Effect of prolactin
So far, science has not fully elucidated the effect of this hormone on the body. It is known to be important for:
- growth and development of mammary glands;
- maturation and release of colostrum;
- increasing the number of milk lobules and ducts;
- conversion of colostrum into milk;
- prolongation of the corpus luteum phase;
- regulation of water-salt metabolism.
In addition, in women it works as a “contraceptive” - it prevents conception during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Prolactin is released and pregnancy does not occur. After weaning the baby from the breast, the likelihood of conception increases again. In men, this hormone, in addition to controlling water-salt metabolism, enhances the release of testosterone and also stimulates sperm growth.
If the level of this hormone is increased compared to the norm, problems with conception may occur.
Complexes with this research
Advanced male anti-aging diagnostics Extended monitoring of key indicators in men aged 40+ 22,630 RUR Composition
Fitness monitoring Examination for choosing physical activity and monitoring the body’s condition 4,160 RUR Composition
Female hormones. Follicular phase Assessment of the hormonal status of a woman in the follicular phase RUB 3,570 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Preventive check-up 6,770 RUR
- Fitness control of sports nutrition RUB 3,010
- Male infertility. Extended examination RUB 18,900
- Male hormones RUB 3,830
- Anti-aging diagnostics. Hormonal balance 4,000 R
Prolactin: when to take it?
On what day should you take prolactin? Blood is donated for prolactin on any day of the menstrual cycle - either in the follicular or luteal phase. At the beginning of the cycle, you can combine tests for other hormones (cycle days 2–5 or 5–8). The follicular phase is suitable for testing blood for sex hormones of the pituitary gland - you can simultaneously take a test for FSH, LH and prolactin (days 3–5 of the cycle). Pregnant women usually take this test on the same day as other tests.
If you have been prescribed a test for the hormone prolactin , when to take it does not matter much: the results are interpreted depending on the day of the cycle. The level of this hormone fluctuates slightly during the cycle, so to determine its concentration, you do not need to worry about what day to take the test. Even if the doctor has prescribed a certain day, but it doesn’t quite suit you, check, maybe it will be possible to reschedule the test and your laboratory will test prolactin on a day more convenient according to your schedule.
2 days before taking the test, you need to refrain from:
- sex;
- stress;
- sweet;
- physical activity;
- examination of the mammary glands.
Since the level of this hormone increases during sleep, the test should be taken 2-3 hours after waking up - not earlier. The test must be taken on an empty stomach. Even if an increase in prolactin is recorded, donate blood 1-2 more times: this way you can make sure that this is not a one-time surge in the hormone.
The units of measurement in which prolactin levels are most often determined are ng/ml - nanograms per milliliter. Laboratories can also measure hormone concentrations in µIU/mL—micro international units per milliliter. To convert units of μIU/ml to prolactin ng/ml, you need to divide the value in μIU/ml by 30.3.
Prolactin: normal in women
Depending on what day of the cycle the tests are taken, the norm in women ranges from 4.5–49 ng/ml, or 136–1483 μIU/ml. According to the phases of the menstrual cycle, the values are as follows:
- follicular phase - 4.5–33 ng/ml, or 136–999 μIU/ml;
- ovulatory phase - 6.3–49 ng/ml, or 190–1484 μIU/ml;
- luteal phase - 4.9–40 ng/ml, or 148–1212 μIU/ml.
Increased prolactin in women during pregnancy
Throughout pregnancy, hormone levels change:
- I trimester - 3.2–43.0 ng/ml;
- II trimester - 13.0–166.0 ng/ml;
- III trimester - 13.0–318.0 ng/ml.
From the eighth week, the hormone level begins to increase. Its highest concentration in the blood is approximately 20–25 weeks. Prolactin levels are very important for the development of a child's lungs. Before childbirth, a decrease in the level of the hormone is observed, and its next increase occurs only during breastfeeding.
Prolactin in men: normal
For men, the normal level of the hormone is lower than for women. In a healthy male body, the concentration should be in the range of 2.5–17 ng/ml, or 75–515 µIU/l.
Prolactin - on what day of the cycle should women take it?
Before going for analysis, you need to know on what day of the cycle to take prolactin - this is crucial for the accuracy of the result:
- if you are prescribed a test for luteotropic prolactin (the first phase of the cycle), then it must be taken 5-8 days before the start of menstruation;
- When studying follicular blood, blood is taken on days 3-5 of the cycle.
The first day of the cycle is the day when spotting appears.
After receiving the results of the study, you must consult a doctor for interpretation and diagnosis, if required. Endocrinologist Georgy Nikitich Romanov has specialized in hormonal disorders in the body for many years and helps people restore health or return to a normal life. He not only provides paid appointments at the medical center, but also conducts online consultations in any way convenient for the client (Skype, VKontakte, Instagram, Viber, etc.).
Prolactin is elevated: symptoms
If prolactin levels are elevated in a male or female body, symptoms may include the following:
- disrupted menstrual cycle (periods are rare or absent);
- problems with conception;
- decreased sex drive;
- discharge from the mammary glands;
- hair growth on the face, chest, back in women;
- weight gain;
- acne;
- lack of ovulation (in women).
When the hormone level is increased compared to the norm, all of the above symptoms may not always be present. Both low and high prolactin , the symptoms of which are easy to notice, may indicate serious disturbances in the functioning of the body.
Effect on fertility
The pituitary hormones FSH and LH cause ovulation. The production of these hormones is reduced by high levels of prolactin, and pregnancy does not occur. If you cannot get pregnant for more than six months, it makes sense to donate blood.
If the body malfunctions, an increased level of this hormone in women can cause not only “sexual coldness” and unhealthy large breast size, but also breast cancer. If a man has elevated prolactin levels, the following symptoms are observed:
- problems with conception;
- impotence;
- increased size of the mammary glands;
- release of colostrum.
If you suspect you have elevated levels of the hormone, symptoms without test results may not warrant treatment. First of all, take tests that will help determine the cause of the malfunction in the body.
Reasons for increased prolactin
There are a huge number of causes and symptoms of increased prolactin, these are the main ones (in the absence of pathologies):
- pregnancy (from the 7th week of pregnancy the hormone level increases sharply);
- strong feelings;
- incorrect readiness for a blood test;
- breast-feeding;
- taking soft drugs;
- use of drugs with hormones.
If a woman has diseases, then some of them will cause an increase in the hormone:
- anorexia (complete lack of appetite due to a mental disorder);
- arolactinoma (benign tumor of the pituitary gland). Symptoms of this disease may include infertility, nausea, blurred vision, obesity, and headaches.
- polycystic ovary syndrome (symptoms include infertility, acne, menstrual irregularities, irritability).
- hypothyroidism (symptoms: bags under the eyes, depression, dry skin).
- kidney disease, diseased liver, malignant lung tumors, etc.
- chest injuries.
Prolactin is elevated: reasons
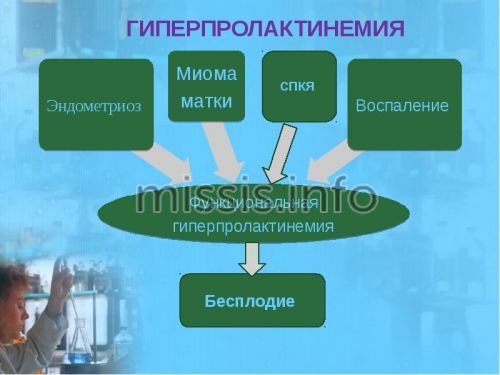
There are two types of hyperprolactinemia:
- physiological (norm);
- pathological (with deviations from the norm).
Physiological hyperprolactinemia causes an increase in prolactin levels in a healthy body for the following reasons:
- pregnancy;
- breastfeeding period;
- intense physical activity;
- deep sleep phase;
- protein-rich diet;
- sexual intercourse;
- emotional overstrain.
Normally, the level of the hormone is increased in men and women early in the morning - between 5 and 7 am. Pathological hyperprolactinemia (an unhealthy increase in hormone levels) can have the following causes:
- pituitary tumors;
- surgical damage to the pituitary stalk;
- radioactive exposure;
- “empty sella” syndrome (compressed pituitary gland);
- hypothalamic tumors;
- damage to the thoracic organs, including operations on the mammary glands;
- benign tumors of the sella turcica;
- endocrine diseases (polycystic ovary syndrome, hypothyroidism, Cushing's syndrome);
- renal and liver failure;
- lack of vitamin B6;
- taking certain medications (including oral contraceptives).
If prolactin is elevated in the body, the reasons may also be associated with obesity. Estradiol is formed in adipose tissue, which in turn provokes an increase in the “lactation hormone”. The more estradiol in the body, the higher the concentration of prolactin. Therefore, most often high levels of the hormone occur in overweight men and women.
What is prolactin
The content of the article
Prolactin is a hormone that is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. One of the main roles of prolactin is the secretion of milk in the mammary glands of nursing mothers. It is also responsible for the proper functioning of the reproductive system. Hyperprolactinemia is a disorder of the endocrine system in which prolactin levels are kept high.
The secretion of prolactin exhibits a diurnal rhythm, that is, its concentration depends on the time of day. Higher levels of the hormone are observed at night during sleep, during meals, exercise, or significant anxiety.
The highest level of prolactin in the female body during pregnancy (a hormone produced in the pituitary gland, placenta, pituitary gland of the child). Then we can talk about natural hyperprolactinemia, that is, excess prolactin. In all other cases, an increase in prolactin is a serious pathology.
How to lower prolactin?
The doctor determines how to lower the hormone level, taking into account the causes of hyperprolactinemia. If the level of the hormone increased during lactation, its level will decrease as soon as you stop breastfeeding your baby. This type of hyperprolactinemia does not require treatment.
Prolactin is elevated: treatment
In addition to blood tests for hormones, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is prescribed. MRI can determine whether high levels of the hormone are associated with the disease: this test helps detect the presence of tumors.
Treatment may include:
- taking medications;
- radiation therapy;
- operation.
The doctor prescribes treatment on an individual basis. At the same time, it takes into account the current state of the body, the presence of allergies to medications, the desire to become pregnant and other factors.
How is a prolactin test performed?
To get an accurate result during analysis, you need to follow a few simple rules. Don't eat anything in the morning. Blood is taken from a vein. The analysis itself is carried out early, namely from 7-9 am
. As a rule, doctors advise carrying out this test on the last day after the start of menstruation and advise coming in a good mood, since stress directly affects the result.

The main thing is to conduct a full examination; on its basis, doctors will be able to give qualified advice and prescribe the right treatment. And self-medication will not lead to anything good, but will only make it worse.