence of a pathology, but not necessarily a cancerous disease, therefore the test results should be analyzed by a doctor in each individual case.
In medicine, tests for tumor markers are not used as a direct method for diagnosing cancer. Their main function is to determine the type of tumor, and after prescribing treatment, to monitor the progress of the disease.
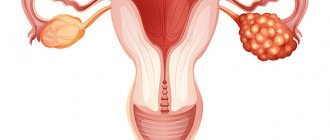
Tumor markers for ovarian cancer
- The CEA marker (CEA - carcinoembryonic antigen) indicates the development of a tumor in the body. As a rule, the level of this protein in the blood increases with colorectal cancer, but it can also be an indicator of lung, pancreatic, liver, and stomach cancer.
- The marker AFP (alpha fetoprotein, alpha FP) determines primary liver cancer. Elevated AFP levels may be an indicator of ovarian cancer. It is also used when it is necessary to determine whether metastases have spread beyond the localization of the tumor.
- The marker CA-125 (carbohydrate antigen 125) is recommended for clinical use in the diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer. In most healthy women, CA-125 blood levels are typically less than 35 units per milliliter (U/mL). But some women have naturally high levels of CA-125, so all test results must be considered individually. Elevated concentrations of CA-125 in the blood may indicate other cancers: uterine cancer,
- fallopian tube cancer,
- liver cancer,
- mammary cancer,
- colorectal cancer,
- stomach cancer,
- lung cancer.
And also for some non-cancerous conditions: during menstruation, during pregnancy, with non-cancerous ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, endometriosis.
- HE4 (epididymal secretory protein 4) is useful as a tumor marker in certain circumstances. A significant increase in HE4 is often present in the blood of women with epithelial ovarian cancer. Ovarian cancer is the fifth leading cause of cancer death in women. Epithelial ovarian cancer is the most common type. It develops from the cells that line the ovaries and accounts for 85% to 90% of this type of cancer.
- The marker CA 72-4 (carbohydrate antigen 72-4) is usually an indicator of gastric cancer, but can also be used to monitor gynecological malignancies. Elevated CA 72-4 levels may indicate the development of ovarian cancer, so the test may be performed in combination with an assessment of the CA-125 tumor marker.
- A test for beta-hCG levels is carried out to exclude germ cell tumors in the ovaries, cervix and uterine body. Also, the increased presence of alpha-FP and beta-hCG in the blood is often the first evidence of relapse of a germ cell tumor and should contribute to the restoration of therapy.
- Inhibin, produced mainly by ovarian follicles, is used diagnostically to exclude stromal tumors in the female gonads. Research into the clinical utility of inhibin for detecting this type of cancer shows that it complements CA-125.
What markers are used to detect uterine and ovarian cancer
Ovarian tumor markers 380 are what are called “female” markers that allow you to identify oncology at an early stage, when there are no symptoms yet and the woman does not even suspect that she is sick.
For the diagnosis to be effective, an analysis is prescribed for CA-125, which is the main marker, and for HE4, which is a secondary marker. Also, this group is often supplemented by AFP and CEA, known as pregnancy markers, but also produced by pathological cells. CA-125 is produced in a certain amount in endometrial cells, as well as serous tissues. And during pregnancy, this protein is expressed by the placenta. An elevated tumor marker may not always mean ovarian cancer, since its amount often changes depending on the phase of the menstrual cycle, the presence of pregnancy and other conditions.
Despite the fact that CA125 is the main one, its specificity for cancer cells is only about 45%, and therefore it is not possible to detect cancer at the germinal level only with its help. Medicine knows of cases where this indicator remained normal in the presence of a cancerous tumor.
HE4 is highly specific and allows detection of pathological formations at a very early stage. It has already been proven that this tumor marker is always elevated in ovarian cancer, while CA125 remains normal. Moreover, unlike other markers, it does not increase in the presence of cysts and other benign pathologies, which emphasizes its high sensitivity to a dangerous disease.
AFP - alpha-fetoprotein belongs to the group of non-specific markers and is prescribed only if other tests have given questionable results. Produced by liver cells and increases in the presence of cancer. More effective in monitoring cancer treatment than in detecting it.
CEA is a cancer-embryonic antigen that is produced in fetal cells during fetal development and reaches normal levels by the end of the first year of life. A minimal increase in the norm indicates the presence of pathology, both benign and malignant.
Tumor markers for breast cancer
Markers CA 15-3 (carbohydrate antigen CA 15-3), CA 27-29 (carbohydrate antigen CA 27-29) indicate the development of breast cancer. This type of tumor is a common cancer among women worldwide, accounting for more than 15% of all cancer cases among women.
Not all breast cancers cause elevated levels of CA 15-3 because some types of cancer cells do not produce excess amounts of the antigen. The level of CA 15-3 increases significantly in the blood when metastases spread beyond the breast, and can also be an indicator of hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver, tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, etc.
CA 27-29 is specific for breast cancer, but can also be found in colon, stomach, liver, lung, pancreatic, ovarian and prostate cancers. Testing for this tumor marker is not used to diagnose the disease. It is limited to the following two functions:
- Monitor the progression of metastatic breast cancer with increasing values corresponding to progressive disease.
- Monitoring the treatment of metastatic breast cancer with a decrease in values corresponding to a positive treatment result.
In clinical practice, a combination of tests for CA 15-3, CA 27-29, CEA is applicable to monitor the dynamics of breast cancer development.
Serum Her-2/neu is used for disease prognosis. In about 1 out of every 5 cases of breast cancer, the cancer cells have a gene mutation that causes an excess of the Her-2 protein.
Tumor marker norms and interpretation
All tumor markers of the uterus and ovaries are present in the body in a certain amount. With age, this amount tends to increase, so the range of numbers is taken as the norm:
| CA125 | normally no more than 0-33 IU/ml, for pregnant women – no more than 100 IU/ml. |
| HE4 | in the premenopausal period up to 70 Pmol/l, after the onset of menopause - up to 140 Pmol/l. |
| REA | from 3 to 5 ng/ml, for benign tumors - 5-10 ng/ml, 7-10 ng/ml - for alcohol addicts, 10-20 ng/ml - for smokers. Higher rates indicate a malignant process. |
| AFP | from 5 to 10 IU/ml. |
In addition to the listed markers, ovarian tumor markers roma are used for screening for suspected cancer - an index of the risk of developing a malignant neoplasm. It is calculated using a formula based on a comparison of results on HE4, CA124.
Deciphered as follows:
- The norm for menstruating women: ROMA >= 7.4% indicates a high risk of epithelial cancer, and if this figure is less than 7.4% indicates a low risk of the disease.
- The norm for postmenopausal women: ROMA >= 25.3% is a high risk, and the indicator indicates the opposite.
Please note that the decoding and calculation of the index is carried out by the doctor of the clinic where the diagnosis is carried out.
How often should you get tested?
Currently, less than 20% of ovarian cancers are detected in the early stages before they spread beyond the affected area. The main reason they go undetected is that the symptoms of ovarian cancer are quite nonspecific. The need for a reliable method for early detection of this disease in asymptomatic women continues to motivate scientists to conduct new research. At the same time, regular physical examinations, pelvic examinations, blood screenings, as well as understanding family history and studying the dynamics of symptoms are important.
- Once a year, it is necessary to take tests for female tumor markers for those who have a family history of malignant tumors in various organs.
- Screening should be carried out with the same regularity for women who have been diagnosed with benign tumors, such as fibroids or fibroids, or tumor-like formations, such as cysts. Women outside the risk group are recommended to be tested once every few years.
- For those who have undergone cancer therapy, the dynamics of the level of tumor markers in the blood must be carried out at strict intervals: every month during the first year, every two months during the second year, every three months during the next three years. Further research is sufficient to carry out 1–2 times a year.
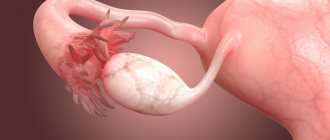
Ovarian tumor marker CA-125
Elevated levels of the CA-125 tumor marker do not always indicate the progression of malignant processes. Like other types of tests, this study can also give false positive and false negative results. Thus, an increase in the level of a specific protein may indicate diseases such as:
- benign ovarian tumors;
- inflammatory processes in the appendages;
- autoimmune disorders;
- adenomyosis;
- endometriosis;
- polycystic disease;
- acute andexitis.
The final diagnosis is made by a doctor after studying the results of studies such as:
- biopsy;
- histology;
- ultrasound examination;
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography.
In what cases is analysis prescribed?
The blood test for the specific protein CA-125 is not standard. The study is carried out only on the indications of a doctor who suspects that the patient has a tumor of a malignant nature.
Common signs that are an indication for laboratory diagnostics:
- A sharp decrease in body weight with a unchanged diet.
- An unreasonable increase in body temperature that persists for a long period - more than 2 weeks.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, intensifying after physical activity or sexual intercourse.
- Deterioration in general health, frequent attacks of nausea, vomiting, dizziness.
- Disturbance in the process of urination and defecation.
- Inflammation of the inguinal and other lymph nodes.
- Increase in abdominal size, asymmetry.
- The presence of spotting and spotting that is not associated with menstruation.
- Chronic fatigue, loss of appetite, drowsiness, loss of performance.
How to prepare for blood tests for tumor markers
- It is better to take the test on an empty stomach in the morning. If the test takes place during the day, do not eat for 8 hours before the test. Drink only water.
- Avoid drinking alcohol 1–2 days before your test.
- Be sure to tell your doctor about taking medications if you cannot stop taking them.
- It is recommended to avoid physical activity and stress for several days before the test.
- Immediately before taking the test, you should rest for 10–15 minutes.
Tissue tumor markers
This type of tumor marker received its name due to the fact that for their analysis it is not blood that is used, but tissue taken from a suspicious tumor or from a nearby tissue area (for example, a lymph node). Biological material is taken using a biopsy. The type of biopsy (obtaining a piece of tissue) is determined depending on the primary diagnosis.
Types of tissue tumor markers:
- estrogen and progesterone receptors;
- tumor markers of proliferation;
- UPA and PAI-1.
2.1. Testing for the presence of estrogen receptors (ER) and progesterone receptors (PR)
Evaluation of estrogen and progesterone receptors is carried out to diagnose breast cancer at stages 3-4 or to detect metastases. The level of receptors for ER and PR can predict how effective hormone therapy will be against breast cancer. If it makes sense to undergo drug treatment, the woman will be prescribed aromatase inhibitors, tamoxifen and estrogen receptor blockers. Normally, receptors are not detected.
2.2 Determination of proliferation markers
These cancer markers are determined by microscopic examination of tissue. During a microscopic examination, a piece of tissue taken through a biopsy is treated with specific antibodies that are sensitive to the detected marker. Enzymes are used to stain cellular and tissue components.
2.3 Determination of urokinase factor plasminogen (UPA) and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1)
Based on the results of the study, oncologists can predict how quickly the disease will develop. UPA is a protein that stimulates tumor growth and metastasis to the lymph nodes. PAI-1 partially blocks the action of UPA, but is also involved in the development of the disease.
The obtained values are prognostically valuable for patients with a newly identified tumor process, which is not accompanied by damage to the lymphatic system. According to the data, with a low UPA and PAI-1, the risk of breast cancer recurrence tends to 0 (even if patients were found to have metastases in the lymph nodes). This means that women will not need chemotherapy sessions in the postoperative period. The norm is up to 3 ng/ml.
You have been diagnosed with breast cancer – where to go?
If you have been diagnosed with breast cancer, you need to act immediately. It is worth contacting an oncology medical institution.
Well-known cancer clinics are located in Europe. Belgium's medical institutions are especially developed in this regard. Among the reasons why it is worth treating breast cancer in Belgian clinics, our patients name the following strengths of the Belgian healthcare system:
- The cost of diagnostic procedures and therapy itself in Belgium is lower than in other European countries. Treatment prices are controlled by the state. For foreign citizens, the cost of therapy will be the same as for residents of the country.
- In Belgium, treatment of cancer patients is carried out according to modern protocols. They involve a comprehensive approach to cancer treatment that increases the chance of recovery and survival.
At the same time, Belgian doctors take into account the individual characteristics of the patient:
- Doctors make all decisions to determine the treatment plan for each patient collectively - comprehensively discussing and evaluating each case individually.
- All doctors involved in the treatment of the patient are present at the consultation (specialists: mammologist, gynecologist, surgeon, chemotherapist, radiologist, radiologists, immunohistochemistry specialists, if necessary, highly specialized cardiologists, gastroenterologists, etc.).
- Such a consultation is held 1-2 times a week during the active diagnostic and primary treatment phases (then their frequency is determined depending on the tumor’s response to the treatment).
- At such a consultation, all the patient’s diagnostic data (mammography, ultrasound, MRI, CT, PET CT) are brought together over time. The slightest fluctuations in blood counts and tumor markers are taken into account.
- Based on the data obtained, a decision is made on the best treatment method for a particular patient.
This approach allows you to individually customize treatment methods:
- refuse chemotherapy in cases where the oncotype study obviously proves its ineffectiveness (applicable only to a certain type of breast cancer);
- carrying out neojuvant chemotherapy for more aggressive types of tumor (in order to establish the evidence base for the “effectiveness of chemotherapy on the tumor”);
- combining chemotherapy with immunotherapy or hormone therapy;
- performing surgery and consolidating the result with radiation therapy;
- many other combinations, strictly selected for a specific case.
After such a clear definition of treatment tactics, adverse reactions appear much less often and the effectiveness of combating the disease is higher. The most important thing that all our patients agree on is that the huge advantage of Belgian doctors is that they see in the patient a person with his fears and concerns, and they try to help the person as a human being, and not just apply a set of therapeutic measures!
How analysis data is interpreted
For most patients, even waiting for test results is a huge stress, and information about elevated levels of tumor markers even looks like a “sentence.” But it is important to know that blood tests are not the ultimate truth, they only set the direction for further diagnosis. Therefore, an increased level of tumor markers requires additional research, the purpose of which is to exclude oncology or confirm and clarify the features (form of cancer, stage, extent of spread, etc.). In addition to the analysis, hardware methods (ultrasound, contrast radiography, MRI, etc.), laparoscopic surgery to determine the stage of disease development, and other methods may be prescribed.
Tests for tumor markers at City Medical offers you to undergo blood tests and other diagnostic procedures that will allow you to accurately assess the state of your health and, if necessary, begin treatment as soon as possible. Among the advantages of contacting our medical center are the following:
- Get results in a short time.
- Modern laboratory equipment that ensures highly accurate results.
- Highly qualified specialists who pay attention to your problems.
- The opportunity to undergo a comprehensive examination in one clinic, without the need to visit different medical institutions.
- Affordable prices that allow you to take care of your health on time and do it at the highest level.
You can make an appointment with the specialist you need and undergo a study by calling the phone number listed on the website, ordering a call back, or filling out the online form.
Genetic tumor markers BRCA1, BRCA2
Mutational changes closely associated with breast cancer are detected in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. The BRCA1 gene encodes a protein of the same name, which is involved in the repair of DNA molecules, maintains genetic stability and regulates the cell cycle.
In the scientific literature, there are more than 500 descriptions of mutational changes in the BRCA1 gene associated with the further development of breast cancer in women and prostate cancer in men.
In women who are carriers of the BRCA1 gene, the likelihood of developing breast cancer ranges from 50 to 85%. In addition, mutations may be associated with the development of tumors in other locations (for example, the digestive system).
The BRCA 1, 2 gene makes it possible to identify hereditary predisposition to the development of breast cancer. Approximately 5% of women will inherit cancer-causing genes from their parents. The interpretation of the analysis result for BRCA1/BRCA2 is as follows: N/N - there is a low probability of developing cancer, it is equal to the population value, N/ins - a high probability of developing a tumor.
What the analysis shows
Tumor markers are special substances that are released into the blood primarily during an oncological process in the body. They can be produced by the tumor itself or formed in healthy tissues as a response to the presence of atypical cells. A small amount of tumor markers in the blood may be natural and is not a sign of ovarian cancer or other malignant process. But exceeding normal values requires additional diagnostic measures, as it indicates the possible development of oncology. With cancer of certain organs, the level of certain tumor markers increases. Thus, during malignant processes in the ovaries, the amount of CA-125 and HE-4 increases. It is these substances that are used as an “indicator”: if their quantity is outside the normal range, this becomes a prerequisite for further research in order to confirm or refute the malignant nature of the disease.
How to feel about the results obtained?
These indicators are used to monitor the condition over time, so it is important to know their initial level. There are no universal tumor markers indicating a specific location, so they cannot be used as an independent diagnostic method.
Indicators may increase during pregnancy, acute and chronic diseases, so they cannot be interpreted unambiguously. Biochemical studies must be confirmed by clinical methods and consultation with specialists.