Abortion is the artificial termination of pregnancy using various methods. Since this procedure is associated with intervention in the body, and even if carried out medicinally in the early stages, it still poses a danger to the body. To reduce risks to a minimum, you need to get tested before and after an abortion.
Types of abortions and timing
The content of the article
The gynecologist decides which abortion will be performed, focusing on the timing of pregnancy. The list of tests to be taken depends on the method of abortion. The longer the period, the more extensive the examination should be.
- Medical abortion is allowed up to 6 weeks; it is the least traumatic and does not cause great psychological trauma.
- Also, for a short period of up to 6-7 weeks, vacuum aspiration is used, in which the fertilized egg is sucked out with a special pump. This method is called a mini-abortion, but it is still associated with mechanical influence. The risks also increase: remaining particles of the amniotic egg will lead to inflammation.
- Surgical abortion is performed between 7 and 12 weeks under general anesthesia. This is a real operation that has an extremely negative impact on a woman’s reproductive health. This is due to the artificial opening of the cervix, which subsequently leads to its weakening, and injury to the walls of the uterus, which become open to various infections.
Contraindications to medical abortion
- You cannot have a medical abortion for women under 18 and after 35 years of age;
- no diagnosed pregnancy;
- over the next three months the woman used an intrauterine device and hormonal contraceptives;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- exacerbation of pulmonary diseases (asthma, bronchitis, etc.);
- endometriosis and fibrous tumors;
- irregular menstrual cycle preceding pregnancy;
- liver or kidney failure;
- pregnancy period is more than 7 weeks;
- taking steroids;
- epilepsy;
- anemia;
- hemophilia;
- scars on the uterus;
- hypersensitivity to Mifeprex or Mifegin.
The recovery process after an abortion should also be discussed with a gynecologist. Abortion does not provide any guarantee against re-pregnancy; contraception should not be neglected.
Please note that after an abortion, pregnancy tests will be positive within a month.
Tests before the first abortion
Abortion of the first pregnancy is especially dangerous. It threatens further infertility and other health problems. Therefore, a young girl going to terminate her first pregnancy must first undergo the following tests:
- Complete blood test with determination of group and Rh factor.
- Biochemical analysis (blood sugar, cholesterol levels).
- General urine analysis
- Analysis - Wasserman reaction or RW (rapid test for syphilis).
- Test for hepatitis B and C.
- HIV test.
- Hemastasiogram (blood clotting).
- Analysis of a smear for vaginal flora.
- HCG analysis.
An ultrasound scan of the uterus is required, during which the doctor makes sure that the fertilized egg is implanted in the uterus and that the pregnancy is indeed uterine. An ultrasound will determine the exact duration of pregnancy.
Despite the impressive list, all tests are completed within 2-3 days, after which the doctor examines the results and sets the time for the procedure itself.
Tests before the second and next abortions
If the patient has already given birth and had several abortions before, she needs to undergo much fewer tests, and they will depend on the type of abortion.
Regardless of the type of abortion, before the procedure begins, the patient undergoes tests, which, depending on the volume of examinations, are divided into minimal, extended and maximum.
Minimal or basic tests are carried out if the woman has already given birth and had abortions before.
- A woman undergoes an examination on a gynecological chair.
- Gives a vaginal smear for infections.
- An ultrasound is performed, which determines the location of the fertilized egg inside the uterus.
The examination is carried out by a gynecologist in order to identify diseases that the patient may not be aware of, but which, during an abortion, can cause a serious blow to health. For example, a follicular ovarian cyst is not a contraindication to medical abortion, but other types of cysts increase in size and even rupture after hormonal exposure. In case of fibroids, curettage is dangerous; it leads to damage to the endometrium and the muscular layer of the uterus, provoking tumor growth. During the examination, the doctor determines whether the size of the uterus and ovaries corresponds to the period of pregnancy, and in case of deviation from the norm, sends for further examination.
A vaginal smear determines the ratio of beneficial and pathogenic microflora. Lactobacilli should predominate, and leukocytes are present in a smear of a healthy woman in minute quantities. Coccus infection, leukocytes and erythrocytes indicate inflammation, a lack of epithelial cells indicates a decrease in estrogen, and gram-negative bacilli indicate vaginal dysbiosis.
Why get tested for Rh factor blood?
The examination necessarily includes tests to determine the Rh factor and blood type, because a negative Rh factor and an abortion performed against its background often leads to complete infertility in the future.
Already during the first pregnancy, in a woman with a negative Rh factor, when the fetus inherits a positive Rh factor from the father, the production of antibodies begins, which enter the embryo’s body through the placenta and begin to destroy its red blood cells (they are perceived as a foreign body due to the opposite Rh factor of the mother).
The fetus experiences oxygen starvation, develops pathologies and in some cases dies. Or, sensing a significant loss of red blood cells, the liver and spleen begin to intensively produce them, increasing in size. An increased amount of bilirubin, a breakdown product of hemoglobin, is produced, causing intoxication of the body, leading to improper development of the baby’s brain.
The antibodies produced by the mother's body during the first Rh-conflict pregnancy are not very active, so there is a high probability of bearing and giving birth to a healthy baby with concomitant therapy.
However, there is a problem: during the first pregnancy, so-called memory cells are produced. During subsequent conception, antibodies are produced in much larger quantities and are more active. A previous abortion especially increases the production of antibodies. Therefore, a woman with a negative Rh factor who decides to terminate her first pregnancy should know that the next baby may never be born. The only right decision is to continue the pregnancy.
To prevent further miscarriage or the birth of a baby with pathologies, the woman in labor is given an injection of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin within 72 hours after the birth of the child. In extreme cases, such an injection is given after an abortion, but it is better that the first pregnancy ends in childbirth.
Possible complications
Despite the small number of complications, it is possible to determine why medical abortion is dangerous. In 85% of cases, adverse reactions in the form of abdominal pain and bleeding are moderate and no special treatment is required.
In other cases, manipulation can lead to the following complications:
· severe pain syndrome;
· profuse bleeding;
· temperature;
· incomplete abortion;
· progressive pregnancy.
Pain in the lower abdomen is observed during the period of expulsion of abortion products. Its intensity may vary, but the individual tolerance threshold also matters.
Bleeding is considered significant if you have to change two pads in an hour, and this condition lasts for at least 2 hours. In this case, vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterus is indicated in order to stop it. In severe cases, surgical cleaning is performed.
In 2-5% of cases, medical abortion is incomplete. Then it is also necessary to perform vacuum aspiration or curettage of the uterine cavity. Less than 1% of cases result in pregnancy progression. If a woman insists on an abortion, then invasive methods are used. Those who have changed their decision must be informed about the possible teratogenic effect of the drugs on the fetus. But there is not enough data to confirm this fact.
Taking medications may cause a slight increase in temperature, but this lasts no more than 2 hours. If the fever lasts for 4 hours or more or occurs one day after taking Misoprostol, this indicates the development of an infectious process. A woman with these symptoms should consult a doctor.
Other complications in the form of dyspeptic symptoms may be a sign of pregnancy itself. For allergic reactions, treatment with antihistamines is necessary.
Why do you need an ultrasound before an abortion?
Ultrasound diagnostics not only confirms the fact of pregnancy, but also reveals the place of attachment of the embryo.
It happens that the patient has all the signs of pregnancy: delayed menstruation, enlarged mammary glands, changes in well-being. The test shows two lines, and there is a pregnancy, but it is ectopic. Ectopic pregnancy occurs in almost 3% - this is a fairly high percentage, so before an abortion you must make sure that the embryo has implanted in the intended place, i.e. uterus. If you start an abortion with an ectopic, severe bleeding begins. The patient expects an uncompleted abortion and other troubles.
Ultrasound is performed at 5-6 weeks from the moment of conception. At this moment, only the transvaginal sensor can see the fertilized egg, so you will have to undergo this procedure for an abortion.
Transabdominal (through the peritoneum) ultrasound is done at 10-11 weeks. However, the sooner the fact of pregnancy, especially ectopic pregnancy, is established, the fewer health consequences there will be after an abortion.
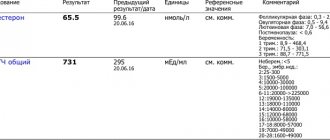
HCG analysis
In the early stages, when an ultrasound still does not show anything, the fact of pregnancy is confirmed by an analysis of human chorionic gonadotropin, a protein produced by the villi covering the embryo.
In a non-pregnant woman, hCG is 5 honey/ml, but already from 1 week from the moment of conception it rises to 25 honey/ml, and by the end of 2 weeks it rises to 300 honey/ml. If the hCG is higher than that of a non-pregnant woman, but lower than the norm, then the patient is diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy. This is perhaps the only way to detect pathology in the early stages. In this case, abortion is performed differently than in a normally developing pregnancy.
Preparing for a medical abortion
At the first visit, the doctor must confirm the fact of pregnancy and set the exact date. To do this, you need to undergo an ultrasound and be tested for hCG, hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections.
The day before a medical abortion, you should stop drinking alcoholic beverages, foods that are difficult for the body to digest, and energy drinks. Women who smoke are advised to reduce the number of cigarettes or quit smoking for a while.
Don't underestimate the preparatory period. The success and absence of side effects while taking the drugs largely depends on it.
Expanded range of tests before surgical termination of pregnancy
If a surgical abortion is planned, the range of tests should be expanded.
- Advanced tests include tests for AIDS, hepatitis B and C, and syphilis.
- To avoid undesirable consequences, the woman undergoes additional urine tests. Using it, the doctor determines whether the patient has problems with the bladder or kidneys.
- You also need to undergo a PRC test for hidden infections that are not detected in a regular vaginal smear. In the case of a surgical abortion, pathogenic microflora will enter the injured uterine cavity. This will cause inflammation, severe bleeding and further infertility.
- A coagulogram reveals blood clotting disorders that lead to serious consequences. Glucose tests identify patients with diabetes mellitus, which increases the permeability of capillaries, arteries and blood vessels. Such patients should think a hundred times before agreeing to an abortion, and, if it is unavoidable, carry it out in accordance with the existing characteristics of the body.
In the presence of serious pathologies, additional studies are carried out. The examination includes examination of the heart, blood vessels, and kidneys. This will prevent complications after anesthesia.
A couple of decades ago, articles periodically appeared in the media that told how a girl died after an abortion or remained infertile. This usually describes cases of illiterate abortions, when the necessary tests were not carried out, the procedure was done hastily without taking into account the woman’s health characteristics.
Despite the negative impact of abortion on reproductive health, patients who contact a good specialist at the clinic retain the ability to reproduce without health consequences.
Advantages of examination in a paid clinic
Modern private medical clinics offer their patients a full range of all necessary studies necessary for the effectiveness of an abortion and minimizing the risks associated with its implementation. Paid clinics have other advantages, for example, friendly, highly qualified staff, the ability to make an appointment in advance, an individual approach to each client and a comfortable atmosphere.
Do you want to find an experienced gynecologist near your place of residence and make an appointment with him? Contact our help desk for private clinics in Moscow “Your Doctor”.