Lactostasis, or stagnation of milk in the breast, is the most common problem among nursing mothers. We will give you some recommendations on how to deal with such a situation. The initial signal of milk stagnation is unpleasant symptoms in the mammary gland area, when any area is painful to touch.
Cost of mammologist services in our clinic
| Appointment with a mammologist with the highest category | 1000 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands with regional lymph nodes in standard mode and using Doppler techniques | 1200 rub. |
| Soft tissue biopsy | 2500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands with regional lymph nodes with technical difficulties | 1500 rub. |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) | |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
Upon palpation, you may feel a lump or compaction that has formed. Another sign of lactostasis is complete hardening of the breasts. Lobules in the mammary gland can be felt.
Causes of pain during hepatitis B
Breast pain during breastfeeding can be the result of physiological and pathological changes in the mammary glands. Different situations require a different approach, so treatment begins with finding the main factor.
It is important to take into account that with mother’s milk the child is able to receive not only nutrients, but also harmful substances, so the presence of any problem has a double risk. The disease can pose a danger to both the woman and the child.
The woman’s condition must be assessed comprehensively. Breast pain during feeding is usually accompanied by additional symptoms.
They require just as much attention because they can point to a key cause.
The following are common reasons:
- increased lactation, excessive milk production;
- cracked nipples;
- natural recovery process after childbirth;
- difficult milk flow;
- lactostasis, congestion of the mammary gland;
- abrupt interruption of breastfeeding;
- inflammatory diseases of the mammary gland, including mastitis.
Quite often, pain is noted in the first month of feeding , when the breasts are just adjusting. The delicate skin of the nipples adapts, cracks may appear on it, which cause discomfort.
Read more about pain and cracked nipples.

The cause may also be a constant and rapid flow of milk. In this case, unpleasant sensations can occur only on one side.
Frequently placing the baby on this breast relieves the feeling of fullness and swelling. If there is a constant flow of milk, you need to express it regularly.
Another cause of discomfort may be the baby's incorrect position. To properly latch onto the nipple, a woman can hold her breast from below.
The child's body is always turned towards the mother.
Another factor is tight underwear. A tight bra can cause congestion. It is recommended to wear special nursing underwear.
Milk stagnation
Stagnation of milk in the ducts, or lactostasis, is one of the causes of breast pain.
Additionally, you can observe thickening and increased pain when pressing. In the area of milk accumulation on the skin, a pronounced vascular pattern is formed.
The problem is more common in women who give birth for the first time. Milk is actively coming in, but the baby eats little, so the breast is not completely emptied.
As a result, swelling and accumulation of infiltrate occurs, which is accompanied by pain and constant discomfort.
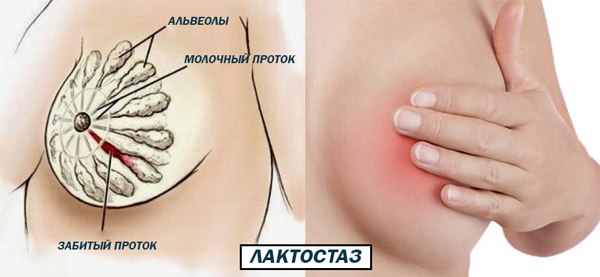
Read more about lactostasis in a nursing mother
Inflammation of the mammary gland
Inflammation of the mammary gland, or mastitis, is often the result of lactostasis, but not always.
The cause may be a bacterial infection (usually staphylococcal).
Decreased immune defenses and difficult childbirth increase the likelihood of illness. Without timely treatment, mastitis can lead to irreversible consequences, including breast deformation.
The most dangerous complication is sepsis, which can be fatal.
You can read more about mastitis here
Lactostasis
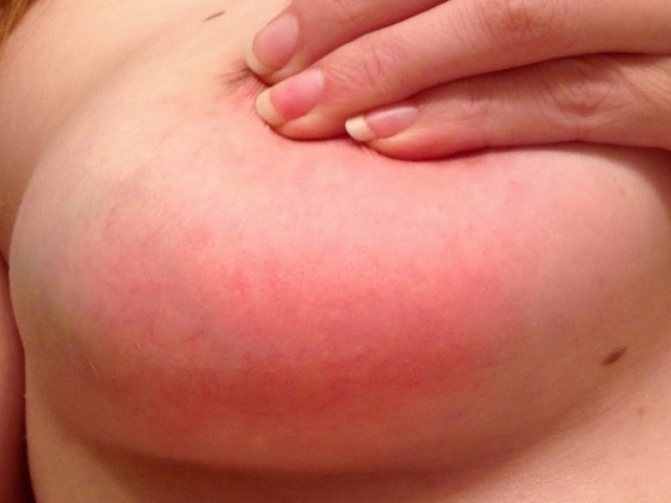
A disease such as lactostasis begins with pain in the mammary glands and an increase in temperature.
The disease is typical for the first months after childbirth; it is due to the fact that a lot of milk is produced, but the baby cannot yet use up that amount.
Lactostasis occurs if the baby sucks the breast incorrectly, that is, it does not capture the entire areola, but only the nipple. In addition, if the baby's lips are turned inward and not outward when latching on the nipple, this is also fraught with problems with the mammary glands.
Incorrect position of the mother during feeding can also lead to lactostasis; in this case, not all milk ducts work, and it is enough if milk is not removed from at least one duct, then the inflammatory process begins.

It is also important to find the right sleeping position; sleeping on one side is not the best option.
Usually in hospitals after giving birth, mothers are taught how to properly attach their baby to the breast. There is no need to be embarrassed to ask about this again and ask the nurses for help, and also ask them to monitor the feeding process.
So how to feed your baby correctly to avoid problems with the mammary glands? There are several recommendations, namely:
- After giving birth, you need to buy new underwear, preferably with a front clasp. You should stop wearing bras that you had before pregnancy; they will not fit and will compress the breasts, and are uncomfortable when feeding;
- When feeding a child, you need to carefully watch from the first minutes how the child sucks the breast: his lips should be turned outward and capture the entire areola. If the child first grabs only the nipple, immediately close his mouth with the little finger and remove the breast. Then they pass the nipple along the lower lip, the baby opens his mouth wide and the areola of the mammary gland is completely inserted into him;
- The child needs to be fed strictly according to the clock, then it is possible to achieve normal milk production, that is, the amount that will be completely fed to the child.
If the temperature remains above the usual norm for several days, but you follow all the rules of feeding and hygiene, and also express milk using a massage of the mammary glands, but this does not change the situation, you need to urgently consult a doctor to solve the problem at the very beginning.
Symptoms and manifestations
When your breasts hurt while breastfeeding, you need to pay attention to your general health and accompanying symptoms - they may indicate a specific disease.
You need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- burning and tingling sensation in the glands;
- the appearance of compactions, nodules, bumps;
- the occurrence of swelling, significant breast enlargement;
- redness of the skin in the area of the glands;
- increased sweating and chills;
- frequent flow of milk, which is accompanied by severe discomfort.
Each symptom can be interpreted differently. It is important to come for an examination to a gynecologist or mammologist.
The doctor will prescribe tests, the results of which will reveal the cause.

A dangerous symptom is pain, which is accompanied by fever. This phenomenon indicates an acute infectious and inflammatory process. In this case, purulent or mucous discharge from the nipples may be observed.
It is almost impossible to confuse this with ARVI, because cough, nasal congestion and other signs are absent. When feeling the breasts, increased density is noted.
If these symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor.
When the culprit of the problem is lactostasis
This problem appears in the lives of half of nursing mothers, and for all of them for different reasons. We remind you that lactostasis is a blockage of the milk duct or, as it is popularly deciphered, stagnation of milk during breastfeeding. This phenomenon can be caused by tight underwear, sleeping on the stomach, improper feeding, stress or physical activity that is incompatible with the rhythm of life of the mother during breastfeeding.
Lactostasis always begins with the appearance of pain in the chest, which tends to increase. An increase in temperature during this phenomenon may pass you by, but in most cases it still occurs. The thermometer may indicate a mark of 37-38 degrees. Sometimes, although much less frequently, the temperature rises to a more dangerous 39 degrees. An important point: the mother should take measurements at the elbow. This is justified by the fact that during lactostasis the temperature in the armpit will be slightly higher.
At the first suspicion, the mother should begin immediate treatment. At the initial stage, defeating the problem is quite simple: the baby must take on this mission. Lactostasis recedes under the influence of correct and more frequent feedings. If for some reason this is not possible, the mother can use a breast pump or express herself.
If the necessary measures were not taken at first, the disease will most likely develop further. The pain may become more severe, the temperature will rise a little more, and these symptoms will likely be accompanied by malaise and fever. The feeding regime will also be disrupted, because for the baby, latching on to the breast will be problematic.
In order to prevent the development of lactostasis during breastfeeding, we urge all mothers, if suspicious symptoms are detected, to make sure of an accurate diagnosis and begin treatment, if necessary.

Main contraindications
For chest pain and other pathological symptoms, there are certain contraindications. They relate to feeding rules and treatment.
A nursing woman with pathological pain in the breast is prohibited from:
- express milk in full;
- warm the chest, apply warm compresses;
- take medications that affect lactation;
- limit your fluid intake;
- self-medicate, take medications without a doctor’s prescription.
Any therapeutic measures are permissible only under the supervision of a specialist. Until then, a woman can worsen the problem if she self-medicates.
What to do to prevent your breasts from “burning”
In case of prolonged negative effects, you should consult a doctor. To alleviate the condition, first of all, it is necessary to eliminate the main cause - stagnation of milk. You need to regularly express breast milk until the gland is completely empty. This is done after feeding by hand or using a breast pump.
To facilitate the flow of milk, the breasts should be lightly massaged before feeding and before expressing. It is imperative to follow the feeding schedule, waiting until the baby is completely saturated. The recommended duration of the lactation period is 12–18 months.
Preventive measures include long rest, hardening - air baths and regular water procedures. Don't overuse drinks. This causes water retention in the body, swelling and congestion. Correctly selected underwear made from natural fabric can prevent unpleasant sensations. The bra should fit well around the chest without squeezing it.
A nursing woman should avoid breast injuries, mechanical damage to the skin, and hypothermia of the glands. After consultation with a specialist, traditional medicine can be used to alleviate the condition. Compresses should only be with such analgesic and antipyretic substances that will not harm the child.
Diagnosis of the disorder
A mammologist treats chest pain. You should contact him as soon as the manifestations become pronounced and it becomes painful to feed the child.
For diagnostic purposes, the doctor prescribes the following studies:
- general mammological examination, breast palpation;
- biochemical and general blood test;
- Analysis of urine;
- examination of milk for the presence of pathogenic microorganisms.

Additionally, an ultrasound examination of the glands may be required. An ultrasound is prescribed for severe breast compaction, the presence of lumps and nodules.
Additional diagnostics are also needed when the cause of the disorder is unclear, when standard procedures do not show deviations.
Mastitis
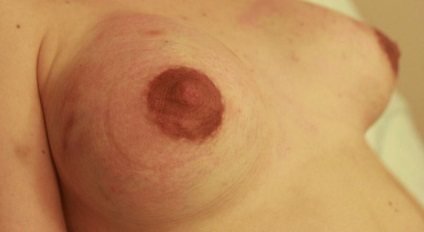
Mastitis is a more severe form of lactostasis when the temperature rises above 37 degrees. There are several types of mastitis, each of which requires a special approach to treatment. Serous mastitis is the initial stage of the disease; there is an increase in temperature to 38 degrees and pain in the mammary glands.
If you do not consult a doctor at the stage of serous mastitis, then the next stage in the development of the disease is infiltrative mastitis, which is characterized by an increase in temperature to 39 degrees, redness of both individual areas of the mammary glands and the entire chest area. At this stage, you can feel lumps in the breast, and pumping is usually difficult.
Soon after the formation of infiltrative mastitis, the disease passes into the form of purulent mastitis. This is the most severe and painful form of breast disease, when the lumps in the breasts look bluish from the outside, pus can ooze from the nipples, and the breasts respond with unbearable pain to the slightest touch.
In this case, emergency care is called, in the hospital the mother is treated with antibiotics, feeding during this period is unacceptable.
Diseases of the mammary glands such as lactostasis and mastitis are similar to each other, especially in the early stages, it can be difficult to distinguish them.
In a conversation about why breast pain and high temperature during breastfeeding: what to do, we first of all advise you to seek medical help in order to make a correct diagnosis; self-medication in this case is not allowed.
With the help of ultrasound equipment, doctors will be able to make an accurate diagnosis in order to begin treatment as early as possible and skip the minimum number of feedings.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
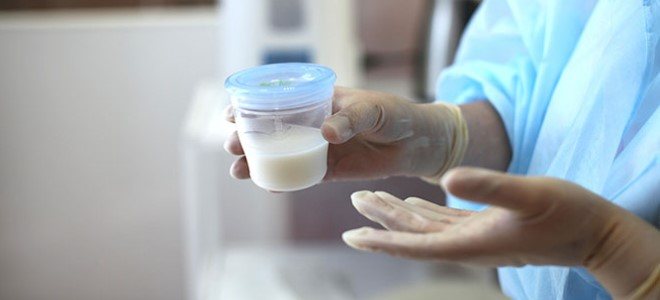
Together with the examination of the mammary glands, breast milk will be required for analysis.
If you experience severe pain in the chest, you should contact a mammologist. You need to hurry if the symptoms are pronounced and do not go away over time, especially if there is a high temperature.
The doctor will examine the mammary glands and order blood, urine and breast milk tests to exclude or confirm inflammation. In some situations, an ultrasound of the mammary glands may be necessary.
If no pathological problems are found, the nursing mother will be advised to improve the lactation process. To do this, you need to visit a doctor who will help you master the technique of putting your baby to your breast. The establishment of lactation continues for 2.5–3 months from the birth of the child. During this period, the mammary glands adapt to feeding and increased workload.
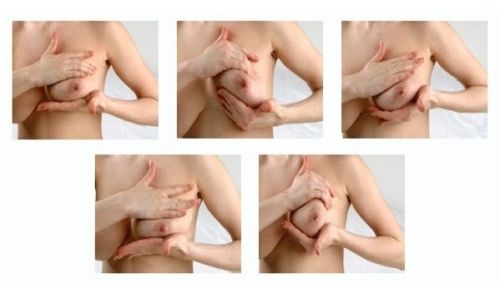
Breast massage gives good results when pumping stagnant milk
It is recommended to breastfeed your baby when he wants it: the more often, the better. Doctors advise not to stop breastfeeding until about a year. This will help regulate the volume of synthesized milk, preventing congestion in the mammary glands.
If the breasts hurt due to lactostasis, a woman is advised to follow these rules:
- Before putting the baby to the breast, do a light massage of the mammary glands.
- Change the child's position every time he eats. This promotes uniform emptying.
- If production is significant, express milk.
- Feed your baby as often as possible.
After the mother has fed the baby, you need to apply a cold compress to the mammary gland. For this purpose, use a wet towel or cabbage leaf that has been in the refrigerator. Following these rules will help you get rid of the symptoms of lactostasis in three days.

The initial or serous stage of mastitis can often be confused with milk stagnation. At this stage there is pain and a slight lump, but no other signs of infection are noticeable. There are cases of spontaneous recovery, when the pain syndrome gradually subsides and the lump completely resolves. However, much more often the disease develops, moving into the infiltrative phase with the appearance of a painful compaction. The infiltrate does not have clear boundaries, and the affected gland itself increases in size. But the skin above the seal remains unchanged.
If treatment is not started, the disease will enter the purulent phase. It is characterized by a deterioration in the general condition of the patient, which is caused by the penetration of toxins from the focus of purulent inflammation into the blood. Further, abscesses and tissue necrosis may appear. How fast and successful the treatment will be depends on the time you visit the doctor. In the final stages, conservative therapy will not help; surgery will be required.
Associated symptoms
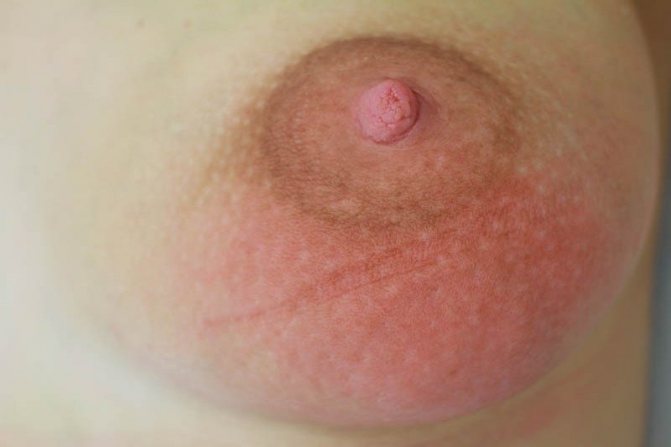
Breast swelling is added to the pain syndrome
The first signs of congestion are pain when pressing on the chest. They can be not only in the nipple area, but also to the left, right, above and below them. At the same time, the gland itself is soft, there are no injuries or bruises on the skin of the chest. If the pain is caused by a strong flow of breast milk, the woman needs to establish proper feeding and systematically express.
Pain in the chest area is often accompanied by additional symptoms indicating that internal pathology is developing. These include:
- microcracks on the nipples;
- “burning” pain, chest pain;
- red spots on the skin;
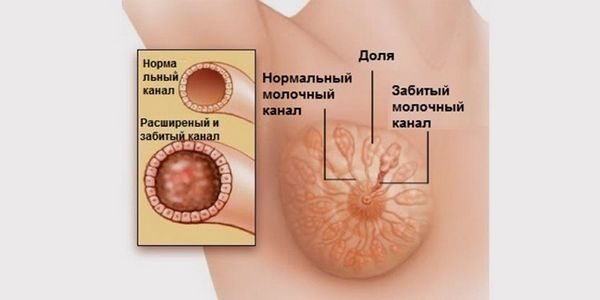
With lactostasis, the milk duct becomes blocked - painful influx of breast milk;
- excessive sweating and chills;
- weakness in the body;
- compactions, nodules, ulcers;
- swelling in the breast area.
With lactostasis and mastitis, the breasts swell, as if shooting through them, the pain is sharp, cutting, concentrated not only on the nipple, but also in the areas on the side where the clogged milk ducts are located. This may be accompanied by an increase in body temperature. If a nursing mother does not notice specific discharge from the nipple, this is lactostasis, which occurs as a result of a violation of the outflow of milk. But with this deviation, the mercury column does not exceed the 38-degree mark.
If a nursing mother has a temperature above 38 degrees and the mammary gland hurts, there is nipple discharge, this indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process - mastitis, which may already be turning into a purulent form. With such an illness, a woman is not bothered by the symptoms of ARVI, but her overall health is like that of a severe flu. On palpation, compaction and severe tenderness of the mammary glands are observed.