Magnetic tomography of the kidneys
MRI of the kidneys with contrast is a method that allows you to obtain detailed images of not only the main filters of the human body, but also the ureters, adrenal glands, and pathological processes in the retroperitoneal space. The introduction of a paramagnetic drug based on gadolinium chelates improves visualization and increases the information content of tomograms, which is especially important in the diagnosis of tumors at an early stage of development. The test does not involve the use of ionizing rays and therefore can be performed without any consequences for most people who do not suffer from decompensated kidney disease and do not have metal in their bodies. To complete the picture, the entire urinary tract is often examined, i.e. including the bladder and urethra (urethra).
- Prices for MRI of internal organs
Kidney MRI with contrast: what does it show?
Magnetic resonance imaging of the kidneys with contrast shows a number of pathological processes in the urogenital tract:
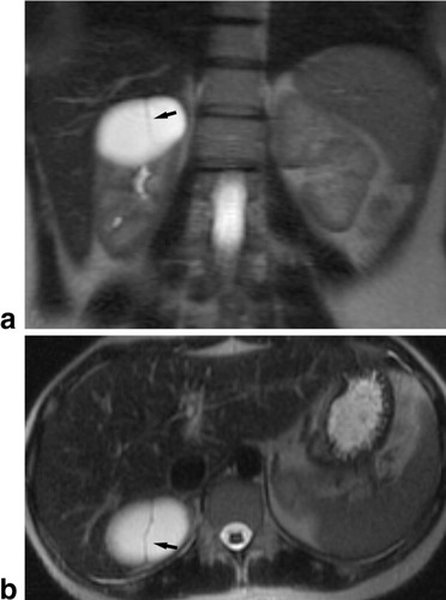
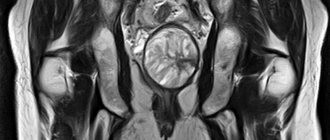
MRI of the kidneys in coronal (a) and axial (b) projections: the arrow points to a renal cyst with a thin wall and septum
- Cysts. Cavities with clear, even contours filled with liquid are classified as a benign type of neoplasia, but under the influence of mutagenic factors (chronic alcohol and nicotine intoxication, radiation, contact with dyes) they may have a tendency to malignancy. MRI of the kidneys shows the features of the formation: size, number of chambers, calcium deposition, clarity of the contour. A simple kidney cyst does not require active surgical tactics (with the exception of a diameter of more than 6 cm, when there is a risk of spontaneous rupture); in the case of a complicated form, surgery is performed followed by a morphological study, which allows the diagnosis to be finally verified. But the tomograms show polycystic disease (many cavities with fluid in both kidneys), which is a congenital condition.
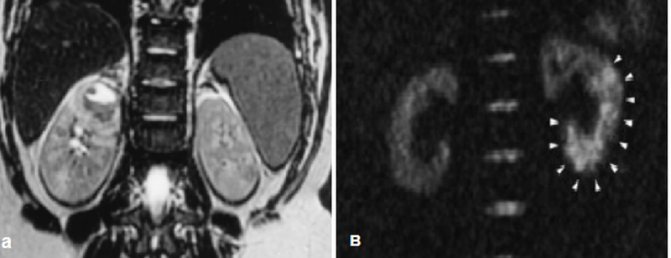
A: Abscess in the upper pole of the left kidney, B: white arrows indicate the ischemic zone during renal infarction
- Inflammatory process. With contrast MRI, the inflammatory process is manifested by expansion of the renal pelvis system, disorganization of the cortex and medulla, edema, and islands with reduced accumulation of paramagnetic substance. The initial method of instrumental diagnosis of pyelonephritis is ultrasound. Magnetic resonance scanning is performed to exclude inflammatory factors, assess renal function, and if a tumor is suspected with appropriate clinical manifestations. MRI shows a kidney abscess, which is an urgent condition.
- Nephrolithiasis. Stone formation is often a finding on MRI of the kidneys with contrast. Before surgery, preference is given to computed tomography, which shows the density of the stone, which is important for the choice of intervention - lithotripsy (crushing) or open removal.
MRI: white arrows show kidneys that are fused at the poles during embryogenesis (horseshoe kidney)
- Congenital anomalies of the urinary system. There are many congenital defects of the urological tract: duplication of the kidney/ureters, absence of an organ, fusion, accessory vessels, narrowing of the ureteropelvic segment, etc. All these pathologies can be seen on MRI of the kidneys with contrast.
- Malignant neoplasms. With the availability of ultrasound diagnostics in the form of screening (mass) studies, the detection of kidney cancer at an early stage (before the onset of clinical manifestations) has increased. MRI shows even a small tumor, which implies surgical treatment. There is a direct connection: the earlier kidney cancer is detected, the greater the chances of a favorable outcome and the opportunity to save the kidney. At the initial stage, a partial nephrectomy is performed, and then an MRI is performed annually in dynamics so as not to miss a relapse.
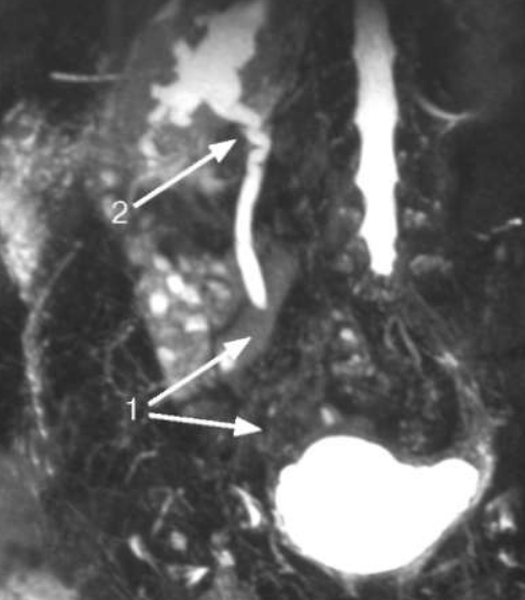
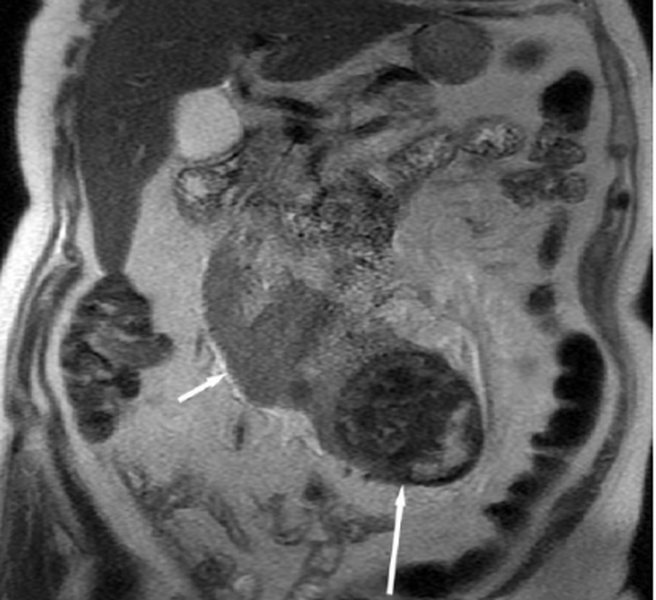
Magnetic resonance urogram shows obliteration of the right ureter in the pelvic region (1) and hydroureteronephrosis (2)
- Narrowing of the ureter. Ureteral stricture can be congenital or acquired. The main danger is a violation of urodynamics (urine outflow), which leads to hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney with a gradual loss of functional ability. Undiagnosed bilateral congenital strictures are especially dangerous due to the development of end-stage chronic renal failure. Retroperitoneal fibrosis—Ormond's disease—causes adverse consequences when connective tissue growths compress the ureter and the vessels supplying the kidney.
- Valves and pathological reflux. Pockets in the ureter interfere with the outflow of urine, resulting in pathological backflow. Stagnation of urine and proliferation of pathogenic microflora leads to persistent infections of the urogenital tract and renal failure. The pathology is more common in children, for whom an MRI of the kidneys is not excluded as part of the diagnosis.
Using magnetic resonance scanning, you can evaluate post-traumatic consequences and diagnose paranephritis (inflammation of the perinephric tissue). An MRI of the kidneys with contrast includes the adrenal glands. Pathological changes in these glands can manifest themselves in the form of a tumor (adenoma) or diffuse hyperplasia. Contrast MRI shows vascular abnormalities, areas of renal ischemia/infarction, and secondary wrinkling.
Conducting research
Magnetic resonance imaging is performed in two ways: conventional and with a contrast agent, which is administered intravenously. Next, it enters the organs through the vessels, and this makes it possible to more accurately see pathological changes. Contrast is also used when it is necessary to check the results of treatment, how much the size of the tumor and all pathological processes have changed.
The components of the contrast agent accumulate in the affected tissues, which shows a more pronounced magnetic signal. They are usually excreted in the urine within 24 hours after the procedure. The most effective use of the contrast method in the event of tumors is that the cells and vessels in the affected area are nourished more intensively and accumulate contrast more noticeably.
Indications and contraindications for MRI of renal vessels with contrast

The benefits of the study should always outweigh the potential harm: read the indications and contraindications for MRI
Paramagnetic drugs are distributed along the vascular bed into organs, which improves visualization and clarity of small structures. Indications for MRI with the introduction of a contrast agent are the following:
- persistent changes in urine tests that are not amenable to drug therapy, frequent relapses of urogenital infection;
- pain in the lumbar region, facial pastiness;
- palpable tumor in the projection of the kidney;
- malignant form of hypertension;
- dysuric disorders: cramps, pain when urinating;
- intolerance to iodine-containing contrast agents;
- danger of performing CT;
- preoperative diagnosis, monitoring the condition over time.
In emergency situations, for example, with a penetrating injury to the kidney or rupture of a cyst, CT is preferable, since the procedure takes less time. Sometimes diagnostics are performed in an operating room.
Contraindications for MRI of the kidneys with contrast
Since magnetic scanning is considered a non-invasive research method, there are few contraindications:
- the presence of metal objects in the body: installed implants, working pacemakers, orthopedic structures, insulin pumps, vascular clips. A tattoo in the lumbar region containing iron can cause skin irritation under the influence of a magnetic field;
- body weight over 120 kg;
- curvature of the spine that prevents a lying position;
- plastered limbs that do not allow getting inside the drum ring.
For patients suffering from claustrophobia, the procedure is performed after the administration of sedatives, plunging the subject into medicated sleep.
Contrasting is not carried out if:
- chronic renal failure with a decrease in glomerular filtration rate less than 30 ml/min and an increase in creatinine levels;
- allergic reaction such as Quincke's edema, anaphylaxis in previous studies;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- The baby is under 4 weeks old. MRI of the kidneys is done for children in specialized urological clinics.
Preparing for an MRI of the kidneys with contrast

To feel comfortable, do not overeat before the MRI procedure; small amounts of light food 40 minutes before the MRI of the kidneys are helpful.
No special measures are required, but for the procedure to be more comfortable, clothing should be loose and made from natural fabrics. If you come to the MRI of the kidneys in a formal suit, you have the opportunity to use a disposable spacious robe. Anything containing metal should be stored or left at home. Magnetic cards, watches, hairpins, jewelry lead to the appearance of defects on films, which calls into question the quality of the examination.
You should not show up for a kidney MRI with contrast hungry, as this may cause increased autonomic symptoms, which are often a response to gadolinium administration. A skinny stomach causes nausea, a metallic taste in the mouth, hot flashes, and drooling. To avoid this, have a light snack 40 minutes before the diagnosis. The other extreme of overeating is that with a full stomach, lying on your back motionless for 40 minutes is not very comfortable. For 2-3 days, give up gas-forming foods: cabbage, greens, legumes, milk, baked goods, alcohol. Take with you your passport, a referral from a doctor, an insurance policy (if the examination is carried out as part of compulsory medical insurance or voluntary health insurance), all available extracts from the medical history, the results of previous ultrasounds, urography, scintigraphy, etc. There are no contraindications to taking everyday medications.
What is included in an MRI of the urinary system?
MRI of the urinary system includes:
- Kidney MRI
- Bladder MRI
- MRI of ureters
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to accurately identify the pathological focus by doing an MRI of only one organ. By undergoing comprehensive research, you reduce the risk of missing pathology and increase your chances of finding the true disease and recovery!
MRI in our center
Power 1.5 Tesla
High image quality
Study for patients up to 250 kg
Burn to disc for free
How is an MRI of the kidneys and urinary tract done with contrast?
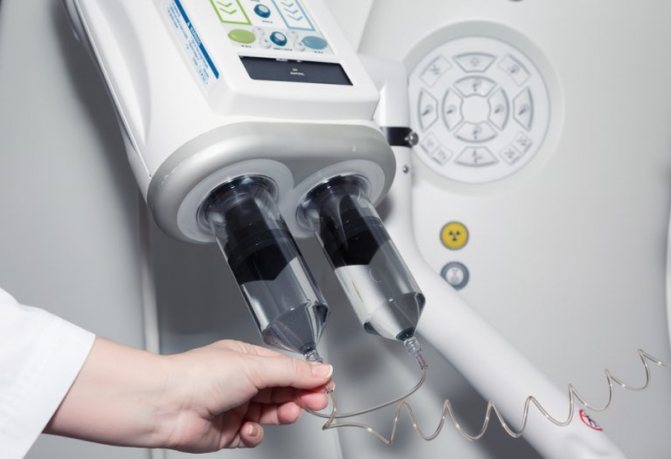
Contrast during MRI can be supplied automatically using an injector
After choosing a clinic and making a preliminary appointment, you need to show up for the procedure. Be sure to tell your doctor about possible pregnancy, allergies to contrast, or metal parts in the body.
If you have diabetes mellitus or persistent hypertension, you may not be aware of concomitant renal failure, and then it is better to first donate blood for creatinine. But contrast-induced nephropathy is an incidentally rare complication, so this measure is not mandatory. Gadolinium and similar paramagnetic drugs practically do not cause significant side effects, unlike iodine-containing agents, therefore MRI is preferable to excretory urography not only in terms of information content, but also in safety. Contrast can be bolus: the substance enters the vein automatically using an injector during certain phases of the study.
For unforeseen situations, there is a button at hand to contact the staff; the procedure is monitored from the adjacent room. After the diagnosis is completed, you can lead your usual lifestyle; there are no restrictions on driving a car or performing precision work. In order for the contrast agent to leave the body faster, it is recommended to increase the drinking regime.
The results will be ready in an hour, all questions can be asked to the radiologist. In 99% of cases, after deciphering the images, the diagnosis is known, but final verification is only legitimate by the attending physician, most often after histology. In the most difficult cases, they resort to collegial evaluation of tomograms.