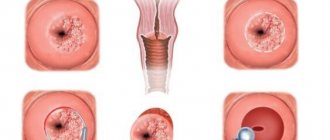
A cervical biopsy is an invasive procedure that involves removing a small piece of tissue from the surface of the organ. The resulting tissue sample is sent to the laboratory for microscopic examination. The duration of the procedure, as well as its consequences, depend primarily on the chosen biopsy method. Most often, after a cervical biopsy, the patient can return to her normal daily routine immediately after the procedure is completed.
What is recommended after undergoing a biopsy?
To speed up regeneration processes after a cervical biopsy, you should follow the rules that will speed up recovery and avoid complications:
- sexual contacts should be avoided. On average, the restriction is valid for a week, but in some cases it can be longer. The restriction time depends on the type of biopsy selected
- It is recommended to avoid douching for the treatment of diseases of the genital organs;
- it is necessary to exclude the use of vaginal suppositories;
- During the week, it is better for a woman not to use tampons and give preference to pads.
A biopsy is a relatively simple procedure that causes minimal discomfort and pain. After the manipulation, minor pain of a spasmodic nature is acceptable. To get rid of them, you can take painkillers, for example, paracetamol and others.
During the rehabilitation period after a biopsy, a woman may experience minor vaginal bleeding or brownish discharge. These signs may appear within 5 to 14 days. Doctors recommend abstaining from any sexual activity and physical exertion until the symptoms disappear.
If the biopsy was performed after examination with a colposcope and treatment of the cervix with a special solution, then a brownish discharge may be noted for several days after the manipulation.
How to prepare for gynecological cleansing
There are emergency and planned gynecological cleanings. If it is possible to prepare for surgery, then we are talking about a planned procedure.
Preparation involves the following steps:
- before the operation, be sure to undergo all the necessary examinations and laboratory tests to make sure there are no contraindications;
- it is necessary to completely shave the pubic and perineal area, and this is best done at home on your own;
- It is recommended to wear socks and a long T-shirt under the robe;
- which will be needed after surgery, and vaginal tampons are strictly prohibited;
- you should come to the operation on an empty stomach;
- after the operation, you must fully follow the doctor’s instructions;
- During the next month after the operation, sexual contact is excluded.
If the operation is performed by an experienced doctor, and the woman follows these simple rules, then, in fact, there should be no complications. Planned surgery is performed a few days before the onset of menstruation. If polyps are removed, then choose the day immediately after your period.
When surgery is performed as an emergency, for example due to bleeding, no preparation is required.
For a planned operation, choose a day when there are 5-6 days left before the onset of menstruation. This is necessary in order to minimize excessive bleeding during surgery and not cause too much disruption in the menstrual cycle. It will start around the right time.
What tests are necessary before gynecological cleansing?
To determine contraindications, tests are performed before surgery. The doctor will definitely order tests such as:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram (blood clotting test);
- blood test for hidden infections: HIV, hepatitis B and C, as well as syphilis;
- Analysis of urine;
- blood test for group and Rh factor;
- cytological examination of a cervical smear;
- vaginal smear.
These indicators are important in order to assess the degree of risk. A general blood test indicates the quantitative presence of red and white blood cells, hemoglobin level, and so on. Based on these indicators, one can judge inflammation and the scale of these processes, as well as the state of other organs in the body.
Checking your blood for HIV, syphilis and other pathogens is no less important. If there are hidden infections, this increases the risk of blood poisoning during the procedure. If the disease occurs in an acute stage, the operation is postponed and treatment is carried out.
If blood clotting is poor, surgical intervention is unlikely because it can lead to bleeding.
A vaginal smear gives an idea of inflammatory processes, as well as hidden infections, and determines the degree of cleanliness.
A cytological examination of the cervix indicates the presence of altered cells that appear during the onset of the oncological process.
Make an appointment and free consultation by calling +7(495) 256-49-52 or filling out the online form
| Select a clinic | Gynecologist appointment | Medical abortion | Surgical abortion |
Our clinics in St. Petersburg
Medical center on Pionerskaya Polikarpov Alley 6k2 Primorsky district
- Pionerskaya
- Specific
- Commandant's
Medical center South-West Marshal Zhukov Ave. 28k2 Kirovsky district
- Avtovo
- Avenue of Veterans
- Leninsky Prospekt
Medical center in Devyatkino Okhtinskaya alley 18 Vsevolozhsk district
- Devyatkino
- Civil Prospect
- Academic
For detailed information and to make an appointment, you can call +7 (812) 640-55-25
Make an appointment
However, an abnormal process may occur - hyperplasia , in which the number of structural elements of tissue increases, leading to their further germination into the deep layers of the uterine wall.
Hyperplasia leads to pathological changes in the uterine mucosa, lack of ovulation and infertility.
If this condition occurs, confirmed by ultrasound data, it is indicated to carry out a procedure - curettage of the uterine cavity . In this case, gynecological cleansing will be both a therapeutic and a diagnostic procedure, because during the curettage process, the resulting material is sent for analysis, which can sometimes help in time to detect a malignant process that has developed in the endometrium.
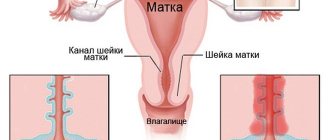
Curettage (curettage) is the removal of the endometrium or its functional layer, carried out both in the cervical canal and in the place where the entrance to the uterus is located.
What examination is carried out before gynecological cleansing?
Before gynecological curettage, the following studies are carried out:
- electrocardiogram (the operation requires anesthesia, and it affects the heart, so the heart must be normal, the type and dose of anesthesia is determined based on the condition of the heart);
- fluorography (to ensure the health of the lungs);
- ultrasound examination (shows the condition of the uterus, problem areas in its cavity, ectopic pregnancy, etc.).
Other types of research may be required, as well as consultation with specialists - an allergist, oncologist, cardiologist. Sometimes an MRI or CT scan is necessary.
Stages of gynecological cleansing
The operation takes place in several stages. At the appointed time, the woman comes to the small operating room and sits in the gynecological chair. The anesthesiologist will ask questions about allergies to anesthesia, previous illnesses, and chronic diseases.
The following is the operation itself:
- The woman is given anesthesia (usually intravenously), which is enough for the entire period of the surgical intervention - 15-20 minutes.
- The patient does not feel pain and does not remember the manipulations that were performed on her. She sees pleasant dreams (modern anesthesia is used) and wakes up in the ward after the procedure;
- The doctor determines the position of the cervix using a speculum and then fixes it with special forceps. The uterus remains fixed during the operation.
- Then a special stick is inserted into the uterine cavity, which measures the length of the cavity.
- Next comes the stage of cervical dilatation. This is done gradually and carefully, using a dilator. The cervix should open to such an extent that you can freely pass a curette - an instrument similar to a spoon with a sharp edge and a long handle - inside. Curettage is performed using a curette.
- Once the cervical canal has opened to the desired size, the cleaning phase begins. A curette is inserted and the doctor uses it to carry out the main work. If the procedure is needed for diagnostic purposes, scrapings from the uterine mucosa are collected in a jar.
- To prevent the doctor from acting blindly, our clinic uses a modern method - hysteroscopy. A hysteroscope is inserted into the uterine cavity - this is a tube with a camera at the end. Using this device, the doctor sees the uterine cavity and all its walls. Cleaning is carried out under the control of a video camera.
- When the scraping is completed, the camera shows whether everything is done. If anything remains, repeated scraping is carried out until the result is what it should be.
- If some formations cannot be removed with a curette, then other instruments are introduced to remove the pathological areas. We are talking about polyps, synechiae, myomatous nodules growing into the uterine cavity.
- The next stage is completion of the work. After curettage, the forceps are removed from the cervix, and then the doctor treats the area of the cervix and vagina with an antiseptic solution. Ice is placed on the abdomen to stop bleeding in the uterine cavity.
- The patient is transferred to a ward, where she sleeps a little and wakes up. It is recommended to spend several hours in the ward or stay overnight. But if the woman feels normal, she can leave the room some time after waking up. The woman does not feel any pain.
How is separate diagnostic curettage performed?
Curettage of the uterine cavity and cervical canal in our clinic is carried out in our own operating room, equipped in strict accordance with current sanitary and hygienic standards. During the operation, anesthetic equipment with constant monitoring of the patient's condition, disposable materials, surgical equipment and instruments from leading manufacturers of medical equipment are used.
The patient is placed in a gynecological chair and the anesthesiologist performs intravenous anesthesia.
The doctor inserts a speculum into the vagina to expose the cervix. Using special forceps (“bullet pins” there is a tooth at the ends of this instrument) it catches the cervix and fixes it. Using a special probe (iron rod), the doctor enters the cervical canal and penetrates the uterine cavity, measuring the length of the cavity.
Curettage is performed with the smallest curette. A curette is an instrument similar to a spoon with a long handle, one edge of which is sharpened. A sharp edge is used to scrape. The scraping obtained from the cervical canal is placed in a separate jar. If curettage is accompanied by hysteroscopy, then after dilation of the cervical canal, a hysteroscope (a thin tube with a camera at the end) is inserted into the uterine cavity. The uterine cavity and all walls are examined. After this, the lining of the uterus is scraped. If a woman had polyps, they are removed with a curette during curettage. After the curettage is completed, the hysteroscope is reinserted and the result is checked. If something remains, reinsert the curette and scrape it out until the result is achieved.
At the end of the procedure, the patient is transferred to a comfortable day hospital ward, where she remains under the supervision of an anesthesiologist and nursing staff until she fully awakens from anesthesia. After the anesthesia wears off, the patient can be discharged from the clinic.
Recovery after gynecological cleansing
After the cleaning procedure, you should follow your doctor's recommendations. They are:
- do not use vaginal tampons in the first month;
- sexual intercourse should be avoided for 4 weeks;
- treat the genitals daily with antiseptic agents until the healing stage occurs;
- reduce physical activity, completely eliminate sports and heavy lifting;
- For the first 2-3 weeks, do not douche, visit saunas, or take baths.
Pastel mode is not necessary, but hypothermia, stress, and long walks should be avoided.
In general, the gynecological cleansing operation is one of the simplest and most comfortable among all that are available in gynecology. After 10 days, you can get the result of the biomaterial examination.
Answers to frequently asked questions:
- How to get tested for gynecological diseases?
- What diseases does a gynecologist treat?
- What tests can be done by a gynecologist?
- How to prepare for an appointment with a gynecologist?
- Where to go with a gynecological problem?
- What symptoms should you consult a gynecologist for?
- How often should you visit a gynecologist?
- What diagnostics can a gynecologist perform in your clinic?
- What gynecological equipment do you have in your clinic?
- Gynecological care in the clinic
- Gynecological care at home
- How to call a gynecologist at home?
- How to make an appointment with a gynecologist?
Preparing for separate curettage
The procedure for separate diagnostic curettage is carried out only in a hospital setting. To perform a diagnostic procedure efficiently, anesthesia is required, no more than half an hour, but the anesthesiologist cannot guarantee its normal course without the necessary set of tests.
Like any operation, especially if there is obvious ill health in the gynecological field, the method is fraught with complications; their treatment will require qualified medical care; additional emergency examination is guaranteed in the hospital, which is impossible when the clinic works on shifts.
Before the procedure, a standard set of primary diagnostics of gynecological diseases is carried out, tests and cultures of the vaginal flora, of course, the state of blood clotting and examinations by specialists: a therapist and an anesthesiologist.
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
Complication of gynecological cleansing
The professional actions of a doctor and anesthesiologist rarely lead to any complications.
However, there may be the following consequences:
- Perforation of the uterus (damage to the walls). It is theoretically possible to pierce the wall of an organ with any of the instruments used. Statistics show that they are more often perforated with a dilator or probe. This occurs when the cervix cannot dilate easily and excessive pressure is applied to the dilator. Or the structure of the uterine walls itself is loose and easily injured. If such an injury occurs, then thanks to special treatment, minor injuries heal on their own, and large ones are sutured.
- Cervical tear. If the fixing pliers fly off, a similar injury may occur. This is not always a doctor’s mistake; the cervix is sometimes loose, and it is difficult to hold the instrument—fixing forceps—on it. Treatment involves stitching a large tear, and a small one will heal on its own.
- Inflammation of the uterus. Such a complication is possible when there was inflammation, or violations of septic and antiseptic requirements were committed. For treatment, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. Typically, such a course is prescribed for the purpose of prevention.
- Hematometra. This is an accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity. Normally, after surgery, blood gradually comes out. But if a spasm of the cervix occurs, the blood remains inside and causes inflammation, which is accompanied by pain. This complication is treated therapeutically, and bougienage of the cervix may also be prescribed to relieve spasm.
- Damage to the mucous membrane. If the doctor scraped excessively and roughly, he could damage the germ layer of the mucous membrane. And this leads to the fact that the mucous membrane stops growing and regenerating. This is the worst complication because it cannot be treated.
- Incomplete removal of tumors and polyps. If something remains, then the pathological process continues. Requires re-cleaning. More often this happens when hysteroscopy is not used and curettage is performed blindly.
In general, such complications rarely occur if the operation is performed by competent and experienced doctors.
After surgery, a course of antibiotics is usually prescribed to prevent inflammation.
Spotting and spotting lasts from 3 to 10 days after surgery. If this does not happen, there is no discharge, you need to contact your doctor to prevent complications in the form of a hematomera. To prevent this complication, nosh-pa tablets may be prescribed.
After surgery, it is advisable to rest more and reduce physical activity to a minimum. You should be alert to such manifestations as increased body temperature, severe bleeding, severe pain in the pelvis, and a putrid smell of discharge.
Headaches, muscle pain, and panic attacks may result from the body's reaction to anesthesia.
Contraindications and possible complications during the procedure
Absolute contraindications are acute infectious diseases and inflammatory processes of the genital organs.
With a careful and correct approach by a specialist to this manipulation, complications can be avoided. However, you need to be aware of the possible complications of curettage:
- perforation of the uterus.
- cervical rupture.
- inflammation of the uterus. Occurs when microbes enter the uterus. Currently, to prevent infection of the uterus after curettage, doctors prescribe a course of antibiotic treatment.
- accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity (hematometra). If, after curettage, a spasm of the cervix occurs, blood, which normally should flow from the uterine cavity for several days, accumulates in it and can become infected and cause pain.
- damage to the mucous membrane (excessive curettage) - if you scrape very hard and aggressively, you can damage the germinal layer of the mucous membrane, which will lead to the fact that the new mucous membrane will no longer grow.
Cleaning the uterus after bleeding
Bleeding from the uterus can occur for several reasons:
- Endometritis - if after an abortion the fertilized egg remains incompletely removed or pathogens such as streptococci, staphylococci, gonococci have entered.
- Bleeding due to hormonal imbalance;
- Hematometra is an accumulation of blood in the uterus due to cervical spasm.
Cleaning is carried out if there are fetal remains or polyps in the uterine cavity. The task of gynecological curettage is to stop bleeding and eliminate the causes that cause it. Otherwise, anemia gradually develops. The doctor prescribes hemostatic agents and drugs that promote uterine contraction.
If the pathology is infectious, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. And in case of hormonal disorders, consultation with an endocrinologist is necessary.
In addition to drug treatment, a nutritious diet is necessary, which contains foods that promote hematopoiesis. These are beef liver, buckwheat, red meat, pomegranate, beets, parsley.
Cleaning after a miscarriage
Miscarriage is artificial, with the help of medications, and natural - with a frozen pregnancy or cervical pathology.
Cleaning is usually carried out during a frozen pregnancy to prevent blood poisoning and bring out the dead embryo.
Gynecological cleansing during a miscarriage is the most effective and does not cause physical pain.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The steps of the procedure are:
- The gynecologist determines whether there are any contraindications to surgical intervention - infections, inflammation of the uterus or appendages, violation of the integrity of the lining of the uterus.
- The operation is performed on a gynecological chair after the administration of anesthesia.
- If anesthesia is contraindicated, local anesthesia may be used.
- The doctor dilates the uterus, inserts a curette into it, and cleanses it.
- It is important to completely remove the placenta and fertilized egg during surgery. After cleaning, the vagina and cervix are treated, and cold is applied to the stomach. After a few hours, the woman can leave the clinic.
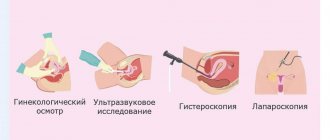
Methods for diagnosing gynecological diseases:
- Calling a gynecologist to your home
- Diagnosis of gynecological diseases
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections in women
- Colposcopy
- HCG tests
- Ultrasound during pregnancy
- Pelvic ultrasound
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted diseases
- Fetal ultrasound
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands
- Ultrasound during pregnancy
- Transvaginal ultrasound
- Ultrasound of the ovaries
- Ultrasound of the uterus
- Cervical smear
- Vaginal smear
- Hormone tests
- Tests for sexually transmitted infections
Therapeutic and diagnostic curettage indications and contraindications:
- for various menstrual disorders
- for dysfunctional uterine bleeding
- for polyps of the endometrium and cervical canal
- after spontaneous miscarriage
- for infertility
- for suspected oncology and endometrial tuberculosis
Absolute contraindications to curettage are acute infectious diseases, inflammatory processes of the genital organs, decompensated chronic diseases of internal organs, pregnancy, etc. Therefore, before therapeutic and diagnostic curettage, a gynecological examination, ultrasound of the pelvic organs, ECG, and clinical and biochemical tests are mandatory. blood, blood for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis.
Cleaning after abortion
Sometimes after an abortion you have to resort to gynecological cleansing. This happens in the following situations:
- After a medical abortion, the embryo did not come out.
- After a vacuum abortion, part of the fetus remained inside.
- After a surgical abortion, the entire fertilized egg was not removed.
Usually, the remains of the embryo in the uterus make themselves known through bleeding and discharge similar to meat slop with an unpleasant odor. Body temperature also increases. This is a dangerous condition. Before gynecological cleansing, the patient is sent for a series of tests and laboratory tests. This is an ultrasound examination of the uterine cavity, a general blood test, a blood test for hidden infections, and a vaginal smear.
Preparing for surgery
- General examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist;
- Refusal to eat on the day of the procedure and the evening before;
- Consultation with an anesthesiologist;
List of tests that should be taken before surgery:
- HIV tests;
- Tests for hepatitis groups C and B;
- RW tests;
- Blood analysis;
- Vaginal smear.
Additional Information:
- Curettage for diagnosing uterine fibroids;
- Curettage during frozen pregnancy;
- The period after curettage;
- Consequences caused by the curettage operation;
- Bleeding after curettage;
- Gynecological cleansing after miscarriage;
- Pregnancy after cleansing;
Why do gynecological cleansing?
Gynecological cleansing is prescribed in the following cases:
- prolonged bleeding with the presence of blood clots;
- bleeding between periods;
- incomplete removal of the fertilized egg during abortion;
- frozen pregnancy, miscarriage;
- infertility;
- endometriosis;
- polyps, fibroids;
- changes in the uterine mucosa, changes in the cervix.
Cleaning is also prescribed when it is necessary to obtain biomaterial for research - mucous membrane from the walls of the uterus.
Indications for gynecological cleansing:
Therapeutic direction of curettage:
- Uterine bleeding;
- Fusion of the walls of the uterine cavity (synechia);
- Polyp;
- Endometritis;
- Hyperplasia;
- Remains of embryonic tissue/fetal membranes after termination of pregnancy.
Diagnostic direction of curettage:
- Changes in the cervix;
- Changes in the uterine mucosa;
- Heavy menstruation with clots;
- Intermenstrual discharge of unknown etiology;
- Infertility;
- Preparation for surgical gynecological intervention.
Is pregnancy possible after cleansing?
After gynecological cleansing, the menstrual cycle is usually disrupted. Recovery takes 4-5 months.
Pregnancy can occur after the menstrual cycle normalizes - this is after about 4 months.
If the cleansing was carried out for the purpose of treating infertility, then after the operation the chances of getting pregnant increase many times over. If the patient plans to become pregnant after curettage, then this should be discussed with the attending doctor.
Common symptoms and manipulations in gynecology:
- Vaginal discharge
- Discharge from the urethra
- Discharge from the uterus
- Intrauterine device
- Female infertility
- Delay of menstruation
- Itching in the vagina
- Brown discharge
- Abortion
- Perineal pain
- Cervical erosion
- Abortion pills
- Vacuum abortion
- Medical abortion
- Surgical abortion
- Cervical biopsy
- Diagnostic curettage
- Folliculometry
- Make an appointment with a gynecologist
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
There are a number of symptoms that indicate the need to see a doctor for medical help. These include:
- elevated temperature, fever;
- significant vaginal bleeding (intensity as during menstruation or heavier);
- sharp pain in the lower abdomen.
In rare cases, discharge may appear yellowish in color or with a pungent and unpleasant odor. This may be a sign of a sexually transmitted infection.
Vacuum gynecological cleaning
Vacuum aspiration is one of the most common methods of abortion. Conducted during pregnancy up to 15 weeks. Manual vacuum aspiration – up to 9 weeks.
The advantages are:
- conventional medical instruments that are inserted into the uterine cavity are not used, as a result, the organ is not at risk of injury;
- in the early stages does not require general anesthesia;
- does not cause much damage to hormonal levels, since pregnancy is still in the early stages of development;
- the operation lasts only 3-10 minutes;
- return to normal life occurs within a few hours:
- minimal risk of complications.
As a rule, in this case it does not take much time to restore health. However, the method also has contraindications, the main one being exceeding the permissible gestational age.
What anesthesia is used before gynecological cleansing?
The curettage operation is quite painful and therefore requires anesthesia. During gynecological cleansing, three types of anesthesia can be used:
- Local anesthesia. The doctor makes injections that eliminate pain in the pelvic area. At the same time, the woman is aware of what is happening and hears the doctors. The disadvantages of such anesthesia are that the woman can still feel some sensations. This type of anesthesia is used if there are contraindications to general anesthesia.
- Sedation. This type of anesthesia is widely used. A special drug is injected into a vein. The patient is half asleep. At the same time, she can hear something, but feels absolutely nothing. This type of anesthesia does not turn off all important systems of the body, but dulls sensations. It is easy to recover from such anesthesia.
- Intravenous (general) anesthesia. This type of anesthesia requires the presence of an anesthesiologist and special equipment. During the operation, the patient is completely asleep, does not hear or feel anything. After the operation she returns to consciousness. It depends on an experienced anesthesiologist how easily a woman recovers from anesthesia. Modern types of intravenous anesthesia are used, the recovery from which is softer.
The doctor decides which anesthesia to prefer based on the individual characteristics of the woman’s body, the duration of pregnancy, and the complexity of the surgical intervention.
Gynecological cleansing during frozen pregnancy
Gynecological cleansing in the event of a frozen pregnancy is the most reliable way to remove a dead embryo. Used for many years all over the world. However, the appropriateness of this procedure is determined by the doctor.
A frozen pregnancy is also determined by a doctor based on indications.
Cleaning is carried out on a gynecological chair using general or local anesthesia. The patient does not feel pain or discomfort. She falls asleep during the procedure and wakes up in the ward after all the manipulations.
The doctor’s task is to remove the dead embryo before infection of the woman’s blood begins. Curettage is performed using a curette inserted into the uterine cavity.
Before the operation, the woman donates blood for analysis, and also undergoes an ultrasound examination, possibly MRI and fluorography.
After a high-quality operation, the woman’s health is completely restored within a month.
The rehabilitation period depends not only on the quality of the operation performed, but also on the state of health of the woman herself and on the duration of the frozen pregnancy. The shorter the period, the lower the risk of complications.
Recovery after uterine curettage
Some patients experience minor pain localized in the lower abdomen during the postoperative period. They can be dealt with by taking any painkillers. Discharge after curettage of the uterine cavity may appear within two weeks. This is not a deviation from the norm and a cause for concern.
The regimen after curettage of the uterus is prescribed by the attending physician. As a rule, if this procedure goes without complications, the patient will be able to return to normal life the next day.
Where to do gynecological cleansing
Despite the simplicity of the operation, such intervention in the body should be entrusted to a trusted clinic and experienced doctors. In our medical institution, medical workers have extensive experience, all services are certified.
Advantages of choosing our clinic:
- Gynecological cleansing of any type of complexity is carried out;
- you can choose any convenient day, as we work seven days a week and holidays;
- the operating room is equipped with modern technology;
- its own laboratory facilities make it possible to obtain full tests, the results are accurate and fast;
- Individual approach, friendly atmosphere and comfortable conditions.
The doctor will also give comprehensive recommendations for successful rehabilitation after surgery. A modern method is used - hysteroscopy.
Which doctor performs gynecological cleansing?
Cleaning the uterus is performed by a gynecologist who has undergone appropriate training and is certified. In our clinic, such surgical interventions are performed by a gynecologist with extensive experience and an impeccable reputation.
Cleaning the uterus is also called curettage. This procedure is carried out for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes.
During the procedure, the doctor removes the top layer of the uterine mucosa for diagnostic testing, and also removes from the uterus the remains of the fertilized egg remaining during an incomplete abortion. Or polyps, fibroids and other tumors are removed.
An experienced gynecologist performs this operation completely painlessly and without complications.
Publication date 2019-11-06