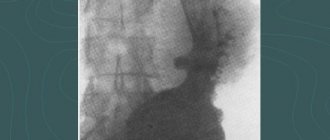
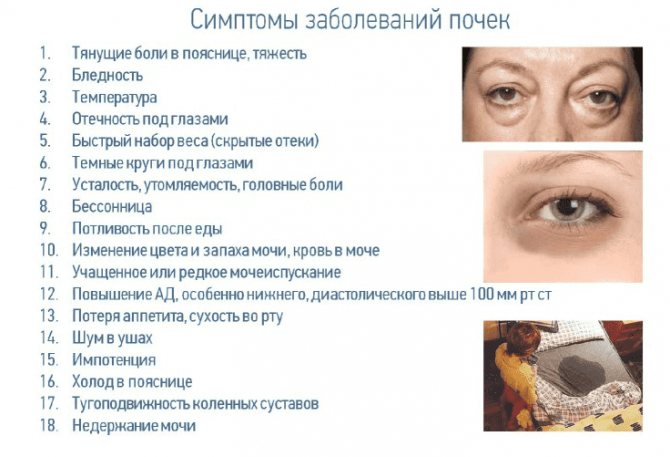
Kidneys are one of the most important organs in the human body. Their function and importance are difficult to overestimate. The main tasks of the kidneys are: filtration (filtration of blood), excretory (removing metabolic products and toxic substances from the body), maintaining the basic acid balance. They also take part in maintaining blood pressure. These are not all the functions of these organs. However, many people develop various kidney diseases during their lifetime. Sometimes they have a characteristic, pronounced clinical picture, and sometimes they can be asymptomatic.
general characteristics
If there are suspicions, as well as specific and nonspecific signs of the development of kidney pathology, specialists refer patients to a series of clinical and instrumental examinations that can more clearly show the picture of pathological processes. The data obtained can be decisive in making the correct diagnosis. The methods of treatment and their effectiveness directly depend on this.
One of the most common diagnostic examination methods is radiography of the kidneys. Its essence lies in obtaining the necessary data on the condition of the kidneys and urinary tract through the action of X-ray radiation, which tends to linger in denser tissues and formations. Visually, this appears on x-ray film in the form of an image and makes it possible to characterize and analyze the condition of the examined area. There are various methods for x-raying the kidneys - how the examination is done depends on the disease and pathological condition.
What are the features of examining children?
X-ray of the kidneys in adults has significant differences from a similar examination in children. Before deciding on the need for an x-ray examination, the child is first sent for an ultrasound examination. Only after an ultrasound, according to the doctor’s indications, can a decision be made to send a small patient for an x-ray.
To avoid unnecessary anxiety on the part of the child, he is given sedatives or light anesthesia is used. During the examination, the presence of a doctor and an anesthesiologist is mandatory. To secure the child in a certain position, the procedure also requires the presence of parents who wear special protective aprons.
If a repeat examination is necessary, it is done after a decent break, so you should try to get everything right the first time. To do this, parents are advised to give their children a cleansing enema before the procedure. It would also be a good idea to take Espumisan a couple of days before the x-ray.
To make the child less worried, you can take with you a pacifier or a toy that does not contain metal parts. With familiar objects, any child feels more comfortable and calm.
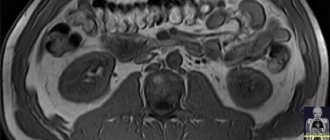
Kidney image without contrast: information content and significance of the study
An X-ray of the kidneys without contrast is usually prescribed at the initial stage of the examination. This diagnostic option is widely used by specialists to determine such basic data as the location of the kidneys, their size, volume, contours, density and other characteristics. This allows you to present a general picture of the condition of the kidneys and suspect pathological processes. An X-ray of the kidneys without contrast, although not highly informative, can provide the attending physician with general data. The advantages of this diagnostic method are:
- fast execution;
- no discomfort;
- cheapness;
- general availability;
- does not require the introduction of special drugs (contrast).
If the clinical picture is unclear or blurred, the patient has nonspecific complaints, and the attending physician has minimal suspicions, it is not advisable to immediately resort to contrast radiography. To begin with, it is better to examine the kidneys without contrast, and if suspicions are confirmed, we can talk about ordering other examinations.
X-ray with contrast agent
An X-ray of the kidneys with a contrast agent is performed when there is a pronounced symptomatic picture of certain diseases or confirmation of suspicions after previous examinations. The essence of the method, like the previous one, is the ability of x-ray waves to linger in denser structures. However, when X-raying the kidneys with a contrast agent, a drug that has X-ray contrast properties is specially injected into the bloodstream. Since the kidneys are continuously involved in filtering the blood, the administered drug ends up in the urinary tract over time, which makes it possible to assess the functional abilities of the kidneys, as well as the condition of the urinary organs and structures.
Advantages
The advantages of kidney urography using a contrast agent are its high informativeness and revealing nature. X-ray of the kidneys with contrast makes it possible to identify many diseases of the urinary system, assess the quality and intensity of kidney function, and accurately determine the localization of the pathological process. This will allow the specialist to choose the most rational treatment.
Side effects from contrast
In some cases, side effects of X-ray contrast agents may occur. The negative effects of water-soluble substances are associated with the chemotoxic effect of iodine and the phenomenon of osmotic toxicity. This phenomenon is characterized by an increase in osmotic pressure at the site of drug administration, which entails damage to the vascular endothelium and blood cells. There are several types of side effects from RHS:
- anaphylactoid (anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema, etc.);
- local manifestation (phlebitis, soft tissue necrosis);
- toxic effects (nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity, etc.).
It is worth noting that these adverse reactions occur extremely rarely, but the risk of their development still exists. That is why this study is carried out under the strict supervision of medical personnel who can provide emergency care.
When is the study scheduled?
X-rays of the kidneys are prescribed according to special indications from the attending physician. It is he who makes the decision to prescribe one or another diagnostic method and evaluates and analyzes the data obtained.
Let's consider the most common situations in which an X-ray examination of the kidneys is performed.
Blood in the urine (gross hematuria)
Macrohematuria is a visual determination of blood in the urine without additional studies. Most often observed with kidney disease or passage of stones
along the urinary tract.
Changes in urine analysis that persist for more than 2 months
These changes may indicate chronic or prolonged kidney pathology.
Suspicion of renal hypertension
A steady increase in blood pressure may raise suspicions among your doctor. As part of a comprehensive diagnosis, fluoroscopy of the kidneys may be performed to identify the cause of hypertension.
Trauma to the abdomen and lumbar region
For penetrating and non-penetrating injuries to the kidneys, an examination is necessary to assess the damage caused.
Pain in the lower back and abdomen
Pain in the lower back and lower abdomen (projection areas of the kidneys) may be a sign of the development of the disease. If symptoms are erased, radiography of this area may be necessary.
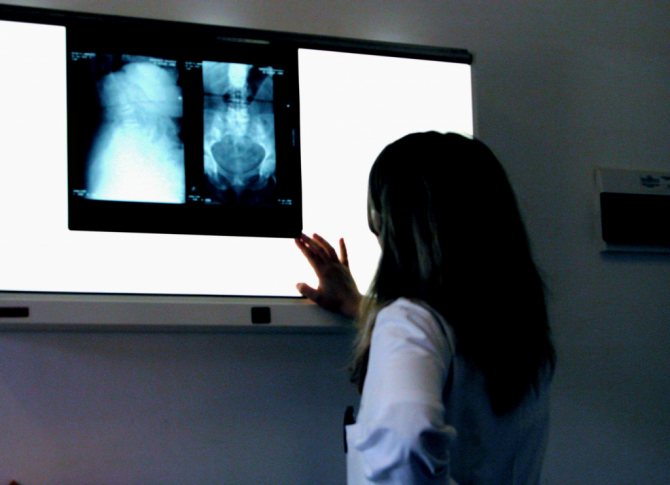
Decoding the research results
A radiologist interprets the results. The conclusion will indicate the size of the kidneys, structural features, and the presence or absence of pathological formations. If there are stones, cysts or tumors, the doctor will definitely indicate their location and size in the test results.
After the conclusion is formed, it is transmitted to the attending physician. Here, a nephrologist or surgeon compares the results of the decoding with other patient tests - blood tests, urine tests, and ultrasound data.
Taking into account all the indicators, the doctor makes a diagnosis and outlines a further treatment plan, taking into account the indications for surgical intervention - planned or urgent.
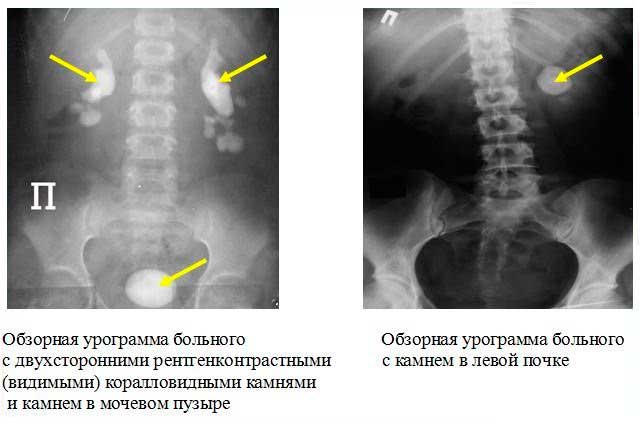
What can be seen in the photo?
Below we will describe what can be determined from the image obtained as a result of the examination.
Developmental anomalies
Various anomalies of kidney development (changes in their configuration, structure, anatomy, etc.).
Nephroptosis
Nephroptosis is a pathological condition characterized by prolapse of one or both kidneys due to injury or pathological processes.
Kidney cyst
Characterized by the development of cavity formation in this organ.
Tumor
It is possible to detect tumors and metastases of various origins and localizations. If there is a suspicion of the presence of tumors, as a rule, additional laboratory and instrumental examinations are prescribed.
What is research
If a contrast agent is used during an x-ray examination, the patency of the natural pathways to and from the organ can be assessed. The results obtained help to draw a conclusion about the functionality of the organ and violations of its activity.
The examination is carried out in specialized diagnostic centers or hospitals. The result of the study is given to the patient or forwarded to the attending physician if it was done in the same institution where the patient is observed. The results come the next day.
How to prepare for research?
The quality of the results obtained depends on preparation for kidney urography. Let's consider what relates to preparatory activities.
Diet
Diet is a key point in preparation for a kidney fluoroscopy. It is necessary to exclude from the diet or minimize the consumption of foods that contribute to gas formation in the intestines for 1-2 days. Air obstructs the passage of x-ray radiation, which distorts the resulting picture and can cause difficulties in analysis.
Carrying out a cleansing enema
Carrying out a cleansing enema is also important in preparation for radiography of the kidneys and is also aimed at reducing interference during the study by evacuating feces from the intestinal cavity.
You should empty your bladder before the procedure
Before taking an X-ray of the kidneys, it is recommended to empty the bladder.
Preparation rules
The doctor will instruct the patient in advance about preparing for a kidney x-ray.
To obtain clear images, it is necessary to ensure that the kidneys are not covered by the shadow of a crowded intestine. Therefore, it is important for doctors that when performing an x-ray, the intestines are freed from digested food and gases.
It is recommended to carry out preparation two to three days before the x-ray. The patient needs to reduce the amount of heavy foods that cause gas formation and take a long time to digest in the intestines. These are beans, cabbage, baked goods, cucumbers, and dairy products.

To reduce bloating, it is recommended to take sorbents - “Simethicone”, “Enterosgel”, “Polysorb”. A day before the x-ray, it is necessary to cleanse the intestines with Fortrans, and before the examination, either have a light dinner or not eat at all.
In the morning before the procedure, you can drink some water and take a walk in the fresh air. For patients with constipation or those who ate before the x-ray as necessary, a cleansing enema is performed.
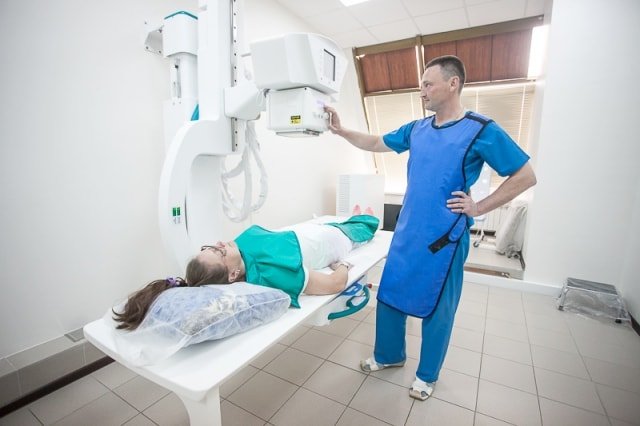
How is the research conducted?
X-rays of the kidneys are performed in a specially equipped room. After the preparatory measures, the patient needs to take the correct position, and further actions directly depend on the x-ray method. Before contrast urography of the kidneys, a special substance is injected intravenously.
After this, a series of x-rays are taken.
Contraindications to X-rays
Below are some contraindications under which this examination is unacceptable.
Iodine intolerance
Iodine intolerance is characterized by the development of an immediate or delayed allergic reaction, which can be life-threatening. In this case, it is unacceptable to take an x-ray of the kidneys with the introduction of contrast. A different research method is selected.
Decreased kidney function: acute and chronic renal failure
A significant decrease in renal function is also a contraindication to contrast radiography. The introduction of an X-ray contrast agent can only worsen the pathology.
Diseases affecting kidney function
Similar to the previous one: the introduction of contrast can provoke a deterioration in the patient’s condition in the presence of such diseases.
What will a kidney x-ray show?
X-ray examination of the kidneys helps to identify the following pathologies:
- stones and sand;
- compression of the urinary tract by stones or tumors;
- incorrect position of the organ (more often – prolapse);
- cystic formations;
- benign or malignant tumors;
- abnormalities in the structure of organs (for example, the presence of only one kidney);
- polycystic disease;
- hydronephrosis;
- pyelitis;
- pyeelectasia;
- glomerulonephritis;
- kidney injuries (ruptures);
- pyelonephritis;
- tuberculous kidney damage;
- ureteral rupture.
Based on the data obtained, doctors make a diagnosis and begin treatment of the patient. This is extremely important, because when kidneys fail, patients experience severe intoxication - poisoning with products of their own production, which will inevitably lead to death without qualified medical assistance.