What does culture from the cervical canal reveal?
The cervical canal of a healthy woman is sterile, but when pathogenic bacteria enter it, inflammation of its walls develops.
This is due to various reasons - lack of hygiene, metabolic disorders, hormonal imbalance. Often, diseases of the genitourinary organs spread to the cervical canal, causing its inflammation. The degree of pathology depends on immunity and the type of infection.
- Bacterial culture accurately identifies pathogens that caused a malfunction in a woman’s body.
- These include pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic infections such as:
- streptococcus;
- staphylococcus;
- gonococcus;
- Proteus;
- E. coli in quantities exceeding the norm;
- Trichomonas;
- yeast fungi.
Bacterial culture from the cervical canal is a procedure that may be prescribed during a routine annual examination as a preventive measure. And also for chronic recurrent inflammation of the genitourinary system and increased leukocytes in the blood.
The main reason for the increased level of leukocytes in the genitourinary system is diseases of the pelvic organs: adnexitis, endometritis, cervicitis, oophoritis, vaginitis.
Detection of pathogenic microflora makes it possible to determine an anti-inflammatory or antiviral drug that can destroy the pathogen and prescribe effective treatment.
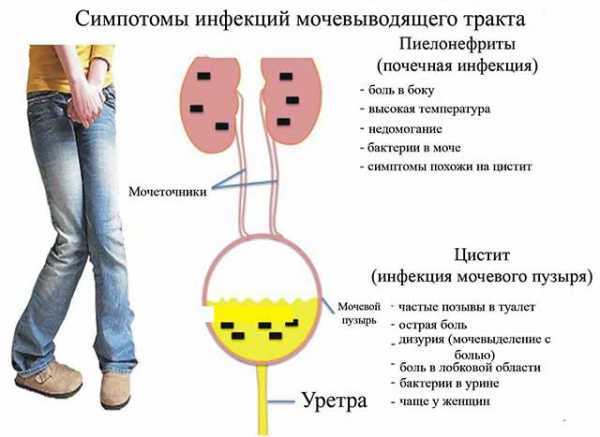
Two types of bacteria “live” on the mucous membrane of the cervical canal: opportunistic and pathogenic. The first type includes microorganisms that, in normal quantities, are part of the microflora.
- Their number is regulated by beneficial bacteria that die when immunity decreases.
- In this case, opportunistic organisms begin to actively multiply and corrode the walls of the membrane, causing inflammation.
- Pathogenic bacteria are an infection that enters the body from the external environment.
Tank culture from the cervical canal during pregnancy
During pregnancy, bacterial culture of the cervical canal is one of the important laboratory tests.
The cervical canal is a part of the cervix in which a large number of microbes accumulate that can harm the unborn child.
Detection of the disease at an early stage makes it possible to immediately begin treatment and guarantee the birth of a healthy baby on time.
When registering, pregnant women undergo a routine vaginal smear. If deviations are detected in the list of outcome indicators, the expectant mother will be sent for additional examination of the cervical canal.
In pregnant women, the cervical canal reaches a length of 3–4 cm, the length of the cervix is up to 2 cm. Both ends of the pharynx are closed and represent a protective barrier for the fetus.
The collection of material is carried out only by an experienced professional, which guarantees the safety of the procedure and does not pose a threat to the life of the fetus.
Decoding the culture tank from the cervical canal
A woman receives the results of a smear 4-6 days after submitting the material. During this period, colonies of bacteria grow. The resulting form indicates all microorganisms that populate the lining of the cervical canal.
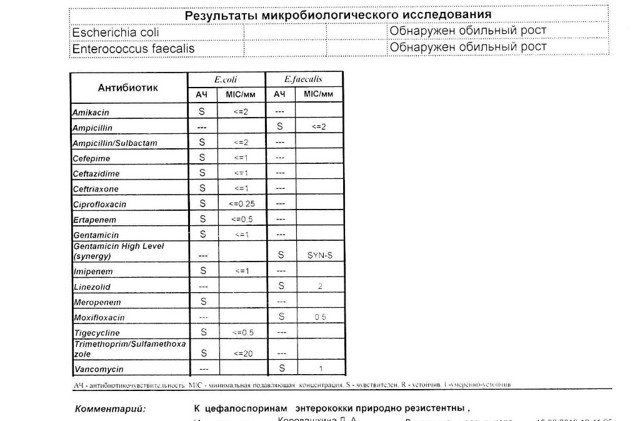
In the photo: an example of deciphering the analysis after a smear from the cervical canal - click to enlarge.
The norm is the presence of leukocytes and fungi in moderate quantities, lacto- and bifido-bacteria (107 CFU/mg, which corresponds to 300-400 million/g), creating a protective acidic environment. E. coli normally contains up to 102 enterococci.
An important indicator in decoding is the number of bacteria, indicating the degree of cleanliness of the cervical canal. In a contaminated mucosal environment, there is a minimal number of microorganisms growing in a liquid medium.
This category includes the minimum number of “resistant” bacteria that can develop in a dense environment (no more than 10 colonies). With the development of the inflammatory process, bacteria capable of multiplying in a dense environment (up to 100 colonies) are found in the smear.
Price
On average, prices for delivery of a sowing tank in Russia range from 800 to 1,400 rubles.
- Bacteria are detected using modern automated methods using new technologies. The sensitivity of the pathogen to antibiotics is determined by microbiological analyzers.
- The next stage is the selection of a drug depending on the identified pathogen. The results of the study are given to patients in accordance with standards that help the attending physician to easily navigate the information provided and make the correct conclusion.
How is a culture taken from the cervical canal?
The analysis is carried out by microscopy of the material on days 4-5 of the menstrual cycle. For a smear test, the cervix is exposed using a speculum. Using a sterile swab or brush, collect mucus from the surface of the epithelium, turning it clockwise several times, trying not to damage the membrane.
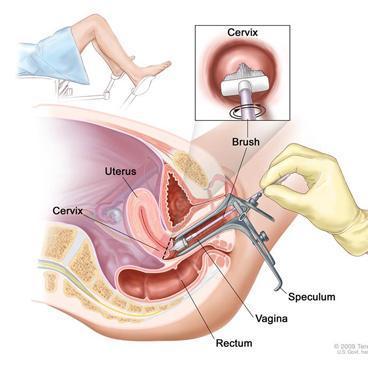
This is how they take a smear from the cervical canal - click to enlarge
The brush is removed and the resulting material is distributed in an even layer on a glass slide, avoiding drying. The glass is placed in an individual bag and sent to the laboratory.
The entire duration of the procedure for collecting material for research is 15 minutes.
If transportation of material is required, then it is carried out only at a temperature not exceeding 20 degrees in a sealed bag - a refrigerator. In laboratory conditions, opportunistic material is placed in an environment favorable for their reproduction.
Each type of bacteria requires individual conditions and time of reproduction. The results at the end of the process are recorded by laboratory staff. The interpretation is carried out by a gynecologist.
Note! Tank culture from a cervical analysis does not reveal the presence of infections such as: herpevirus, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, chlamydia (penetrating into cells and affecting the nucleus). This type of microorganism can be detected by PCR diagnostics (polymerase chain reaction).
How to prepare for a cervical smear?
Proper preparation for a painless procedure ensures reliable results. The doctor writes a referral to the patient and talks about the nuances that need to be taken into account before taking the test.
A gynecologist takes tests on a pregnant woman. Sexual contact is avoided for several days before the procedure. Do not take medications or contraceptives.
If a few days before the scheduled date of delivery, vaginal examinations were carried out using a speculum, then it is advisable to postpone the procedure. It is forbidden to do douching, which distorts the vaginal microflora. To maintain hygiene, use regular boiled water without using detergents.
Before visiting the treatment room, wash only in the evening .
1-2 hours before the appointment, refrain from urinating. The procedure does not cause discomfort or pain to the patient.
Tank culture from the cervical canal for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics
When we come to the gynecologist, with complaints or for prevention, we are always asked to lie down on a chair for examination, so that the doctor takes smears for analysis. A so-called flora smear is absolutely always taken. The result, if the laboratory is nearby, can be in 10-15 minutes.
I somehow got a paid appointment with a doctor, and during my stay in his office, they also analyzed my smear. A flora smear shows the number of leukocytes, squamous epithelium, mucus, as well as the presence of fungi and Trichomonas.
If there are no fungi or trichomonas, but the number of leukocytes is increased, the doctor will prescribe a local broad-spectrum antibacterial drug. That is, one that is guaranteed to defeat any microorganisms.
And it doesn’t matter which microorganisms caused the inflammation. The medicine will "kill" them all.
But sometimes this stroke alone is not enough. You need to find out the exact set of pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms, their quantity, and also determine which antibacterial medicine is best to treat it. Then a tank is taken to culture the cervical canal for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics (ab).
How is cervical canal culture performed?
The cervical canal connects the uterus to the vagina. In shape, this part of the female reproductive system resembles a spindle: on the outside it is connected to the vagina, and on the inside to the uterine cavity using an internal opening.
How the organ works
The mucous membrane covers the cervical canal from the inside. In shape, it resembles a cylinder, which consists of epithelium and produces female secretions.
The channel serves as a conducting tunnel. Discharge during menstruation passes through it, and sperm penetrate into the uterus.
The width of the canal is individual for each woman, but on average it is 7 mm. The shape changes over the years. Changes occur due to:
- childbirth;
- abortions;
- age;
- changes in hormonal levels and microflora.
Every year, every woman is required to take a culture from the cervical canal.
Culture and smear of material
When bacteria or pathogenic microorganisms enter the vagina, endocervicitis, an inflammatory process, develops. The normal state of microflora guarantees compliance with hygiene rules. Causes of endocervicitis:
- violation of hygiene rules;
- decreased metabolic rate;
- inflammation of the genitourinary system;
- hormonal instability;
- incorrect antibacterial therapy.
The disease occurs in chronic and acute forms. Women's immunity and the structure of bacteria influence the degree of development of the inflammatory process.
The disease may not appear for a long time.
To determine the infection, a smear and culture of the flora from the cervical canal of the vagina are analyzed. The gynecologist prescribes microscopy of the obtained material. A smear is taken using a special brush and then analyzed.
A day before the smear, the woman does not douche and excludes sexual intercourse so that the result is reliable. A smear from the cervical canal will show normal if the analysis results correspond to the following numbers:
- lactobacilli – 10×7;
- yeast fungi – 10x2;
- E. coli – 10x2;
- enterococci – no more than 10x2 CFU/ml.
Bacteriological culture
More often, a smear is taken from the cervical canal from pregnant women to check the condition of the reproductive organ.
The culture tank is assigned second, if necessary, after the first general analysis. If a high level of white blood cells is first detected, then the patient will be given a bacteriological culture. The procedure involves studying the flora and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
How is it carried out?
The woman lies down on a special chair. Afterwards, the doctor inserts the brush into the vagina and makes a scraping. The material from the cervical canal is placed in a test tube filled with a liquid substance and carefully closed.
Pregnant women are examined in exceptional cases. Often, the expectant mother is worried that this will harm the embryo. But a miscarriage will not happen if the doctor takes a smear.
The cervical canal in pregnant and non-pregnant women is quite long. Therefore, the instrument will not reach the fetus. The study is not mandatory. An analysis is carried out if there is evidence.
The collected material consists of cells and mucus that make up the microflora of the female organ. The material is placed in a test tube with a nutrient medium.
Nutrients help microorganisms develop. They determine the state of the internal microflora.
Watch a video about performing a culture from the cervical canal:
results
A positive result is given if the examination shows the presence of microorganisms. In this case, the exact level of development and growth position are established.
If, as a result of the study, there is no growth of microorganisms in the nutrient liquid medium, the woman’s vaginal microflora is contaminated.
If there is growth of a certain type of bacteria, inflammation has developed due to this pathogen. High growth of bacteria is observed with weakened immunity, metabolic disorders, instability or disruption of hormonal levels, and inflammation of the genitourinary organs.
Functioning of the cervical canal in pregnant women
During conception, the cervical canal changes color: before pregnancy, the hue of the space between the pharynx is bright pink, and after it is blue. With the appearance of blueness, the gynecologist determines the onset of pregnancy.
Mucus changes during pregnancy: it forms a dense plug. It protects the fetus by preventing pathogenic bacteria from entering the uterus. The time for the plug to peel off occurs individually: for some, 1.5 weeks before birth, for others, 2 hours.
Cervical fluid consists of elements:
- mucin;
- lysozyme;
- proteins;
- polysaccharides;
- electrolytes;
Moreover, 50% of its composition is water.
Estrogen and progesterone form cervical mucus. The first hormone causes the secretion to be produced abundantly during menstruation. Progesterone reduces this function to a minimum, making the mucus more dense.
During childbirth, the cervical canal begins to open up to 10 cm. This helps the woman easily endure the birth of the baby.
In some cases, the expectant mother is diagnosed with isthmic-cervical insufficiency. This means weak cervical support for the rapidly growing fetus. The development of pathology in pregnant women is recorded by the 18th week. The embryo grows and moves.
Sometimes, according to indications, surgery is prescribed to tighten the cervical canal. The seal is removed when it is time to give birth.
A woman should have a smear and culture done by a doctor. Both procedures are straightforward and completely painless. Timely testing eliminates the risk of developing infertility.
Interesting topic? Share your opinion in x.
How the organ works
The mucous membrane covers the cervical canal from the inside. In shape, it resembles a cylinder, which consists of epithelium and produces female secretions.
The channel serves as a conducting tunnel. Discharge during menstruation passes through it, and sperm penetrate into the uterus.
The width of the canal is individual for each woman, but on average it is 7 mm. The shape changes over the years. Changes occur due to:
- childbirth;
- abortions;
- age;
- changes in hormonal levels and microflora.
Every year, every woman is required to take a culture from the cervical canal.

What to do if there is growth in the culture from the cervical canal
Often, after visiting a gynecologist, a woman is prescribed a laboratory test - bacterial culture from the cervical canal. Not everyone knows what it is, why it is needed and what information it can give?
What is the cervical canal?
The cervical canal is the transition from the vagina to the body of the uterus; it has a conical shape with a hole in the center through which the vagina communicates with the uterus. Normally, the length of the canal is 3–4 cm; it is part of the cervix. The external os of the canal exits into the vagina, and the internal os into the uterine cavity.
One of its main functions is protecting the uterus from infections and pathogenic microorganisms; cells located inside the canal produce mucus, its consistency is determined by the stage of the cycle.
Mucus at the beginning and end of the menstrual cycle is more viscous with increased acidity; most microorganisms do not survive in such conditions. In the middle of the cycle, the level of estrogen increases, and the mucus changes its structure, becoming more liquid with an alkaline environment.
During these few days, sperm have a chance to enter the uterus and meet the egg there.
If pregnancy occurs, under the influence of the hormone progesterone, a plug is formed from the mucus in the cervical canal, which protects the fetus from infections from the outside.
Cervical canal fusion
Overgrowth of the cervical canal can be congenital or acquired. Overgrowth (atresia) of the cervical canal leads to partial or complete closure of the walls of the opening and prevents the passage of menstrual blood.
The causes of atresia can be:
- infectious diseases suffered in childhood (diphtheria, mumps);
- poor quality scraping;
- damage by cancer;
- traumatic birth;
- abortion injuries;
- damage by endocervicitis;
- cauterization of the cervical canal;
- advanced inflammatory processes of the internal genital organs;
- elderly age.
Primary atresia is diagnosed during the first menstruation without finding a way out; menstrual blood accumulates in the uterus and stretches it, the girl feels a general deterioration in health and if she does not consult a doctor in time, the blood further spreads through the fallopian tubes and can cause purulent inflammation.
Acquired (secondary) atresia is diagnosed when a woman consults a doctor about infertility. Stagnant blood clogs the tubes, and the egg does not have the opportunity to enter the uterine cavity. The diagnosis can be established using ultrasound, hysterosalpingoscopy, MRI, and sounding. This pathology is treated by bougienage of the cervical canal.
The bougienage operation is performed in a hospital and takes about 30 minutes. If the infection is complete, then the manipulation is performed under general anesthesia, and if not significant, then under local anesthesia. After the operation, if general anesthesia was used, the patient is discharged for home treatment the next day, and with local anesthesia, the patient is released on the day of the operation. The duration of home treatment lasts 10 days, wound healing drugs and anti-inflammatory suppositories are prescribed.