Dates
Most experts recommend conducting a GTT examination during pregnancy between 24 and 26 weeks of gestation. By this time, a physiological decrease in insulin sensitivity occurs.
If it is impossible to carry out a GTT analysis at the specified time, appointments up to 28 weeks are allowed . Examination at a later stage of pregnancy is possible with the direction of a doctor. By the beginning of the third trimester, the maximum decrease in insulin sensitivity is recorded.
It is not advisable to prescribe a glucose tolerance test before 24 weeks in women without concomitant risk factors. A physiological decrease in insulin tolerance is rarely observed in the first half of pregnancy.
However, there are risk groups for carbohydrate metabolism disorders. Such women are advised to undergo a glucose tolerance test twice during pregnancy. The first blood test is prescribed at the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy - between 16 and 18 weeks. The second blood draw is carried out as planned - from 24 to 28 weeks. Sometimes women are shown an additional test for glucose testing during pregnancy in the third trimester of pregnancy.
How to take it
The first logical question that women ask during pregnancy is at what period of time GTT is performed.
A glucose tolerance test is done in the first trimester along with a number of other tests. In order to properly undergo the examination, you must carefully prepare:
- exclude nervous disorders;
- limit physical activity;
- do not make significant changes in the diet - eat as usual (do not follow any diets);
- do not eat food (within 8 hours before the test).
The test is not performed if there are any diseases in the acute stage, even in the case of a common runny nose. Any changes of this kind will greatly affect the results of the study, so these options must be excluded.
GTT is done on an empty stomach (you can drink water, but not during testing). It is carried out by drawing blood from a vein 3 times, with an interval of 1 hour between the second and third sampling:
- First, blood is drawn.
- After this, a special sweet liquid (glucose syrup of a certain concentration) is drunk.
- For the next hour, the patient should not eat, drink, or exercise - all this can greatly distort the test results.
- The next blood draws are carried out an hour and two after the first analysis.
- After this time, after taking the cocktail, the blood sugar level in a healthy person returns to normal. This is what the test results should reflect.

Must consult a doctor
If the readings are high and not within normal limits, an immediate consultation with a doctor monitoring the pregnancy is prescribed. If the first test shows an elevated sugar level, a repeat appointment will most likely be scheduled to rule out a possible error. There are a number of reasons why a false result is possible:
- the eight-hour diet was not followed before donating blood;
- significant changes in diet during the three days before the test (increased or insufficient carbohydrate intake);
- carbohydrate metabolism disorders;
- excessive physical activity;
- stressful state;
- infectious diseases (including respiratory acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections);
- taking any medications that affect carbohydrate metabolism (warn your doctor about the use of medications).
Indications
A single blood test as a test for glucose tolerance during pregnancy is indicated for all expectant mothers. Glucose for the glucose tolerance test as an analysis allows you to diagnose pathology and select effective treatment in the early stages.
Every woman has the right to decide for herself whether to undergo a glucose test. If there is any doubt, the expectant mother may refuse the study. However, doctors recommend mandatory GTT testing during pregnancy for all pregnant women.
Most cases of gestational diabetes are asymptomatic. The disease poses a serious threat to the life and health of the fetus. What is a glucose tolerance test? This is precisely what a glucose tolerance test is for during pregnancy, in order to make a diagnosis before symptoms appear.
There are 7 risk groups for which a glucose tolerance test is indicated at least twice:
- Expectant mothers with a history of gestational diabetes.
- Presence of concomitant obesity - body mass index above 30.
- If sugar is detected in a clinical urine test.
- History of the birth of a child weighing more than 4000 grams.
- The age of the expectant mother is over 35 years.
- When diagnosing polyhydramnios during an ultrasound examination.
- Presence of patients with carbohydrate metabolism disorders among relatives
The listed groups of expectant mothers are strictly not recommended to refuse to undergo a glucose tolerance test.
Features of reducing sugar levels
Symptoms of a lack of glucose in the body can be observed at certain times of the day (morning or evening), and their severity depends on the degree of reduction in blood glucose. If the sugar level drops to 3.4 mmol/l, then the person feels irritability, low tone, decreased performance and general weakness or lethargy. As a rule, to correct the condition, it is enough to take carbohydrate foods.
When a lack of sugars is associated with the development of diabetes mellitus, the patient feels:
- sudden loss of strength;
- violation of thermoregulation and, as a result, hot flashes or chills;
- increased sweating;
- frequent headaches and dizziness;
- muscle weakness;
- decreased concentration and memory;
- frequent feelings of hunger, and after eating food - nausea;
- drop in visual acuity.
Critical situations are accompanied by convulsions, uncharacteristic gait, convulsions, fainting and coma. It is important to promptly pay attention to the manifestation of severe hypoglycemia and provide competent medical care.
A glucose tolerance test shows low values if:
- the patient takes medications that help reduce the level of simple sugars, for example, insulin;
- The person being examined exhibits insulinoma. The disease is accompanied by the formation of a neoplasm, which begins to actively secrete a substance similar to insulin. A third of the neoplasms occur in a malignant form with the spread of metastases. The disease affects people of all ages: from newborns to the elderly.
The prognosis of the outcome depends on the nature of the tumor; in case of benign tumors, complete recovery is observed. Malignant neoplasms with metastases significantly worsen the prognosis. However, it should be emphasized that mutant tissues are highly sensitive to the effects of chemotherapeutic drugs.
Reduced values are also recorded after prolonged fasting of the examined patient or after intense physical exercise. The diagnostic significance of such results is low. It is necessary to exclude the influence of external factors on the biochemical composition of the biomaterial and repeat the study.
Glucose and blood sugar - the same thing or not?
The answer to this question depends on the context of the concepts being considered. If we are talking about analysis for sugar and glucose, then the concepts have equivalent meaning and they can be considered interchangeable synonyms. The use of both terms will be considered correct and appropriate.
If we answer the question from the point of view of chemistry, then the equivalent equation of concepts is not correct. Since sugar is an organic substance of low molecular weight carbohydrate. Sugars are divided into mono-, di- and oligosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars; glucose belongs to this subgroup. Oligosaccharides contain from 2 to 10 simple sugar residues, and disaccharides are a special case of them.
How often should you take the GTT?
Doctors referring for the study: therapist, pediatrician, endocrinologist, surgeon, gynecologist, cardiologist.
A glucose tolerance test during pregnancy is mandatory for women with increased risk factors. For example, a history of thyroid disease, known cases of impaired glucose tolerance in close relatives, or abuse of bad habits.
For patients over 45 years of age, the study is recommended to be carried out once every 3 years. However, in the presence of excess body weight and high risk factors (similar to pregnant women), it is advisable to perform GTT at least once every 2 years.
If the fact of impaired glucose tolerance is established, the study is carried out once a year.
Preparation
How is the glucose tolerance test performed: mandatory preparation is required for the reliability of the test results for the expectant mother. It includes the withdrawal of drugs from the group of corticosteroids, hydrochlorothiazide and antiepileptic drugs. They stop taking them three days before the proposed study.
10-12 hours before the glucose tolerance test during pregnancy, the expectant mother is prohibited from eating any food. It is not recommended to drink water, tea or other liquids in the morning before the examination. You should also not brush your teeth or use chewing gum.
Fasting for less than 10 hours is prohibited. Some foods can take a long time to break down in the gastrointestinal tract and cause false positive results. Also, you should not fast for more than 14 hours - this promotes enhanced absorption of glucose into the tissue.
Cigarette smoking affects the reliability of the study results. The expectant mother is prohibited from consuming nicotine 12 hours before the expected test. It is also not recommended for a woman to be nervous - stress contributes to false conclusions.
Norm of analysis
The norm for a glucose tolerance test during pregnancy is that when carbohydrate metabolism is normal, the sugar level after fasting does not exceed 5.1 mmol/l. Such numbers indicate the physiological functioning of the pancreas - proper basal secretion.
After an oral glucose tolerance test in any sample, plasma glucose normally does not exceed 7.8 mmol/l. Normal test values indicate sufficient insulin secretion and good tissue sensitivity to it.
Sugar norm, in mmol/l
After a 10-12 hour fast
Up to 5.6
Within 2 hours after taking the solution
Up to 7.8
Contraindications
There are a number of patient health conditions that are direct contraindications to performing a glucose tolerance test. First of all, we are talking about the patient’s sometimes individual intolerance to glucose, the introduction of which into his body can lead to a sharp and severe reaction. In this case, it is necessary to carry out measurements without a glucose load, however, it should be noted that sugar intolerance in most situations is the key to its normal concentration in the blood, since the patient’s health does not allow him to consume high-carbohydrate foods.
Another contraindication is any gastrointestinal disease in the acute stage, but in this case it will be enough to replace oral GTT with intravenous one. The test will have to be postponed if the patient is diagnosed with inflammatory and infectious diseases, as well as acute toxicosis. Finally, it is not recommended to carry out the analysis in the post-operative period and when the patient is prescribed strict bed rest.
Danger to the fetus
If all rules are followed, a glucose tolerance test during pregnancy is safe for the unborn child. That is why expectant mothers should not refuse the test. Why do they do it? The expected benefit from the examination is much higher than the expected risk.
Possible harm to the fetus is associated with analysis with existing contraindications. Acute hyperglycemia during the test can contribute to temporary oxygen starvation of the unborn child. However, such an outcome is possible against the background of concomitant type 2 diabetes.
Alternative Methods
An alternative to the study is to calculate glycated hemoglobin. The analysis reflects blood sugar saturation over the past 3 months.
Normally, glycated hemoglobin is up to 5.5%. In diabetes, its value corresponds to 6.5% and higher. The diagnosis of prediabetes is made at intermediate figures of the indicator.
In gestational diabetes, glycated hemoglobin is usually between 6 and 6.5%. However, with pathology, it is possible to obtain normal test results.
A home glucometer is also used to determine blood glucose levels. The device determines the sugar level from your finger. Its use is absolutely safe for the health of women and children.
An alternative to fasting glucose levels is to measure them after a night's sleep. The upper limit of normal corresponds to 5.6 mmol/l. An analogue of the oral test is eating foods rich in carbohydrates. Normally, blood sugar from a fingertip should not exceed 7.8 mmol/l.
Interpretation of glucose tolerance test results during pregnancy
So, if the fasting blood glucose concentration is less than 5.1, this is normal, above 7.0 is manifest diabetes; if it exceeds 5.1, but at the same time is below 7.0, or 60 minutes after a glucose load - 10.0, or after 120 minutes - 8.5 - this is GDM.
Tab. 1 Threshold values of venous plasma glucose for the diagnosis of GDM
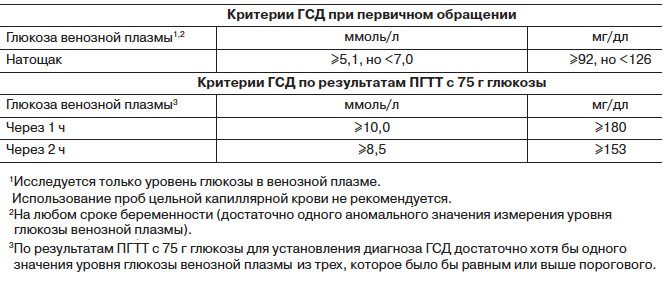
Tab. 2 Threshold values of venous plasma glucose for the diagnosis of overt diabetes during pregnancy
The correct approach to identifying and treating diabetes (if necessary) significantly reduces the risks of complications during pregnancy and childbirth itself and the degree of threat of developing diabetes in the distant future in women predisposed to it.