Description
A blood test for the hCG hormone is possible as early as 6 days after the expected conception. It will accurately determine whether the girl managed to get pregnant and will also show the general condition of the body. The test is much more effective than a standard strip test, which may well show an incorrect result.
Urgent analysis is a necessary procedure through which pathology is identified or its absence is stated. In cases where it is only necessary to diagnose conception, medicine makes do with a standard blood test for the hCG hormone.
Blood for hCG: when to donate
It is advisable to take a blood test to detect the level of hCG to establish the fact of pregnancy seven days (or later) after the expected conception. Quantitative indicators of hCG in the blood make it possible to accurately determine the duration of pregnancy. Further observation of changes in hCG levels allows you to understand how harmoniously the pregnancy is progressing. A doctor may prescribe an hCG test during pregnancy as part of the 1st comprehensive screening - a double test, in the third month of gestation or as part of a second examination - a triple test, in the fourth - fifth month of pregnancy. In the first trimester, regular monitoring of hCG levels is especially important if there is a risk of spontaneous abortion; in the second trimester, it allows the doctor to track the dynamics of fetal development.
The actual date of conception in pregnant women with late ovulation and an unstable cycle, as a rule, is quite different from the period that doctors assume. In this case, the actual gestational age can be assumed by analyzing hCG: its elevated level will allow us to judge the current period.

Indications for use
An in vitro hCG blood test has several good reasons to perform it:
- Statement of the fact of the appearance of the fetus.
- Conducting a study of the girl’s hormonal background, timely detection of failures and violations.
- Regular monitoring of the condition for the appearance of pathological types of pregnancy: A) Frozen pregnancy, the embryo stops developing at a certain period. B) Ectopic pregnancy, in this case the zygote is attached to the fallopian tube, and not to the walls of the uterus.
In addition, examination of the sample allows us to determine the presence of infectious diseases, various types of disturbances in the functioning of the body, ailments, etc. Among them can be diagnosed: tetanus, diphtheria, herpes, HIV, hepatitis and others. Therefore, the procedure is mandatory for all women.

Absolutely any diagnosed and confirmed disease poses a serious threat to a woman’s body and to a developing child. If the results obtained show deviations from the norm, the attending physician must refer the patient for additional examination.
Human chorionic gonadotropin-hCG (total)
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a complex protein molecule (drimer) with a molecular weight of about 46 kDa. HCG is a specific pregnancy hormone. It is produced by the syncytiotrophoblast of the placenta. The hCG molecule contains two subunits - alpha and beta. Subunits identical to the alpha subunit of hCG also have pituitary hormones: thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). The beta subunit (β-hCG) is unique. Her study allows for immunometric testing of the hormone.
After fertilization, the concentration of the hormone increases so much that after 6-8 days the presence of pregnancy can be determined by the blood serum, and after another 1-2 days - by the content of β-hCG in the urine. This is the basis for a quick test strip that allows you to carry out initial diagnostics without leaving your home.
In the first three months of pregnancy, hCG, acting on the corpus luteum, activates the production of progesterone and estrogens (female sex hormones) - they support pregnancy. The effect of hCG on the corpus luteum is similar to the effect of luteinizing hormone, whose task is to ensure its viability. This “patronage” lasts until the placenta is fully formed (up to 16 weeks) and the fetus and the placenta begin to produce the necessary hormones themselves. A male fetus, under the influence of hCG, which stimulates Leiding cells, begins to produce testosterone, a male sex hormone that affects the formation of male genital organs.
Human chorionic gonadotropin is produced by trophoblast cells - the outer surface membrane covering the embryo, due to the growth of which the embryo attaches to the wall of the uterus. It is detected in the female body 5-6 days after conception. The process of hCG production lasts throughout pregnancy, its amount becomes twice as large every one and a half days during the 2-5th week during normal pregnancy. The highest concentration is observed at 10-11 weeks, after which the levels gradually decrease. The level of hCG directly depends on the number of fetuses - the hormone content increases in proportion to it.
If the concentration of the hormone is reduced, this may be evidence of an ectopic pregnancy or a threat of failure. To determine possible abnormalities in fetal development, along with the study of hCG levels, alpha-fetoprotein and free estriol tests are used. A triple complex of prenatal diagnostics is carried out in the period from 14 to 18 weeks.
In addition to being an indicator of pregnancy, hCG is a tumor marker. The hormone is produced by malignant tumors formed from trophoblastic tissue, germinal cells of the ovaries and testes.
Human chorionic gonadotropin is determined in the range of 1.2 – 1,125,000 mU/ml.
Types of analysis
Today, two types of hCG analysis are used in medical practice:
- General. The procedure is necessary to determine the total fraction of the hormone and is used only in the early stages. It is also used as an opportunity to confirm the presence or absence of pregnancy. While this study is current, dipstick tests may not be 100% accurate. A general analysis is carried out regularly until the 19th week of gestation.
- Free hCG fraction. A specific study aimed at identifying malignant tumors in a woman’s body during pregnancy. This test can also be used for men. By determining the level of hCG in the body of both sexes, it is possible to timely diagnose diseases such as testicular cancer, hydatidiform mole, and pathological formations. In relation to the developing fetus, this testing allows us to determine the presence or absence of Edwards and Down syndrome in the child. If hCG levels are elevated, the woman is at risk. However, this does not provide a 100% guarantee that the fetus will develop pathological abnormalities.

Preparing for analysis
Preparation for analysis for the presence and level of hCG is carried out in the same way as a standard blood draw for general diagnostics of the body’s condition. The collection is made early in the morning, so for 8-14 hours you must refrain from eating, drinking alcoholic beverages and tobacco. It is necessary to exclude physical and psycho-emotional stress, and completely eliminate stress factors.

If necessary, taking a sample for research can be carried out during the day, at least 4 hours after a light meal. The accuracy of the study makes it possible to establish the fact of conception already 1-2 days after the delay of the menstrual cycle. However, taking into account the individual characteristics of each woman’s body, it is recommended to carry out testing 3-5 days after the delay of the cycle. This makes it possible to avoid the possibility of false results, with 100% probability of diagnosing the presence or absence of a fetus.
If testing does not give clear results, it is repeated after 2-3 days
Cost and terms
The cost and timing of determining results depend on the type of testing chosen:
- Standard test. The cost of standard testing is 500 rubles. The time required to collect results is up to 1 day.
- Urgent test. The cost of urgent testing is 900 rubles. The time required to collect and organize analyzes takes only 3-5 hours.
Please note that depending on the location of the clinic, prices may vary slightly.

Analysis transcript
The test form displays the level of hCG in the woman’s body. Based on the level of indicators, you can determine how the fetus is developing. Normal values for a healthy person are within 5 mU. Already in the second week of pregnancy, levels can range from 25 to 300 mU.
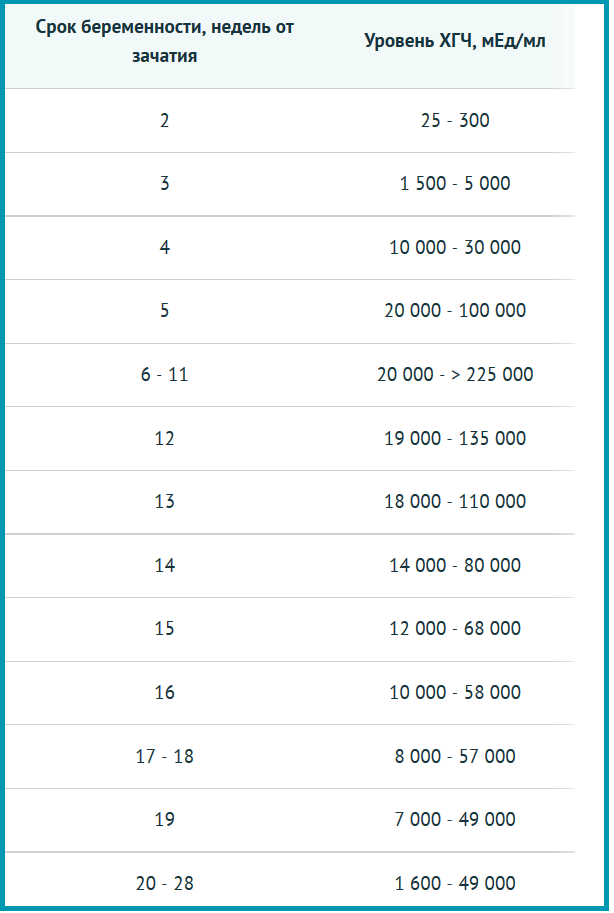
If, after taking tests for more than 2 weeks, hormone levels are in the range from 5 to 25 mU, it is recommended to test again. This is due to the fact that low levels of the hormone may indicate a number of abnormalities and pathologies:
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Frozen pregnancy.
- Fetoplacental insufficiency.
Repeated testing is also carried out if the indicators exceed the norm. High results may indicate:
- The existence of more than 1 fetus.
- Development of gestosis.
- Diabetes.
- Risk of congenital pathologies.
- Incorrectly diagnosed gestational age.
The reliability of in vitro hCG is quite high. The obtained indicators make it possible to determine the presence or absence of conception after 2 days after the fact of a delayed menstrual cycle has been established.

After determining the presence of a fetus, the obstetrician-gynecologist determines the type of pregnancy to make sure that it proceeds normally and the child has the opportunity to fully develop.
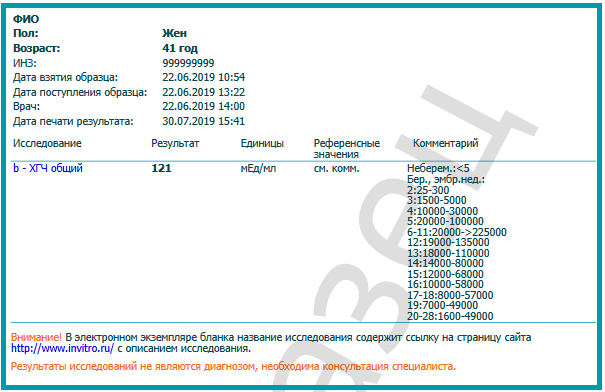
To confirm positive fetal development, testing is carried out in parallel with an ultrasound examination of the pelvis.
Reasons for deviation of hCG from the norm
Very often, during IVF, several blastocysts are implanted into the body of the expectant mother at once. In this way, it is possible to increase the chances of implantation of at least one embryo into the uterine wall. In some cases, implantation of all blastocysts implanted in the uterus is observed, which leads to multiple pregnancies. In such a situation, during a blood test, the hormone content in the plasma is high.
Low hCG
If hCG slowly increases after IVF, this may indicate the following conditions:
- fetal freezing;
- threat of spontaneous abortion;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Tests are taken at least 2-3 times to determine the dynamics of increase or decrease in plasma hormone levels. If it is in a borderline state, the expectant mother is prescribed hormone injections. Maintaining hCG at normal levels reduces the risk of miscarriage.
A sharp decrease in hCG
After IVF, the likelihood of fetal death is high, so the level of gonadotropin in the blood is monitored until the 2nd trimester. A critical decrease in hCG levels is a good reason to seek help from a fertility specialist.
Important! To eliminate the possibility of high error in the results of the hCG test, it is recommended that tests be taken in the same laboratory.
Hormonal instability increases the risk of miscarriage or pathological intrauterine development of the fetus. If such a problem is detected, the woman is sent to the hospital for conservation. Artificially maintaining hormonal balance helps prevent miscarriage and normalize the course of pregnancy.