In the first year of life, quite a lot of diseases, defects and anomalies in the development of internal organs do not have obvious manifestations.
Ultrasound allows you to correctly diagnose in the early stages of the disease, prescribe treatment in a timely manner, and often improve the prognosis and quality of life of the child.
The importance of timely ultrasound is emphasized by the fact that its use in young children is strictly regulated by the Orders of the Ministry of Health and Social Development, which allows its use in screening (that is, mass) diagnostic programs and detection of diseases at the earliest stages.
Absolutely every person has encountered an ultrasound examination. Currently, there are practically no organs that cannot be “seen” using ultrasound. Restrictions exist only for the lungs and bones.
Examination of children under 1 year of age
using ultrasound has a number of advantages compared to other types of examinations - it is not painful, not dangerous, quite fast and, most importantly, very informative. Even very premature babies weighing less than 1 kg can be examined.
Main research:
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys and urinary tract, hip joints, brain (neurosonography), ultrasound of the heart (echocardiography) and other organs.
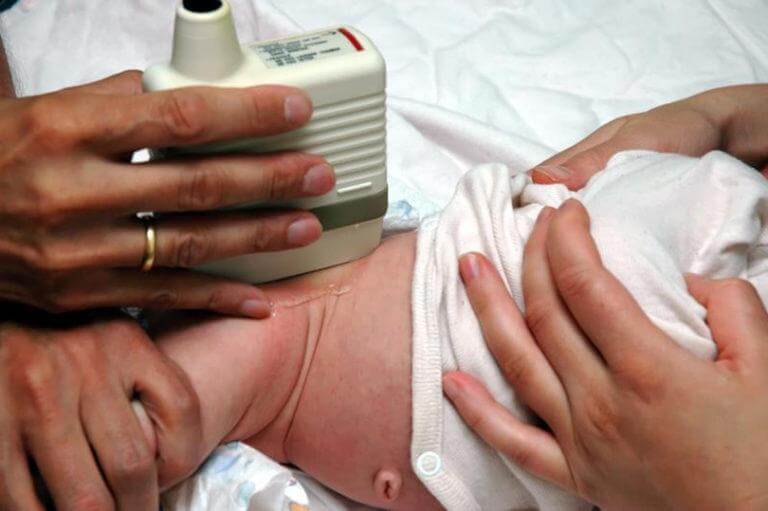
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Conducted for all children at the age of 1 month at the first full examination in a children's clinic.
The study evaluates the size of the abdominal organs, their structure and relative position, as well as the presence of additional formations, inflammatory changes, and traumatic injuries. Based on the results of an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, damage to the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, and pancreas can be detected. The most often excluded are:
- inflammatory diseases (hepatitis - inflammation of the liver, cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder, pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas);
- congenital developmental anomalies;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- parasitic infestations (infection with worms);
- cholelithiasis (formation of stones in the gall bladder and bile ducts).
Preparing for the study. Preparation for an abdominal ultrasound is very important. The study is carried out strictly on an empty stomach! You cannot eat, drink, or take medications. This is the main condition for high-quality implementation of the procedure. The baby’s gastrointestinal tract must be absolutely calm, since gases, peristalsis, and digestion change the image and distort the result of the study, and also simply mechanically block part of the organs being examined.
Indications for NSG
Neurosonography in newborns is performed in maternity hospitals. The study is prescribed if the following indications exist:
- Prematurity. This term is used to refer to the condition of a fetus born before the end of the normal period of intrauterine development. A baby born is considered premature if the gestational age (the period lasting from the first day of the last menstrual period until birth) is less than 36 weeks.
- Low results of assessing the condition of the newborn. It is performed using the Apgar score at 1-5 minutes of life. Within normal limits, this indicator should be equal to 7 points. NSG is carried out in cases where the child receives less than 7 points 5 minutes after birth.
- Low body weight. In newborns, this figure can be within the normal range from 3 to 3.5 kg. Minor deviations are allowed. Body weight not exceeding 2800 g indicates the possible presence of serious pathologies. With this indicator value, NSG is carried out.
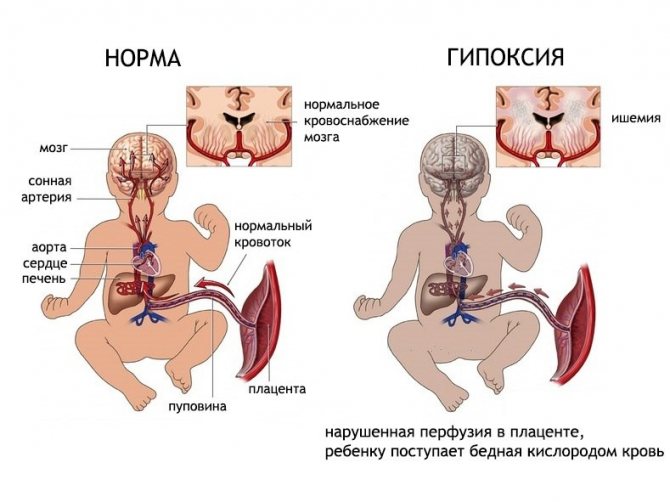
Indications for the study are also a history of chronic intrauterine hypoxia, infectious diseases in the newborn child and his mother, and asphyxia that occurred during childbirth. Neurosonography is also necessary in the presence of clinical signs of dysfunction of the central nervous system (constant trembling, tremors of the limbs and chin, decreased motor activity), multiple stigmas of disembryogenesis (small deviations in the anatomical structure of any organs).
Neurosonography of the brain
After discharge from the maternity hospital, NSG is prescribed to children in the 1st month of life. The study is carried out in a children's clinic. After the 1st month of life, neurosonography in children is performed for the same indications as in newborns (prematurity, low birth weight, signs of central nervous system damage and multiple stigmata of disembryogenesis). Repeated examinations are prescribed if indicated and to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
Ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract

Performed on all babies at the age of 1 month. Additionally, a study is prescribed for suspected inflammation (usually changes in urine analysis - detection of leukocytes, red blood cells, mucus), injuries to the back and abdomen, pain, and suspected congenital malformations. This study allows us to draw a conclusion about the functioning of the infant’s urinary system, evaluate the structure, shape, location of the kidneys and ureters, as well as the shape, size, volume of the bladder, the condition of its walls, and the volume of residual urine after urination. During the examination, it is possible to draw a conclusion about the functional state of the kidneys and bladder, and find the cause of urination disorders.
Preparing for the study. Preparing for an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder also requires meeting certain conditions. A full bladder is required for a full examination. Therefore, you need to take a bottle of water with you or prepare for breastfeeding before the test. It is quite difficult for a baby to catch the moment of urination, but just in case you should have a “strategic supply” of liquid with you. The approximate amount of liquid is at least 100 ml.
Indications for the procedure
To exclude congenital brain pathologies, conduct neurosonography at least once on all children under one year of age. The procedure is mandatory for premature and weakened infants.
Indications for neurosonography:
- Unusual head shape in infants and abnormalities of the facial skeleton;
- Intrauterine/birth hypoxia (acute oxygen deficiency);
- Suspicion of infectious diseases of the brain;
- Birth injuries;
- Difficult childbirth;
- Symptoms of neurological pathologies (convulsions, lack of reflexes and psychomotor abnormalities, low muscle tone);
- Bulging of the fontanelle;
- Brain herniation;
- Body weight is less than the established norm (2280 g).
If necessary, the study can be scheduled several times (with a break of 1–2 months): this is necessary to track the dynamics of changes.
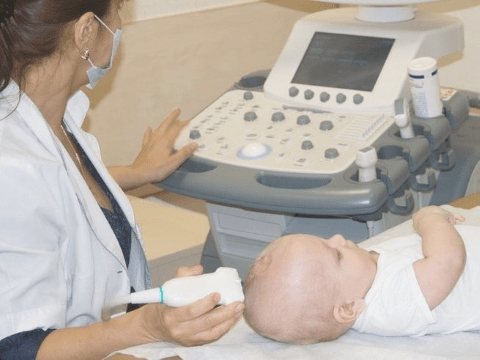
Ultrasound of the brain (neurosonography)
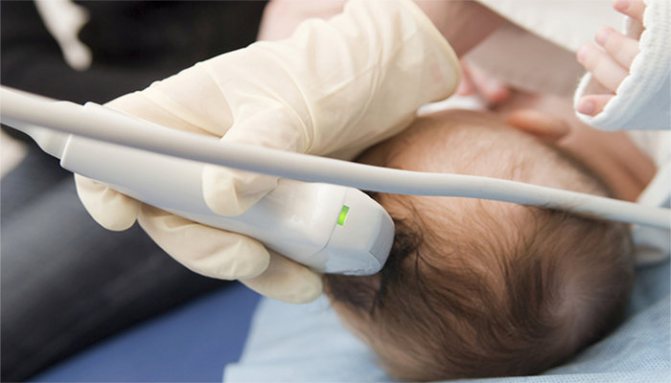
This is a rather unusual study, which can be carried out in an extremely limited period of time - until the fontanelles on the baby’s head close. Fontanas are acoustic windows that, unlike bone tissue, do not interfere with the passage of ultrasonic waves. The large fontanelle usually closes by the end of the first year of life, but in some children this happens earlier - already at the 3-4th month of life. Neurosonography is performed on all children at the age of 1 month. Early ultrasound of the brain makes it possible to study its structure, diagnose possible structural changes (ischemic lesions, cysts, neoplasms, hemorrhages, pathological widening of structures), identify many pathological conditions of the central nervous system before their clinical manifestations, make a diagnosis in time and prescribe adequate treatment, which , in turn, leads to a significant improvement in the prognosis for the life and health of the child.
Preparing for the study. No special preparation is required for neurosonography. It is advisable that the child be active during the study.
Carrying out the procedure
Neurosonography in a child is performed using special ultrasound equipment. The doctor places the sensor in the area of open fontanelles, which makes it possible for ultrasound waves to freely penetrate into the structures of the brain. Thanks to this, an image corresponding to the reflected waves appears on the monitor, on the basis of which a conclusion is drawn about the state of the brain.
Neurosonography does not require any preparation and can be performed even on a sleeping baby. The procedure does not bring any discomfort and lasts 10-15 minutes.
Ultrasound of the hip joints
It should be performed on all children in the first month of life, regardless of the presence or absence of indications. Ultrasound allows you to identify pathology of the hip joints (delayed development of the joint, dislocation, subluxation, dysplasia - underdevelopment of one or both joints) and begin treatment even before the appearance of clinical signs. Starting treatment at a later date significantly worsens the child’s quality of life and leads to the need for surgical intervention.
Unlike X-ray examination, which shows only bone tissue and joint spaces, ultrasound of joints allows you to examine ligaments, tendons, joint capsule, cartilage, and synovium. It is extremely important for early diagnosis, because it records the initial changes in the joints.
Preparing for the study. No special preparation is required for ultrasound of the hip joints. The procedure takes about 5 minutes and is completely painless for the child.
Evaluation of results
Ultrasound examination allows you to study:
- Condition and structure of brain tissue. Darkening in the image allows one to suspect the presence of tumors, cystic formations, and hemorrhages. Increased tissue density can also be a symptom of inflammatory processes.
- Large vessels and choroid plexuses. Enlargement of some areas of the vessels may indicate the presence of an aneurysm.
- Ventricles of the brain. Changing their size makes it possible to diagnose pathologies such as rickets or hydrocephalus.
- Symmetry of brain structures. Slight asymmetry is considered a variant of the norm.
Identification of any abnormalities is a reason for the doctor to prescribe other studies, such as electroencephalography or rheoencephalography.
Timely diagnosis of neurological pathologies allows treatment to begin in the early stages of the disease, on which its effectiveness directly depends.
Preparing for the examination
In some cases, you need to prepare specifically for an ultrasound examination. This does not apply to neurosonography. Anesthesia or special drug preparation is not required before performing NSG. The only recommendation for parents is to feed the child before the examination (a well-fed baby will sleep).
There are no contraindications to the examination. Neurosonography can be performed even in those babies whose general condition is assessed as severe. If the child is in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit, the scan is done in an incubator (a special device in which a sick or premature baby is placed).
Why is this research necessary?
The baby goes through many tests, both during pregnancy and during childbirth. External factors that are not capable of causing harm to an adult - banal infections, medications, household and professional hazards - can become a disaster for a nascent life. And, naturally, the brain, as the most complex and vulnerable structure of the human body, is most susceptible to these influences. During the first year of a baby’s life, doctors have the opportunity to prevent the consequences that may arise due to certain problems in the brain. The sooner treatment is started, the more likely it is that the child will grow up healthy.
Scheduled ultrasound for a baby at one month
So, when you have celebrated “porridge”, it is recommended that your child do the following:
- Neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain);
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space (kidneys, adrenal glands);
- Ultrasound of the hip joints
If, during auscultation of the heart, the pediatrician hears a murmur in the child, then it is also necessary to conduct echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) to exclude heart defects. Competent pediatricians prescribe an ultrasound of the heart when any murmur is detected, even if the murmur has a so-called “chordal” hue.
Who undergoes neurosonography?
Neurosonography is mandatory for all premature babies. Children who required intensive care or resuscitation after birth, with birth trauma or after traumatic obstetric care, large newborns, and babies with intrauterine growth retardation. In addition, the study is prescribed for children with defects and anomalies of other organs and systems. But, in general, every child needs to have neurosonography done at least once. To exclude changes that may manifest themselves only after a year, when the fontanel has already closed.