Hello!
My baby is 14 days old, but I constantly worry about him. Either I can’t put him to sleep, then he’s all shrunk, shaking his arms and legs, and I don’t know how to help him.
Now I have added anxiety about my breasts. I began to experience tingling sensations during feeding, and I don’t know what it could be. What if this is an indicator that there is a lot of milk or maybe you need to go to the doctor?
Please tell me why I have these feelings? Do they harm the baby? What to do with them?
Marina.
Marina, congratulations on the birth of your baby! You are now going through a difficult, but very interesting period in your life. Yes, you have to learn a lot and figure out what may bother the baby, but soon it will become easier and you will rejoice at his first smiles, laughter and successes.
About the basics of child care: bathing, swaddling, rocking, proper carrying, see the online course Happy Motherhood: Methods of Gentle Care>>>
Tingling in the chest is a common sensation after childbirth. And even with older babies, mothers encounter such sensations, so today I will tell you all the possible reasons that can lead to tingling in the chest.
Causes
During pregnancy and especially after childbirth, increased synthesis of prolactin occurs. It is needed to produce breast milk. In this case, the mammary glands increase in size, the ducts become overfilled with breast milk.
These changes are the cause of physiological chest pain during breastfeeding. They are due to adaptation to the lactation process, but prolonged pain cannot be ignored. Only a doctor can distinguish physiological changes from pathology.
You need to see a doctor if:
- intense pain is present for a long time;
- the woman’s general condition has worsened;
- a mass formation has appeared in the chest;
- there is a rash, peeling, irritation on the skin of the breast or bleeding cracks on the nipples.
If you have the listed symptoms, you need to undergo an examination by a mammologist to determine the cause of the pain and take adequate measures.
Why do my breasts burn, tingle and itch during feeding? Painful sensations are often associated with restructuring of a woman’s body. Letting down of milk (especially for a new mother) can cause burning and tingling in the breasts; This goes away after feeding or pumping. Also, causes of pain during any period of lactation include:
- rapid flow of milk before, after or during feeding;
- wounds, cracks or other injuries on the surface of the nipples;
- lactostasis (milk stagnation) or, as a result, a complication - mastitis (inflammation of the mammary gland);
- mastopathy (benign breast disease not associated with breastfeeding);
- incorrectly chosen bra.
The degree of discomfort depends on the woman’s pain threshold. One nursing mother may feel the usual tingling sensation in the mammary gland during lactation, while another may experience pain not only in breastfeeding, but also in touching it. In any case, a woman should monitor her health and conduct preventive examinations more often to prevent possible complications.
Flushes of milk
Not all young mothers know about such a thing as the hormone oxytocin. It is he who is responsible for reflexes during labor and lactation. At first, a woman may even have complaints that her breasts hurt during feeding, or that there are unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen or in the nipple area. Oxytocin increases blood flow, which causes increased milk production even when simply remembering the baby or thinking about previous feeding.
Often, breast pain in a nursing mother appears precisely because of an excess of milk: the baby is full and has to express the rest. In this case, it is important to learn the correct technique for putting your baby to the breast, maintain a daily routine and follow a certain schedule. Then milk will be produced in the right quantity without excess.
Milk flow is one of the causes of breast pain. If the baby does not have time to eat everything, then milk must be expressed.
At first, when the baby does not yet know how to attach to the breast, you have to interrupt the feeding yourself by pulling out or tearing out the nipple. However, such careless actions can lead not only to pain and burning during breastfeeding, but also to injuries (wounds, cracks, abrasions, bruises), which, in turn, are the causative agents of infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Also, excessive sterility will not lead to anything good. Overly clean mothers often make the mistake of washing off with soap not only possible dust and dirt, but also the necessary, kind of beneficial microflora. The woman is deprived of a protective film that has bactericidal and moisturizing properties, and the child does not fully develop immunity to external irritants. This is one of the reasons why a nursing mother’s breasts hurt, the skin dries out and becomes injured, and wounds and cracks appear on the nipples.
Often the causes of complications are improperly selected underwear, which rubs or strongly compresses the mammary glands. During lactation, you will have to give up the sexy breast-lifting bra for the sake of health. Special equally beautiful underwear has also been created for nursing mothers.
Thrush
Thrush is a Candida fungus that appears as a white coating and cracks on swollen, dry nipples. In this case, feeding and expressing milk causes severe pain in the breasts of the nursing mother due to damage to the milk flow. You can cope with the disease on your own only in the initial stages, but breastfeeding in this case should be stopped.
If a young parent does not want to deprive the baby of breast milk, then you should immediately consult a doctor who will suggest a quick and safe method of treatment, select and prescribe the right medications. Self-medication can only cause complications, because if thrush takes you by surprise, then you are already doing something wrong.
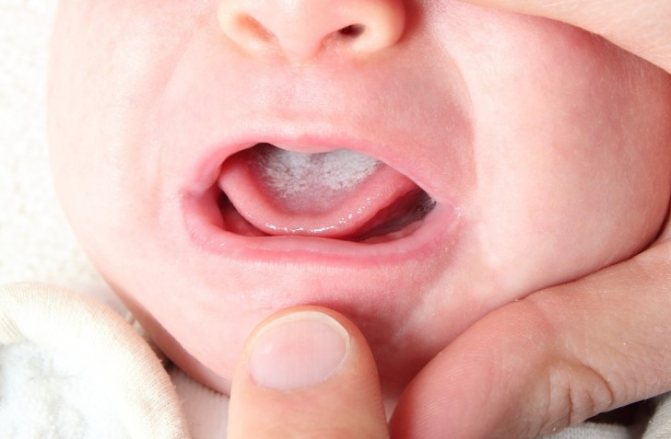
If hygiene rules are not followed, thrush may appear on the woman’s chest and in the child’s mouth, which must be treated immediately after detection.
Lactostasis
What are the reasons?
The situation when breast pain during lactation and fever can be caused by the following factors:
- congestion of the glands, hypothermia;
- lack of sleep;
- overwork;
- excessive thickness (fat content) of milk;
- incorrect use of sucking technique by a child if he is initially accustomed to a pacifier;
- incorrect position when applying or uncomfortable position during sleep (on one side or on the stomach);
- abnormal features of thoracic anatomy;
- stagnation of milk due to non-compliance with hygienic recommendations for breast and nipple care;
- development of viral infection in the human body;
- presence of cracks in the nipples;
- anemia, lack of hemoglobin in the blood;
- decreased properties of the immune system.
It is worth noting that while in the hospital, a woman can turn to the medical staff for help and get information about how to properly attach the baby to the breast. This applies to young mothers, first-time mothers, since their lactation is not regulated, milk is produced in excessive quantities and comes in.
If your breasts hurt during lactation, the reasons should be determined immediately.
It is necessary to regulate the feeding process, as well as maintain the same time intervals. The most correct position is one in which the child grasps the areola simultaneously with the nipple completely, while the mouth should be wide open and the lower lip turned down.

It often happens that the breast hurts during lactation due to milk flow.
Why do you feel tingling in the mammary glands?
Women of reproductive age most often complain about tingling breasts. This feeling can be caused by various reasons, so before prescribing treatment, specialists first determine what factors provoked its occurrence:
- Natural ones do not pose a threat to women.
- Pathological - indicate the presence of ailments and abnormalities in the body.
Based on this, further therapeutic measures are determined.
Let's look at the key features of the physiological and pathological reasons due to which a woman may be bothered by tingling in the chest area.
| Physiological factors | Features of the manifestation of unpleasant discomfort |
| Pregnancy | The feeling of the presence of a “needle” in the breast of expectant mothers is due to dramatic changes in its structure, which are preparing for feeding. A particularly pronounced tingling sensation is observed in the last stage of pregnancy. There is a proliferation of glandular tissue, which begins to compress the nerve endings, which provokes: - tingling; - tingling; - slight pain. |
| Lactation | If there is colitis in the breast tissue during breastfeeding, then this is due to the formation of colostrum, and then the influx of milk, as indicated by: - itching; - burning. |
| Premenstrual syndrome | 2-3 days before the onset of menstruation, hormonal surges occur, which causes: - swelling of the glands; - stabbing discomfort in the breast; - slight pain in the glands. Such symptoms are pronounced and are cyclical (occur monthly before the onset of menstruation and disappear before ovulation.) |
The above factors are not considered a deviation and in most cases, when they occur for a short time, do not require therapeutic correction.
If there is a tingling sensation in the chest, and everything is normal with pregnancy, breastfeeding and the menstrual cycle, perhaps the woman has some kind of hidden disease, which does not necessarily relate to the mammary glands.
The table briefly summarizes the features of the most common causes of pathological tingling in the mammary gland.
| Pathological causes | Nature of the disease |
| Mastitis | Develops during lactation due to: - improper breastfeeding. - rare application of the baby to the breast, which provokes stagnation of milk in the breast. |
| Mastopathy | Manifests itself in one or both breasts. |
| Diseases of the cardiovascular structure | With heart defects and pathologies of blood vessels, a stabbing symptom in the gland appears in its left part closer to the heart. |
| Deviations in the endocrine system | Hormonal imbalance occurs in women of all ages and provokes a painful tingling sensation in the glands. |
| Neuralgia | Pinched nerve endings are often expressed by tingling, accompanied by other symptoms. |
| Spine pathologies | Lordosis. Scoliosis. Trauma after impact. Cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis. Intervertebral hernia. |
| Tumors in the breast | There can be benign and malignant forms. |
Features of treatment depend on the diagnostic results. Based on this, the type of therapeutic intervention is determined:
- Conservative.
- Surgical.
If diagnostics of a woman’s body show that tingling in the breast is not caused by pathological processes, symptomatic treatment is prescribed. In particular, in case of endocrine abnormalities, it is necessary to take hormonal drugs that help bring hormone levels back to normal.
However, taking such drugs is dangerous due to a number of side effects, so their alternative option may be:
- Vitamins and microelements.
- Herbal remedies.
- Dietary supplements.
- Iodine-containing products.
- Enzymatic drugs.
- Anti-stress drugs.
- Sedative medications.
Tingling in the chest, as one of the symptoms of menopause, cannot be treated. The doctor can only prescribe some medications to reduce the intensity of the unpleasant symptom. In addition, a specialist may recommend:
- Breast massage.
- Systematic hygiene procedures.
- Review of rest and sleep patterns.
- Cold and hot shower.
- Moderate physical activity.
- Wear only a comfortable, non-squeezing bra.
If a woman has benign neoplasms, surgical treatment is most often prescribed than medication. Seals of a malignant form are eliminated exclusively by surgery, which involves excision of the tumor with partial removal of adjacent breast tissue.
After the operation, drug therapy is carried out using:
- Painkillers.
- Immunostimulating.
- Antitumor.
Specific names of drugs, their combinations and dosage should be selected only by the attending physician.
Phytotherapy
Folk remedies will help:
- Cabbage or burdock leaf - for swelling and pain in the chest.
- A compress of juice or grated beet pulp relieves tingling.
- Herbal infusion prepared from dog nettle, peony and valerian (1 tablespoon of the collection is brewed with 200 ml of boiling water, left for 3 hours and started to be taken 2 weeks before the onset of menstruation).
- After ovulation is completed, a decoction of yarrow, red brush and hogweed is useful (1 tablespoon per 250 ml of boiling water, heat in a water bath and leave for 30 minutes).
If stabbing pain in a woman’s nipple or in the rest of the mammary glands is not associated with pathological factors, in order to avoid its cyclical manifestation it is recommended:
- Lead a correct lifestyle.
- Avoid stress and negative situations, and if necessary, take mild sedatives (motherwort, valerian).
- Walk outdoors regularly.
- Don't stop breastfeeding.
- Be examined by a mammologist at least once a year and perform independent palpation of the breast once a month.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Engage in moderate exercise.
- Review your diet.
It is also important to follow all medical recommendations if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, problems with the menstrual cycle, etc.
This important process takes about three months from the moment the baby is born.
During this period, a woman may be bothered by:
- constant leakage of milk not associated with feedings;
- spontaneous leakage of milk from the nipple of the other breast when feeding the baby;
- increased discomfort in the chest and nipples when the interval between feedings is more than 4 hours;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen with infrequent breastfeeding.
After three months of breastfeeding, the young mother notices that many unpleasant moments associated with feeding have disappeared. There is no pain in the nipples, a sufficient amount of milk is produced, and feeding the baby does not cause discomfort.
How to treat headaches while breastfeeding
The main problem of medicinal elimination of such conditions is related to the fact that the composition of the drugs can penetrate into the child’s body through mother’s milk and have a direct damaging effect. Therefore, whenever possible, a nursing woman should avoid the use of chemicals. The best way to combat headaches is to rest, ventilate rooms, and walk in the fresh air with your child. You should minimize negative stress influences and listen to quiet and soothing music.
Please note: If these measures are not enough, and the headaches are severe and occur frequently, then you can resort to medication. But this should be done only after mandatory consultation with a doctor. Self-administration of medications is strictly prohibited!
Prohibited drugs include:
- Analgin and the entire group of drugs containing this substance;
- Acetylsalicylic acid and combination medications with Aspirin;
- painkillers containing codeine and caffeine.
Preference should be given to:
- Nurofen;
- Ibuprofen;
- Ibuprom;
- Paracetamol.
The dosage and form of the medicine (tablets, syrup, capsules) should also be prescribed only by a doctor, taking into account the individual characteristics of a nursing woman. In case of contraindications to medications, headaches due to hepatitis can be treated using acupuncture, laser, microresonance therapy, acupressure techniques, physical therapy and special manual therapy techniques.
Incorrect grip
Early breastfeeding is important, that is, a newborn baby should be fed within an hour after birth. If the baby cries or is worried, he needs to be fed. You can’t take his breasts away; after he’s eaten, he’ll let go of it himself. These simple rules will ensure sufficient milk production, satiety of the baby, and the desired duration of lactation.
To avoid pain during breastfeeding, a young mother should teach her baby to latch onto the breast correctly. To do this, a woman, preparing for feeding, runs her nipple along the baby's lower lip; reflexively, he opens his mouth wide. The mother pulls the baby's head to the breast so that he captures not only the nipple, but also the nipple area. In this case, the nipple is at the level of the root of the tongue, so it is not injured by the gums.
Otherwise, you need to stop feeding and re-attach the baby to the breast, helping him to latch onto the breast correctly. Complications of improper latch include cracks, abrasions of the nipples, insufficient milk consumption for saturation, increased gas production in the baby.
Recommendations
Young mothers often face difficulties when breastfeeding. When unpleasant symptoms appear, the most important thing is to regulate the flow of breast milk in a timely manner and not to start the process, to learn how to attach the baby correctly so that he completely grasps the nipple and areola with his mouth, turning his lips outward.
Experts recommend:
- apply the baby more often when symptoms of lactostasis appear, so as not to lead to heavier breasts and stagnation of milk;
- adhere to the correct feeding regimen, but at the same time do not refuse the child upon request if milk arrives in excessive quantities;
- massage the breasts if necessary, treat with ointments and gels according to the doctor’s recommendation.
It is very important to establish natural lactation, in which milk comes taking into account the child’s requirements. If necessary, use a breast pump and remove excess in a timely manner, express after feedings until the feeling of heaviness disappears. You are allowed to massage the nipple area in a circular motion, preferably under running warm water.
The lactation period is no less important time than pregnancy. It is necessary to avoid drafts and mechanical influence on the chest. It is important to express milk in a timely manner.
Every woman should know why breast pain hurts during lactation in a nursing mother and what to do in this case.

Manifestation of characteristic and alarming symptoms
Since stabbing pain in the mammary gland can appear for various reasons, you should know in what cases its occurrence may signal danger to the body.
As doctors emphasize, a serious symptom is manifested by a feeling of the presence of needles in the left area of the bust or its middle, which indicates the development of:
- Intercostal neuralgia.
- Spinal diseases.
- Hypertension.
- Thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery.
- Ischemia.
- Heart attack.
- VSD.
- Aneurysm (enlargement) of the aorta.
- Mitral valve prolapse.
In this case, it is necessary to focus on the following nuances:
- With heart defects, a tingling sensation begins on the left side or at the top of the chest.
- Burning pain in the middle or left side of the chest and the inability to take a deep breath - pre-infarction clinic or heart attack (you need to urgently call an ambulance).
- Paroxysmal painful discomfort from the bottom of the left chest indicates the presence of: angina pectoris, ischemia, irregular heart rhythm.
The presence of intercostal neuralgia does not pose a clear threat to a woman’s body, but it does cause significant discomfort, thereby worsening the quality of life. Pathology manifests itself due to pinched nerve endings.
Characteristic symptoms of neuralgia:
- Tingling can be either on the right or in the area of the left half of the chest.
- Manifestation of acute discomfort in different areas of the chest, including the side.
- The pain may intensify when turning or changing the posture of the body, taking a sharp breath and be accompanied by a cough.
It is worth noting that neuralgia can easily be confused with symptoms of heart disease, therefore, without clarifying the diagnosis, you should not take any heart medications, which is fraught with disastrous consequences.
If there is colitis on the right side of the chest, and discomfort is present all the time, then this indicates the presence of such diseases:
- Pleurisy.
- Flu.
- Tonsillitis.
- Bronchitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Oncology.
- Hernia.
- Osteochondrosis of the breast.
- Rachiocampsis.
Benign and malignant formations often occur for a long time without any symptoms or are manifested by minor discomfort. The development of cancer is accompanied by the manifestation of a characteristic clinical picture:
- The chest begins to hurt very much and stabbing inside it.
- Discharge from the nipples appears, having different colors and thickness.
- Rapid growth of the tumor.
What does tingling in the middle of the sternum mean:
- Ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
- Dysfunction of the gallbladder.
- Endocrine problems.
- Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region.
- Spinal lesions (Bechterew's syndrome).
- Schmorl's hernia.
Pathologies of the spine and joints are characterized by stabbing discomfort that radiates to the sternum and back, for example, in the presence of osteochondrosis - a sharp pain that occurs after physical activity or a rapid change in weather. Although the tingling may radiate to the breast area, its main location is the neck or thoracic region of the spine.
Breastfeeding a baby is a normal natural process. For some women, lactation occurs painlessly, without causing any discomfort, while for others it occurs with difficulties due to the presence of certain disorders in the body.
Many breastfeeding women experience pain and tingling during breastfeeding. Unpleasant signs occur both in the nipples and throughout the mammary gland. As mentioned above, a slight tingling sensation is not considered a deviation from the norm, as it occurs due to the flow of milk. However, you should be wary if:
- The thickening and tingling occurred at the same time.
- Pathological fluid is released from the nipples.
- There is severe pain in the chest.
Such signs often indicate the development of:
- Tumors.
- Lactostasis.
- Cyst.
- Mastitis.
- Mastopathy.
- Neuralgia.
- Heart and vascular diseases.
- Disturbances in the endocrine system.
Lactostasis develops due to blockage of the milk ducts and is accompanied by fever, breast swelling and severe pain.
Mastitis most often appears in the first days of lactation and is difficult to cure. In addition to the stabbing sign, it is accompanied by:
- Formation of compactions.
- Swelling.
- Swelling.
- Hardening.
- Increased body temperature.
- Feeling of compression of the breast.
- Redness of the skin of the chest.
- Loss of breast sensation.
- Acute painful discomfort in one breast.
To prevent milk stagnation, you need to learn how to properly attach your baby to the breast and avoid interruptions in feeding. The development of mastitis in a woman who is not breastfeeding is a sign of infection (can be eliminated by prescribing a course of antibiotics).
Mastopathy is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Seal.
- Burning.
- Tingling.
- Purulent discharge from the nipples.
- Severe pain when pressing on the gland.
Women with the onset of menopause may also experience periodic tingling in the breast, accompanied by aching pain. Such manifestations in medicine are considered the norm, however, given their constant nature, it is necessary to pay more attention to their presence. This is especially true for older women, since after the age of fifty, such clinical signs may indicate oncology.
However, for this age category of women, a tingling symptom does not always indicate cancer. There are other reasons for its occurrence:
- Hormonal surges. With the onset of menopause, the synthesis of certain hormones decreases, which causes hot flashes, breast pain and swelling, and the appearance of clear discharge from the nipples.
- Imbalance of fatty acids. An imbalance in their balance provokes swelling and hardening of the breast tissue, increased sensitivity of the nipples when touched and tingling.
- Psycho-emotional tension, stress. With the onset of menopause, the female body's susceptibility to stressful situations and psychological stress increases, which is manifested by tingling discomfort and other unpleasant sensations in the chest and other parts of the body.
Causes of lactostasis and their elimination
Some causes of lactostasis will be listed below. They can be eliminated without bringing the process to a deplorable state.
- Physiological characteristics of the structure of the mammary glands. Milk production causes the production of oxytocin and leads to discomfort and tingling as the breasts fill with milk. After 2-3 weeks, the symptoms will go away and lactation will become normal.
- Nipples are not developed. It is necessary to determine the most comfortable position for the baby when feeding, so that there is no excessive pressure on the chest.
- Too much milk coming in. Expressing should begin from the first weeks of feeding, the process should gradually normalize.
- Congestion in the glands of the chest. Their cells begin to produce milk. Do not allow overflow to occur; use a breast pump as needed.
- My chest hurts and I have a high fever. There is a high probability of mastitis, if it is purulent, then it is no longer possible to do without a course of treatment using antibiotics.
- Breast pain during lactation, regardless of incoming milk. In this case, the reason may lie in disease of the milk tubules and mammary glands; consultation with a mammologist is required.

You need to understand that a woman should not experience any pain when feeding. In particular, there is no need to vigorously massage the mammary glands once again in order to increase the flow of milk. This is precisely what can cause unpleasant symptoms, including the development of inflammation. Breast milk should come gradually, increased hot flashes should alert the woman. Perhaps the reason is that the milk is too thick, meaning the mother should reconsider her diet.
Is it dangerous when breast pain and chills occur during lactation?
Tides
Hot flashes are a physiological phenomenon that does not require treatment. This name is associated with the sensations of a woman: the breast is filled from the inside, the nipple hardens and swells. The temperature may rise slightly. Read more about other reasons for fever after childbirth →
Often, a nursing woman notices painful sensations of a bursting nature in the chest area. They indicate the intense secretion of milk by glandular tissue, its accumulation in the ducts and are a signal for feeding the baby. Especially often, lactation is accompanied by unpleasant sensations, tingling, burning in primiparous women at the very beginning of the feeding procedure.
Lactostasis
This phenomenon is associated with stagnation of produced milk, a violation of its secretion from the milk ducts. With this pathology, the milk ducts are blocked by condensed milk.
The causes of lactostasis can be:
- incorrect position of the child or mother during feeding;
- mechanical damage and compression of a woman’s breast (injuries, tight underwear);
- violations of pumping technique and improper nipple capture;
- long breaks between breastfeeding;
- short feeding time;
- holding the breast while sucking;
- hypothermia of the mammary glands;
- hyperlactation;
- insufficient fluid intake.
A clearly defined, painful, compacted area appears in the mammary gland. The skin in this area becomes hot to the touch, tense, and hyperemic. Your temperature may rise.
What to do? Regular light breast massage should be performed during and before feeding. Take a position that is comfortable for feeding, changing the position of the baby each time. It is important to practice frequent application specifically to the sore breast to completely empty the milk ducts. Apply compresses made of cloth moistened with cool water to the area of compaction.
If, after following these simple rules, the symptoms do not go away within two days, you should seek medical help. After the doctor's permission, you can carefully rub absorbable ointments into the skin over the lump or take other therapeutic measures. Possible complication if left untreated: non-infectious mastitis.
Preventive actions
To prevent pain during feeding, it is recommended:
- Put your baby to your breast more often . This will allow for uniform milk production and avoid stagnation.
- Do not take the baby off the breast . Wait until the sucking reflex stops. If you need to finish the feeding process, put your clean finger into your baby's mouth and gently pull out the nipple.
- Wear a bra that fits properly , and choose models made from natural materials.
- Learn and master the correct technique for pumping and latching your baby . When the nipple is grasped correctly, it is located deep in the mouth. This way the baby will not be able to injure the breast.
- Maintain breast hygiene . They do not need to be washed very often; this removes the protective lubricant and dries out the thinnest skin. Do not wipe your nipples with a towel - it damages the skin. If necessary, lubricate the nipples with special products.
- Prevent the baby from falling asleep during feeding and using the nipple as a pacifier.
It is especially important for the chest to ensure access to air. Therefore, walk around the house with your chest bare more often.
Are diagnostics and examinations necessary?
Painful discomfort in the form of stabbing sensations in the chest is typical for women of different ages, so before prescribing treatment, the doctor insists on a mandatory examination of the body.
The doctor will conduct a visual examination and palpation of the breast, establishing the presence of:
- Asymmetries.
- Swelling.
- Redness.
- Condition of neighboring lymph nodes.
Then a laboratory and hardware examination is prescribed.
Laboratory diagnostics:
- General blood test.
- Blood sugar test.
Hardware examination:
- Ultrasound of the breast (if there are lumps, cysts, etc.).
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland (if disturbances in the production of hormones are suspected).
- X-ray of the spine in the cervicothoracic area (to exclude or confirm problems with the spine).
- ECG (to clarify the presence of cardiovascular diseases).
- Biopsy (if there is a lump). The benign or malignant origin of the neoplasm is determined.
How to treat?
It should be immediately noted that self-medication is excluded, especially if infection of the breast glands is suspected, when it is simply forbidden to apply warm compresses, as they will increase bacterial growth and lead to inflammation.
Mothers should understand that home methods such as placing a cabbage leaf on the breast will not be effective enough. This will only help at the initial stage of lactostasis. Mastitis is treated exclusively with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. The algorithm of therapeutic actions will be determined by one or another form of the disease.
It is well known that many drugs for women during lactation are prohibited, and the use of antibiotics is a last resort. Naturally, with fever and severe pain, you can take a tablet of Ibuprofen, Paracetamol or No-shpa. Safe is “Bepanten” - an anti-edematous and anti-inflammatory cream that can treat cracked nipples without harm to the child’s health, even if it gets into his mouth.
Why a nursing mother's breasts hurt during lactation is of interest to many. We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the recommendations of experts on this matter.
Mastitis
Pain during breastfeeding can be caused by an inflammatory process. It is a consequence of lactostasis or infection due to non-healing cracked nipples, breast injuries, exacerbations of chronic infections. Severe pain during breastfeeding always indicates pathology.
The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Poor general condition (high temperature, nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite).
- The pain is intense, often pulsating.
- Swelling, redness, hardening of the breast.
- Local increase in temperature (hot chest skin).
If such manifestations occur, the mother needs to take all measures to combat lactostasis. Particularly important is frequent breastfeeding or expressing milk using a breast pump.
It is necessary to monitor the nature of the discharge from the nipple. If, instead of milk, a discharge resembling pus appears, feeding should be stopped and immediately consult a specialist. The appearance of pus indicates the formation of an abscess, which can threaten the life of the mother.
In the early stages of mastitis, the same treatment tactics are used as for lactostasis. In advanced cases, antibiotics are prescribed; in case of complications, surgery is performed.
Danger of mastitis
In nursing mothers, lactostasis is a common occurrence in the first months after childbirth. Usually it goes away when the regime gets better, the woman adapts and chooses a comfortable position for breastfeeding. If during breastfeeding your breasts begin to hurt and the temperature rises above 37 degrees, does not go away and lasts for several days, although milk is regularly expressed and the baby is fed frequently, you should immediately consult your doctor. In this case, the reason may lie in mastitis - an infection of the breast glands that is more serious than lactostasis. A therapeutic anti-inflammatory course will be required.
You need to know that with lactostasis the temperature does not rise above 37-38˚. In order to notice the pathology in time and stop its progression, it is necessary to measure the temperature from time to time.
If the indicator exceeds 39, you can no longer postpone your visit to a specialist. It is possible that the glands of the breast have become infected, which is typical for thrush or mastitis. A baby's latch on to the breast usually causes unbearable pain. Mastitis can be caused by untreated lactostasis, in which the infection penetrates through microcracks. A purulent, infiltrative, serous form of pathology may appear.
If a woman experiences such symptoms, first of all she needs to find out the causes of chest pain during lactation. Treatment should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor so that the nursing mother and baby are not harmed.

Cracked nipples
Mild redness, swelling and pain in the nipples are acceptable when breastfeeding immediately after childbirth. Gradually these unpleasant phenomena disappear. Reasons: improper capture and expression of milk, thinning, microtrauma of the skin of the breast and nipples due to frequent washing. Read more about proper breast care and hygiene for a nursing mother →
To reduce pain in the first days after childbirth, you can express about 20 ml of milk before starting feeding. The nipple will then become softer. You should not suddenly remove the nipple from the baby’s mouth, as this can cause injury. When the baby is full, he will release the breast on his own.
Cracked nipples are a pathology that is dangerous due to its complications. If they are detected, you should consult a doctor.
Prevention:
- After feeding, it is advisable not to put on a bra immediately;
- avoid the use of rough underwear;
- teach the baby to suck properly (with capture of the areola);
- Treat the slightest abrasions in the nipple area immediately after feeding with sea buckthorn oil.
Possible complications of cracked nipples are mastitis, the development of septic processes (penetration of Staphylococcus aureus, fungal infection).
Stimulants
My milk has arrived. The chest is swollen and hurts. What to do?
Translation and editing by Natalia Gerbeda-Wilson
Between the second and sixth days after birth, milk “comes in.” Before the milk came in, the baby sucked “first milk” or colostrum. Colostrum contains all the necessary nutrients, as well as antibodies and other immune factors that protect the baby from disease. The process of changing colostrum into milk takes about two weeks.
When the milk comes in, the breasts swell so much that they seem about to burst. The breasts become fuller not only due to an increase in milk volume, but also due to the influx of additional blood and fluid that is needed to prepare the breasts for feeding. The degree of breast engorgement depends on the woman: for some, the breasts increase very little, and for others they swell very much. As a rule, engorgement subsides within 12-48 hours from the time the milk arrives. When milk comes in, it is especially important to feed your baby more often. When a baby sucks milk, the breasts make room for excess fluid, which builds up during the postpartum period.
Measures to prevent or reduce breast swelling:
- Feed as early and often as possible. Try to feed for the first time as soon as possible after the baby is born. Put your baby to your breast at least ten times a day.
- Check that the baby is well attached to the breast and that he is latching well. (See How to Latch Your Baby to the Breast.) Feed whenever your baby shows signs of being ready to suck—rapid eye movement, trembling closed eyes, muscle tension, clenched fists, body flexing, vocalization, hand sucking, or grasping. mouth, search reflex (touching the cheek with anything causes the head to turn towards the touched object). Wake your baby for feedings if he sleeps more than two to three hours at a time during the day or more than four hours at night.
- Let your baby nurse on one breast for as long as he suckles. Usually the baby either falls asleep or lets go of the breast when he is full. Do not limit the time you suck on one breast to a certain number of minutes.
- If your baby is not latching or is not latching well, express milk by hand or with a breast pump as often as if your baby were nursing.
- There is no need to limit yourself in drinking. Research shows that fluid restriction is not effective in reducing breast swelling due to milk supply.
Frequent breastfeeding helps most women reduce breast soreness after milk comes in. However, in a small number of women, breasts still become engorged despite frequent feedings. If frequent breastfeeding doesn't help you, try
Light breast massage
Place your palm on the very top of your chest, just below your collarbone. Gently stroking the breast in a circular motion, move your palm towards the nipple. This massage is convenient to do in the shower, over a sink or basin with warm water, periodically washing the chest.
Warm compresses, massage, cold compresses
Another way to reduce engorgement is to use warm, moist compresses and expressing milk right before feeding. Do not apply a warm compress to your breasts for too long, as this can lead to increased swelling and inflammation. Cold compresses can be applied between feedings to reduce pain and engorgement. Cold compresses cause the blood vessels to constrict, thereby reducing swelling in the breasts. Despite popular belief, cold does not cause chest colds or mastitis. To make a cold compress, take a plastic bag, put ice in it, tie the bag so that melting water does not leak out of the bag, wrap the bag with a handkerchief or linen kitchen towel and apply it to your chest.
Cabbage compresses
A common folk method for reducing the pain of swollen breasts is compresses made from cabbage leaves. For compresses, you can use either leaves at room temperature or chilled in the refrigerator. To make a cabbage compress, wash the inner leaves of the cabbage head, cut off any hard veins, and lightly knead them, such as rolling a rolling pin (or water bottle) over the leaves several times. Wrap the breasts in cabbage leaves. You can wear a bra on top. Replace the leaves every two hours or when they wilt. If you experience a rash or allergic reaction, stop using cabbage compresses. Do not get carried away with this method as sometimes excessive use of cabbage leaves can lead to less milk production. Experts recommend stopping making cabbage compresses as soon as the swelling subsides.
If you experience any of the following symptoms, seek immediate medical attention:
- Breast engorgement does not go away, despite all the measures described above.
- You develop symptoms of mastitis, including a fever above 38°C (100.6°F), red/tender/swollen breasts or both breasts, chills, or a flu-like feeling.
- The baby cannot latch onto the breast.
- The baby does not have enough wet and dirty diapers (see the article “Does the baby have enough milk?”)
- Breast engorgement leads to flattening of the nipples and hardening and swelling of the areola (nipple circle). In turn, it is difficult for the baby to latch onto the breast. In this case, a new method called areola pressure softening (RAD, English: Reverse Pressure Softening) may come in handy. Pressure softening, as the name suggests, softens the areola to make it easier for the baby to latch onto the breast and suck out milk. When pressure is applied to the areola, milk may or may not flow out.
Softening the areola with pressure
K. _ Gene Cotterman RNC , IBCLC ( [email protected] )
What is “pressure softening of the areola”?
Areola pressure softening (APS) is a new way to soften the areola to make it easier for a newborn baby to latch on to the breast and suck milk, especially in the postpartum period, when both mother and baby get used to feeding. Breastfeeding should not be painful. If the areola is soft and pliable, the baby can, painlessly for the mother, pull the nipple deep into the mouth so that the tongue and gums can press on the milk ducts under the areola. (Breast sucking is different from sucking on artificial nipples.)
The new method is different from expressing milk by hand. When pressing on the areola, milk may or may not flow.
In what cases can RAD be used?
The technique of softening the areola with pressure is well suited for the first days after childbirth, when the areola has become hard, the breasts are swollen, or it is painful for you to feed. The arrival of milk itself is not always the only cause of engorgement of the mammary glands. If you skip or delay feedings, the tissue around the milk ducts, like a sponge, retains excess fluid, but the baby never sucks out this fluid. Giving intravenous fluids or using medications, such as artificial oxytocin (Pitocin), can cause further tissue fluid to accumulate. It may take seven to fourteen days for the body to get rid of excess fluid. If you use a breast pump, try not to pump for too long in one sitting, and also avoid setting the pump to a deep vacuum cycle. Prolonged pumping and strong pulling of the areola with a breast pump can lead to increased swelling.
Feel the areola and the tissue underneath well. How do they feel to the touch – soft and pliable like an earlobe or lips? Or hard and inflexible like a chin? If your areola is hard and you can't put any pressure on it, it's time to try the pressure softening method. The areola softening technique should be done before each feeding. The duration of use of the RAD technique depends on several factors: whether the swelling of the areola has subsided; Do you hear your baby regularly swallowing while sucking? Does it hurt when you put your baby to your breast without softening the areola before feeding? Establishing painless feeding, when the breasts have stopped swelling and the baby is suckling effectively, takes a week, sometimes it takes a week or longer.
Mechanism of action of RAD
Softening the areola with pressure temporarily moves the swelling back and up into the breast. This makes it possible to change the shape of the areola and also helps to pull the nipple outward. Pressing on the areola sends a special signal to the back of the breast to move milk to the front of the breast (this is called the let-down or milk ejection reflex), and the baby, in turn, can suck milk out with the help of the tongue when the milk has flowed to the front of the breast. RAD, in combination with gentle massage of the upper breast towards the nipple, helps to express milk by hand or slowly and carefully with a breast pump.
Where to press?
The most important thing is to soften a circle of 2.5 cm or larger around the base of the nipple. It will be easier for the baby to suckle if you also soften the breast in the place where the baby's chin rests. Softening the areola with pressure should not cause pain or discomfort.
How to use the areola pressure softening technique
K. _ Gene Cotterman RNC , IBCLC ( [email protected] )
Illustrations by Kyle Cotterman, Dayton, Ohio
- Choose one of the areola pressure softening techniques as shown in the illustrations below. If you will be applying pressure not by yourself, but by someone else, explain to your assistant that the technique can be used both from the front, standing right in front of you, and from behind.
- Place your fingers on the areola (areola) so that they touch the nipple. If the areola is very swollen, i.e. very firm to the touch, lie on your back and/or have someone press the areola over your fingers.
- Gently and firmly press on the areola. Direct the pressure inward, towards the ribs.
- Hold your fingers in this position, applying even pressure on the areola for one to three minutes.
- Relax, breathe evenly, sing a lullaby, or ask someone to time it. If you can't see your areola, ask someone to hold a small mirror for you.
- Try to see if the areola has become softer. If the areola is still hard, repeat the procedure again. The method of softening the areola with pressure can be used an unlimited number of times until the hardness and swelling of the areola decreases. Sooner or later, indentations will appear on the areola, and the baby will be able to latch onto the breast.
- Instead of finger pressure, you can use the soft ring of the pacifier. To do this, take a pacifier with a flat ring and cut off its end.
- Try to put your baby to your breast as soon as you remove the nipple ring from your breast, while the areola is soft.
Pressure with one hand, the so-called “flower pressure” (translator’s note - fingers folded like a flower). Nails should be cut short. When applying pressure, the fingertips are slightly tucked and positioned on the areola where the baby's tongue would rest.
Pressing with two hands is a one-step technique. Nails are cut short. The fingertips are tucked under and touching the base of the nipple.
Assisted pressure. The assistant places his fingers on top of yours to apply pressure.
.
Pressing with both hands is a two-step technique. Pressure is applied with two or three straight fingers on the sides of the nipple. The joint of the first phalanx touches the nipple. Repeat pressure on top and bottom of the nipple.
Pressing with both hands is a two-step method. Pressure is applied with two straightened thumbs. The base of your thumbnails should be level with your nipple. Repeat pressure on top and bottom of the nipple.
Trick using a soft pacifier ring: Cut off the end of the pacifier. Place the ring on the areola and press with your fingers.
- https://www.llli.org/...ngorgement.html
Thrush
Pain in the mammary gland during breastfeeding can be a symptom of candidiasis (thrush). The following signs are characteristic: nipple cracks do not heal for a long time, the skin around it is dry, reddened, painful, sometimes covered with a whitish coating.
This phenomenon is dangerous for the child, he can become infected from a sick mother, so a nursing woman should urgently consult a doctor. He will prescribe antifungal ointments to treat the affected skin areas.
For preventive purposes, the baby is prescribed an antiseptic solution to treat the mouth after contact with the breast. This is especially necessary when white plaque appears on the mucous membranes of the baby’s mouth. At the same time, the general condition suffers - the child is worried and refuses to breastfeed. The disease cannot be started, otherwise the prescription of fungicidal drugs for oral administration will be required.
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of lumps in the mammary gland, it is recommended:
- Feed your baby on demand, not by the hour. The baby regulates milk production himself.
- Apply the baby correctly. The baby empties the breast fully only when the areola is captured. If the child sucks only the nipple, then the woman constantly develops lumps and cracks.
- Avoid bottles and pacifiers. Auxiliary accessories are harmful to lactation. They cause incorrect sucking technique and inadequate grip of the areola.
- Rest and avoid stress. Oxytocin is required to empty the milk ducts. Fatigue and stress block its production.
- Don't get too cold. Lumps in the breast appear due to narrowing of the milk ducts. One of the causes of spasms is hypothermia.

In Soviet times, doctors recommended expressing until the last drop so that there would be no lumps in it. However, pumping provokes hyperlactation - one of the causes of lactostasis. Therefore, regular pumping, feeding by the hour, supplementary feeding from a bottle and using pacifiers is a direct path to hyperlactation and compactions.
Vasospasm
Severe vasospasm of the mammary glands is observed in women suffering from Raynaud's syndrome and other autoimmune diseases. Clinical signs: burning pain after feeding, white color and coldness of the nipple after finishing feeding.
Sometimes the disease may first appear after childbirth due to a decrease in immune defense. A woman should consult a doctor for advice. With his approval, you can perform a light breast massage.
It is necessary to exclude cooling of the breast and sudden changes in temperature (after feeding, wrap the breast with a warm cloth to prevent overheating). Do not drink strong tea, coffee, or alcohol. Read more about proper nutrition for a nursing mother →
How to relieve pain?
How to get rid of pain during breastfeeding? This question worries many women who are faced with this problem.
Simple manipulations will help:
- frequent breastfeeding;
- teaching the baby how to properly latch on to the nipple;
- expressing a small amount of milk before feeding if there is severe swelling of the breast and nipple;
- expressing milk between feedings using a breast pump.
To get rid of pain due to stagnation of milk, you need to improve its outflow by increasing physical activity. Bend over and shake your chest - this simple manipulation sometimes works well.
The following steps must not be taken:
- take medications to reduce breast milk production;
- refuse breastfeeding due to pain;
- Express milk frequently and completely;
- limit fluid intake;
- use thermal procedures, including alcohol compresses, on the mammary gland area;
- wear tight clothing;
- take incorrect positions during sleep and during feeding.
The question of how to relieve pain during breastfeeding should be decided with the participation of a doctor. The woman’s task is not to endure discomfort, but to contact a mammologist in a timely manner to prescribe the necessary examinations and select methods to overcome the pain syndrome. This will prevent dangerous complications and preserve the health of mother and baby.
Symptoms that should not be ignored
With mastitis, the symptoms are similar to lactostasis:
- temperature 39 ˚С;
- the mammary glands become very swollen and hardened;
- there is an accumulation of infiltrate in the glands, the lymph nodes under the armpits are enlarged;
- It becomes difficult to express milk.
The purulent form of mastitis is especially dangerous, in which the temperature suddenly rises to 41 degrees, the pain in the breasts of a nursing mother intensifies, pus comes out of the nipples, and the skin around the areolas becomes bluish. This indicates the accumulation of pus and stagnation of milk.
If a woman gets sick, she will most likely need hospital treatment and curtailment of lactation for a while. Strong therapy is carried out using antibacterial drugs. Only after completing the treatment course can breastfeeding be continued.
Experts recommend treatment at the initial stage, without weaning the child. Fortunately, there are now safe local remedies that can be used to treat breasts in the presence of lactostasis.
It is forbidden to continue feeding the baby if there is mastitis; you should consult a pediatrician. You may have to temporarily switch to artificial feeding if your breasts hurt badly during lactation.