Ectopic pregnancy, according to doctors, is the most unpredictable and dangerous gynecological disease, which, unfortunately, is not so rare - it accounts for approximately 0.8-2.4% of all pregnancies. Moreover, in developed countries there is a tendency to increase the number of ectopic pregnancies with the incidence of infertility in 70-80% of cases of operations performed.
In addition, this disease poses a direct threat to a woman’s life. Therefore, it is so important to know its main symptoms and signs, so that in case of the first suspicions, immediately contact a medical institution for examination and help.1
What is an ectopic pregnancy
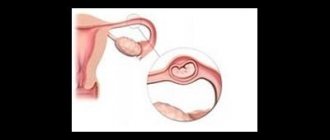
An ectopic pregnancy is a pathology that is characterized by the location of a fertilized egg and its subsequent growth outside the uterus. In order for pregnancy to develop normally and be safe for the mother’s body, the fertilized egg must pass through the fallopian tubes into the uterine cavity and there penetrate into its mucous membrane. But during an ectopic pregnancy, for one reason or another, the embryo does not enter the uterus and is attached to some other place, where it begins to develop.
Depending on the place of its attachment, ovarian, tubal, abdominal and other types of ectopic pregnancy are distinguished. The subsequent development of the embryo leads to the destruction of the organ to which it is attached, which is fraught with life-threatening bleeding.
Pregnancy developing in the ovary can be external, i.e. progressing on the ovarian capsule and internal, occurring directly in the follicle (the vesicle in which the egg matures). It can occur if the sperm enters the follicle from which the egg has not yet had time to come out. Therefore, fertilization and attachment occurs immediately. Sometimes the egg manages to be fertilized immediately after being released from the follicle and remains there, attaching to the ovary. Ovarian tissue is very elastic, and there are cases where women carried a child there until the very late stages of pregnancy.
A cervical ectopic pregnancy occurs when, for some reason, the fertilized egg slips out of the uterus, rolls down and becomes attached to the cervix. This type of pathology is the most dangerous for women - in about half of all cases, death occurs, and during surgery the uterus is completely removed.
Abdominal ectopic pregnancy is divided into primary, when the attachment of the egg immediately occurred in the abdominal cavity, and secondary, in which the fertilized egg was released into the abdominal cavity from the fallopian tube. If the fertilized egg attaches where the blood supply is insufficient, it will quickly die. In other cases, its development may continue, which is fraught with damage to internal organs and abnormalities in the development of the fetus, up to its intrauterine death due to developed oxygen starvation.
In 99% of cases, a tubal ectopic pregnancy occurs, in which the embryo develops in the fallopian tube.
Reasons for appearance
Attachment of the embryo outside the uterine cavity is caused by a violation of the patency of the fallopian tubes or a change in the properties of the fertilized egg itself.
This can lead to:
- inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs. Most often, ectopic pregnancy is caused by sexually transmitted infections - chlamydia, trichomoniasis, etc., which provoke inflammation, narrowing and deformation of the fallopian tubes.
- consequences of abortions, especially multiple ones. These situations are fraught with adhesions and inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs, and changes in the tubes.
- use of an intrauterine device. When using such contraceptives for more than 5 years, the risk of ectopic pregnancy increases 5 times. This is due to changes that accompany the presence of a foreign body in the uterus.
- hormonal disorders that can be caused by stimulating egg maturation, preparation for IVF (in vitro conception), or the use of strong hormonal drugs.
- operations performed on the fallopian tubes or other internal organs.
- malignant neoplasms of the uterus and appendages.
- improper development of the fertilized egg.
- endometriosis (growth of the uterine lining inside and outside the uterus).
- congenital malformations of the organs of the reproductive system.
- smoking (the risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy increases 3 times).
- constant stress and overwork.
- woman's age over 35 years.
However, cases of development of this problem in absolutely healthy young women who are not included in any of the listed risk groups are very common. The risk of re-developing this pathology occurs in approximately 25% of women who have had it.
Possible causes of ectopic pregnancy
Main risk factors:
- infectious and inflammatory diseases - previously suffered or passed into the chronic phase - inflammation of the uterus, appendages, bladder are considered one of the main causes of ectopic pregnancy.
- Inflammatory processes in the ovaries and tubes (previous difficult births, multiple abortions, spontaneous abortions without going to a medical clinic), leading to fibrosis, the appearance of adhesions and tissue scarring, after which the lumen of the fallopian tubes narrows, their transport function is disrupted, and the ciliated epithelium changes. The passage of the egg through the tubes becomes difficult and an ectopic (tubal) pregnancy occurs;
- congenital infantilism of the fallopian tubes - irregular shape, excessive length or tortuosity with congenital underdevelopment are the cause of improper functioning of the fallopian tubes;
- pronounced hormonal changes (failure or insufficiency) - diseases of the endocrine system contribute to the narrowing of the lumen of the fallopian tubes, peristalsis is disrupted and the egg remains in the cavity of the fallopian tube;
- the presence of benign or malignant tumors of the uterus and appendages - narrowing the lumen of the fallopian tubes and interfering with the advancement of the egg;
- abnormal development of the genital organs - congenital abnormal stenosis of the fallopian tubes prevents the advancement of the egg to the uterine cavity, diverticula (protrusions) of the walls of the fallopian tubes and uterus make it difficult to transport the egg and cause a chronic inflammatory focus;
- a history of ectopic pregnancies;
- change in the standard properties of the fertilized egg;
- slow sperm;
- certain technologies of artificial insemination;
- spasm of the fallopian tubes, which occurs as a result of a woman’s constant nervous overstrain;
- the use of contraceptives - hormonal, IUDs, emergency contraception, etc.;
- age of the pregnant woman after 35 years;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- long-term use of drugs that increase fertility and stimulate ovulation.
The first signs of an ectopic pregnancy
In the first stages, an ectopic pregnancy, the symptoms of which depend on its duration, may have virtually no symptoms - except perhaps a delay in menstruation, as in a normal pregnancy. Otherwise, at 1-2 weeks this pathology does not make itself known. But already at 3-4 weeks, the first signs of an ectopic pregnancy may appear, in addition to the typical symptoms for a normal pregnancy (delay, nausea, breast tenderness, increased basal temperature):
- dull nagging or sharp pain in the lower abdomen (can be on the right or left) of varying degrees of intensity;
- pain radiating to the lower back or rectum;
- bloody spotting from the vagina, not similar to menstrual discharge;
- breast pain and enlargement;
- pain during sex.
During an examination by a gynecologist in the early stages, you can identify an enlarged and softened uterus, as well as softening and cyanosis of its cervix. In the area of the appendages, an enlarged and painful fallopian tube or ovary with no clear contours can be felt. If upon palpation (palpation) a tumor-like formation is detected in the appendages, the doctor compares the existing symptoms and prescribes additional examinations necessary in this case.
Between 4 and 20 weeks, an ectopic pregnancy can result in rupture of the fallopian tube or other organ to which the embryo is attached. This leads to severe internal bleeding. If complications occur, the first signs of an ectopic pregnancy can be expressed in severe, piercing abdominal pain, accompanied by severe weakness up to loss of consciousness, pallor, rapid pulse and bloody discharge from the vagina. Sometimes symptoms of a tubal pregnancy occur only at the time of its termination. Acute pain in the lower abdomen appears suddenly against the background of good general health. As a rule, this occurs 4 weeks after the delay, and the pain radiates to the hypochondrium, collarbone, anus or leg. Attacks of pain can be repeated several times and last for several minutes or several hours. But in cases where internal bleeding is minor, an ectopic pregnancy may go unrecognized. Weakness, nausea, dizziness and a slight increase in temperature appear, which is explained by the absorption of spilled blood in the abdomen. However, if bleeding in the abdominal cavity continues, the condition will worsen, the pain will intensify, and the bleeding will recur.
Complications and their signs
Often, expectant mothers do not rush to see a doctor, which is why the disease remains undiagnosed. This is very dangerous because it leads to rupture of the appendages, intra-abdominal bleeding and peritonitis. Complicated ectopic pregnancy manifests itself at a period of more than one month with the following symptoms:
- sharp stabbing pain in the lower abdomen, on the right or left side;
- increased sweating, weakness, rapid heartbeat;
- Possible heavy uterine bleeding;
- positive symptoms of peritoneal irritation.
Ectopic pregnancy, complicated by rupture of the adnexa, usually manifests itself at a period of more than one month. It is at this time that the embryo reaches a large size and becomes capable of rupturing the tube.
Attempts at self-medication and ignoring the problem are dangerous. Pregnancy should be under the supervision of a specialist - then you can be sure that complications will not occur at any stage.
Methods for determining ectopic pregnancy
To determine if a woman has an ectopic pregnancy, the following examinations and tests are performed:
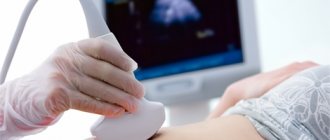
1. Ultrasound of the pelvic organs. This method allows you to determine pathology at the end of the first month of its development. If an ultrasound is performed through the vagina, an ectopic pregnancy is detected at approximately the 4th week, if through the abdomen - at the 5th week.
2. Determination of the level of hCG (pregnancy hormone) in the blood. Using this analysis, the fact of pregnancy is determined. The presence of an ectopic form can be suspected if the concentration of hCG in the blood of women increases more slowly than during normal pregnancy.
3. Determination of the level of progesterone (another pregnancy hormone secreted by the ovaries) in the blood. During an ectopic pregnancy, its content is lower than during a normal pregnancy.
4. Laparoscopy (examination of internal organs through a small incision). Such an examination is carried out when there is a suspicion that a woman has already experienced internal bleeding due to an ectopic pregnancy. Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia and, by introducing a special video camera into the abdominal cavity through small holes, the pelvic organs are examined. If during an internal examination the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is confirmed, the study immediately proceeds to surgery.
The easiest way to detect this disease is after the ectopic pregnancy has terminated - as a rule, this occurs at 4-6 weeks. If this pathology develops without spontaneous interruption, its presence must be determined within 3-4 weeks using hCG analysis and ultrasound.
Early signs
As a rule, ectopic pregnancy is recognized early. As doctors note, such a pregnancy can develop in any woman who is sexually active and does not use contraceptives. True, the use of protective equipment also does not guarantee the 100% absence of such a pathology: condoms may break, you may forget to take a pill, or reduce its activity by taking antibiotics or alcohol.
One of the main symptoms, says Alexey Polstyanoy, is a delay in menstruation. This is the same sign for both intrauterine and ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, if such a sign appears, you should not wait for how the situation will end; you should go to the doctor. “The second sign may be a change in the mammary glands - they become thicker and increase in volume. Which, however, happens during normal pregnancy,” says the gynecologist.
The third sign of a potential ectopic pregnancy may be a positive test. True, with reservations. “It can be dubious, for example, the control line is clear, and the second line is unclear, barely outlined. This is already a reason to suspect an ectopic one. It may also be that the test is negative, but signs of pregnancy are present - it’s also worth getting checked,” advises Alexey Polstyanoy.
Doppler ultrasound during pregnancy: features, indications, results Read more
Possible complications
The most important and dangerous complication of an ectopic pregnancy is large internal bleeding, which can lead to the death of a woman in just a few hours or even tens of minutes. It is also possible that an ectopic pregnancy may recur in the future or that infertility may develop due to damage to the fallopian tubes. In addition, shock due to internal bleeding can impair the functions of other internal organs, not just the reproductive system.
Due to the fact that an ectopic pregnancy can develop in organs with a rich blood supply, which in particular include the ovaries and the areas where the fallopian tubes enter the uterus, surgery to remove the embryo can result in the removal of one of the fallopian tubes, the removal of one of the ovaries and even the removal of the uterus with both fallopian tubes. But even if all internal organs are preserved, an ectopic pregnancy still reduces a woman’s chances of further conception and normal childbearing. Sometimes, after the operation, an inflammatory process and intestinal obstruction develop, and seals form in the pelvis.
In order to minimize the negative consequences of ectopic pregnancy as much as possible, after the operation it is necessary to undergo anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy. The hormonal background and protective resources of the woman’s body must be fully restored before the next pregnancy, otherwise the risk of recurrence of the pathology or the development of secondary infertility will be too great. From a medical point of view, you can plan your next pregnancy no earlier than six months to a year after the operation.
Run to the doctor at the first symptoms! An ectopic pregnancy is an extremely dangerous condition for a woman’s health and life, therefore, if any suspicious symptoms and especially acute abdominal pain appear, it is necessary to consult a doctor or call an ambulance as soon as possible. And if the diagnosis is confirmed, you will either be prescribed an termination of this pregnancy, or an operation will be performed to eliminate the consequences of the tubal abortion that has occurred. Today, both surgical and medical methods are used to treat ectopic pregnancy. The specific method is determined by the attending physician based on the patient’s condition and the severity of the disease.
Treatment and recovery
The least traumatic method of treating ectopic pregnancy is medication. But it can be resorted to only in the earliest stages of the development of pathology. It is usually used in cases where an ectopic pregnancy is accidentally discovered during a gynecological examination, since women tend to tolerate changes in their condition “to the last.” To get rid of the pathology, a special hormonal drug is introduced into the woman’s body, which stops the development of the embryo and provokes an artificial miscarriage. This method appeared relatively recently. It requires a thorough preliminary examination of the woman before the procedure and highly qualified medical personnel. Under no circumstances should you try to find the name of these drugs on the Internet and resort to the method of medicinal termination of intrauterine pregnancy on your own!
Sometimes doctors combine surgical and medicinal methods, injecting a woman with a drug, after which the incorrectly attached fertilized egg is detached and then removed by squeezing. Further restorative treatment is aimed at eliminating inflammatory processes in the appendages on the opposite side. Usually, a woman’s recovery after surgery occurs quite quickly - especially if it was a laparoscopic intervention (an operation performed through small incisions). The wounds heal completely in 2-3 weeks, but for another 2-3 months the woman should avoid physical activity and try to prevent constipation. Also, after treatment for an ectopic pregnancy, it is customary to take a hCG test several times to make sure that there are no fragments of the ovum membrane left in the woman’s body, which can continue to grow and eventually turn into a tumor.
To summarize, we can say that in the case of an ectopic pregnancy, it is better for a woman to play it safe than to delay her visit to a specialist in the presence of frightening symptoms. It is advisable to see a gynecologist immediately when a delay occurs, so that he can determine its true cause and, if necessary, quickly prescribe treatment. If an ectopic pregnancy was treated in a timely manner, a woman can become pregnant again in the future, paying attention to the prevention of this pathology.
Womenfirst
- Ectopic pregnancy: early diagnosis and treatment Babajanova Gulzhakhon Sattarovna, Khojaeva Dilufar Nuriddinovna, Razikova Komola Khasanovna 2021 / Biology and Integrative Medicine
- Analysis of the reproductive health of patients after ectopic pregnancy Erkenova S.E., Ergalikyzy A., Kaldybekova A.K., Kurbanova M.O., Shadenova E.E., et al. 2021 / Bulletin of the Kazakh National Medical University Murtazin A.I. Obstetrics and gynecology. Standards of medical care. Quality assessment criteria. Formulary. 2021
- Prediction and prevention of recurrent ectopic pregnancy: abstract of thesis. Magomedova Patimat Aripovna; - Moscow, Scar pregnancy - a new type of ectopic pregnancy Maltseva L.I., Fattakhova F.A., Zamaleeva R.S., Kurtasanova E.S., Khruleva G.Kh. 2021 / Practical medicine
RUS2124800-2 from 03/20/2020