When breastfeeding, mothers often face a variety of problems. It is simply impossible to prepare for all unpleasant surprises and know what measures to take in a given situation. To the unknown, you can add a woman’s unique ability to prepare for the worst and beat herself up with or without reason.
For example, when breastfeeding hurts and the temperature rises during breastfeeding, a nursing mother often panics. If you're experiencing these two common symptoms, we urge you to stay calm and tell you what it might mean.
The percentage of mothers for whom breastfeeding was immediately established and was not accompanied by any problems is not too large. The reality of motherhood is that completely unexpected symptoms can appear on any day. The most common include discomfort and even pain in the chest area and fever.
The wrong tactics of behavior in this case may be to ignore poor health. You should not tolerate these signals from the body: it would be more correct to understand the reasons and take the necessary measures. You will find out what two common symptoms mean, why they often appear together and whether they can harm the baby.
Cyclic mastodynia
Growing up is a difficult period for a girl, when her body is rebuilt, turning from a child’s to an adult’s. Strong hormonal surges affect growth, coordination, even character. Due to an increase in the concentration of progesterone and estrogen, active growth of the mammary glands begins. Their ducts lengthen and branch, glandular tissue grows, and a fatty layer accumulates.
The nerve fibers in the glands grow more slowly and often do not keep up with the growth of the gland, which forces them to be in a tense, stretched state, and causes discomfort to the owner. During adolescence, girls often begin to experience pain in their breasts and nipples; the sensations can be aching, pulling, or burning. In this case, the body temperature can rise to low-grade fever and reach 37.0-37.5 °C. Sometimes nausea and vomiting are added. These unpleasant sensations are especially pronounced a few days before the onset of menstruation.
Unfortunately, there is no effective treatment for this condition, as it is normal and necessary for a girl's development. In severe cases, doctors recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and painkillers to relieve symptoms. Typically, the manifestations of cyclic mastodynia stop or decrease to insignificant by the age of 15-18 years. But sometimes symptoms can return during pregnancy or menopause.
Prevention
To prevent milk from stagnating in the milk lobules, you need to follow some rules.
- Wear comfortable underwear that is not tight or stiff.
- Take care of your breasts, starting from pregnancy, harden them by washing them with cool (but not cold!) water, wiping them with a rough towel. Before breastfeeding, perform hygiene procedures with your breasts, wash your hands, and do the same after feeding your baby.
- Don't expect the cracks to go away on their own. Now there is a large selection of ointments and gels that will cure this ailment in a short time.
- Attach your baby to the breast correctly; in the first month of his life, let's suckle on demand, so that we can then build a routine and improve the flow of milk.
- Try not to be in a draft; during breastfeeding, women's breasts are especially sensitive and can easily get cold.

If you follow these simple rules, then you will not learn from your own experience what lactostasis and mastitis are!
Lactostasis
You can often hear complaints from nursing mothers that their breasts hurt and their temperature has risen. Lactostasis, that is, stagnation of milk, is a very common phenomenon, especially in women who have given birth for the first time. As a rule, this leads to:
- incorrect or too infrequent attachment of the baby
- wearing a tight bra
- traumatic compression of the chest during sleep
In rare cases, physiological characteristics are to blame - narrowing of the milk ducts, high density of mother's milk, or sluggish sucking of the baby.
If a nursing mother has a sore breast, you should gently massage it, especially the lobes where there is tension or hardening, and try to express the milk as much as possible manually, using a breast pump or by properly attaching the baby. Advanced lactostasis, if an infection enters the chest, can develop into lactation mastitis, a much more serious disease.

There is no better treatment than prevention
Unpleasant symptoms such as high fever and chest pain during breastfeeding are always easier to prevent than to look for their cause and treat. By following a few simple recommendations, you will avoid a number of problems that so often attack mothers. Everyone knows the truth that prevention is the best treatment, and for mothers it is of paramount importance. So, in order to avoid chest discomfort combined with elevated temperature, adhere to the following principles:
- It is very useful for pregnant women to harden the skin of their nipples. To do this, give your breasts a break from tight underwear as often as possible, rinse your mammary glands with cool water and dry them with a fairly rough towel.
- The optimal feeding regime will be according to the baby's demand. Frequent feeding of the baby to the breast can guarantee the absence of lactostasis and all the ensuing consequences. Sometimes it makes sense to pump extra milk.
- Learn the correct feeding technique, remember to change positions and make sure your little one is latching correctly. If you doubt your own knowledge or skills, we advise you to contact a breastfeeding specialist - this is becoming increasingly popular and saves many mothers.
Always visit your doctor promptly and take all necessary tests. If you have any disease, such a responsible approach will help to detect the problem in time.
Lactation mastitis
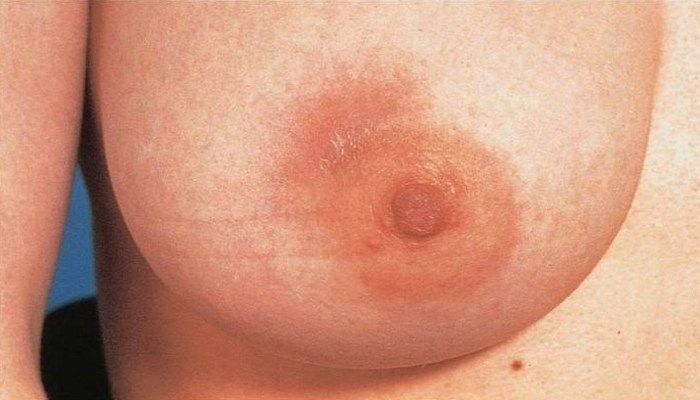
Since the appearance of small cracks in the nipples is almost inevitable during feeding, it is recommended to pay increased attention to breast hygiene. If a bacterial infection gets inside through a crack, breast milk will serve as an ideal environment for its development and spread. The signs will be:
- a sharp increase in temperature (with lactostasis it usually stays within 37-38 degrees, in rare cases up to 39, and with mastitis it can exceed 40 degrees)
- redness of the skin of the chest
- edema
- strong pain
Mastitis is characterized by local damage to the gland, so it should be suspected when one breast hurts and the temperature has risen to 37 °C.
Treatment of mastitis must begin as early as possible, since the infection develops very quickly. If you suspect mastitis, you should never give milk to your baby, but it must be expressed. In addition, it is necessary to start antibacterial therapy. It is better to immediately consult a doctor for timely selection of the drug and its dosage. Advanced mastitis can lead to the formation of an abscess and require surgical intervention.
Treatment and medications
The basis for the treatment of lactostasis and mastitis is regular breastfeeding, if permitted by the doctor, as well as the procedure of complete expression using a breast pump.
Recommendations:
- In the early stages of the disease with breastfeeding, after consultation with a specialist, the most painful mammary gland should be given to the baby first.
- In order for milk flow to increase and spasms to not occur, it is recommended to drop 4 drops of Oxytocin on the tongue before feeding.
- Before feeding, you can take a warm shower and perform a light massage of the mammary glands - in a circular motion towards the nipple.
- After feeding, the remaining milk is expressed until a feeling of lightness is formed in the mammary glands. Then you can apply an ice pack wrapped in a towel to your chest for a quarter of an hour.
- This procedure must be repeated every 2 hours without breaks, even at night.
- You should also position the baby correctly to the breast, so that his lower lip is on the hard part of the nipple.
With normal lactostasis, this treatment may be quite sufficient. For mastitis, additional medications are needed.

If the temperature is above 38 degrees, then the doctor will prescribe medications that lower it, containing Paracetamol or Ibuprofen.
If wounds are observed on the nipples, then it is possible to use local therapy, for example, Purelan-100, Bepanten and others.
For more serious manifestations of mastitis, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
Mastitis
Similar to lactation mastitis in breastfeeding women, inflammation can appear on the breasts of women of any age. The infection can penetrate through damaged skin, wounds, cracks, and tears. In the vast majority of cases, the causative agent of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. Mastitis should be suspected even if the temperature is 38 °C and the chest hurts. And even more so if:
- the temperature jumped sharply to high values (39-41°C)
- swelling appeared on the chest
- redness
- there is a burning sensation and itching
- strong pain
As a rule, one mammary gland, left or right, is affected. The temperature will help determine the location of the lesion; the chest literally “bursts with heat” in the affected area, the touch is painful. There may be discharge from the nipples that is sulfurous or purulent.
If you suspect mastitis, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible; self-medication can lead to serious consequences. Up to removal of the affected lobe of the breast or death as a result of developing sepsis (bacterial blood poisoning). Antibacterial and detoxification therapy is mandatory; it is important not to self-medicate or rely on untested methods.
Before menstruation
The situation begins to noticeably worsen before the onset of menstruation. During this period, the highest concentration of prolactin is observed in the blood, and the end sections of the mammary glands expand as much as possible. Pain in the chest becomes unbearable, and in severe cases there is an increase in temperature. In some cases, the patient begins to experience nausea and a burning sensation in the chest, and she completely loses her ability to work.
The clinical picture usually improves markedly after the onset of menstruation. Unfortunately, there is no effective therapy for this disease that can relieve all symptoms. The condition can be alleviated by the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are often used for the symptomatic treatment of headaches and toothaches. However, it should be noted that their impact is not sufficiently expressed. As a rule, in many girls the disease goes away on its own as soon as a clear menstrual cycle is established.
In what cases does the temperature still rise and the chest hurt?
Breast injuries
Sometimes, although not often, the mammary gland can be injured. For example, as a result of an accident or traffic accident. In this case, after the injury, the chest hurts, the temperature rises, and lumps can be felt in the chest in places where the fatty tissue of the breast is damaged. Over time, necrosis of this adipose tissue occurs. In this case, the affected area hurts greatly, and intense itching or burning may be felt.
General intoxication of the body occurs, nausea or vomiting, general malaise, and loss of appetite may be present. In place of the dead tissue, scar tissue forms, and the mammary gland may change shape, a lump may appear, or the nipple may become retracted. These symptoms resemble signs of breast cancer, so consultation with a doctor is necessary to rule out breast cancer.

Breast tuberculosis
This rather rare disease occurs, most often as a secondary lesion in women who have suffered from pulmonary tuberculosis for a long time. You should be wary of:
- change in breast shape
- appearance of skin ulcers
- aching or bursting pain
- pulmonary symptoms (cough, sputum discharge, chest pain, shortness of breath).
The diagnosis must be confirmed using chest x-ray and biopsy. Treatment is prescribed only by a doctor, and it includes long-term (from a year or more) complex therapy, supportive therapy and, if possible, medications that alleviate symptoms.
Aromatherapy can help reduce fever and relieve pain
Aromatherapy is used for various diseases to relieve stress, feel peace and pleasure. The method is ancient. Came from Eastern medical practices.
It cannot be considered as a primary means of healing. Prior consultation is required due to the risk of allergic reactions to essential oils.
Lavender oil is used to relieve pain. Inhaling the vapors of this oil helps eliminate breast swelling and normalizes hormonal balance. Relaxation sets in. The central nervous system calms down.
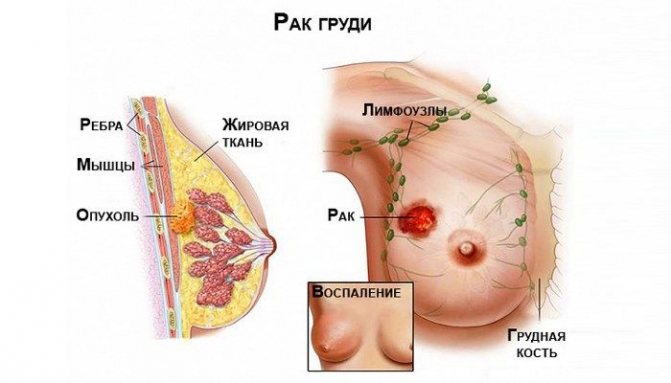
Breast cancer
In recent decades, very sad statistics have emerged in our country regarding the incidence of breast cancer in women. Often women do not pay attention to disturbing symptoms until it is too late. You should see a doctor if:
- chest hurts
- temperature 37-38 °C
- the shape of the breast has changed, the left and right mammary glands are asymmetrical
- nipple retracted
- a lump can be felt inside or a lump sticks out outside.
In this case, there may be no pain at all, or there may be a variety of pain sensations - shooting, aching, burning, stabbing pain.
What to do and what to take if there is chest discomfort and slight fever
When minimal symptoms appear, you need to listen carefully to this condition. If it doesn't change, you can take an over-the-counter analgesic. This is the case if the woman is not carrying a child and is not breastfeeding.
Otherwise, consultation with a specialist is required. If you feel unwell for a long time (more than two weeks), consult a therapist.
There is no point in lowering the temperature below 38 degrees. If this threshold is exceeded, medical attention is required. Pregnant women are often advised to take one paracetamol tablet.
Recovery must begin with a correct diagnosis. At the initial appointment, provide all the required information about yourself, explain how long ago the problem began to bother you.
After the initial appointment, the therapist will refer the patient to a specialist doctor, who will prescribe diagnostic procedures and direct treatment based on the data obtained during the examination.