Scientific editor: M. Merkusheva, PSPbSMU named after. acad. Pavlova, medical practice. March, 2021.
Synonyms: carcinoembryonic antigen, CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen, Carcinoembryonic Antigen, CEA.
Cancer embryonic antigen (CEA) is a protein component of the blood, a tumor marker that is used in the diagnosis of benign and malignant processes in the gastrointestinal tract. A healthy body produces CEA in minimal quantities, but under the influence of unfavorable factors (smoking, poor diet, etc.) its level may begin to increase.
CEA analysis allows for the timely detection of malignant processes in the large intestine and other organs (rectum, stomach, lungs, ovaries, mammary glands).
General information
Cancer embryonal antigen was first identified in 1965 in a patient with colon cancer. This enzyme of protein origin begins to be produced in the fetus from the moment the gastrointestinal tract organs (esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, intestines) are formed. At this time, the concentration of the substance reaches its limit. After the birth of a child, a small amount of CEA remains in the blood plasma, which tends to decrease with age. The substance is found in residual quantities not only in the blood, but also in the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract and lungs, the epithelium of the mammary glands, on mucous surfaces, in the cerebrospinal and ascitic fluid. After birth, the gene that is responsible for the production of embryonic antigens should normally be deactivated.
An increase in CEA levels in adults is observed during a pathological (usually benign or malignant) process, inflammation, autoimmune diseases, as well as during pregnancy (increases by the 3rd trimester, but the values remain normal or long-term smoking.
Note: the habit of smoking leads to an increase in CEA in the blood, which indicates an increased risk of cancer. In a healthy person, the norm of CEA in the blood is up to 2.5 ng/ml of blood, while in a smoker it can reach 5 ng/ml or more. Complete
smoking cessation in just 3 months leads to a significant improvement in pulmonary function parameters and a decrease in serum CEA.
CEA analysis allows early diagnosis of malignant processes in the following organs:
- primarily cancer of the colon and rectum;
- bronchi and lungs;
- gastrointestinal organs (including the pancreas);
- pelvic organs (uterus and appendages, prostate gland);
- mammary glands;
- liver metastases;
- metastases to bone tissue.
What is the tumor marker CEA?
Tumor markers themselves are the result of the activity of cancer cells in the body, and appear simultaneously with them, concentrating in those places where the disease develops.
It was with their help that it became possible to detect cancer tumors in the early stages, when there are no obvious symptoms.
CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen)
, or
CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen)
is a protein that appears in certain tissues during fetal development during pregnancy. Immediately after childbirth, a woman’s level drops. In children it is also found in minimal concentrations. An increase in antigen levels in the blood may be a sign of the development of cancer.
Indications
An oncologist, a surgeon, a functional diagnostician and a competent therapist can give a referral for analysis and give an interpretation of the results of the study for the CEA tumor marker.
First of all, a specialist prescribes a test for CEA in the blood if there are alarming symptoms indicating the development of a benign or malignant process:
- sensation of a foreign body in the body, visual identification of a tumor and/or palpation;
- constipation, feeling of incomplete bowel movement, rectal bleeding;
- severe chest cough for a long time, shortness of breath;
- causeless increase in body temperature, fever;
- sweating during night rest;
- indigestion, lack of appetite;
- chronic weakness and lethargy, decreased strength, muscle tone;
- a sharp decrease in body weight without objective reasons;
- rapid loss of fluid from the body;
- hyperthyroidism (hypersecretion of thyroid hormones);
- an increase in the number of moles on the body over a short period of time;
- bleeding of unknown origin;
- long-term healing of wounds on the body;
- aching and nagging pain without an established cause.
In addition to the above symptoms, a CEA test is prescribed in the following cases:
- determination of the type, location, stage of the malignant process, the presence of metastases;
- choosing a conservative cancer therapy regimen and assessing its effectiveness;
- determining the effectiveness of surgical treatment of the tumor (CEA should return to normal 2 months after surgery). Moreover, CEA levels are often high at the time of relapse, even if they were normal before the initial tumor was removed, so CEA testing should be performed regularly long after surgery, regardless of whether high levels were present at the time of initial diagnosis.
- standard analysis for suspected benign or malignant processes in the gastrointestinal tract, especially the rectum or colon;
- if there is a suspicion of tumors of the breast, lungs, ovaries, tumor metastasis to the liver and bones;
- planned analysis for patients over time after completion of oncology treatment.
An annual study of the concentration of CEA in the blood is carried out for patients who are at risk for the following factors:
- heredity (first-degree relatives had cancer of internal organs);
- work in hazardous industries (risk of poisoning by toxins, radioactive components, radiation exposure);
- living in an unfavorable region with a high level of radioactivity, close to industrial enterprises;
- abuse of solarium (artificial tanning increases the likelihood of benign and malignant processes), sunbathing;
- elderly patients over 60 years of age with a burdened medical history (alcohol or cigarette abuse, presence of second- and third-degree relatives with cancer of internal organs).
What does the CEA tumor marker show?
The antigen is synthesized by the organs of the gastrointestinal tract
to stimulate active cell proliferation during fetal development. Thus, thanks to REA, the child grows normally. A small amount of antigen is sufficient to perform this function.
If an increase in the concentration of the tumor marker CEA is detected in venous blood, this may indicate a disease.
High levels of CEA were first observed more than 50 years ago in a person with colon cancer.
. The marker was initially thought to be specific only for this disease. Indeed, most often with the help of such an analysis, cancerous tumors are diagnosed in the intestines, especially the colon and rectum. However, its functionality is not limited to this.
A tumor marker helps diagnose:
- oncological tumors (benign and malignant) at the initial stage of development: cancer of the gastrointestinal tract, thyroid gland, breast;
- formation of metastases, secondary cancer;
- relapse that occurs after surgery at a stage when symptoms have not yet appeared;
- quality of treatment. CEA shows how successful the previously conducted complex therapy for oncological tumors was.
REA is normal
Important! Standards may vary depending on the reagents and equipment used in each particular laboratory. That is why, when interpreting the results, it is necessary to use the standards adopted in the laboratory where the analysis was carried out. You also need to pay attention to the units of measurement.
In babies in the womb, the indicator is overestimated and may remain so for some time after birth. As a rule, the analysis is carried out on adults, where reference values will differ for people with and without nicotine addiction.
- for non-smokers: 0 - 3.8 ng/ml;
- for smokers: 0 - 5.5 ng/ml.
Important! The interpretation of the results is always carried out comprehensively. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based on only one analysis.
Preparing for a blood test for rhea
Proper preparation for any analysis reduces the risk of false results and increases the accuracy of the study. The biomaterial for the criterion under consideration is blood serum, which is collected in special vacuum sterile disposable tubes from the patient’s cubital vein. Recommendations for preparation:
- 1 day before, exclude fatty, smoked and fried foods from the diet, and at least 8 hours before donating blood, do not eat food. This rule is explained by the fact that during the digestion of food, the production of enzymes in the human body is activated, some of which are similar in chemical structure to tumor markers. Neglecting the recommendation will lead to the risk of obtaining false positive results;
- in the evening before collecting biomaterial, you are allowed to drink clean, non-sweetened water without gas, and in the morning - 1-2 glasses of water. This will reduce the risk of hemolysis and the formation of blood clots in vitro;
- half an hour before the procedure, it is necessary to exclude physical and emotional stress, which leads to changes in the functioning of the hormonal and endocrine systems and, as a result, unreliable results. 15 minutes before donating blood, calm down and sit in the laboratory in a comfortable position;
- It is necessary to limit the intake of any medications in consultation with your doctor for at least 1 day. If it is impossible to cancel life-saving medications, it is important to notify laboratory staff about their use. In this case, when selecting reference values, not only gender, age, alcohol and smoking abuse, but also medication use will be taken into account.
The duration of research in private clinics is 1 day, not counting the day of taking the biomaterial, and the price starts from 550 rubles.
Increasing values
If the permissible values (6.5 – 10 ng/ml) are exceeded, the development of a benign process in internal organs is suspected, but the initial stage of cancer cannot be ruled out. If CEA has reached 10 ng/ml and continues to rise, then additional studies are used to diagnose oncological processes in the body. As a rule, in cancerous tumors, the cancer embryonic antigen can increase several times, and in the presence of metastasis, the rate exceeds the norm by several tens of times.
Increase to 10 ng/ml
An increase to 10 ng/ml may indicate the following pathological processes:
- neoplasms of internal organs (neurinomas, lipomas, polyps, fibromas, cysts, etc.);
- ulcerative processes in the mucous membrane of the stomach and colon;
- benign liver tumors (hepatocellular adenoma, hemangioma) and diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis, acute alcohol or chemical intoxication, nodular hyperplasia);
- respiratory diseases (pneumonia, bronchitis and others);
- Crohn's disease (granulomatous inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract);
- emphysema (pathological expansion of the alveoli of the lungs);
- tuberculosis;
- inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, including the pancreas (pancreatitis);
- renal failure;
- cystic fibrosis (severe damage to the exocrine glands).
- autoimmune diseases;
- smoking
CEA is greatly increased
When the CEA concentration increases to more than 10 ng/ml, the following malignant processes are suspected:
- cancer of the rectum, colon or colon (CEA is more enlarged with right-sided organ damage);
- cancer of the respiratory system (lungs, bronchi, pleura);
- stomach cancer (additionally, tests for CA 19-9 and CA 72-4 are prescribed);
- cancer of the female genital organs (uterus and cervix, ovaries), prostate gland in men;
- oncology of other internal organs (less commonly): mammary glands, esophagus, thyroid gland (medullary carcinoma), bladder, liver, etc.;
- metastases in bone tissue, liver.
Table: sensitivity of CEA to diseases:
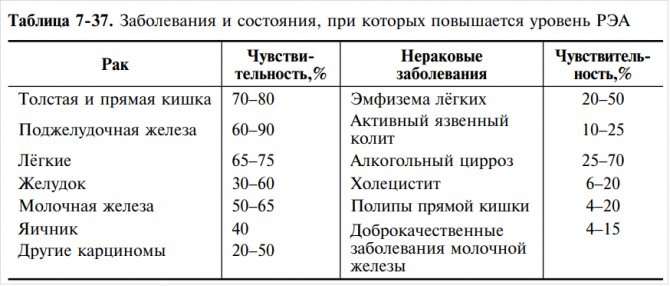
An increase in CEA concentration of more than 20 ng/ml before treatment indicates tumor metastasis.
Indications for taking a blood test for rhea
If the presence of a neoplasm is visually determined during an ultrasound examination, the doctor will issue a referral for CEA. Symptoms indicating the development of cancer pathology in the human body:
- lumps in the mammary glands;
- change in nipple color;
- changes in the shape and size of the mammary glands;
- pathological discharge from the nipples;
- failure of the regularity of the menstrual cycle;
- bloody stool or bleeding from the anus;
- vaginal discharge mixed with blood and a strong unpleasant odor;
- frequent urge to urinate without relief;
- bloating;
- constant nausea;
- sudden weight loss or weight gain without objective reasons;
- constant sweating;
- hardening of the lymph nodes;
- increased fatigue, drowsiness, psycho-emotional disorders.
The study is mandatory when receiving treatment for oncological pathologies in order to determine the effectiveness, as well as after surgical removal of the tumor - to monitor the possibility of the spread of metastases. After completing cancer therapy, each patient is observed for a long time and tested for tumor markers for the purpose of early detection of relapse.