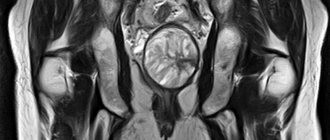
How is ultrasound done?
The principle of operation of an ultrasound device is one, but there are several ways to examine the ovaries, and the choice of examination method will depend on age characteristics and diagnostic purposes. This or that ovarian ultrasound method is prescribed directly by the attending physician. It is he who will be able to accurately determine which of the following methods is more informative in a particular situation. Methods of ultrasound of the ovaries: 1. The transabdominal ultrasound method is carried out using an external sensor, which is installed in the projection of the ovaries and passed through the wall of the abdominal cavity. This method is suitable for medical examinations and primary diagnosis of gynecological pathologies. This method is not informative for overweight women, since adipose tissue can have a large volume and not transmit ultrasonic waves to the required depth. About 15 years ago, the transabdominal examination method was the main and almost the only method in diagnosing female organs. Now doctors more often prescribe the transvaginal method, whose information content is much higher. 2. Transvaginal ultrasound of the ovaries is done using a probe that is inserted into the woman’s vagina. This method is the most accurate. During it, the visualization of the organ is much better, and with its help, doctors can assess the condition of the uterus and follicles. A transvaginal ultrasound examination will show pathologies such as ovarian cysts, polycystic diseases, and tumors better than transabdominal ones. 3. The transrectal method is an alternative to the transvaginal type of diagnosis. It is usually prescribed to young girls with intact virginity. This study is carried out with a thinner sensor, which is inserted into the patient through the rectum. It also has good information content for the diagnosis of cysts and tumor formations of the ovaries.
Surgical treatment of ovarian cancer
The goal of surgical treatment is to remove as much of the primary tumor and its metastases as possible. The operation that is preferred for ovarian cancer is extirpation of the uterus and appendages and resection of the greater omentum (i.e. complete removal of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries on both sides). For patients who want to preserve reproductive function, it is possible to perform unilateral removal of the appendages with adequate staging and no changes in the preserved structures.
For ovarian cancer, there is such a thing as cytoreductive surgery, an operation that is performed to reduce the volume of the tumor. It can be optimal (when the volume of the residual tumor does not exceed 1 cm in the greatest dimension) and non-optimal (the volume of the residual tumor is more than 1 cm). For patients who did not undergo maximum cytoreduction at the first stage, it is possible to perform an intermediate cytoreductive operation if there are positive dynamics or stabilization during chemotherapy.
Make an appointment with an oncologist-gynecologist
Restrictions
Ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus is a fairly fast and reliable method of examination. And yet, it is possible to make a diagnosis when it comes to tumor formation only by approaching diagnosis in a versatile and comprehensive manner. Unfortunately, it is impossible to accurately assess the tumor based on ultrasound results and distinguish its nature. To clarify whether this tumor is malignant or has a different nature, it is necessary to resort to histological examination or MRI of the pelvic organs with contrast.
| Ultrasound service of pelvic organs | Price, rub | Promotion Price |
| Ultrasound of the bladder with determination of residual urine | 800 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis in women and men with an abdominal sensor | 1200 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the pelvis in women with a vaginal probe | 1300 rub. | |
| Comprehensive pelvic ultrasound with abdominal and vaginal probe | 1400 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of folliculogenesis | 750 rub. | |
| Ultrasound cervicometry | 1100 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the prostate gland with a rectal probe | 1500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the scrotum (testicles, appendages) | 1000 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the prostate and bladder with an abdominal probe | 1900 rub. | |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the pelvis with an abdominal probe + ultrasound of the mammary glands) | 4200 rub. | 2999 rub. |
| Comprehensive ultrasound (ultrasound of the abdominal organs + ultrasound of the kidneys + ultrasound of the thyroid gland + ultrasound of the prostate gland with an abdominal probe) | 3300 rub. | 2499 rub. |
Preparing for an ultrasound of the ovaries
Transvaginal, transrectal and transabdominal ultrasound are different from each other, and you need to prepare for each individually. Although there are a few things to consider when preparing for any of these procedures:
- The first thing you will need to do is to give up food that causes flatulence 2-3 days before screening. This includes baked goods, all legumes, lactic acid products, and sauerkraut. It will be useful to introduce boiled vegetables, lean meat (beef or chicken), steamed fish, and water-based porridge into your diet. If there are problems with the intestines and you suffer from increased gas formation, it is recommended to start taking medications: Espumisan, Mezim-Forte or activated carbon. All this must be done a day or two before the study.
- On the day of the procedure, all medications that are taken on an ongoing basis must be discontinued.
- Don't forget about basic hygiene of the groin area.
Transvaginal ultrasound of the ovaries and uterus is performed with a full bladder. Therefore, the patient needs to take about 1 liter of water without gases and not urinate before screening. You won’t be able to drink so much water at one time; you need to drink in small portions. You can drink the first 0.5 liters of water at home if you live near the clinic. If you need to spend time on the road, it would be better to come to the clinic half an hour before the examination and while waiting for the procedure, drink the required amount of liquid in small portions. During transrectal examination (through the rectum) the night before, the last meal should be no later than 18.00. Before going to bed, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines naturally or with the help of an enema and a mild laxative. In the practice of doctors, there are cases when the ovaries cannot be examined on ultrasound. This may occur due to improper preparation and formation of gases in the intestines or due to a congenital anomaly, adhesions due to a tumor or inflammation. Then doctors carry out differential diagnosis using MRI of the pelvic organs.
Systemic drug treatment (chemotherapy) for ovarian cancer
For ovarian cancer, different chemotherapy options can be used depending on the stage of the disease.
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is preoperative chemotherapy for patients who cannot undergo surgical treatment at the first stage. When the desired effect is achieved, the patient subsequently undergoes surgical treatment.
Adjuvant chemotherapy is postoperative chemotherapy, carried out in the postoperative period in patients depending on the stage of the disease; in the early stages it is carried out in patients with intermediate and high risk (determined by the attending oncologist depending on certain characteristics).
Curative chemotherapy is carried out in the case of initially widespread disease or the presence of relapse of the disease.
When the disease relapses after previously administered platinum-based chemotherapy, attention is paid to the time from the end of treatment until the relapse occurs. If less than 6 months have passed since the end of chemotherapy or a relapse occurred during chemotherapy, the tumor is considered not sensitive to platinum drugs (platinum-resistant), and these drugs are not used in further treatment. Chemotherapy for patients with platinum-resistant disease is usually characterized by low antitumor effect and short life expectancy.

If 6 months or more have passed, the tumor is sensitive to platinum drugs (platinum-sensitive). With the development of a stable and long-term effect after platinum-containing chemotherapy, there is a high probability of a repeated response to treatment regimens with platinum derivatives.
As first-line therapy (i.e., what is used first), in the absence of contraindications, combinations based on platinum drugs are used, for example, paclitaxel at a dose of 175 mg/m2 with carboplatin AUC6 every 3 weeks for 6 courses of treatment. Carboplatin can also be combined with gemcitabine, docetaxel, liposomal doxorubicin, but in accordance with European recommendations, the combination of carboplatin with paclitaxel is in first place in terms of evidence.
Norm
The concept of normal ovaries depends on the stage of the cycle and the age of the patient.
At the beginning of reproductive age, the ovaries are the same size in all women. By the beginning of natural decline, by the age of 40, the size of the glands decreases. Normally, the ovaries have lumpy outlines due to the follicles. During normal reproductive activity of the body, there should be 9-10 follicles. If there are significantly fewer of them, this makes us think about pathological changes in the reproductive sphere. The diameter of the follicles is about 3-5 mm. During maturation, the dominant follicle increases to 24 mm. It consists of a fully mature egg, which is released from the follicle at the end of ovulation. Author: Telegina Natalya Dmitrievna
Therapist with 25 years of experience
What do the ovaries do?
The ovaries do 2 important things for the female body - these are:
- produce and release eggs (oocytes) in the middle of each menstrual cycle,
- produce the female hormones estrogen and progesterone.
Ovarian function is controlled by the action of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, released from nerve cells in the hypothalamus, which send their messages to the pituitary gland to produce luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). They enter the bloodstream to control your cycle.
You are born with all the eggs you will ever need, approximately a million immature oocytes in each ovary left and right. By puberty, when you have your first period, the number of eggs will be between 200,000 and 400,000 per ovary. Here's a stunning fact: If a woman is pregnant with a girl, it means she is also carrying her potential grandchildren. After this, about 1000 germ cells are lost every month.
During the childbearing period, approximately 300-500 eggs develop and are released during ovulation. Ovarian reserve and fertility work optimally between the ages of 20 and 30. Around age 45, the menstrual cycle begins to change and the pool of follicles decreases significantly. The events that lead to ovarian aging remain unclear. Variability in the onset of aging may include environmental factors, habitual (lifestyle) or genetic factors.
After menopause, the ovaries stop releasing eggs and atrophy (shrink). Due to loss of function and a sharp decrease in estrogen production, postmenopausal women typically experience symptoms such as hot flashes and lack of vaginal moisture. Estrogen deficiency also increases the risk of developing osteoporosis, which can lead to bone fractures.
Does your stomach hurt on the left or right? Find out what to do if you have a cold in your ovaries...
Functions of the ovaries in the menstrual cycle
Although your cycles may be irregular at the beginning, they will eventually become approximately 25-35 days between the first days of each period.
Every month, approximately 10 to 12 egg follicles begin to develop. One will continue to produce a mature egg. The rest will be dissolved in the ovarian tissue. Around day 13-14-15 in the menstrual cycle, this mature egg will be released as a result of ovulation. After ovulation, the empty follicle called the “corpus luteum” will produce progesterone and other hormones necessary for the “fixation” of a possible pregnancy in the uterus for about 14-15 days. Progesterone helps prepare and thicken the uterine lining for implantation if an egg is fertilized by a sperm. If conception does not occur, progesterone levels decrease, the corpus luteum degenerates, and menstruation begins.
Ovarian hormones
The ovaries in women are sensitive to the effects and changes of the endocrine or hormonal system. They react and produce their own female sex hormones needed by the body. In fact, the second important role of the ovary is to secrete sex hormones - estrogen, progesterone and very small amounts of androgens - which cause the development and maintenance of typical female sexual characteristics. If there are indications, you can find out their level in the female body by taking blood tests for hormones.
The ovaries are also an important source of testosterone for women, especially after menopause.
In addition, the ovaries also respond to FSH and LH, which are produced by a small gland in the brain called the pituitary gland. FSH, or follicle stimulating hormone, causes estrogen levels to rise and a group of egg follicles to grow each month. As one follicle becomes dominant and reaches maturity, higher levels of estrogen cause a surge in LH (luteinizing hormone), causing ovulation.
Once conception has occurred, the corpus luteum does not lose its ability to function and continues to secrete estrogen and progesterone, allowing the embryo to implant into the uterine lining and form the placenta. At this stage, fetal development begins and the function of the ovaries in producing hormones passes to the placenta.