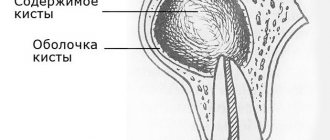
When a root canal infection occurs, a formation called a cyst may develop at the top of the tooth root, which appears as a pus-filled cavity with a fibrous lining on the inside.
A cyst, also often called a periodontal abscess, can gradually enlarge over time, causing serious discomfort to a person. The cyst located on the teeth of the upper jaw has the highest growth rate, which is facilitated by more porous bone.
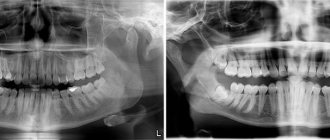
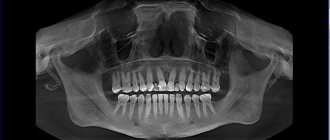
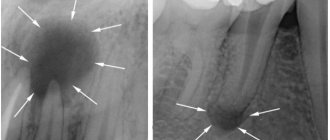
If we look at the x-ray, then a strong darkening in the upper region of the root is a cyst.
Diagnosis of dental cysts
Since at an early stage the disease has practically no symptoms, it can be very difficult to determine. Nevertheless, there are certain diagnostic methods that allow you to identify a cyst:
- external examination, the task of which is to determine whether there is growth of the capsule in the gingival tissue;
- checking the integrity of existing fillings (if there are any violations in the root part, they begin to collapse, which is noticeable to the naked eye);
- X-ray;
- tomography of the jaw.
The surest way to make a diagnosis is an x-ray: the capsule filled with cystic fluid will appear as a bright white area (its shape can be round or oblong) located under the gum pocket.
Based on the location of the formation and the current stage of development of the disease, the doctor will be able to prescribe the most effective treatment.
Symptoms
The insidiousness of a dental cyst lies in the fact that its appearance at first is almost asymptomatic. It makes itself felt when the purulent sac has already reached a fairly large size. Active growth of an abscess occurs when the immune system is weakened. People often learn about it during acute respiratory diseases or viral infections, when the body weakens due to the fight against the disease.
In the early stages, pathology can be detected by the following signs:
- slight pain in response to tactile stimuli - biting or pressing on the crown;
- soreness of the gums near the problem area.
When the cavity has increased significantly, acute toothache, swelling and swelling of the gums and cheeks appear. Since this is an infectious disease, there is an increase in body temperature, weakness, and general malaise. A tumor may appear on the gum, which will gradually increase and sooner or later a fistulous tract will appear in it, through which pus from the cyst will enter the oral cavity.
A dental cyst is diagnosed based on the results of radiography. On an x-ray it appears as a dark spot at the apex of the root. Sometimes pathology is detected completely by accident, examining a neighboring tooth.
Maxillary sinus cyst
Types of cysts
To prescribe the most effective treatment, the dentist needs to determine the type of cyst and identify why it formed.
Cystic formations are:
- radicular (occur at the root of the tooth or in close proximity to it);
- residual (formed after tooth extraction);
- retromolar (formed as a result of problematic eruption of wisdom teeth).
Based on their origin, cysts are divided into:
- odontogenic (they are caused by various dental diseases);
- non-odontogenic (their formation is not associated with dental diseases).
Separately, it is worth highlighting follicular cysts, which contain the tooth germ: they are formed as a result of improper care of baby teeth.
Classification of dental cysts
There are not many types of cysts, so understanding them is not difficult. Four main types are distinguished by location:
- wisdom tooth cyst;
— a cyst due to an illiterate (unprofessional) installed dental crown;
- a cyst that arose as a result of the influence of a third-party infectious disease (sinusitis);
- a cyst localized in the area of the front teeth.
At the same time, a classification is used based on previous circumstances preceding the occurrence of the cyst:
- a disease caused by poor-quality removal of one or more teeth;
— periodontal type cyst, provoked by an inflammatory process in the gums;
- a cyst caused by the growth of a wisdom tooth (retromolar or paradental);
- a cyst that occurs in children, first during the period of the appearance of milk (follicular) teeth, and then molars (eruption cyst);
— a cyst that arose as a complication of periodontitis (radicular);
— a situation is also possible in which the tissue forming the tooth degenerates (keratocyst).
Main symptoms of an abscess
A dental cyst may not reveal itself for a long time: a person may not realize that there is something wrong with his teeth and gums. Sometimes an abscess causes mild pain when biting or pressing on the gum. But barely noticeable and far from constant pain can force few people to go to the doctor: a cyst at this stage of development is discovered by chance when a person goes to the dentist about completely different teeth.
An infection in the abscess cavity can worsen if immunity decreases: the process of pus formation accelerates, severe pain appears, the cheek swells, the person feels weak and lacks strength, and the temperature rises.
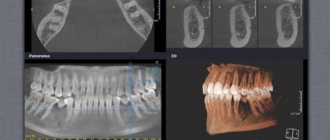
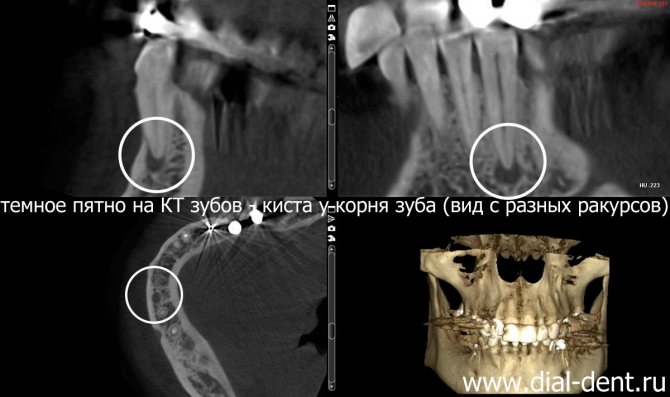
Diagnosis using dental CT
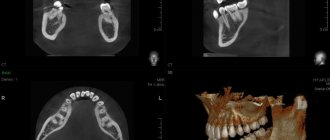
A dental computed tomogram (dental CT) is an informative diagnostic tool for dentists. Using a dental CT scan, you can determine the exact number of roots of a tooth, branches, bifurcation of roots, the presence of impacted teeth, the presence of inflammation at the roots of teeth (periodontitis), the condition of bone tissue, the sufficiency of bone for the installation of dental implants, the location of the jaw nerve and much more. Dial-Dent has its own tomograph, so a CT scan is done right in the clinic, in a few minutes. The doctor can immediately view the CT result and make the correct diagnosis.
Quite often, dental CT results reveal problems that the patient was not even aware of. In this case, a CT scan of the teeth was done before installing the implants. A CT scan of the teeth revealed inflammation at the roots, which over time could lead to loosening of the tooth and its loss. The patient did not even remember that this tooth had ever hurt. At the moment, nothing bothered me, and only the attentiveness of the orthopedic dentist S.V. Tsukora helped to notice the problem in time. At Dial-Dent, before dental prosthetics, they always do a full CT scan in order to see the condition of the entire oral cavity and not miss asymptomatic diseases that can reduce the quality of prosthetics.
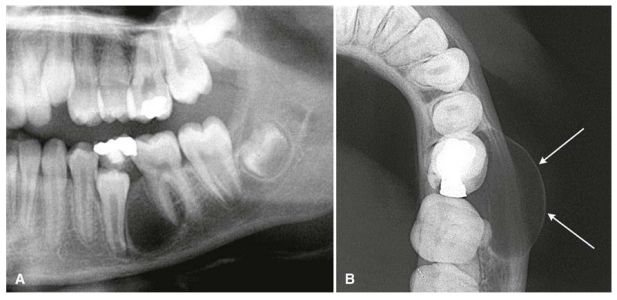
A fragment of a dental CT scan, which clearly shows a cyst:
Why does a cyst occur?
The main reason for the development of an abscess is the appearance of infection in the root canals. But there can be several reasons for infection:
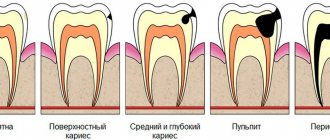
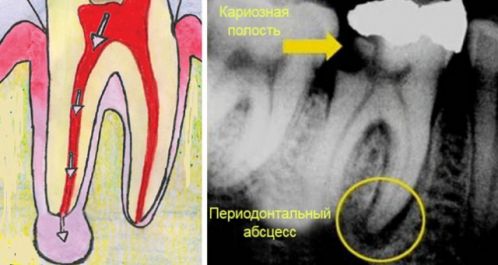
- Advanced caries that has developed into pulpitis due to ignoring the need for its treatment. In the tissues on which the carious formation has appeared, pathogenic microorganisms settle, first entering the pulp, as a result of which its inflammation begins, then, if the pulpitis is not treated, penetrating beyond the boundaries of the tooth, resulting in a periodontal abscess.
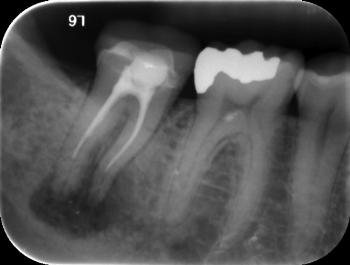
- Unsatisfactorily filled root canals. Canal filling is a fairly common procedure that dentists have to perform during treatment. However, despite the routine nature of the operation for a dentist, not all specialists, due to lack of experience or due to inattention, carelessness and the desire to complete the work as quickly as possible, do it efficiently. The canal must be sealed along its entire length, since in the unsealed part there is a high probability of infection, which, just as in the case described above, will sooner or later go beyond the boundaries of the tooth and lead to the appearance of an abscess. Official statistics on poorly filled canals are depressing: in more than half of the cases, dentists make mistakes during the procedure, which subsequently result in the appearance of a cyst. In the picture, the unsealed part of the canal is always clearly visible. Sometimes it happens that the root canal is completely filled, but the material used for filling is loose, which is also not good.
Causes of cyst formation
The penetration of bacteria into dental tissues is the main factor in the formation of cysts.
The infection may appear:
- due to injury;
- due to caries;
- due to improper treatment of dental canals;
- under the influence of infectious diseases of the nasopharynx;
- in cases where the tooth crown is poorly installed;
- due to deterioration of human health.
All these factors influence the possibility of the occurrence of cystic neoplasm of teeth, however, the most common causes include:
Untreated caries and pulpitis
- Cariogenic microorganisms are found in large numbers in tissues damaged by caries. If it remains untreated for a long time, bacteria begin to slowly move into the pulp, causing an inflammatory process - pulpitis. If pulpitis is not treated, the infection begins to move to the root apex area, through the root canals. There it provokes the emergence. chronic periodontitis. The size of the infectious focus under the root gradually increases. Thus, a tooth with a cyst appears.
Poorly filled root canals
- During the treatment of periodontitis and pulpitis, the root canals are filled. Filling is considered correctly carried out when it is carried out to the root tip. When the canal is not completely filled with a filling, an infection begins to develop in the area that remains empty, penetrating beyond the root, it provokes the development of a cyst.
Tooth cyst: treatment
Treatment can be divided into therapeutic (use of drugs) and surgical (gum incision and root resection).
Conservative treatment is justified if:
- no unsealing required;
- if the canal is unsatisfactorily sealed along its entire length;
- if the diameter of the cyst is large (over 1 cm), which is accompanied by pain and swelling noticeable even to a non-specialist.
Surgery is recommended when:
- there is a pin in the channel;
- there is a crown on the causative tooth;
- the root canals are unsealed at the upper part of the root for 1/3 of their length;
- The gums swell, which is accompanied by pain.
External features
A cyst on the root of a tooth looks like a dense capsule with yellow contents inside. It can reach several centimeters in size. Granuloma is a cyst whose diameter is no more than 0.5 cm.

Deputy Chief physician Sergey Evgenievich Brodsky
Sign up for a free consultation
+7
X-ray examination
The best way to view a neoplasm. In the picture, a dental cyst looks like an elongated dark-colored spot with smooth, well-defined boundaries. Most often it is localized in the upper part of the root or located near the coronal part, which has not yet erupted. Photo of a dental cyst on an x-ray
Description of therapeutic method of treatment
This method takes a lot of time, requiring a lot of patience from the patient (you will have to visit the dentist more than once), a lot of free time and significant financial expenses.
The process consists of a number of sequential stages:
- First, the doctor works with the canals. The dentist looks to see if they have been filled: if not, the pulp is removed, and the canals are processed using the instrumental method; if they were, then they need to be unsealed before proceeding with subsequent actions.
- The cyst contains pus, which is why after unsealing and getting rid of the pulp, repeated thorough rinsing of the canal with an antiseptic solution will be required.
- A potent medicine is removed from the apex of the root.
- The canal is temporarily filled with a paste that has an antiseptic effect.
- Since the medicine needs to be changed once every certain period of time, the patient will have to come to the dentist every time for this over the next couple of months. After the next change of medication, the canal is again filled with medicinal paste.
- From time to time, an x-ray is taken to monitor the progress of treatment and evaluate its progress. If the cyst in the picture becomes smaller over time, then this indicates positive dynamics.
- When the cyst shrinks, the doctor fills the canal with gutta-percha - this filling is permanent and periodic refilling is not required.
- Installation of a seal.
But even after placing a permanent filling, the patient still must visit the doctor for an image for another two to three months. It should show a reduction in the size of the existing abscess and restoration of natural tissue.
How to treat
Today, doctors are trying to eliminate the disease without resorting to tooth extraction. The unit is pulled out only if it is completely contained in the inflammatory capsule and its tissue is significantly destroyed.
In other situations, therapy may be:
- surgical;
- conservative.
Surgery
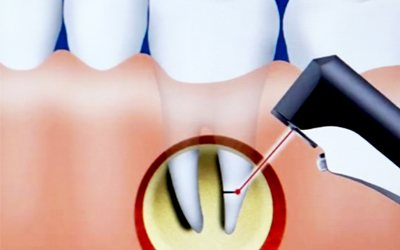
Cystectomy is a procedure aimed at removing the cyst and the changed part of the root apex. The technique is considered highly effective. Its only drawback is its difficulty.
Less commonly, for cystic changes, hemisection is performed. The operation is indicated for complete destruction of the tooth root. During treatment, the dental surgeon removes the capsule with its contents, the altered root and part of the crown. This leaves a serious hollow defect. It is closed by laying special composite materials and installing a crown (if necessary).
Conservative therapy
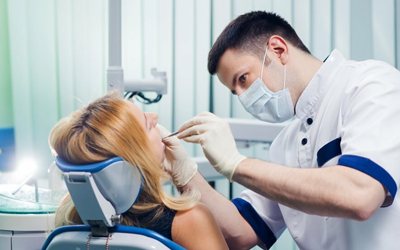
Does not involve surgery. The doctor does not make an incision to access the capsule. Instead, he drills out the roots and treats them. The fact is that the tip of the tooth root connects to the cyst, so after drilling, the contents of the cavity immediately flow out.
When this happens, a medicinal composition and a special anti-inflammatory paste are placed into the canals. Afterwards the filling is carried out. The disease is considered to have resolved if after six months the treated area is not visible on the image.
Conservative treatment helps most patients, so the main emphasis is placed on it when fighting the described disease.
Depophoresis - an innovative method of conservative treatment
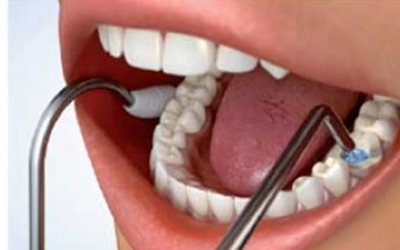
The most modern conservative treatment method is depophoresis. It does not require drilling of channels. The doctor exposes only the mouth of the canal, after which he inserts a thin electrode into it. The second electrode is pressed into the patient's cheek. Then it delivers a weak current discharge, along with which copper/calcium hydroxide passes through the channel. It penetrates even the most inaccessible areas, instantly kills pathogenic microorganisms, and destroys necrotic cells. Depophoresis is repeated three times. This is enough to clean the fabrics. Afterwards the tooth is filled. This technique is very effective. It allows you to get rid of the problem forever in 99% of cases.
Drug treatment of dental cysts
If the size of the mass is less than 1 centimeter, your doctor may recommend trying medication.
The range of prescribed drugs usually includes:
- antibiotics (for example, azithromycin, amoxicillin, etc.);
- immunomodulatory agents (arbidol, dibazon);
- antihistamines (ketotifen, acrivastine, etc.).
Depending on the individual characteristics of the development of the disease, multivitamin complexes and antifungal drugs may be prescribed. On average, treatment takes about 2 weeks minimum; every 4 days it is advisable to visit a dentist, who, after an examination, will adjust the medication intake.
Surgery
Removal of a dental cyst is carried out in cases where:
- there is a pin in the channel;
- there is a crown on the tooth;
- the equine canals are thoroughly sealed by 2/3, the filling is missing only at the apex of the root;
- cyst diameter exceeds 1 cm;
- constant swelling of the gums, accompanied by pain.
Removal of a dental cyst is carried out using several surgical methods:
1. Cystectomy
An operation during which, in addition to the bag of pus, the infected area of the root is removed. Resection is performed after orthograde filling of the canal. Without this manipulation, removal of a dental cyst will be ineffective. Afterwards, a surgical intervention is performed in which the root apex is removed and the canal is retrogradely filled with a material that is resistant to tissue fluid.
Resection is performed only if there are a number of indications for it:
- The importance of the tooth in combination with obstruction of the canals;
- Lack of positive results from endotherapy for 3 years.
2. Hemisection
Removing part of the tooth and cyst using this method is the least gentle option. If there are no ways to save the tooth root, this procedure is performed. The doctor removes the cyst, the root and the area of the tooth above it. After the operation, the resulting defect on the tooth is hidden under the crown.
Hemisection is performed in cases where the anterior root of a tooth cannot be saved, but at the same time one of the roots can still be saved.
3. Cystotomy
The operation is performed in cases where there is a need to remove the membrane to extract pus from the canal. Cystotomy is advisable to perform in cases where removal of a dental cyst is impossible due to a number of circumstances. Such obstacles include the large size of the cyst or the likelihood of causing damage to tissues adjacent to the inflammation. Surgery is performed under local anesthesia.
4. Laser removal of dental cyst
Treatment and removal of dental cysts using a laser in Moscow is a new modern method of treating the disease. It is fast, painless and highly effective. During the operation, a laser is introduced into the tumor through the tooth canal. The laser beam gradually removes (coagulates) the cyst and disinfects the root. Surgical laser treatment of a dental cyst lasts about one and a half hours, depending on the size of the cystic cavity. Laser removal of a maxillary sinus cyst can last up to 3 hours. The rehabilitation period after laser removal of a dental cyst is negligible.

Removal of a tooth cyst
The operation is called root resection. It takes no more than an hour: the procedure time depends on the location of the damaged tooth (back teeth are easier and faster to treat, front teeth take much longer).
The operation consists of the following steps:
- A couple of days before the procedure, the canals are sealed (days, not weeks, otherwise early filling can cause purulent inflammation).
- Immediately before the operation, the doctor gives the patient a pain-relieving injection - local anesthesia (it does not hurt, the only thing is that it may hurt a little when the injection begins to “go away”).
- The gum is cut, exposing the bone. A hole is made in the bone tissue near the tooth in which the cyst has formed, for which a drill is used (due to the anesthesia, the patient will not feel anything).
- The hole will allow the doctor to see part of the root and the cyst attached to it. This area of the root is cut off with a drill and removed from the resulting wound using tweezers.
- Since the cyst occupied a certain space in the tissue, after removal a cavity appears in its place. If the cyst is large, the doctor fills it with synthetic bone tissue, which stimulates the growth of normal bone.
- The dissected mucosa is sutured, and for a more effective outflow of the ichor, a drain is installed, which must be removed after a few days.
Resection in no way affects the lifespan of the tooth. The doctor’s task is to completely get rid of the cyst, since even leaving the slightest remnant of it can lead to its re-formation.
How much does it cost to remove a tooth cyst in Moscow?
The price (cost) of removing a cyst and preserving a tooth in Moscow starts from 8,000 rubles. If, after removal of a dental cyst, bone grafting and bone augmentation with the installation of a membrane are required, the cost of treatment starts from 15,000 rubles.
What to do after removing a tooth with a cyst?
- High-quality dentistry in Moscow
- Cost of dental treatment
- Dental treatment under a microscope
- Treatment of pulpitis under a microscope
- Treatment of dental canals under a microscope with an endomotor
- Dental treatment is inexpensive and high quality
- Retreatment of tooth canals
- Why do adult teeth become loose: should they be treated or removed?
- Clasp dentures: turnkey prices!
- How to Order a Dental Treatment Plan Online
- Microdental prosthetics
- Prosthetics for complete absence of teeth
- Repair of removable dentures
- Crown made of zirconium dioxide with a key
- Cost of dental restoration
- Dental restoration
- Cost of veneers
- Clinic specialists
Just pick up the phone and call us!
+7
We will definitely make you an offer that you cannot refuse!
Removal or treatment of a dental cyst?
The question is of great importance for people who are afraid of dental operations.
Before deciding on a treatment method, you need to consider a number of nuances:
- if you treat the cyst with medication, it will take at least 3 months; in case of surgical intervention, you will have to visit the doctor only 3-4 times;
- Nowadays, in most surgical operations, a laser has replaced the scalpel, but in some cases it is still impossible to do without traditional incisions;
- if there are deep cracks on the tooth, you cannot do without surgical intervention - no modern medications will help in this case;
- Regardless of the chosen treatment method, the probability of cyst recurrence is about 10%.
In any case, the final decision regarding the method of treatment remains with the doctor, who, based on the analysis of the x-ray and other measures, can make the right choice about the development of the disease.
Treatment of dental cysts - is it possible to cure teeth and who treats them?
Depending on the chosen tactics, manipulations are carried out by a dentist-therapist or a surgeon. Therapy can be conservative (using a special paste) or surgical (with complete removal of the formation). The final decision on which method should be used rests with the attending physician, as it depends on many factors.
At home
Alternative medicine offers many options, arguing that treatment in this way is completely natural, very inexpensive and very effective (however, the effect is not guaranteed by anyone). Rinsing with solutions of chamomile and calendula, rubbing with clove oil, garlic, and even cauterization are suggested.

Folk remedies for treating dental cysts do not have a proven medical effect, but they can hold back tumor breakthrough for some time. There are often cases when neoplasms open on their own as a result of unconventional intervention, which contributes to the development of complications, including severe ones, in particular, those that pose a serious danger to the patient’s health. Therefore, rinses, lotions and other manipulations can only be used with the permission of the attending physician.
Dentists are against self-medication using prescriptions from the Internet and magazines, especially in cases where infection of the body is possible. A dental cyst can break out - what should the patient do at home? Unfortunately, there are no acceptable methods of self-treatment for purulent formations; you should always first see a dentist. Only a specialist can solve the problem without harm to the client’s health.
Conservative method
The therapeutic method of getting rid of pathology less than 0.8–1 cm in diameter is the longest and most expensive, but it has a significant advantage: it does not require surgical intervention. First of all, the tooth is unfilled (if necessary), the cyst underneath is treated later. If the canals have not been treated previously, the painful pulp is cleaned out first.
The fibrous capsule filled with purulent contents is washed with antiseptics (possibly several times, depending on need). After this, the doctor injects a drug into the open cavity, which later fills the roots, but this is a temporary measure. Most likely, in the future you will have to make a couple more visits to the dentist to change the substance, as well as for the final filling.
The doctor decides whether to remove or treat a dental cyst: sometimes a conservative approach is not effective enough, and then a decision is made to remove the formation.
Efficiency at all stages is monitored using X-ray equipment. If the doctor finds that the therapy was successful, he restores the crown using available methods. After the procedure, you must visit your dentist for several months to make sure that the tumor has been eliminated.

Treatment with medications
The scheme includes:
- antibiotics (amoxicillin, azithromycin, ciprofloxacin and the like);
- antihistamines at the doctor's discretion.
Depending on the situation, antifungal agents and multivitamin complexes may be prescribed, but you need to know that the latter are used only in cases of vitamin deficiency and based on test results.
Tooth cyst - what is it, how to treat conservatively
Since this is a localized dental disease, treatment uses local anesthesia depending on the needs of the patient and the characteristics of his body. First, the crown is unsealed or opened, after which the oral cavity is cleaned and medication is injected into the treatment area. This stage can be repeated several times if purulent inflammation recurs. At the end of treatment, a permanent filling is placed.
If the canals were initially treated poorly, the question arises whether to re-treat them. This raises several difficulties:
- unsealing is a long and complex process; you will have to spend about 2 hours in the dental chair;
- Pain and discomfort may be present during the retreatment stages;
- You need to constantly be in touch with your treating dentist and visit him immediately if necessary.
If you are ready to monitor the situation throughout the entire period and respond to every nuance, the doctor will probably agree to try to correct the error, but in 20-30% of cases his actions will still not be effective (due to factors beyond his control). Repeated therapy is often not covered by compulsory medical insurance, and you will most likely have to pay for the manipulations out of your own pocket. This is the reason why sometimes doctors do not offer retreatment, insisting on extraction straight away.
Surgical removal
There are three types of operations that are used in such cases:
- Cystectomy is a tooth-preserving procedure in which the tumor and the mobile part of the root around it are removed. It is performed on both the lower and upper jaws.
- Cystotomy is also an organ-preserving procedure, in which only the fibrous wall is excised and the contents flow out.
- Hemisection - before removal, an examination is carried out, according to the results of which part of the crown is also excised. It is used only in case of a very grown tumor, if it is not possible to preserve the bone around it.
In severe and advanced cases, the tooth is removed along with the purulent cavity.
There is also a treatment method for treating cystic formations and root canals with a laser.
Treat or pull out a tooth
When the question arises: “Is it possible to somehow cure a dental cyst or should it be removed,” you need to consider several aspects:
- duration of therapy - in the case of medications it is 3-4 months, while surgical procedures take a maximum of 3-4 visits to the dentist;
- tolerability of treatment by the patient - there are situations when it does not work (in 30%);
- if the tooth is severely damaged, it will have to be extradited, at least partially.
There are many high-quality and beautiful implants on the modern market, but doctors try to preserve the dentition, resorting to removing elements only in extreme cases. In addition, implanted crowns are significantly more expensive and may not take root.
When is surgery necessary?
Whenever possible, dentists try to preserve as much tissue as possible, but there are also direct indications for which treatment can only be surgical:
- the presence of a pin and the risk of fracture when removing the structure;
- obstruction of root canals;
- frequent tumor suppuration during attempts at therapeutic intervention;
- the presence of a bridge that rests on the causative tooth (then the crown will still have to be redone and reinstalled);
- root perforation.

Removal is also indicated if the dental cyst looks like a tumor with severe symptoms - whether it is treated or not is decided by the doctor.
Complications of a cyst on the root of a tooth
If the cyst was detected too late, complications cannot be ruled out. The following scenarios are possible:
- deformation of the dentition, which is fraught with the installation of removable orthodontic appliances to correct the situation;
- purulent inflammation that develops into abscesses and fistulas;
- pulp destruction;
- damage to healthy teeth;
- blood poisoning and further transfusion.
The only way to avoid complications is timely detection of the disease, so it is extremely important to visit the dentist at least once a year, even if there are no obvious reasons for this.
Why is a cyst under a tooth dangerous and its consequences?
Possible complications:
- root destruction with subsequent tooth loss;
- periostitis - inflammation of the periosteum;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw bone - a growing cyst provokes purulent-necrotic processes that lead to destruction of bone tissue;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes located near the affected area;
- chronic sinusitis (may appear when a purulent sac grows into the maxillary sinus);
- spontaneous fracture of the jaw - occurs when the dental cyst enlarges excessively;
- the appearance of phlegmon - diffuse acute purulent inflammation.
In the worst cases, death is possible. When the contents of the cavity enter the bloodstream, sepsis develops - blood poisoning. In addition, a cyst from a benign tumor can degenerate into a cancerous one.
Formation of a cyst on the root of a tooth
Is it possible to get rid of a cyst without visiting a doctor?
Dental treatment has long ceased to cause severe pain, which has become possible thanks to the development of medical technology, but many people still do not like the hassle of going to the dentist, delaying the visit until the last minute.
A person who notices a cyst often tries to get rid of it with the help of strong antibiotics, hoping that the drugs will eliminate pathogens and stop the inflammatory process. However, none of the most modern medications will change the situation for the better if you do not get rid of the infected tissue, treat the root canals with an antiseptic and do not seal them thoroughly. Yes, antibiotics are also needed, but they play the role of an auxiliary, not a primary remedy.
All other traditional methods of treatment (applying lotions, rinsing with various solutions, using homeopathy) bring temporary relief and do not solve the problem. The pain may subside, and the cyst may even decrease slightly for a while, but the inflammatory process will continue to progress.
An abscess is quite insidious because it can develop over a long period of time without any symptoms at all. Dentistry knows many examples when a cyst grew to enormous sizes, turning into a pus-filled sac 6 cm in diameter. In such advanced cases, saving the tooth becomes extremely problematic.
How does the disease develop?
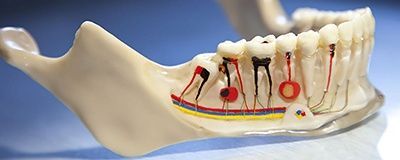
The process begins with periodontitis, when the tissue located between the jaw bone and the tooth root becomes inflamed. As a result, the tissues located around the root begin to grow abnormally. Initially, the size of the neoplasm does not exceed five millimeters (it is called a granuloma). Growing and enlarging, it becomes covered with a membrane and transforms into a cyst.
There are cases when the cyst grows so much that it eats away the bone around the tooth. With the next exacerbation of inflammation, it opens, forming a channel to the outside through the gum mucosa. Such a channel is called a fistula or fistula tract.
It is worth noting once again the insidiousness of this disease, which not only negatively affects the condition of the roots of the teeth, but also affects the general condition of a person. At the initial stage, the pathology develops almost imperceptibly and can only be detected during a visit to the dentist. Pronounced symptoms appear in the later stages of the disease as a result of tumor growth and destruction of bone tissue.
The main danger of a cyst is the fact that, by corroding the bone, it deprives the patient of the opportunity to install an implant in place of a lost tooth without complex manipulations.
Prevention measures
To avoid cyst formation, you need to:
- brush your teeth twice a day, or better after every meal. If this is not possible, then it is worth purchasing an irrigator that will allow you to rinse the mouth;
- once a year take a photo of the jaws and maxillary sinuses;
- correct any dental disorders at an early stage, preventing their development;
- try not to injure the jaw;
- Visit the dentist twice a year to examine the condition of your teeth and gums.
What will happen if left untreated?
Ignoring the symptoms of the disease leads to dangerous consequences for health. Thus, the patient may encounter:
- destruction of roots, their strong loosening;
- jaw fracture;
- tumor formation;
- purulent abscess;
- periostat;
- osteomyelitis.
The disease can cause the development of sepsis. This is a very serious condition in which the infection enters the blood and quickly spreads throughout the body.
Choosing a clinic for cyst treatment
A large number of hospitals and dental offices have now opened, but not all of them provide truly high-quality services: situations where people, having parted with money for treatment, not only did not get rid of the disease, but ended up with an even bigger problem, are, unfortunately, not uncommon .
To avoid mistakes, you should try to find out the following information before your visit:
- how long has the dentist been practicing, does he have enough experience to perform surgical interventions;
- The clinic also has dental microscopes in its arsenal, which allow us to examine the affected area in as much detail as possible and efficiently fill the canal.
Choosing a professional doctor is the key to quality treatment the first time.
Traditional methods of treating cysts
It is necessary to understand that a cyst is not just inflamed tissue in which you can overcome the inflammation and everything will heal on its own. A cyst is a formation that arises from tissues that are not in the place where they are supposed to be. Any anti-inflammatory drugs (or traditional methods) can relieve an exacerbation, but it is impossible to remove foreign tissue. In addition, active treatment with traditional methods can lead to a “blurred” picture of the disease and difficulty in diagnosing and choosing the optimal treatment tactics.