Why do you need to do an ultrasound after childbirth?
Ultrasound of the uterus after childbirth, especially if there was a cesarean section, helps specialists monitor the condition of the woman’s internal organs. Having identified deviations from the normal course of recovery in time, the doctor can prescribe a course of treatment.
In addition, during surgery, a scar from the suture may remain on the inner surface of the uterus, which will affect subsequent births. Therefore, experts recommend that an ultrasound scan of the uterine scar after a cesarean section be performed.
How does the uterus change after cesarean section?
The uterus is large and has a damaged inner surface. Over time, the process of healing and reduction occurs. Ultrasound records a decrease in the size and weight of the uterus, but after a cesarean section the process occurs more slowly and is accompanied by postpartum discharge.
It is important for the specialist to monitor the condition of the internal organs after surgery and stimulate the speed of their recovery with the help of medications, if necessary. Therefore, regular ultrasound of the uterus is especially important after a cesarean section.
Interpretation of postpartum ultrasound results
Criteria for the normal state of the uterus according to ultrasound in the postpartum period (3rd day):
- The shape is close to spherical, the tone is increased.
- The cavity is slit-like, with clear contours, width in the upper part is up to 1 cm, in the lower part up to 1.5 cm.
- A small number of blood clots are acceptable.
- The bottom above the pubic symphysis is at a height of 10–13 cm.
- The endometrium (inner layer of the uterus) has a folded structure.
- Weight about 600–700 g.
- At the site of placental rejection there is a rough wound surface with thrombosed vessels.
- A small amount of gas and decidual tissue (the layer between the placenta and uterus) is torn away is acceptable.
- The normal size of the uterus is: length 125–135 mm, width 120–130 mm, anteroposterior size 65–68 mm.
Pathology by ultrasound:
- Subinvolution of the uterus is a pathological slowing of contractions. On ultrasound, the size exceeds the norm, there are hyperechoic (dark gray) inclusions in the cavities (a large number of blood clots and placental remnants). This condition can lead to infection. The shape of the uterus is spherical.
- Signs of endometritis (infection of the uterine cavity) - ultrasound reveals a decrease in tone (thinning of the uterine wall), a large number of blood clots, placental tissue, accumulation of gases in the cavity (looks like a hypoechoic formation - light gray, white).
- Remains of placental tissue and membranes can cause postpartum hemorrhage; it is important to remove them in time. Bleeding may also occur 6–8 weeks after birth.
Also see ultrasound pathology after childbirth:
How is an ultrasound of the uterus performed after a cesarean section?
Most often, the examination is carried out on the first day after birth using a transabdominal method.
, that is, through the abdominal wall.
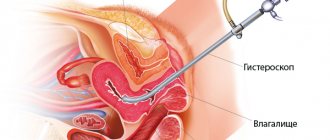
A transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus
is performed after a cesarean section, when a specialist needs to determine the condition of the cervix. Then the sensor is inserted into the vagina. The question of when to perform an ultrasound of the uterus after a cesarean section and how to do the examination is decided by the specialist based on an analysis of the patient’s condition.
How will the inspection take place?
At your first visit to the gynecologist after discharge from the maternity hospital, the doctor will ask in detail about how the birth proceeded and how it ended, how the postpartum period proceeded or is proceeding, fill out a medical record, paste into it the documents you submitted from the maternity hospital, and be sure to conduct an examination on the chair.
During natural childbirth, ruptures of soft tissues, cervix, and perineum are possible. Immediately after childbirth, an obstetrician-gynecologist examines the woman’s birth canal and applies sutures. While the woman is in the maternity hospital, the sutures are processed, and before discharge (approximately on the fourth or fifth day), the external sutures are removed. At the same time, the obstetrician-gynecologist recommends not sitting down, not lifting heavy objects, and strictly observing personal hygiene for 6-8 weeks. If these recommendations are not followed, there may be complications: suture dehiscence, suppuration.
During the examination, it is important for the doctor to assess the condition of the external genitalia: whether there are stitches on the perineum, labia and in what condition they are. It is also necessary to examine the walls of the vagina and cervix. Failure of sutures on the walls of the vagina can lead to the formation of fistulas (through holes - for example, between the rectum and vagina).
If the cervix is not sufficiently formed (has an irregular shape), then this is most often due to undetected tears or broken sutures on the cervix. In this case, it is necessary to apply secondary sutures, otherwise it can lead to chronic inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis) and infertility. The gynecologist will take smears from the cervix and vagina for analysis. This analysis will allow you to determine the onset of inflammation in the vagina or cervical canal and prescribe treatment in a timely manner, preventing the spread of infection.
By feeling the body of the uterus and ovaries, the doctor assesses their size and consistency. A flabby, painful, enlarged uterus indicates the onset of endometritis (inflammation of the mucous layer of the uterus).
If the birth ended with a cesarean section, then you should consult a doctor a few days after discharge from the maternity hospital. After a caesarean section, the contraction of the uterus is somewhat slower due to the incision and suture, which disrupt the structure of the muscle fibers.
Both the doctor and the young mother must be sure that the postoperative suture is healing well and will not cause any trouble in the future. Proper care of the postoperative suture at home is very important. After a hygienic shower, the seam must be lubricated with brilliant green (a solution of brilliant green); The underwear that comes into contact with it should be cotton and loose, not constricting. Treatment of the seam with medications should be carried out until crusts form on it.
What will an ultrasound of the uterus show after a cesarean section?
The recovery period can last up to 6 weeks after birth. Within a month and a half, involution of the organs of the reproductive system occurs - they return to their pre-birth state. The process can be complicated, so the size of the uterus, shape and other important changes after cesarean section should be monitored by a specialist using ultrasound data.
By the end of 3 days, the shape of the uterus should become round. In the future, changes in the contours of the uterus on ultrasound will be more and more noticeable; by the 5th day after cesarean section it should become oval. With normal postpartum recovery, the uterus will be pear-shaped within a week.
Another important indicator of normal involution is the position of the uterus. On the 4th day, it takes a position between the navel and pubis. On an ultrasound of the uterus, done on the 9th day after a cesarean section, it will be higher than the womb.
Uterus dimensions
Normally, a decrease in uterine ultrasound is more and more noticeable every day after a cesarean section. On the 2nd day, its normal length and width will be 13.6-14.4 cm and 13.3-13.9 cm, respectively. On an ultrasound of the uterus on the 4th day after a cesarean section, it should normally be 11.5-12.5 cm in length and 11.1-11.9 cm in width. On the 8th day it should not exceed 10.6 cm in length and 10.5 cm in width.
An ultrasound can determine the weight of the uterus; every day after a cesarean section it should decrease. On the 7th day, the organ should weigh 500-600 g, after two weeks - 350 g. On the 3rd week, the normal weight for the uterus is 200 g, and after six weeks - 60 g.
Clots in the uterus after cesarean on ultrasound
Clots on an ultrasound of the uterus immediately after a cesarean section are concentrated in the upper sections. With normal recovery, after seven days there should be fewer clots and they should move downwards.
If clots continue to appear on an ultrasound of the uterus for a long time after a cesarean section, an inflammatory process has most likely begun. Then the uterus will contract more slowly than it should, and its internal cavity will be deformed and expanded.
Interpretation of ultrasound results of the cervix after childbirth
The involution process normally lasts about two months. During this time, the cervix should decrease in diameter and lengthen.
After each subsequent birth, the length of the cervix decreases slightly. If before the first pregnancy its indicators are on average 3.5-4 cm, then before the second they decrease to 3.2-3.8 cm.
The diameter of the cervix also decreases, but even after recovery it will be larger than before the first pregnancy.
An ultrasound after childbirth can reveal a bend in the cervix and blockage of the pharynx with blood clots.
What kind of discharge is normal after cesarean section?
Immediately after surgery, constant monitoring is required. Specialists watch the patient’s standing and carefully monitor the amount and nature of discharge from the uterus. In the first 5-7 days, they resemble discharge during menstruation, but are more abundant (up to 500 ml). The discharge is usually red and contains clots.
Over time, the number of lochia decreases and their color becomes darker. By 4-5 weeks there are very few of them. The color of the discharge is dark. The process of restoration of the uterine mucosa ends by 6-8 weeks. By this time, the discharge should not differ from the discharge before pregnancy.
Control procedure
A standard postpartum ultrasound examination is performed 2–4 days after the date of birth. In case of unnatural delivery (cesarean), the doctor prescribes the timing of the procedure on an individual basis. An urgent ultrasound should be done when a woman exhibits the following symptoms:
- copious separation of clots;
- intense outflow of blood from the vagina;
- febrile or pyretic body temperature (38–41 °C);
- unbearable pain in internal organs;
- pain, swelling, wetting of the postoperative suture (in case of cesarean section).
Based on the results of ultrasound diagnostics, conservative therapy or emergency surgery is prescribed to eliminate the complications that have arisen. A control ultrasound is performed in the maternity hospital and only after this the woman is discharged home. A re-examination should be done in a week.
Preparation and execution
Since the birth process is already over and there is no amniotic fluid, to visualize the uterus before the study, it is necessary to fill the bladder. The amount of liquid you drink should be at least two liters. In case of an urgent procedure, fluid is administered through a catheter, followed by the prescription of diuretic medications.
After childbirth, an ultrasound is usually performed abdominally, that is, externally. Transvaginal (internal) examination is informative only when examining the cervix. The organ itself is still too voluminous, so an intravaginal sensor will not give an objective result. The time interval of the procedure is from 20 to 40 minutes, depending on the health of the reproductive system.
Study parameters
Postpartum examination of the patient’s reproductive system is aimed at identifying possible pathologies leading to complications. The assessment is made according to the following parameters:
Ultrasound of the genitourinary system
- contractility, location and size of the uterus;
- the presence of organic formations (pieces of the “baby place”, blood clots, fragments of the fetal membrane);
- the presence of excess fluid in the uterine cavity;
- possible inflammatory processes of the endometrium;
- condition of the postoperative suture (if a caesarean section was performed);
- general condition of the pelvic organs.
The indicators obtained during ultrasound diagnostics are compared with average standards. If there is a discrepancy between the values, the patient is prescribed special treatment. In case of an uncomplicated postpartum period, it is recommended to visit a gynecologist after a month. At your appointment, the doctor will determine the need for ultrasound monitoring.
Changes in the uterus: immediately after delivery, a week later, after 5 weeks
Service cost*
| NAME | PRICE (Kolomenskaya) | PRICE (Vidnoe) |
| Transabdominal ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages (using a Voluson, Mindray, Logiq device) | 1850 rubles | 1850 rubles |
| Transvaginal ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages (using a Voluson, Mindray, Logiq device) | 2050 rubles | 2050 rubles |
| Transrectal ultrasound examination of the uterus and appendages (using a Voluson, Mindray, Logiq device) | 2050 rubles | 2050 rubles |
We accept payment:
*Attention! The indicated prices are provided as reference information and do not constitute a public offer. Check current prices by phone and directly in clinics.
Standard indicators of the reproductive system in the postpartum period
Features of the restoration of the internal genital organs depend on the method of delivery (naturally or through cesarean section).
Rehabilitation after natural childbirth
After the natural birth of the baby, an ultrasound examination procedure is prescribed from the second to the fourth day. In case of complicated labor, if uterine rupture is suspected, an ultrasound scan is performed immediately. Upon longitudinal examination, the uterus has an ellipsoidal shape. The organ is localized in the middle part of the small pelvis. Some downward displacement is observed after the birth of two or more children or one large baby.
The study can track the dynamics of decrease in uterine weight and narrowing in size. The decrease in volume of the uterus and its movement towards its natural location occurs gradually. The rate of advancement is 1–2 cm daily. In terms of weight, the organ loses about half its mass in the first week (400–500 grams). Further weight loss occurs smoothly, approximately 100 g per week, to the initial 90–100 grams. The main indicators that the doctor measures on the monitor during the examination relate to the uterus itself and the uterine cavity.
Average digital parameter values
| Parameter/value in millimeters | Second postpartum day | Fourth day | One week from the date of birth |
| Uterus | |||
| Length | 136–144 | 115–125 | 94–106 |
| Width | 133–139 | 111–119 | 95–105 |
| Anterior-posterior size | 68–72 | 65–71 | 61–68 |
| Uterine cavity | |||
| Length | 149–153 | 89–95 | 70–78 |
| Width | 104–116 | 40–46 | 31–35 |
| Anterior-posterior size | 52–71 | 30–50 | 28–36 |
Ultrasound diagnostics after caesarean section
Rehabilitation of the reproductive system after cesarean section lasts longer, since the weight and size of the uterus after surgery increases, on average, by 40% compared to natural labor. During an ultrasound, the doctor can observe small hematomas in the area of the postoperative scar. They are not dangerous, but they make it difficult for ultrasonic waves to pass through. Swelling of the scar may indicate the onset of an inflammatory process in the endometrium.
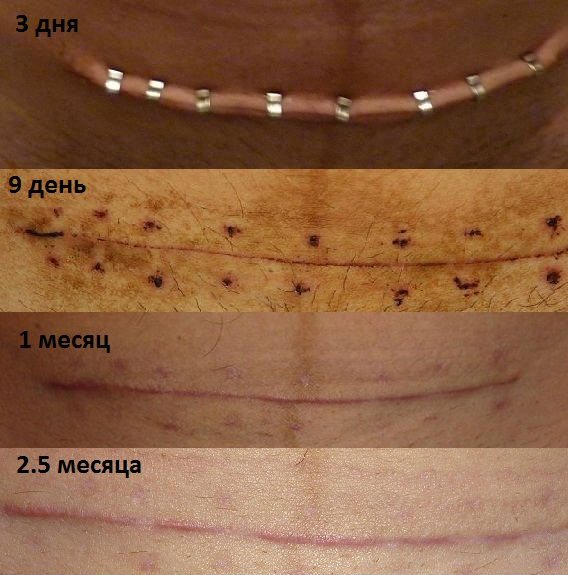
Optimal condition of the postoperative scar
The uterus decreases by 200–250 grams in the first seven days. The organ returns to its original weight parameters in approximately eight weeks. It takes on its original form no earlier than 10–12 days. The main measurement parameters (length, width, anterior-posterior size) also lag behind those for natural childbirth. After surgical delivery, a more thorough ultrasound diagnosis of the ovaries and blood vessels is carried out to ensure their integrity.
The control ultrasound procedure is prescribed individually, depending on the results obtained.
Ultrasound before discharge from the maternity hospital
An ultrasound examination of the internal genital organs is performed for every woman who has given birth 3-4 days after birth, before discharge from the hospital. During the procedure, the doctor checks the condition of the uterus, ovaries and cervix through the anterior abdominal wall. Ultrasound through the vagina in the first days after childbirth is not used due to the large size of the uterus. Using a transvaginal sensor, it is difficult to thoroughly examine all parts of this organ.
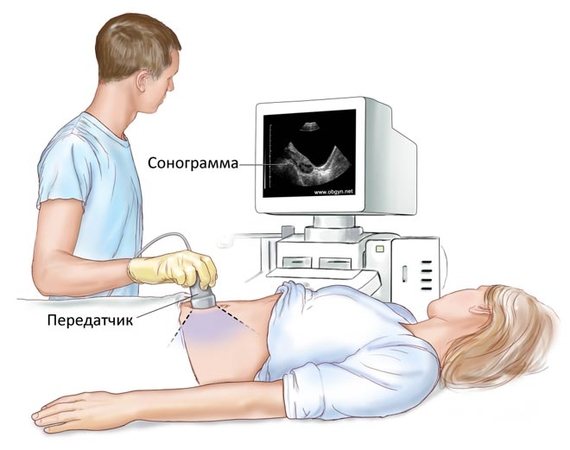
Transabdominal ultrasound
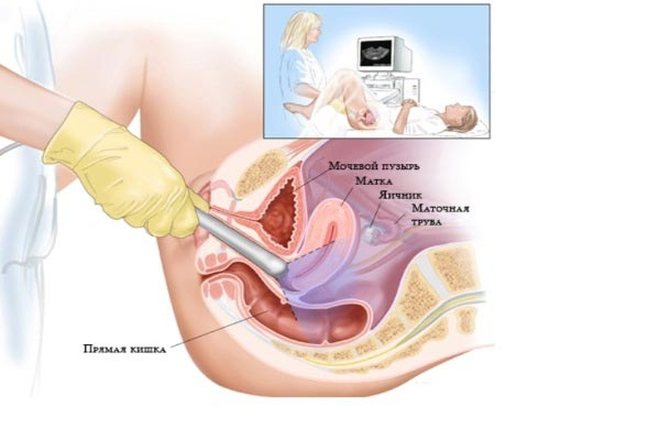
Transvaginal ultrasound
After childbirth, the uterus gradually returns to its pre-pregnancy state. This process is called involution. An ultrasound diagnostic doctor determines the condition of the woman’s internal genital organs and gives permission for discharge from the postpartum department. It is important to consider the following indicators:
- Do the dimensions of the birth canal correspond to the norms?
- Are blood clots present and in what volume?
- How the placental site heals.
- Is the structure of the inner surface of the uterus homogeneous?
- What is the condition of the uterine veins?
- If there was a caesarean section, the doctor checks the condition of the suture.
Normal indicators of the uterus after childbirth
If the birth took place without complications, then the involution of the birth canal occurs at a normal pace.
An ultrasound scan 3-4 days after birth reveals small amounts of blood clots in the upper parts of the uterus. After 7-8 days they descend closer to the exit from the organ cavity. Immediately after birth, the uterus is shaped like a ball, after 3 days it becomes an oval, after 7 days it takes on a pear shape. The tone of the pelvic floor muscles is restored. They gradually shift the uterus to its previous location. Immediately after birth, the fundus of the uterus is located 4 cm below the navel, a week later - in the middle of the distance between the pubic bone and the navel.
The weight of the uterus is also determined by ultrasound. Immediately after giving birth, she weighs 900-1000 grams. A week later - 500-600 gr. After 2 weeks it’s already 350 gr. By the end of the postpartum period, after 5-7 weeks, it returns to its previous volume - 60-70 grams.
By the end of the postpartum period, the uterus returns to its pre-pregnancy size
What problems does ultrasound reveal?
Using an ultrasound examination, the doctor can diagnose postpartum complications in a timely manner:
- Bleeding. Ultrasound examination reveals the presence of a large volume of liquid blood and clots in the uterine cavity. The causes of postpartum hemorrhage are problems with blood clotting, difficult labor, and a bleeding placental site.
- Endometritis. The inflammatory process is defined as the heterogeneous structure of the mucous membrane of the inner surface of the uterus. The cause of endometritis is a complicated course of childbirth, delayed discharge in the uterine cavity, and chronic foci of inflammation in the body. Read more about endometritis in our article (…)
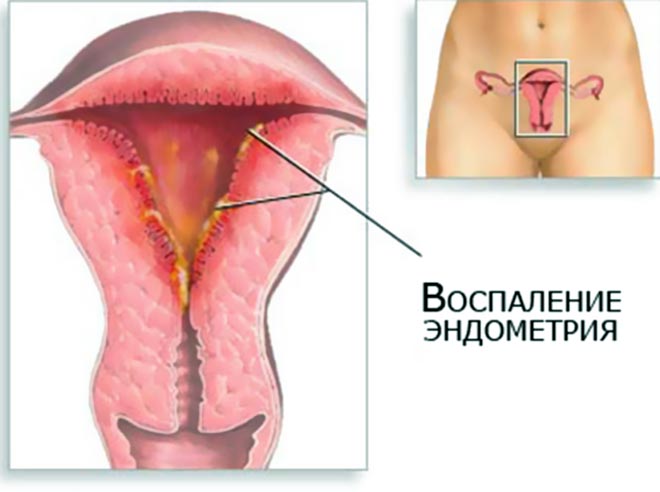
- Subinvolution of the uterus. This diagnosis is made in the case of a slow decrease in size of the organ. The discrepancy between the size of the uterus and postpartum norms occurs due to a violation of its contractility.
Ultrasound after childbirth helps to timely determine the rate of uterine involution, and as a consequence of postpartum complications. If the contractions are weak, the doctor will prescribe medications that will make it contract more actively.
Indications for urgent ultrasound
In some cases, the recovery period is delayed. This is associated with the occurrence of postpartum complications. If, after discharge from the maternity hospital, a woman is bothered by changes in the nature of discharge or pain, she should consult a doctor. The following symptoms may be indications for an ultrasound:
- The suture hurts after a cesarean section or ichor comes out of it.
- Failure of the postoperative suture or inflammation of the tissue around it.
- The discharge suddenly increases and has an unpleasant odor. This indicates endometritis.
- The woman's body temperature increased. The inflammatory process is accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
- Bleeding began and the pain suddenly became intense. The cause may be a placental polyp. This pathology is a proliferation of the mucous membrane at the placenta insertion site.
It is often possible to establish the cause of the pathology only by ultrasound. Therefore, if these symptoms appear, you should definitely consult a doctor.
If childbirth and the early postpartum period passed without complications, and the first ultrasound showed that the uterus is recovering normally, then the woman needs to visit a gynecologist after the end of lochia. And after the examination, if necessary, do an ultrasound.
Ultrasound during the postpartum period can be performed as often as necessary. Ultrasonic waves do not harm a woman's health.