Troponin test is a biochemical analysis of blood composition, which makes it possible to detect the presence of the protein troponin (Tn) in it. This protein leaks into the bloodstream from cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells) that die during a heart attack.
In the blood plasma of a healthy human body, the concentration of troponin protein is very low, which is practically undetectable during diagnosis. This protein is present only in myocardial cells.
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction is necrosis of areas of muscle tissue of the heart organ, in which myocardial cells die without the right to be restored. At the moment of cell death, Tn enters the bloodstream, and its concentration can reach several thousand units.
The cardiac troponin index may be an indicator of myocardial infarction in the diagnostic study of heart attack.
What is troponin?
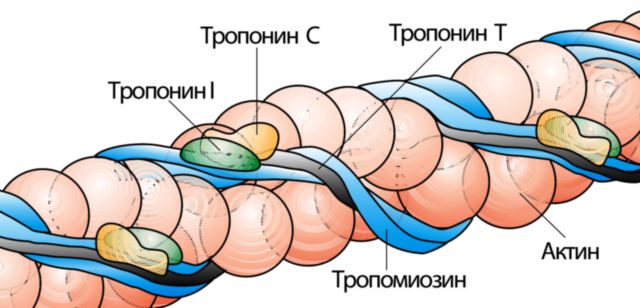
During a heart attack, not only this protein enters the bloodstream, but also other substances are found in the blood, but only troponin is associated with the cells of the myocardial tissue. The troponin protein complex in myocardial cells contains isoforms that interact with each other: T, C and I.
Each type of troponin protein has its own functional responsibilities: some perform their function in the ability of the heart muscle to contract, others are responsible for the condition of the heart tissue. All types of troponins differ from each other in molecular weight.
Troponins T and I, which are contained in isoforms, have 3 types:
- Cardiomuscular type
- Cardiomuscular slow type,
- Cardiomuscular type is fast.
Isoforms T and type I are most specific to myocardial muscle, therefore they are called cardiac troponins
.Damage and destruction of myocardial cells leads to the fact that the troponin complex disintegrates. Its individual isoforms penetrate into the blood plasma within a few minutes. At this time, their concentration can be diagnosed using modern equipment (laboratories and rapid troponin test).
The troponin test for heart attacks has been used for 10 years. The sensitivity of the biochemical analysis for the protein troponin is about 100.0%.
The troponin test indicates one isoform of the protein in the blood plasma, this is T, or I. For diagnosis, venous blood is taken in a volume of several milliliters. Protein concentration is determined in blood plasma or serum.
Standard indicators
In every healthy organism, during the physiological process of myocardial cell death, the plasma level is determined to be quite low.
The standard indicator of troponin type T which, without the presence of pathologies of the cardiac organ in the body, ranges from 0.010 ng/ml to 0.10 ng/ml. The unit of measurement for troponins is nanogram/liter (ng/L).
The protein index increases not only during a heart attack, but also for the following reasons:
- After surgery on a cardiac organ,
- Acute coronary syndrome,
- Damage to skeletal muscle cells
- Sepsis,
- Inflammatory process in the pericardium, pericarditis,
- Inflammation of the myocardium, myocarditis,
- Injury to the heart muscle
- Hypovolemia accompanies cardiogenic shock, hypovolemic, as well as septic shock,
- Reduced level of blood pressure (BP) in the bloodstream,
- Supraventricular type of tachycardia,
- In case of atrial fibrillation with atrial fibrillation,
- Left ventricular hypertrophy caused by hypertension
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy,
- Hemorrhagic stroke,
- Ischemic stroke,
- Vasculitis of the coronary arteries,
- Severe anemia
- Endothelial dysfunction of coronary vessels without cardiac ischemia,
- Dissection of the aortic walls, aortic insufficiency,
- Disorders of the aortic valve,
- Amyloidosis and sarcoidosis.
One of the reasons why protein levels increase.
Extracardiac pathologies that cause an increased troponin index in the blood:
- Therapy with medical chemicals,
- Overdose of catecholamines,
- Intoxication of the body due to snake bites,
- Toxins from a scorpion sting,
- State of myxedema coma,
- Severe large-scale burns,
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pulmonary hypertension,
- Bleeding inside the cerebral cortex,
- Chronic renal failure,
- Alcohol intoxication in acute and severe form.
Bleeding inside the cerebral cortex.
If the pathology of the cardiac organ occurs in a typical form, then an ECG (electrocardiography) can be done to determine it, but if the disease develops in an atypical form and the cardiogram does not provide accuracy in the examination, then to diagnose a heart attack, it is necessary to use a troponin test through a biochemical blood test.
A quantitative troponin test is carried out only in laboratory conditions, and the result of its study will be a specific digital result.
Troponin test with normal troponin I protein:
| Concentration up to 0.50 µg/l | Myocardial infarction in acute form is not established |
| From 0.50 mg/l to 2.0 mg/l | Acute myocardial infarction is confirmed |
Troponin test with a normal troponin T index:
| Concentration less than 0.40 µg/l | Myocardial infarction is not diagnosed and a repeat test is ordered in a couple of hours |
| From 0.40 µg/l to 2.30 µg/l | Acute myocardial infarction is confirmed, but requires additional research |
| More than 2.30 µg/l | Proven infarction in the acute stage of the disease |
In what time period is it relevant?
In case of a heart attack, determining the level of troponins will help make a diagnosis even after a few days. An increase in protein concentration is observed a couple of hours after the onset of the disorder, and the indicators persist for several weeks.
An electrocardiogram will help determine abnormalities in heart rhythm, and a troponin test will reveal the exact cause of the abnormalities.
The need for such a test may arise if the patient exhibits signs of an attack in the form of:
- suffocation;
- chest pain;
- strong feeling of weakness.
With a typical heart attack, it is easier to determine the problem, but in the case of an atypical form, it is possible to accurately diagnose the pathology thanks to the troponin test. With its help you can always count on accurate information.
Cardiac markers
In the first few hours of the progression of a heart attack, it is quite important to determine the situation and establish an accurate diagnosis of the attack. The life of the patient depends on the efficiency of doctors.
Previously, the doctor received information through instrumental research:
- The picture of clinical symptoms is severe and burning pain in the chest,
- Results by ECG method,
- Biochemical indicators myoglobin, creatine kinase index, lactate dehydrogenase index.
Recently, the mechanism of diagnostic studies of heart attack has changed. The first analysis that is done during an attack is a troponin test and an instrumental ECG method.
Using this examination strategy, it is now possible to recognize myocardial ischemia in the first couple of hours from the moment the first signs of pathology appear, which allows for a timely diagnosis with minimal damage to the heart muscle.
The sooner a troponin test is performed, the sooner drug therapy for a heart attack is started, and the greater the patient's chance of survival.
The specificity of the method for studying the troponin test in the pathology of the first myocardial infarction is 100% and this is its advantage over other methods. During the second attack of a heart attack, Tn do not react strongly to it, although they have an increased level.
In the second case of infarction, more information can be obtained from the MV QC indicator. MB is myoglobin, and CK is creatine kinase.
Troponin complex
Troponin is not just a single-celled substance that takes part in the work of the heart, it is a whole complex containing 3 units. Each component has its own distinctive characteristics in terms of amino acid composition, weight, and location in the myocardium.
According to its functions in the heart muscle:
- Tn type T properties of this molecule bind to tropomyosin, with the help of which the regulatory complex is attached. In the cells of myocardial tissue (cardiomyocytes), troponin T is 2 times more than troponin I. Tn I has a different amino acid composition and is found in myocytes of other myocardial tissues,
- Tn type I is a substance that puts pressure on ATPase activity. Although this troponin is in lower concentration in the myocardium, its sensitivity is much higher than Tn T,
- Tn type C. This marker is not involved in diagnosis, because the Tn T and Tn C markers in the myocardial muscles are identical and there is no way to decipher it. This troponin binds to calcium molecules.
Troponin molecules.
Troponin is a regular complex of protein molecules that are found in the blood in small quantities in a healthy normal body.
In the damaged state of the muscle tissue of the heart, the troponin complex is quickly broken down, and releases troponin protein molecules from the damaged and collapsing heart muscle during necrosis. During a heart attack, troponins increase in plasma several hundred times.
A troponin test is used for diagnostic study of indicators during a heart attack.
The troponin test can also be used during therapy to monitor drug treatment and adjust it as necessary.
What is this indicator
Troponin is a regulatory complex consisting of three proteins that is found in cardiac muscle tissue. These elements are responsible for the contractility of the organ.
If the person’s health is normal, then these proteins should not be detected in the blood. A heart attack is a pathological condition caused by an acute circulatory disorder in the area of the heart muscle. Due to lack of oxygen and nutrients, the area that is not receiving blood begins to die and troponins are released into it, which can be seen with a test.
The presence of this protein in the blood is observed only in the event of a heart attack, so analysis of the indicator provides an opportunity to accurately make a diagnosis.
Troponins play an important role in the functioning of the heart. They regulate its relaxation and contraction. The influence of these elements ensures easy sliding of the striated muscles. Most of all it contains troponin T. It is several times higher than the amount of other types.
In the process of diagnosing myocardial infarction, the presence of troponin in the blood is taken into account. If I and T were detected, this indicates the course of necrotic processes in the muscle tissue of the heart. Each of them remains in the blood serum for a certain time, which greatly facilitates the diagnosis process.
Troponin I in a quiet state helps prevent the formation of bridges between myosin and actin and is responsible for changing the configuration of the troponin complex.
This protein is highly cardiac specific. Its increase is observed three hours after the onset of ischemic disorders. A high level can be detected within 5-10 days, but without a second phase of increase.
Troponin T has the maximum molecular weight. With its participation, the troponin complex joins tropomyosin. In a normal state, this indicator in the blood is 0.0064 micrograms. The process of getting into it consists of two phases:
- An increase in level is observed in the period of three to eight hours from the onset of the attack. The largest amount of protein from the destroyed cell begins to be released 12-18 hours after an acute disruption of the blood supply.
- The second stage of increase is observed on the third day after the attack as a result of the slow release of the troponin-tropomyosin complex from the necrotic focus.
After a week, the indicators are completely normalized to zero.
If the permissible blood flow was restored in the early stages of the development of the pathology, then the maximum amount of troponin T is observed in it after 14 hours, and the next increase will be lower than the first.
How long protein levels remain high in the blood depends on the size of the lesion. If it was extensive, an increased amount of type T is detected within three weeks from the onset of the attack.
Troponin T during myocardial infarction allows us to identify the exact time of onset of the development of the pathological process, even if the patient himself did not notice it. The protein is highly sensitive to the slightest violation of the integrity of muscle fibers and immediately enters the blood.
Most often, a test is performed for the presence of troponin I. This indicator indicates the development of myocardial infarction. For a more accurate diagnosis, the analysis can be combined with other markers of the pathological process.
Troponins are also called cardiac markers. Their level in blood serum is determined:
- If an elderly person needs surgery.
- For diseases of infectious origin that impair the functions of the heart.
- To determine the degree of myocardial endurance before general anesthesia.
- To identify pathological processes in the organs of the cardiovascular system at the beginning of development.
- To study the dynamics of the disease after treatment.
There are other studies that accurately show the development of necrotic disorders in the heart muscle. They also occupy an important place in the diagnosis of infarction. In addition, they can determine:
- C-reactive protein.
- Myoglobin.
- Creatine kinases.
- Troponin I and T.
The latest cardiac markers have appeared in diagnostics recently. The high information content of the technique is associated with the specificity of protein compounds. The analysis allows you to obtain accurate results if the disease is at an early stage of development. Determination of protein levels is carried out several days after the attack, the information content of the study does not change.
WE RECOMMEND: Deciphering a blood test for cholesterol
How to do a troponin test?
In case of a heart attack, the main thing is not to miss the time for emergency treatment, so the ideal solution would be to use the rapid troponin test method. This heart attack testing can be performed by the patient himself or by an emergency doctor. The rapid troponin test is a qualitative method for diagnosing troponin.
Quantitative diagnostics of troponin in the blood can only be done in a clinical laboratory. This is quite a long time compared to quick and emergency express diagnostics. The rapid troponin test is performed in 12 minutes to 20 minutes.
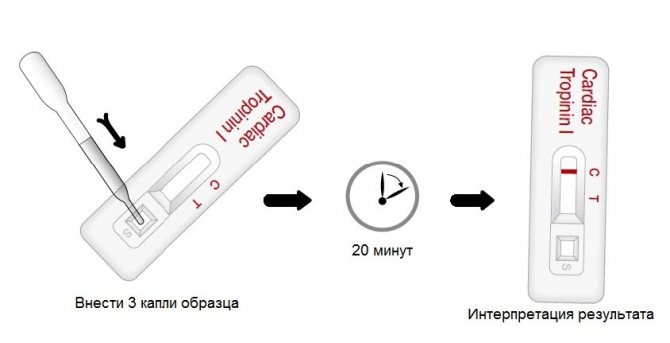
Test procedure.
The mechanism of action of this express is very simple. On the test device, according to the instructions for use, it is necessary to apply a few drops of blood to the application area where antibodies are present, upon touching which the molecules react and a complex is formed. Within 15 minutes the reaction reveals the presence of troponins, if present.
According to this test, red blood cells are separated, and plasma with markers enters the detection zone, in which there is a signal line where the protein streptavidin is applied, as well as a control line with immobilized troponin. The control line is with antibodies.
A change in color on the troponin express test indicates the presence of troponin molecules in the plasma. When the control line is colored, this indicates that the testing was carried out according to the rules.
Explanation of testing using the express method:
- 1 band stained negative, no troponin detected in plasma,
- 2 stripes are colored positive, there is troponin in the blood,
- If no stripes appear at all, then the test is not suitable for use.
Price for systems for determining troponin
Express tests for determining Tn type I in serum, plasma and blood.
Available in all pharmacies:
- Troponin express test kit for identifying Tn I molecules from the manufacturer Wondfo.
- Express Test for troponin from the manufacturer Formed.
- Troponin express test for measuring troponin in blood, plasma and serum, from .
Each troponin test kit includes:
- Test - cassette, tightly packed in foil,
- Pipette for collecting and dispensing blood,
- Instructions for using the test.
Testing blood for troponin in the laboratory
Tn T or Tn I is studied by taking a blood sample into a test tube. This analysis can be performed immediately, or the blood sample can be frozen.
Testing method:
- Tn type I and type T can be used for diagnosis. They are both useful markers of infarction and give the same clinical indicators,
- It is impossible to use the troponin test from different manufacturing companies in diagnosis, because such comparisons cannot be made. The result of a comparison study, the troponin test Tn T and Tn I, will not be correct in this situation, even if they have the same reference limits,
- Compare in one analysis: you can only test from one manufacturer, from one production lot number. Only in this case can you be 100% confident in the result of biochemistry,
- Troponin T is studied according to a developed system of standards, troponin I does not have such a system,
- The first time blood is taken for a sample at the first symptom of a developed heart attack, if the troponin level is not determined, it is necessary to repeat the diagnosis after 2-3 hours,
- With such precision in the technique, it is possible to timely track the development of a heart attack, as well as monitor the dynamics of recovery.
Causes of high troponin concentration coronary syndrome
Troponin test is a method for studying blood composition during a heart attack.
And it involves determining the plasma level of troponin concentration:
- Troponin T (Tn T) in coronary syndrome appears in the blood 2-6 hours after blockage of the coronary artery occurs. The increased index is maintained for up to 14 calendar days, and sometimes up to 21 calendar days,
- Troponin I (Tn I) is one of the earliest markers that can be diagnosed 2 hours after the onset of symptoms of coronary syndrome; activity manifests itself during the first day and this troponin continues to be in the blood for up to 7 calendar days.
Troponin type I
The etiology of troponin I in the blood, in the composition of plasma and serum, is in the first place coronary syndrome caused by myocardial infarction. Also to destroy the troponin compound complex and release Tn I into the blood.
There are other reasons:
- IHD (coronary heart disease) in chronic form,
- Damage due to muscle trauma on the skeleton.
Cardiac ischemia
For these reasons, the concentration of troponin Tn I in the serum is only 10% less than during a heart attack and coronary insufficiency. Kinetics shows the yield of a given protein molecule as a two-phase line curve, on which the concentration in the serum increases within 2 hours.
The maximum concentration accumulates 16–20 hours after the first symptoms of the pathology (this is the first maximum phase). After this, the concentration decreases and after 60 hours, a repeated surge in the accumulation of troponin in the blood appears (the second phase of accumulation).
For other reasons, Tn I increases only once. Troponin returns to normal levels after 7 calendar days; in rare cases, there is a delay in the body for up to 14 calendar days.
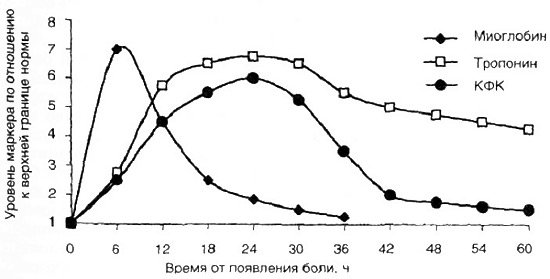
Dynamics of the main cardiac markers during myocardial infarction
Troponin type T
Troponin type T is a cardiac marker that has less specificity for myocardial infarction. The marker reacts not only to pathologies of the cardiac organ, but also to non-cardiac causes. Therefore, the etiology of this marker is much broader than that of Tn I. In addition to acute coronary insufficiency syndrome, as well as heart attack.
This troponin increases when:
- Angina pectoris
- Small focal infarction,
- After coronary artery bypass surgery,
- Angioplasty of coronary arteries,
- Heart transplant (noted until 3 calendar months),
- Myocarditis.
With these pathologies, there is an increase in the composition of the blood, or in the blood plasma, of troponin, but the level of molecules of this protein will not be as high as with a heart attack.
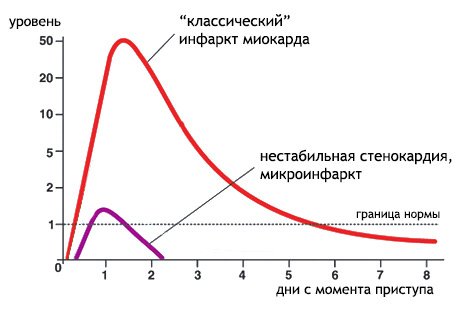
Differences in the dynamics of troponin levels in acute MI and unstable angina
How is the test done?
If you do the troponin test yourself, strictly follow the instructions that come with the strips.
In general it looks like this:
- massage the tip of your finger;
- pierce the skin;
- squeeze out the blood and place it on the indicator strip (4 drops are enough);
- mark the time (start the timer);
- wait a maximum of 15 minutes.
After this period of time, the strip indicators begin to color. If the color has changed on only one indicator, then the result is considered negative. If all the stripes are colored, you have a myocardial infarction.
Additional recommendations:
- the decoding of the test is indicated in the instructions for use;
- be sure to re-test to clarify the diagnosis (this should be done after 5 or 6 hours);
- It is advisable to carry out a troponin test at least 3 and maximum 6 hours after the onset of the first symptoms of myocardial infarction.
The troponin test, which is performed in a medical setting, differs from test strips because it is possible to determine the concentration levels of troponins T and I in a laboratory setting. Consequently, high accuracy of the result is ensured.
Comparative kinetics
If we compare all three troponins in the same proportions and under the same conditions, then we can see that troponin T has its own clear and characteristic differences.
Comparative kinetics of Tn T with Tn I and with Tn C:
- After the development of pain, TnT accumulates in the blood within three hours. This indicator is determined by the state of the blood flow system in the ischemic area,
- Over the next 72,100 hours, the TnT level rises and increases its concentration from the initial one, by at least 40-50 times, and sometimes even higher. The maximum concentration occurs after 100 hours, then this index stops and continues for 7 calendar days,
- After 7 calendar days it begins to decline. The decrease occurs slowly and this marker is detected in the blood for up to 20 calendar days.
Tn T indicator during thrombolytic therapy
During emergency and intensive thrombolytic therapy, troponin T in the blood changes 2 times within 100 hours:
- The first phase of peak concentration occurs 14 hours after the first symptoms of damage to the myocardial heart muscle,
- The second phase of high concentration occurs after 100 hours of therapy and this troponin value is lower than during the first surge.
Also, with favorable dynamics of healing of acute myocardial infarction, a decrease in troponin levels occurs on the 5th day and after a week from the moment of the heart attack is completely reduced.
Test indicators
Troponin levels alone are not used to diagnose or rule out a heart attack. A physical examination, medical history, and ECG are also important. Your doctor may also want to know whether troponin levels are consistently elevated over a series of tests or whether they rise or fall over a period of several hours.
In people with angina, high troponin levels may indicate their condition is worsening and they are at increased risk of a heart attack.
Elevated troponin levels are associated with:
- abnormally fast heartbeat;
- high blood pressure;
- blockage of a pulmonary artery by a blood clot, fat cells, or tumor cells;
- chronic heart failure;
- coronary artery spasm;
- inflammation of the heart muscle, usually due to a virus;
- active exercises (marathons or triathlons);
- trauma that damages the heart, such as a car accident;
- weakening of the heart muscle;
- long-term kidney disease.
High rates can occur as a result of certain medical procedures:
- cardiac angioplasty/stenting;
- cardiac defibrillation or electrical cardioversion;
- open heart surgery;
- radiofrequency ablation.
Recommendation!
A heart-healthy lifestyle with a nutritious, low-fat diet and regular exercise is the best way to prevent heart disease and heart attacks.
Decoding
The troponin level that indicates a heart attack is above the reference range. For example, if the norm is specified as 0.00 0.40. Then 0.41 is technically positive, although very weak, and 10 is very positive. Levels above the reference range may indicate heart damage, but there are other causes. When interpreting the study, it is important to know the laboratory's reporting reference range.
Even a slight increase in levels will mean heart damage. A very high reading is a sign that a myocardial infarction has occurred. In most patients who have had a heart attack, the value rises within 6 hours. After 12 hours, almost everyone who has had a heart attack will have elevated protein levels. The reading may remain high for 1-2 weeks after the heart attack.
Test reliability
Troponin tests are incredibly more sensitive than the older markers. The early assay has virtually no false positives from skeletal muscle injury and, when used in a narrowly defined population, has high sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing acute myocardial infarction.
Limitations of the study relate to the high detection limits of early assays. Most experts were inclined to think that any detectable troponin was associated with necrosis or infarction. Levels may be elevated in various chronic conditions such as renal failure or heart failure, or in acute conditions such as sepsis. Now, with increasing analytical sensitivity of assays, troponin is detected in many patients with myocardial necrosis due to causes other than acute myocardial ischemia from - for plaque rupture.
Advantages of biochemical analysis for the detection of troponin
The basis for conducting a biochemical analysis for troponins (troponin test) is the suspicion of the beginning of the formation of foci of necrosis in the heart muscle in acute coronary syndrome.
The troponin regulatory complex is the first marker for determining large-focal and small-focal infarction in the heart muscle, because the molecules of the complex are one of the first to begin to disintegrate during necrosis and enter the bloodstream.
A troponin test can be performed in the following situations:
- An acute attack of myocardial infarction, with a non-specific increase in markers,
- Subacute form of heart attack. Troponin testing is ideal as a late marker, since by the time of the study the CK markers and the CF-CK marker have already reached standard values,
- During thrombolysis and to evaluate its results,
- To determine the extent of ischemic damage to the heart muscle,
- To determine an asymptomatic attack of a heart attack before surgical intervention in the heart muscle,
- For acute coronary syndrome, which may be caused by a heart attack,
- To control treatment with drugs of the heparin group.
Acute coronary syndrome
Methods for testing cardiac troponins are being improved, more highly sensitive antibodies are being developed, which makes it possible to quickly determine the level of myocardial damage.
It is possible to determine an accurate diagnosis already 2 hours after the first signs of a heart attack using the troponin test. And for coronary syndrome and heart attack, time is the main indicator in saving human life.
Why is a troponin test done for a heart attack?
The troponin test is used to determine the presence of pathological areas in the myocardium. With its help, you can detect the primary stage of development of a heart attack. The strips are also used to track the course of the disease during treatment and rehabilitation.
Why is a troponin test recommended for suspected myocardial infarction:
- it is possible to determine the prognosis of treatment outcome;
- the size of ischemic lesions is assessed;
- silent type of heart attack is excluded;
- the risks of the disease are identified;
- the results after thrombolysis are assessed;
- the period of the disease is determined: for example, in the subacute phase the TnT marker is significantly exceeded.
Specificity of cardiac markers in myocardial infarction
In patients with an attack of coronary syndrome and myocardial infarction, the first test, a troponin test, may give a negative presence of troponin protein molecules in the blood. This happens with repeated large-focal, as well as small-focal infarction. Therefore, it is necessary to know the dynamics of growth and apply timely repeated testing.
| Troponin T has its own specific dynamics | the cardiac marker has the properties of increasing the index after 3 hours and up to 8 hours, |
| reaches a maximum concentration from 12 hours to 100 hours, | |
| the normal value occurs after 14 calendar days. | |
| Troponin type I has its own specificity in growth dynamics | the cardiac marker has the properties of increasing the index after 4 hours and up to 6 hours, |
| reaches its maximum concentration in the first day - from 12 hours to 24 hours, | |
| the norm occurs in 10 - 21 calendar days. |