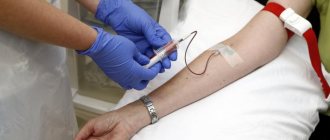
How to take hCG
During pregnancy, blood must be donated on an empty stomach, and at least eight hours must pass after the last meal. Keep in mind that drinks also count as meals. You are only allowed to drink water in the morning, and it is better to do this for the last time no later than half an hour before the test. If you monitor hCG concentrations over time, then you need to take a blood test at the same time of day, preferably in the morning. A blood test for pregnancy, like all hormone tests, is taken from a vein. If blood collection is not tolerated, you can ask the nurse to perform the procedure in a lying position. During comprehensive pregnancy screening, it is better to undergo an ultrasound and test on the same day. This will allow the doctor to get a more complete picture of the development of the fetus. As a rule, the results of the hCG analysis are ready within 1-3 days.
Preparing for analysis
In order for the blood test for hCG to be passed successfully, and its results to be as reliable as possible, it is necessary to follow a number of simple rules:
- a few days before the test, you need to exclude salty, pickled, spicy, fried, spicy and fatty foods from your diet;
- a few hours before the analysis, you must stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- on the day of the study, physical and emotional overload must be excluded;
- If you take any medications on an ongoing basis (especially if they are hormonal drugs), then you must inform your doctor about this before the test.
Blood for hCG: when to donate
It is advisable to take a blood test to detect the level of hCG to establish the fact of pregnancy seven days (or later) after the expected conception. Quantitative indicators of hCG in the blood make it possible to accurately determine the duration of pregnancy. Further observation of changes in hCG levels allows you to understand how harmoniously the pregnancy is progressing. A doctor may prescribe an hCG test during pregnancy as part of the 1st comprehensive screening - a double test, in the third month of gestation or as part of a second examination - a triple test, in the fourth - fifth month of pregnancy. In the first trimester, regular monitoring of hCG levels is especially important if there is a risk of spontaneous abortion; in the second trimester, it allows the doctor to track the dynamics of fetal development.
The actual date of conception in pregnant women with late ovulation and an unstable cycle, as a rule, is quite different from the period that doctors assume. In this case, the actual gestational age can be assumed by analyzing hCG: its elevated level will allow us to judge the current period.
Interpretation of test results for hCG
The results of the analysis are interpreted by the attending physician.
At first, hCG doubles every 2-3 days. It reaches its peak at 10-11 weeks. 7-10 days after birth, the hormone is no longer detectable in the blood and urine.
According to the data obtained, the hCG level can be:
- normal. Normal indicators indicate the onset and progress of pregnancy. The values after conception change every day, week. They depend on the reagents used. Therefore, the laboratory usually indicates in the decoding the hCG norm for the gestational age.
- elevated. Elevated levels of the hormone are also physiological. They are observed in cases of multiple pregnancy. The higher the numbers, the more embryos a woman carries. This is a diagnostic sign that helps the doctor in diagnosis if an ultrasound has not yet been done. Among the pathologies, the amount of human chorionic gonadotropin is affected by diabetes mellitus and congenital defects in the fetus.
- reduced. A significant decrease indicates intrauterine fetal death. Borderline results are possible with ectopic pregnancy. The threat of miscarriage and functional insufficiency of the placenta are also manifested by low human chorionic gonadotropin.
Chromosomal pathologies, most often trisomy, are manifested by a decrease in the level of hCG, with an increased PAPP-A. This test, or double test, is included in pregnancy screening at the end of the first trimester. It allows you to identify a risk group for trisomy and expand the examination of pregnant women during subsequent screenings. It must be compared with data obtained from ultrasound, since individual abnormalities do not always indicate pathology. All screening indicators are processed by a computer program that takes into account the age of the pregnant woman, obstetric history, etc.
If the values are normal, pregnancy management continues according to the usual plan. If hCG levels are increased or decreased, the cause of the deviations must be established and eliminated. To do this, other pathology markers are checked and a repeat or expert ultrasound is performed. If the result is questionable, a genetic study is indicated, and only after this it is decided whether to terminate the pregnancy.
Tests during pregnancy
Prenatal screenings determine the level of not only hCG, but also b-hCG, a component of human chorionic gonadotropin, the quantitative indicators of which allow the specialist to judge how harmoniously the pregnancy is proceeding. From the first to the second semester, the amount of this hormone fraction should progressively decrease. This indicates normal fetal development. Excessive or insufficient amounts of b-hCG should be a reason for additional examinations. As for hCG itself, its level increases progressively and, as a rule, reaches a peak by the seventh week of pregnancy, after which it gradually decreases. By the end of pregnancy, its concentration reaches a level of 15,000-60,000 IU/l.
The test will allow your doctor to:
- Detect pregnancy early;
- Identify multiple pregnancies;
- Diagnose ectopic pregnancy;
- Monitor pregnancy to identify the threat of miscarriage and other pathologies of fetal development;
- Monitor the effectiveness of therapy for threatened miscarriage;
- Monitor the effectiveness of induced abortion;
- Identify the cause of the absence of the menstrual cycle (amenorrhea);
- Diagnose tumor diseases;
- Monitor tumors;
- Assess the effectiveness of surgery to remove tumors;
- Assess the effectiveness of chemotherapy;
- Identify recurrent tumors.
HCG analysis: decoding
| gestational age | hCG norm, IU/L | |
| weeks from conception | obstetric weeks | |
| 1 — 2 | 3 — 4 | 25 — 300 |
| 3 — 4 | 5 — 6 | 1500 — 5000 |
| 4 — 5 | 6 — 7 | 10000 — 30000 |
| 5 — 6 | 7 — 8 | 20000 — 100000 |
| 6 — 7 | 8 — 9 | 50000 — 200000 |
| 7 — 8 | 9 — 10 | 40000 — 200000 |
| 8 — 9 | 10 — 11 | 35000 — 140000 |
| 9 — 10 | 11 — 12 | 32500 — 130000 |
| 11 — 12 | 13 —14 | 27500 — 110000 |
| 13 — 14 | 15 — 16 | 25000 — 100000 |
| 15 — 16 | 17 — 18 | 20000 — 80000 |
| 17 — 21 | 19 — 23 | 15000 — 60000 |
HCG analysis decoding.
HCG analysis: explanation, 1st trimester (B-fraction)
| week of pregnancy | b-hCG norm, ng/ml |
| 9 | 23,6 — 193,1 |
| 10 | 25,8 — 181,6 |
| 11 | 17,4 — 130,4 |
| 12 | 13,4 — 128,5 |
| 13 | 14,2 — 114,7 |
HCG analysis: explanation, 1st trimester (B-fraction)
HCG blood: decoding, 2nd trimester (B-fraction)
| week of pregnancy | b-hCG norm, ng/ml |
| 14 | 8,9 — 79,4 |
| 15 | 5,87 — 62,0 |
| 16 | 4,67 — 50,0 |
| 17 | 3,33 — 42,8 |
| 18 | 3,84 — 33,3 |
HCG blood: decoding, 2nd trimester (B-fraction)
HCG analysis: price
Prices for determining the level of hCG in the blood vary - from 255 to 800 rubles. The Lab4U laboratory can accurately and quickly determine the level of hCG. The price of such a study will be 50% less than the cost of similar studies in Invitro, Gemotest and other laboratories. Remember that if you take hCG as part of pregnancy monitoring (weekly), then it is better to do this in one laboratory, since the hCG levels in different laboratories are not the same and depend on the research method, reagents, etc. The Lab4U laboratory always indicates reference values of analysis results. All you have to do is compare them with your own result. You can also inquire about the acceptable ranges of hCG hormone concentrations during your week of pregnancy from your doctor or Lab4U laboratory technician. Remember that only a doctor can give a detailed interpretation of the test results, taking into account your individual state of the body, concomitant diseases, and characteristics of the course of pregnancy.
Reduced amount of hCG
Reduced concentrations of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood plasma of the expectant mother are observed in the following cases:
- With an ectopic pregnancy (hCG levels rise very slowly or stop growing altogether);
- A difference from normal values of more than half the reference value may indicate a risk of miscarriage;
- In case of development of chronic placental insufficiency;
- Increasing the amount of hCG.
A significant increase in the level of hCG in the body of the expectant mother leads to:
- In case of early toxicosis or gestosis;
- During multiple pregnancy (hormone levels increase in proportion to the number of fetuses);
- With intrauterine infection;
- In case of complications of pregnancy with diabetes mellitus;
- With chorionepithelioma;
- With hydatidiform mole;
- In case of fetal chromosomal abnormalities;
- In case of regular use of gestagen.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, beta-hCG, b-hCG, Human Chorionic
Early diagnosis of pregnancy: determination of hCG levels
What is hCG?
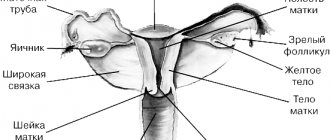
HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is a special pregnancy hormone, which is an important indicator of the development of pregnancy and its abnormalities. Human chorionic gonadotropin is produced by the cells of the chorion (the membrane of the embryo) immediately after its attachment to the wall of the uterus. Based on a blood test for human chorionic gonadotropin, the doctor determines the presence of chorionic tissue in the body, and therefore the onset of pregnancy in a woman.
When can a test be performed to determine hCG levels?
Determining the level of human chorionic gonadotropin in the blood is the most reliable method for determining pregnancy in the early stages. Human chorionic gonadotropin appears in a woman’s body 5-6 days after fertilization. A common rapid pregnancy test, which every woman can use at home, is also based on the determination of human chorionic gonadotropin in the urine, but the required level of this hormone in the urine to diagnose pregnancy is achieved several days later.
In the absence of any pathology, in the first weeks of pregnancy the level of the hormone doubles every 2 days, and its maximum concentration is reached by 10-11 weeks of pregnancy. After week 11, the hormone level gradually decreases.
An increase in the level of human chorionic gonadotropin during pregnancy can occur with:
- multiple births;
- toxicosis, gestosis;
- maternal diabetes;
- fetal pathologies, Down syndrome, multiple developmental defects;
- incorrectly determined gestational age;
- taking synthetic gestagens, etc.
Elevated values can also be seen within a week when tested after an abortion procedure. A high level of the hormone after a mini-abortion indicates a progressive pregnancy.
Low levels of human chorionic gonadotropin during pregnancy may indicate incorrect timing of pregnancy or be a sign of serious disorders, such as:
- ectopic pregnancy;
- non-developing pregnancy;
- delay in fetal development;
- threat of spontaneous abortion;
- chronic placental insufficiency;
- fetal death (in the II-III trimester of pregnancy).
Determining the level of human chorionic gonadotropin is part of a triple test study, the results of which can be used to judge the presence of certain abnormalities in fetal development, but an accurate diagnosis cannot be made. The study only allows us to identify women at risk. In this case, women will need to undergo serious additional examination.
What is the role of the hCG hormone in the human body?
In addition to establishing the fact of pregnancy, by quantifying the level of this hormone, one can judge the nature of the pregnancy and the presence of multiple pregnancies.
The most important task of human chorionic gonadotropin is to maintain the pregnancy itself. Under its control, the synthesis of the main pregnancy hormones occurs: estrogen and progesterone. In the first trimester, until the placenta is fully formed (up to 16 weeks), human chorionic gonadotropin maintains the normal functional activity of the corpus luteum, namely the production of progesterone.
Another important function of human chorionic gonadotropin is to stimulate ovulation and maintain the viability of the corpus luteum.
When does a doctor order a hCG test?
In addition to diagnosing early pregnancy, human chorionic gonadotropin is determined by:
among women -
- to detect amenorrhea;
- eliminating the possibility of ectopic pregnancy;
- to assess the completeness of induced abortion;
- for dynamic monitoring of pregnancy;
- if there is a threat of miscarriage and suspicion of an undeveloped pregnancy;
- for the diagnosis of tumors - chorionepithelioma, hydatidiform mole;
- for prenatal diagnosis of fetal malformations;
for men -
- for the diagnosis of testicular tumors.
How to take a blood test for the hCG hormone?
The independent laboratory INVITRO offers a laboratory test to determine the level of human chorionic gonadotropin.
The test is taken by taking blood from a vein, preferably in the morning and on an empty stomach. A laboratory test is recommended to be carried out no earlier than 4-5 days of missed menstruation, and can also be repeated after 2-3 days to clarify the results. To identify fetal pathology in pregnant women, it is recommended to take the test from 14 to 18 weeks of pregnancy.
In a comprehensive diagnosis of fetal malformations, it is also recommended to take tests to determine the following markers: AFP (alpha-fetoprotein), E3 (free estriol), and also do an ultrasound.