Colposcopy is a method for diagnosing diseases of a woman’s external genitalia and precancerous conditions of the cervix. The procedure is carried out using a colposcope - a binocular microscope, which can additionally be equipped with a video or photo camera.
At the MLC, the diagnostic procedure is carried out using modern equipment, which makes it possible to obtain images of the vaginal mucosa and cervix, enlarged by 10-30 times, and to conduct a targeted biopsy when studying tumors.
What is colposcopy during pregnancy and how is it performed?
Colposcopy is a diagnostic method that involves examining the surface of the cervix under magnification. It is used in gynecology to identify a number of pathologies: dysplasia, leukoplakia (leucoplakia, Leukoplakia), cervical erosion, malignant and benign neoplasms, vascular pattern disorders, endometriosis (Endometriosis) of the vaginal cervix. In addition to disorders affecting the cervix, an indication for colposcopy during pregnancy may be a preventive assessment of the condition of the walls of the vagina and vulva.
There are two types of colposcopy performed during pregnancy:
- Survey (simple) colposcopy involves exclusively visual examination of the female genital organs without the use of chemical solutions and color filters.
- During extended colposcopy, the doctor applies special chemical reagents to certain areas of the mucosa to detect the presence or absence of altered cells. They are safe for mother and fetus. Typically, during extended colposcopy, a 3% acetic acid solution and an aqueous solution of potassium iodide (Schiller test) are used. When a weak solution of acetic acid is applied to the mucous membrane, a spasm of small blood vessels occurs, followed by expansion of the vascular network. Carrying out the Schiller test during colposcopy causes brown staining of the stratified squamous epithelium of the surface of the cervix and does not stain the altered mucosa. If, as a result of the use of reagents, any area of the cervix or vaginal walls raises doubts in the gynecologist, he scrapes this area for subsequent laboratory testing for oncocytology.
To conduct the examination, the doctor uses a special optical or video device - a colposcope. It is a device equipped with an illuminator and powerful lenses that allow you to obtain an image magnified by 3-40 times.
Expert opinion
Thanks to multiple magnification during colposcopy, the doctor is able to assess the color of the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix, identify possible areas of damage, and apply special chemical solutions to the examined areas.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
Colposcopy during pregnancy is performed in a gynecological chair. A plastic or metal speculum is inserted into the vagina to ensure optimal viewing. The optical head of the colposcope is placed at a distance of about 15-20 cm from the entrance to the vagina, and the resulting image is displayed on a computer monitor. The duration of the procedure depends on its type: a regular colposcopy takes about 10 minutes, and an extended examination takes about 20 minutes.
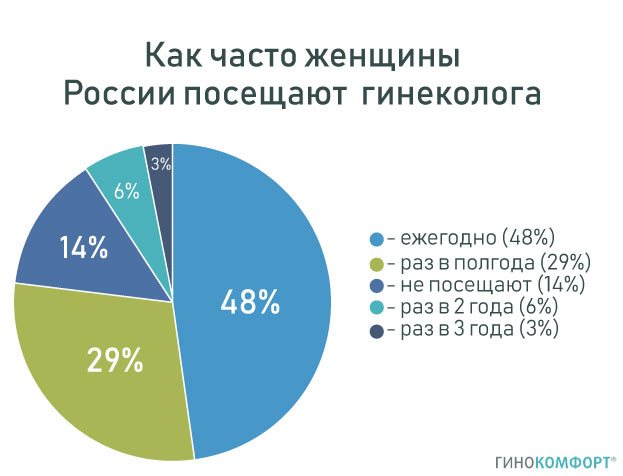
Visit to the gynecologist, statistics
The essence of colposcopy during pregnancy is practically no different from a similar study of non-pregnant women. The only difference is that the cervical canal during pregnancy is covered with a denser layer of mucus, which can impair visibility and complicate diagnosis. Therefore, colposcopy during pregnancy is usually performed by gynecologists-obstetricians who have experience in performing such manipulations on pregnant women.
It is also important to note that only a doctor can interpret the results of colposcopy.
What is colposcopy?
Gynecological examination, which is carried out using a colposcope - a medical optical or video device.
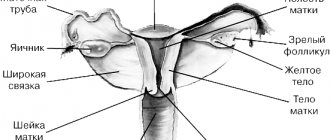
During the procedure, the doctor carefully examines the vaginal part of the uterus and cervix, vagina and vulva under magnification.
Medical equipment used
Optical colposcopes are devices that have built-in lenses (optical unit) and a powerful light source with adjustable brightness. Modern devices allow examining the tissue under study under magnification up to 30–40 times.
Video colposcopes are equipped with high-resolution digital video cameras that provide high-quality and color images. The “picture” is transmitted to the colposcope or computer monitor. The image is saved in the memory of the device or computer, which makes it possible to subsequently compare the results of several studies.
Colposcopy of the cervix during pregnancy: why is this procedure prescribed?
Colposcopy is included in the list of mandatory diagnostic measures that are carried out at the stage of pregnancy planning. If the patient has been identified with certain disorders affecting the vaginal mucosa, cervix and cervical canal, it is recommended to conduct the necessary studies and, if necessary, their treatment before conceiving a child. If the pregnancy was unplanned and no preliminary examinations were carried out, the doctor may prescribe a colposcopy for the expectant mother during pregnancy. What is it for?
Expert opinion
Colposcopy during pregnancy is performed solely for indications and not for prevention.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
While carrying a baby, a woman's hormonal background undergoes significant changes.
In some cases, this can lead to erosion or ectopia of the cervix. These concepts are not the same in meaning, although many women mistakenly confuse them.
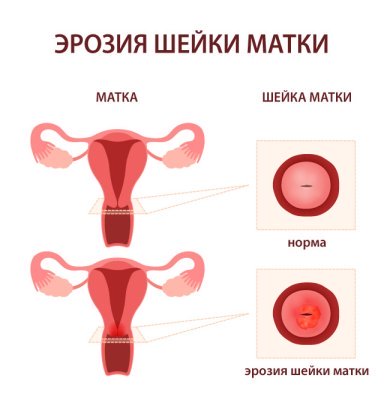
Cervical erosion is a collective concept and implies any identified changes. Includes, for example, true erosion, caused by a defect in the cervical mucosa by trauma, inflammation, burn, etc. True erosion is a bright red, easily bleeding area on the cervical mucosa, the appearance of which is caused by desquamation of the stratified squamous epithelium. This condition must be treated, since when pathogenic microbes enter the affected area, inflammation can begin, which is dangerous for both the pregnant woman and the child. In addition, cervical erosion is more susceptible to stretching and tearing during childbirth. Ectopia is a normal variant and is a replacement of squamous stratified epithelium with columnar epithelial cells. However, in both cases (both with true erosion and with ectopia), there is a danger of transformation of healthy cells into atypical ones with the subsequent development of benign or malignant neoplasms.
This requires treatment and taking this disease into account during delivery. In addition to suspicion of the occurrence of erosion during pregnancy, colposcopy is done in case of fear of the development of an oncological process or a polyp of the cervical canal.
In addition, if a pregnant woman notices symptoms such as unusual vaginal discharge, vulvar rash, vaginal itching and burning, tenderness in the lower abdomen, pain during urination, or spotting after sex, she is also advised to undergo a colposcopy.
Is it possible to have a colposcopy during pregnancy?
The answer to this question depends on the general health of the expectant mother, the nature of the course and duration of pregnancy. In any case, colposcopy should be carried out exclusively with the consent of the woman herself: the doctor can only advise whether or not to perform colposcopy, and the decision is made by the pregnant patient.
However, sometimes this diagnostic procedure is undesirable and there are certain contraindications. For example, colposcopy is not recommended if there is a threat of miscarriage in the early stages. This is due to the risk of bleeding and spontaneous abortion.
It is also undesirable to do colposcopy in case of placenta previa and the threat of premature birth.
A cervical biopsy during pregnancy is performed only if precancer or cervical cancer is suspected.
“Look” from the inside: why do you need colposcopy?
The examination helps to diagnose diseases in a timely manner with subsequent monitoring of the effectiveness of treatment.
Basic goals
1. Detection of pathologically altered tissue areas - neoplasms of the female reproductive system in the early stages.
The most serious is cancer of the female reproductive system. In the world, cervical cancer ranks 2nd in the frequency of malignant tumors among women; in the Russian Federation it ranks 6th. Every year, 200–300 thousand women die from this pathology in the world, and about 6,000 patients in the Russian Federation.
2. Choosing the optimal treatment method: cauterization with medications, removal with a laser, surgical instrument, etc.
3. Evaluation of treatment results and dynamic monitoring of previously detected pathological formations.
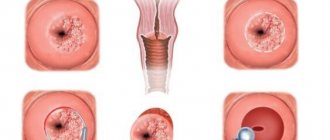
Detected diseases:
* cancer of the cervix, vagina and vulva;
* erosion/ectopia - mucosal cells from the cervical canal move to the vaginal part of the cervix (looks like ulceration on the mucous membrane);
* dysplasia is the most common form of cervical precancer, in which the normal structure of mucosal cells on the surface of the cervix is disrupted;
* cervicitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal;
* anogenital condylomas or warts - formations in the form of papillae or flesh-colored nodules and many others.
Preparing for colposcopy during pregnancy
To obtain accurate results, it is recommended to follow simple rules for preparing colposcopy during pregnancy:
- a couple of days before the diagnosis, it is recommended to avoid vaginal intimacy;
- It is undesirable to use vaginal suppositories, tablets, gels and foams;
- To wash before colposcopy, you do not need to use soap or washing gel - clean warm water is used instead;
- On the eve of colposcopy during pregnancy, vaginal douching is not recommended.
What to take with you? You don’t need to take anything special with you for the procedure; you should try to follow the above recommendations.
How to prepare?
1–2 days before the examination, it is recommended to abstain from sexual intercourse, douche, and not use vaginal tampons and medications (suppositories, creams, gels, tablets).
When is the best time to do it?
The most optimal time is 2-3 days before the start of menstruation or in the first 2-3 “clean” days after the end of menstrual bleeding. If necessary, the examination is carried out on the day of visiting the doctor.
How long does the procedure take?
Usually on average - about 15-20 minutes, maximum - up to 30 minutes.
It hurts?
The examination is painless, but discomfort or discomfort may occur.
How is colposcopy performed?
The procedure is performed by a gynecologist. The woman lies down on a gynecological chair, a gynecological speculum is inserted into the vagina, and the cervix is fixed between its doors.
Then the doctor conducts an examination using a colposcope mounted on a tripod at a distance of 20–25 cm from the gynecological chair. The device itself is not inserted into the vagina.

What sensations are normal during and after colposcopy during pregnancy?
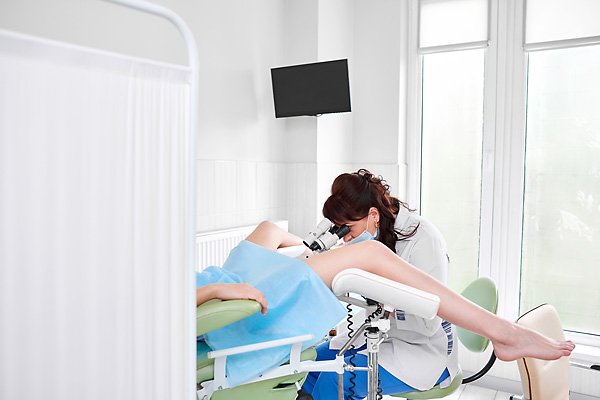
During the examination, a pregnant woman may feel slight discomfort caused by the insertion of a speculum. The bursting feeling provoked by this manipulation is not dangerous, so the patient should simply relax and try not to pay attention to it.
If a biopsy is performed during colposcopy, the woman may feel a slight tingling sensation that goes away on its own within a few hours (less often, days) after the colposcopy. The same applies to testing with acetic acid: a slight burning sensation is a natural reaction of the mucous membrane in response to the application of the reagent during extended colposcopy. You can reduce these unpleasant sensations with the help of Gynocomfort restoring gel. The product copes well with vaginal discomfort caused by gynecological manipulations (including colposcopy). It contains active ingredients such as lactic acid, tea tree oil, chamomile extract, panthenol and bisabolol. Restoring gel "Ginocomfort" reduces vaginal discomfort, ensures rapid regeneration of the mucous membrane after diagnostic procedures, and helps maintain a normal level of vaginal acidity. The product underwent clinical trials at the Department of Dermatovenereology with the clinic of St. Petersburg State Medical University under the leadership of Sokolovsky E.V. and Ignatovsky A.V. and showed excellent results, the gel also has the necessary documents and quality certificates.
What can be the consequences of colposcopy? If, after a colposcopy, a pregnant woman discovers slight spotting from the vagina, this is not a reason to panic. In most cases, they are caused by a reaction of the mucous membrane to chemical reagents.
Expert opinion
Sometimes (especially if a biopsy was performed during colposcopy) a small amount of blood may be present in the discharge. The only cause for concern can be heavy discharge accompanied by pain - in this case, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Oksana Anatolyevna Gartleb
What to expect after the study?
If a simple colposcopy was performed, there are usually no consequences. The woman leads a normal life without any restrictions.
Discharge from the genital tract is possible for several days:
* during an extended study, they may have a green, yellow or brown tint - remnants of the drugs used to conduct test samples;
* bloody and spotting - after a biopsy.
Discharge is normal, is not dangerous and does not require treatment.
Sexual intercourse is possible after the cessation of vaginal discharge, but it is usually recommended to abstain from it for 10–14 days from the date of the study.
Colposcopy: examination of the cervix, video
is not responsible for the accuracy of the information presented in this video clip.
Source – Oasis of Health Sources:
- COLPOSCOPIC CHANGES IN THE CERVIX DURING PREGNANCY. Kogan Ya.E., Gafarova A.A. // Practical medicine. – 2021. – No. 7 (108). – pp. 18-21.
- METHODS FOR STUDYING THE CERVIX IN PREGNANT WOMEN. Sidorova I.S. Atabieva D.A. // Obstetrics, gynecology and reproduction. – 2013. – No. 2. – 15-19.
- ALGORITHM FOR MANAGEMENT OF PREGNANT WOMEN WITH CERVICAL PATHOLOGY. Yusupoka M. A., Ismailova D. U., Matmuratova S. O. // Interactive science. – 2017. – No. 2 (12). – pp. 84-88.
- Pregnancy: cervical difficulties. Cervix of the uterus in pregnant women: normal picture and disease. N.V. Zarochentseva // Gynecology, obstetrics, infertile marriage. - 2014. - T. 18.
- Diseases of the cervix and modern methods of their diagnosis (literature review). HELL. Atabieva, T.V. Pikuza, R.A. Chilova, E.V. Zhukova, N.S. Trifonova // Bulletin of modern clinical medicine. — 2021. — Volume 9. — Issue. 4.
- Pregnancy and cervical diseases: frequency, gestational complications, maternal and perinatal outcomes. Kolomoets E.V. // Author's abstract. dis. Ph.D. honey. Sciences E.V. Kolomoets. - Moscow. - 2012. - P. 25.
- https://www.tosnocrb.ru/novosti/kolposkopiya/
- https://infobaby.org/colposcopy-during-pregnancy/
- https://www.pubfacts.com/detail/19550217/The-management-of-cervical-intraepithelial-neoplasia-during…
- https://www.longdom.org/open-access/diagnostic-and-therapeutic-endoscopy-in-pregnancy-when-why-and-h…
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30118992
Popular questions
The first pregnancy had placental abruption at 12 weeks.
I spent a week in the hospital. All that remained was yellow discharge. In the evening after discharge, the discharge changed to brown, to dark blood. This is fine? There should be no bleeding during pregnancy. This indicates a threat of interruption and requires treatment in a specialized department.
We are planning a pregnancy. According to my last ultrasound on the 18th day of the cycle, I had an M-echo of 0.6 cm and a cyst in the right ovary 3.3 * 2.4. in the left there are 16 follicles, with a diameter from 0.4 to 0.6. 1. Can I get pregnant in the next cycle with a cyst and is it dangerous? 2. How by day of the cycle and in what dosage can you take vitamins for follicle growth and endometrial growth (folic acid, vitamin E, vitamin C, group B, etc. are of interest)
First of all, it is necessary to find out the nature of the ovarian cyst and the reason for the multifollicularity of the second ovary. I will also note that the M-echo for this day of the cycle does not correspond to the norm. I recommend that you see an obstetrician-gynecologist during this cycle. Conduct a test for STIs, since most often it is this factor that leads to such changes. Perform an ultrasound on days 5-7 of the cycle to monitor the condition of the ovarian cyst. And only then discuss the feasibility of vitamin therapy according to the phases of the menstrual cycle.
Good afternoon At the appointment, the gynecologist, before examining with a speculum, irrigated the vagina with a solution of hydrogen peroxide. I'm 20 weeks pregnant and have some erosion. Will this harm the baby?
Hello! This antiseptic will not harm the baby; it acts locally, only on the mucous membranes where it is applied.
Hello! At 31 weeks and 4 days of pregnancy, they diagnosed stage 2 placenta maturity, is this dangerous? My doctor doesn’t say anything or prescribe anything, maybe I should go to another doctor?
Hello!
According to ultrasound, not only the degree of maturation of the placenta is important, but also hemodynamic indicators in the feto-placental complex, the amount and nature of amniotic fluid, and the condition of the fetus. In such cases, fetal hypoxia and microcirculation disorders are prevented. You can consult and carry out preventive treatment in a maternity hospital. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist