RDW standards
Normally, the relative spread width Er RDW-SD is constant and amounts to 37 – 47 fl.
A pathological deviation in the size of erythrocytes from the norm or anisocytosis is noted when RDW-SD values are more than 60 fL. On the histogram, this means that the value of the relative width of the volume distribution is increased if the spread of erythrocytes in the sizes of the smallest and largest Er on a straight line drawn along the OY axis at the level of 20% is greater than 60 fl.
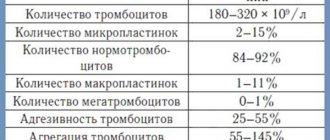
Norms for the coefficient of variation of erythrocytes RDW-CV - volume distribution width, table.
The normal distribution width of erythrocyte cells changes during pregnancy and is by trimester:
- in the first – 11.7 – 14.9%;
- in the second – 12.3 – 14.7%;
- in the third – 11.4 – 16.6%.
The RDW-SD indicator is characterized by increased sensitivity to the appearance of microcytes. RDW-CV exhibits particular sensitivity to anisocytosis, the occurrence of deviations in the size of Er blood.
The level of anisocytosis of a blood sample reflects the heterogeneity (variability) of red blood cells in size.
There are different degrees of anisocytosis:
- The first – 30 – 50% Er deviate in size from the norm.
- The second – 50 – 70% of transformed cells.
- Third – more than 70% of Er deviate from the standard.
Analysis transcript
Red blood cell RDW indices obtained when processing a sample with hematological automatic analyzers are necessary for early diagnosis:
- deficiency of Fe, folate, vitamin B12;
- types of anemia;
- morphology of erythrocytes - structural features and sizes;
- myeloproliferative diseases affecting the bone marrow.
Decoding of the analysis data is carried out taking into account all erythrocyte indices. When interpreting the distribution width Er, the MCV value is of particular importance.
Raising RDW
The index of erythrocyte volume distribution is increased in anemia caused by B12 deficiency, and this means that the number of macroerythrocytes in the blood is increased, and the histogram is shifted to the right.
If the volume distribution width is increased, but the erythrocyte index such as MCV is increased, we can assume:
- hemolytic anemia;
- B12 deficiency;
- cold agglutination is a disease associated with the appearance in the blood of antibodies that glue red blood cells to each other in response to the action of cold.
Increased RDW (wide distribution of erythrocytes) and increased MCV in liver diseases, anemia caused by lack of vitamin B9.
An increase in the distribution width with a reduced index of average erythrocyte volume is observed in diseases:
- thalassemia;
- iron deficiency.
An increase in the Er spread width with normal MCV values may indicate:
- for a lack of vitamins B9 and B12;
- on the development of iron deficiency.
With increased values of the distribution width in the blood, accelerated destruction of red blood cells occurs, which is why the liver and spleen work at the limit of their capabilities. This leads to disruption of their functions, which manifests itself:
- the appearance of excess bilirubin;
- high Fe content;
- enlarged spleen.
Lower RDW
A decrease in the volume distribution width of Er means that there are cells of similar sizes in the blood. The boundaries of the spread of the RDW-CV value are narrowed in the following cases:
- oncological diseases - myeloma, leukemia;
- hemolysis - destruction of red blood cells;
- injuries with significant blood loss;
- deficiency of iron, B vitamins.
When decreasing RDW-
CVs up to 10.2% suggest macrocytic or microcytic anemia. In these forms of the disease, red blood cells are predominantly increased or decreased in size compared to the norm.
Microcytic anemias include iron deficiency, iron saturation, and iron redistribution. Macrocytic anemia develops with hypothyroidism, pregnancy, liver disease, hematopoietic disorders in the bone marrow, lack of copper, vitamins B12, and folic acid.
The most accessible and highly effective diagnostic method in modern medicine is a clinical blood test. Such a study is prescribed in almost all cases when a person seeks medical help for various ailments. Any changes in the blood composition allow a specialist to suspect the development of various diseases at an early stage of their development. In addition, with the help of analysis, it is possible to identify the causes of the appearance of one or another symptom. During a blood test, the laboratory evaluates the parameters of absolutely all blood elements, of which there are more than 20 today. Among them is an important RDW indicator in a blood test - the erythrocyte index
. The abbreviation stands for “width of distribution of red blood cells by volume.”
Reduced RDW: pathology and norm
In a healthy person, red blood cells have the same shape, density and color . In cases of deviations, especially in autoimmune diseases and oncology, a malfunction occurs at the microcellular level when newly formed cells do not receive enough of certain components, and in fact are not able to perform their functions. This leads to anemia, a pathological condition in which the body does not receive the required amount of oxygen, that is, the metabolic function of red blood cells is disrupted.
The erythrocyte distribution index is determined during a general blood test. In some cases, if a specific disease is suspected, only this index can be determined in the analysis. In most cases, the RDW is determined together with the average MCV volume, since these indices (volume and quantity) are interrelated and help determine the type of anemia. The fact is that for a complete assessment of the condition of red blood cells, not only their shape is important, but also the quantity in the blood. And if elevated values occur with a frequency of 1 in 10,000 people, then decreased values occur extremely rarely and always indicate serious health problems.
A blood test to determine RDW can be performed both routinely (during medical examinations) and according to indications when there are suspicions of abnormalities in hematopoietic function. The analysis is mandatory before surgery, in childhood and during pregnancy.
Why is RDW needed?
As mentioned above, this index allows you to evaluate the qualitative composition of red blood cells, taking into account their dimensions.
But what does this give? The fact is that red blood cells are similar to each other, like twin brothers , which allows them to replace each other at the right time or stick together into blastulas. If cells increase in size, their need for nutrition also increases, and accordingly their life expectancy is short. This in turn affects the overall level of red blood cells in the blood and human health.
The more cells die, the more bilirubin and iron are released, which in turn places an increased burden on the liver, which will malfunction and cannot cope with the processing of these substances.
The RDW index is directly related to anisocytosis, a pathological process in which the shape of red blood cells changes, which affects their volume and size. Anisocytosis is a complex chemical process that affects all blood cells.
We invite you to watch a video on the topic
How is it determined?
The erythrocyte distribution index is calculated as a percentage, the norm of which varies from 11.5 to 14.8.
It is determined using a mathematical formula, in the form of the ratio of modified red blood cells exceeding the maximum permissible volumes to the total mass of red blood cells.
Today, laboratories use computer technology to determine the percentage of deviation from the norm without manual calculations. The output data is presented in the form of a histogram , which displays a curve indicating possible modifications of red blood cells.
What do the results depend on?
Norms are determined depending on age, gender and the presence of physiological processes occurring in the body. For children in the first year of life, the norm is considered to be 11.5-18.7%. After a year, the digital values tend to the generally accepted norm - 11.5-14.5%. In women, the upper limit may shift to 15.5%, which is explained by frequent changes in hormonal levels: pregnancy, breastfeeding, taking hormonal contraceptives, menopause.
Blood is taken in the morning (before 9 am) on an empty stomach. It is important that before blood sampling the person does not take any medications and is in a balanced state.
Index Variations
For a more detailed in-depth study of the erythrocyte distribution index, two values are considered :
- RDW-SD - determines the standard deviation from the norm, expressed in femtoliters. The indicator is in no way related to MCV, since it shows the quantitative value of the difference between the largest and smallest cells.
- RDW-SV - shows how much the volume of red blood cells differs from the average. It is defined as the percentage of all deformed cells to the total red blood cell mass.
How to properly prepare and take a general blood test
A general blood test is a basic study that is carried out for the following indications:
- prevention, with the aim of early detection of probable pathologies;
- diagnosis of diseases;
- control of therapy;
- before surgical interventions;
- monitoring the progress of pregnancy.
A general blood test includes counting the number of blood cells (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets), determining hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit level, erythrocyte and platelet indices, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. A complete blood test includes a leukocyte count.
For preventive purposes, a general blood test should be taken annually. Persons from risk groups (with a family history, chronic diseases, occupational hazards, during pregnancy, etc.) may require this study to be performed more frequently - 2 times a year, 1 time every 3 months, and sometimes more often.
Blood for a detailed general analysis, which includes the determination of erythrocyte indices, including the RDW indicator, is usually taken from a vein. In some cases, capillary blood may be collected from a finger. Blood is donated in the morning on an empty stomach, at least eight hours after the last meal. Before donating blood, you should avoid mental and physical stress and stop smoking. It is advisable not to carry out medical procedures the day before.
Anisocytosis
The process of transformation of the volume of red blood cells is called anisocytosis. To identify the indicator of erythrocyte anisocytosis, it is necessary to take blood from a finger or from a vein, and then diagnose it in the laboratory using RDW. With the help of modern devices, it becomes possible to quickly and most accurately test blood.
How can you determine if RDW is elevated in a blood test?

In what cases is analysis necessary?
A blood test for RDW is carried out in cases where a person undergoes a general test, prescribed routinely or for diagnosing pathologies of various kinds, as well as before surgical interventions. The specialist may also suggest donating blood to determine this indicator if the patient is suspected of anemia.
Such an examination is primarily intended for differential diagnosis of types of anemia and for monitoring their therapy. Sometimes RDW in a blood test is increased in a child.
Thanks to modern analyzers, you can quickly and efficiently conduct a blood test, assess the condition of red blood cells and determine the characteristics of subsequent treatment. The number of red blood cells of various sizes per microliter of blood is counted. Using analyzers, the average erythrocyte volume is calculated and the degree of deviation of this parameter from the normal value is established. The result is displayed in the form of a histogram. There is a possibility of getting a false positive result when the RDW level in the blood test is elevated, but the person is healthy. This is due to the large number of modified red blood cells in the blood, which are called macrocytes. To increase the reliability of the analysis, a study of the Price-Jones curve is required.
The most accurate result of a study on RDW SD with standard deviation and RDW CV (with coefficient of variation) is a manual calculation, but this method is labor-intensive and time-consuming, as a result of which it is now almost never used.
If all indicators correspond to the norm values, the result is negative. If the blood test shows an elevated RDW, the result will be positive. Most often, in such a situation, a repeat analysis is needed, the purpose of which is to determine the exact cause of the changes, since after one blood draw the diagnosis cannot be considered final. This is due to the fact that the indicator can increase immediately after a blood transfusion or surgery. Therefore, if the result is positive, a repeat blood donation with further analysis of the histogram is necessary in any case. Red blood cells are capable of being distributed and modified quite often and quickly.
Blood is taken from a vein in the elbow area on an empty stomach. In small children and infants it is most often taken from the finger.
Ways to reduce RWD
First of all, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease - the cause of increased RDW values. Below are additional options that can help you improve your health and reduce your RDW.
Balanced diet
Eating a healthy and balanced diet helps prevent nutritional deficiencies. It is especially important that the diet contains the recommended amounts of iron, folic acid and vitamin B12. [R, R, R] Correcting nutritional deficiencies can improve blood cell production and lower RDW values.
Reduce alcohol consumption
Reducing alcohol consumption may help reduce damage to red blood cells. [R,R] In addition, alcohol also reduces the absorption of nutrients such as vitamin B12 and folic acid, which are essential for the production of red blood cells. [r, r]
More physical activity
People who do little or no physical activity show higher levels of RDW. [r, r]
Exercise, including light intensity exercise, has been shown in research to improve RDW scores. [r, r, r]
In a study of more than 8,000 people, as the amount of exercise time per week increased, the risk of showing increased levels of RDW decreased by 11%. [R]
Quit smoking
Smoking increases oxidative stress. Higher RDWs are identified in smokers and are associated with the number of cigarettes smoked per day as well as the duration of smoking. [R]
Treatment
If the erythrocyte distribution index is low or above normal, the first step should be to treat the underlying disease. In some situations, therapy is limited only to:
- changing your usual diet;
- refusal to consume alcohol;
- introducing foods fortified with iron and other micronutrients into the menu;
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes.
In other circumstances, therapy will be purely individual:
- when cancerous tumors are detected, they turn to medical intervention, radiation treatment and chemotherapy;
- for gastrointestinal pathologies, drug tactics and diet therapy are used;
- myelodysplastic syndrome is eliminated through the use of physiotherapeutic procedures and other conservative methods.
Recovery is spoken of in such cases: improvement in well-being and complete absence of clinical signs, positive dynamics regarding changes in general blood test parameters.
When to retest
If too little blood sample was taken, or an error was made, the result may be a false positive or a false negative. Reasons for a false positive result in women may include heavy periods, uterine bleeding, or blood loss during childbirth.
If the RDW blood test differs slightly from the norm, an additional study is prescribed if the MCV is higher or lower than the normal level.
A repeat test is required if the erythrocyte index deviates from the norm by 2% or more. In this case, anemia or a malignant tumor may develop.
How to lower the level of RDV
To find out how to normalize this blood count, the specialist must refer the patient for additional examinations.
In any case, therapy should be carried out with an integrated approach, which consists of the use of certain medications and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Sometimes, if necessary, surgery may be prescribed
.
Thus, RDW is an important indicator that helps diagnose various pathological processes in the body. In addition, it allows you to determine the type of anemia.
Decreased and elevated levels
The situation in which RDW is increased, that is, we have more red blood cells than the required volume, is quite dangerous. The fact is that one of the main disadvantages of macrocytes is their shortened lifespan. This in itself is bad, since you need to somehow maintain the total number of red blood cells at normal levels.
But what is even more important is that the number of simultaneously disintegrating red cells increases and, as a result, the flow of released iron and bilirubin increases. This increased flow begins to tax the liver, which is now working in overdrive.
In addition, some of the macrocytes, due to their diameter, are not able to squeeze through the diameter of the capillaries and the spleen is involved in their disposal. The load on it leads to its increase in size, and the spleen begins to put pressure on the intestines and stomach. Surrounding tissues and organs may be damaged.
An increase in RDW values of more than 15% indicates the development of pathological conditions in the body. Most often, RDW is increased when:
- Combination with high MCV values with increased RDW – liver damage due to alcoholism, hemolytic anemia, megaloblastic anemia, vitamin A hypovitaminosis.
- Combination with low MCV values with increased RDW – low hemoglobin levels, iron deficiency conditions, the most initial manifestations of thalassemia.
- The combination with normal MCV values with increased RDW is a manifestation of iron deficiency anemia, a decrease in vitamin B12 and/or folic acid, which leads to macrocytic anemia.
A decrease in RDW values below 10.2% occurs in the presence of the following pathological processes in the body:
- Microcytic anemia.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Vitamin B6 deficiency.
- Blood loss.
- Impaired absorption of iron.
- Parasitic infestations.
With normal RDW values, accompanied by a decrease in MCV, they speak of:
- Frequent blood transfusions, in which there is a dissociation in the formation and presence of blood cells.
- Severe thalassemia.
- Hemorrhagic processes due to chronic blood loss, to which the human body does not respond at the onset of the disease with any external manifestations.
- Removal of the spleen due to traumatic injuries - in this case, a sharp redistribution of blood cells is observed, as well as a delay in the formation of blood elements due to the absence of one of the important hematopoietic organs.
- Malignant neoplasms in which the cellular growth of the blood system is inhibited.
- Conducted chemotherapy, where, as during chemotherapy treatment, suppression of the cellular elements of the blood system is observed.
- Development of myelodysplasia.
Important! Very often, the onset of various diseases is missed due to insufficient diagnosis.
A timely, complete, and most importantly competent study, first of all, of blood parameters will tell the doctor about many changes in the human body. This will not allow you to miss the onset of many diseases, even such as malignant neoplasms of various localizations.
Normal RDW values
Normal RDW values are the same for men and women. The range of normal RDW in adults is 11.5 – 15.5% , but may vary slightly depending on the reagents used by different laboratories.
In newborn children, normal RDW values are increased to 14.9 – 18.7% due to stress at birth and adjustment to life outside the mother. But as children grow older, their normal RDW values gradually approach those of adults.
At the same time, with age, red blood cells become more varied in size (volume), which leads to an increase in RDW. [R]
Norm of RDW indicators (CV and SD) in a blood test: examination and interpretation
A simple general analysis, well known to everyone, checks quite a lot of different indicators, so you can easily identify an increased or decreased indicator
All blood components are important for the normal functioning of the circulatory system, so they must be monitored all the time
It is important that there is a norm for the content of RDW indicators. What each content in a blood test means, the doctor must decipher and determine: this or that indicator is increased or decreased
Otherwise, it is necessary to urgently begin treatment, because the slightest disturbance may indicate signs of the disease.
The study will determine the level of RDW-SD and RDW-CV
Regardless of a person's age, the blood test for RDW should be approximately the same. There is a certain standard, so only minor deviations are allowed. As for the results directly, this norm ranges from 11% to 15%. If the result is slightly or even significantly elevated, you should immediately consult a doctor for additional examination and undergo the necessary treatment.
If the norm goes beyond the permissible values and the indicator is lowered, then this is also nothing good. It is better to see a doctor and get examined. But there is no need to worry prematurely, because there are quite a lot of people who live happily ever after with such results. This is explained solely by the individual characteristics of each person.
What is RDW and why is it analyzed?
RDW (Red cell Distribution Width) is an indicator of the dissimilarity of red blood cells in the blood. Ideally, they should all be the same, with an average diameter of 7.1–7.9 micrometers. A deviation in the smaller (microcytes) or larger (macrocytes and megalocytes) direction of more than 30% indicates possible diseases.
A blood test for RDW is performed during medical examination or before surgery. Chronic fatigue, fatigue, and drowsiness may also be a reason for referral to this study.
Deviation of the indicator from the norm
Together with other erythrocyte indicators, MCV calculation can help in the early detection of some processes leading to the development of anemia.
MCV is an important indicator in determining anemia
An MCV in the range of 80–100 fL characterizes the erythrocyte as a normocyte, below 80 fL as a microcyte, above 100 fL as a macrocyte. Thus, if the MCV value is below the normal range, then the anemia is considered microcytic, if higher - macrocytic. Normocytic anemia may also occur, in which the erythrocyte index is within the normal range.
Microcytic anemias:
- sideroblastic;
- iron deficiency;
- Thalassemia.
Anemia that may be accompanied by microcytosis:
- lead poisoning;
- disruption of porphyrin synthesis;
- hemoglobinopathies.
Normocytic anemias:
- hemolytic;
- aplastic;
- hemoglobinopathies;
- conditions after bleeding.
Anemia that may be accompanied by normocytosis:
regenerative phase of iron deficiency anemia.
Macrocytic and megaloblastic anemias:
- vitamin B12 deficiency;
- folic acid deficiency.
Anemia that may be accompanied by macrocytosis:
- hemolytic anemia;
- myelodysplastic syndromes;
- liver diseases.
Low MCV level
In some cases, the MCV level may be lowered. What does it mean? One reason is acute and chronic poisoning (for example, lead). Chronic kidney failure can also cause the index level to be too low. In this case, toxins and metabolic products that poison the blood are not excreted by the kidneys.
One of the reasons for low MCV levels is kidney failure
Long-term decreased iron levels in the body and anemia can cause low index levels. Hemoglobinopathy, which is a group of disorders characterized by changes in the structure of hemoglobin, can also cause low MCV levels.
The most common causes of microcytic anemia are iron deficiency (due to inadequate dietary intake, gastrointestinal bleeding, or heavy menstruation), thalassemia, sideroblastic anemia, or other chronic diseases.
High MCV level
There are many reasons why the average red blood cell volume may be elevated. One of them is liver disease, including cirrhosis. Often, a high red blood cell index is caused by alcohol abuse. After stopping its use, the indicator returns to normal values within 2–4 months.
High MCV levels may be due to alcohol abuse
Hypothyroidism can cause this biochemical reading to be too high. With this pathology, the thyroid gland is inactive and the level of its hormones is reduced.
Another pathology accompanied by increased MCV is bone marrow aplasia and reticulocytosis. The value of the index increases with myelofibrosis, a disease in which the bone marrow is replaced by fibrous tissue.
A transient increase in this indicator is observed in diabetic ketoacidosis. Some medications can also cause high levels of MCV. For example, a deviation from the norm in women when deciphering a blood test for MCV may be associated with the use of contraceptives.
RDW increased: association with diseases
Elevated RDW values may indicate, but do not diagnose or confirm, the following diseases: [p, p, p, p]
- Lack of iron in the body or vitamin deficiency
- Lack of B vitamins, including B12 and folic acid
- Anemia (various types, including sickle cell anemia)
- Inflammation
- Insomnia
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Blood loss due to hemorrhage (including surgery)
- Thalassemia
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- Cancer
- Alzheimer's disease
- Alcoholism
- and others.
However, RDW may still be at normal levels in people with leukemia , or with certain types of anemia (such as aplastic anemia ). Therefore, it is important to look not only at the RDW value, but also at the relationship with other markers. [R]
Preventive measures
What to do when the red blood cell distribution index is low?
A highly qualified doctor during a consultation will most likely ask the patient to take the test again, because the RDW indicator is almost never underestimated. Since this suggests that all cells are ideal in their parameters, but this cannot happen in principle
If the indicator is confirmed by repeated analysis, then a full examination of the body’s condition is carried out, paying special attention to oncological examinations
You can prevent a reduced RDW by following these simple rules:
The diet should be balanced, which includes plenty of fresh fruits, lean meats and vegetables. It is recommended to breathe fresh air as often as possible. An active lifestyle will help prevent a decrease in the RDW index
It is very important not to skip routine medical examinations, during which most often serious deviations from the norm are detected that have no external symptoms
As a result, we learned that the red blood cell distribution index reflects their dimensions relative to each other and makes it possible to learn about their biological value. A decrease in RDW is very rare, but if the erythrocyte distribution index is decreased, this means that various pathologies may be present.
The index is calculated based on the results of a general blood test, but can only be fully valid in conjunction with the MCV indicator, since they are closely interrelated.
Lower RDW
Situations where the RDW indicator is reduced are rare. A deviation from the norm to a lesser extent indicates the development of dangerous diseases and pathological processes in the body that require diagnosis and immediate treatment.
Why is this happening
The resulting value is below normal means that red blood cells lose their function due to some congenital and acquired diseases. The main reasons why a reduced CV occurs in a blood test:
- Profuse bleeding due to injuries or wounds. Bleeding in the uterine cavity or stomach poses a threat to health, and in some cases, life.
- Previous surgical interventions, during which resection of an internal organ was performed.
- Disturbances in metabolic processes, as a result of which food entering the body is poorly digested and remains in the stomach, where it ferments, thereby provoking a purulent process.
- Changes in hormonal levels - this factor is typical for women.
- Low concentration of vitamins and iron.
- Blood diseases characterized by the loss of red blood cells of their functions.
- Oncological neoplasms, mainly tumors of the lungs and brain.
- Pathologies of an autoimmune nature, as a result of which new red blood cells do not receive enough important components, which affects their parameters and functionality.
The cause of low RDW may be anemia - microcytic hypochromic anemia. In this pathological process, red blood cells have an irregular shape, differ in size and quickly die due to the fact that such blood cells do not represent biological value in the body.
If there is a suspicion that the test result was false positive, the blood will have to be taken again, carefully following the doctor’s recommendations. Factors such as smoking before taking the test, excessive psycho-emotional arousal, and eating food immediately before taking biological material can affect the result of the analysis.
Taking certain medications can also cause a false positive result. Therefore, if a patient is forced to constantly take medications for medical reasons, the laboratory assistant must be informed about this.
The erythrocyte distribution index RDW SD is decreased or increased in a child, normal in a blood test
A general blood test is a mandatory diagnostic procedure for children.
It allows you to get acquainted with the characteristics of erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets: their number, erythrocyte, leukocyte and platelet indices.
One of the parameters that UAC shows is RDW. Let's consider what this indicator means and whether you should worry if it is elevated or decreased in children.
RDW and its varieties
What is RDW? The abbreviation stands for Red Cell Distriburion Width. This is one of the general clinical blood test indices, indicating the distribution of red blood cells by volume. By deciphering the index readings, the laboratory technician identifies the presence of red blood cells, which vary in shape and size.
The task of red blood cells is to transport hemoglobin along with oxygen molecules. Successful functioning depends on the shape of the cell - a biconvex disk. The change in volume is called anisocytosis.
There are two varieties of RDW:
- rdw-cv - shows the severity of anisocytosis;
- rdv-sd - indicates the difference between the sizes of red blood cells.
RDW has a direct correlation with another UAC indicator - MCV. MCV index is the average volume of the red cell.
Purpose of the analysis
The erythrocyte index is included in the UAC. The attending physician can purposefully send a patient to donate blood if the following ailments are suspected:
- oncological pathologies;
- iron deficiency anemia;
- diabetes mellitus;
- liver damage.
Diagnosis of the erythrocyte count is indicated for the following symptoms:
- hereditary predisposition to thalassemia;
- lack of iron in the body;
- weakness, dizziness, hyperhidrosis and other signs of anemia;
- infectious diseases with a long course;
- profuse blood loss.
With pathologies of the form, blood cells cannot perform their main function - to carry oxygen to organs and remove waste products. RDW shows the percentage of red blood cells with a changed shape.
Normal indicators
What indicators are considered normal? The table provides information with a breakdown of the values of two types of index for children and adults:
| No. | Index | Meaning |
| 1 | RDW-SD | 39-46 femtoliters |
| 2 | RDW-CV | Adults - 10.9-15.6% |
| Children - 15-19.1% |
In some cases, additional diagnostics are required, since the value remains normal in some ailments:
- Spherocytosis. A hereditary pathology in which red blood cells are round rather than biconcave.
- Aplastic anemia. Stopping the growth and maturation of cells in the bone marrow. Without treatment, patients die within a few months.
- Some types of hemoglobinopathies. A congenital disorder of the structure of the hemoglobin protein, which causes pathology of red blood cells. This class of diseases includes sickle cell anemia and thalassemia.
What do increased readings mean?
The RDW index is elevated - what does this mean? An increase in the distribution of red blood cells by volume indicates various ailments of the circulatory system. To make a correct diagnosis you should always look at the MCV. The table shows the breakdown of analyzes when RDW is increased, depending on the MCV indicator:
| № | MCV increased | MCV is normal | MCV reduced |
| 1. | Liver damage due to alcohol abuse | The onset of iron deficiency anemia is a violation of hemoglobin synthesis due to a lack of iron in the body. | Iron-deficiency anemia |
| 2. | Hemolytic anemia - increased destruction of red blood cells | Macrocytic anemia | Thalassemia - decreased formation of polypeptide chains included in the structure of hemoglobin |
| 3. | Megaloblastic anemia due to deficiency of cyanocobalamine and folic acid. It is characterized by the presence of immature red blood cells - megaloblasts - in the hematopoietic brain. | — | — |
| 4. | Retinol hypovitaminosis | — | — |
What does it mean if the indicator is reduced?
What does it mean when RDW is below normal? As with an upgrade, if it's downgraded you should look at the MCV value:
- low MCV - pathology of the liver or spleen;
- high MCV - cancer lesions with metastases to the bone marrow.
If the index is down slightly, then you probably don't need to worry. It can fluctuate due to hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, after drinking alcohol or fatty foods. In infants the rate is slightly lower. This is normal and goes away after a few weeks; parents should not worry about their child.
Decoding
Anisocytosis of red blood cells is determined by a hematology analyzer, which produces a histogram plotting the number of RBCs of different volumes in the sample.
If the analysis is carried out manually, the value of the red blood cell coefficients of variation is calculated from the histogram curve and formula. Manual calculation of parameters is rarely used, because does not provide the necessary accuracy of the result.
A positive test result is when the rate of erythrocyte anisocytosis exceeds the norm. If the result is within the normal range, the test will be negative.
The RDW designation characterizes the heterogeneity of red blood cells:
- RDW-CV in a blood test is a relative value measured as a percentage (%);
- RDW-SD is an absolute parameter measured in volume units of femtoliters (fl) or µm3.
Comparison of the scatter of RBC volumes in the sample is carried out with normal values of 80-100 fl.
Relative index is a value that reflects the distribution of red blood cells, showing by what percentage the red blood cell volumes differ from the average volume.
The value of the absolute indicator indicates how many femtoliters the volumes of red blood cells differ. The calculation is done according to the histogram graph.
The level of relative anisocytosis depends on the value of the MCV parameter (mean blood cell volume). The calculated value of the relative indicator of erythrocyte anisocytosis is obtained by multiplying 100% by the ratio of the standard coefficient to MCV.
The RDW-SD parameter in a blood test allows you to determine how many femtoliters the smallest and largest red blood cells differ from medium-sized red cells.
Normal values
The values of the distribution width of erythrocytes according to norms do not depend on gender. They are the same for an adult of any gender. With age, normal coefficient values do not change.
If heterogeneity does not exceed the norm, it means that the red blood cells are approximately the same size. The norm for absolute anisocytosis in adults is 37-47 fl.
Normal RDW levels for women and men are 11.5%-14.5%.
In women during pregnancy, the normal value of the parameter changes by trimester (%):
- first trimester - 11.7-14.9;
- second trimester - 12.3-14.7;
- third trimester - 11.4-16.6.
In children, the normal level varies. The first 6 months after birth, RDW values are higher than the adult norm. Gradually they decrease.
RDW standards for children (%):
- up to 6 months - 14.9-18.7;
- after six months - 11.6-14.8.
The result of the calculation of relative anisocytosis, which the patient receives in the analysis, is often elevated or normal. A decreased RDW-CV most likely indicates an error.
If the anisocytosis of red blood cells is slightly higher than normal, most often the deviation is random. This value becomes clinically significant for diagnosis when it exceeds 60 fl.
A decrease in the absolute coefficient of anisocytosis has no significance for diagnosis.
Increased level
Red blood cells are heterogeneous in size and hemoglobin saturation. If anisocytosis is higher than normal, it means that there are blood cells in the bloodstream that are different in volume from the normal range.
Normally, each cell goes through a life course, during which its volume changes. Cells of different sizes are simultaneously present in the blood:
- microcytes, characterized by their small sizes, not exceeding 6 microns;
- normocytes corresponding to normal sizes, in the range of 6-8 microns;
- macrocytes, characterized by large sizes exceeding 8 microns;
- megalocytes, with a diameter > 12 microns.
Normal human RBCs fall within the normocyte range on average. An increased value of heterogeneity is possible with the appearance of microcytes and megalocytes.
The heterogeneity of erythrocytes is characterized by the degree of anisocytosis:
- The first degree corresponds to 27-50% of defective cells.
- Anisocytosis of the second degree is characterized by 55-70% of modified blood cells.
- The third degree of anisocytosis is characterized by the presence of more than 75% of such cells. Their sizes deviate from the norm.
- With the fourth degree of anisocytosis, all 100% of the cells are defective.
If the relative width of the distribution of red blood cells by volume is increased, it means that more than 50% of the cells deviate from the norm.
Relative coefficients of erythrocyte heterogeneity may increase when:
- leukocytosis with a sharp increase in the number of leukocytes;
- lack of nutrients necessary for hematopoietic processes (iron, B vitamins);
- microcytic anemia;
- myelodysplastic syndrome;
- hemolytic crisis;
- malignant tumors that metastasize to the bone marrow;
- RBC agglutination;
- poisoning with heavy metals (lead);
- Alzheimer's disease.
The anisotropy coefficient of erythrocytes increases in vascular diseases. Increased RDW in intoxication caused by alcohol abuse.
If the blood was tested after surgery, severe bleeding, heterogeneity above normal may also be noted. In such a situation, the result exceeds the acceptable standard deviations as a result of the increased production of juvenile cell species.
Symptoms of increased RDW
In a situation where deviations in the functioning of the circulatory system exceed a minor degree, the body begins to send alarm signals in various ways.
The following signs may indicate that rdw is elevated:
- Strong and systematic increase in temperature.
- Profuse sweating.
- General fatigue, loss of activity, drowsiness.
- A sharp, without a fundamental change in mood.
- Occasionally, yellowing of the skin occurs.
If you notice the above symptoms, you should not self-medicate or hope that it will “go away on its own.” After all, taking a general blood test at a clinic or the nearest laboratory and asking a therapist for a transcript will not be difficult. Especially in comparison with the possible consequences if anisocytosis is allowed to develop to degrees II, III, IV.
It is important to understand that the importance of blood testing is very great. When rdw in a blood test is elevated, only a qualified doctor will be able to make the correct diagnosis based on the data obtained
In addition, adding to them possible additional symptoms that may concern the patient. And, as you know, the disease is easier to prevent or eliminate at the initial stage.
A general blood test is a common type of test. The letters and numbers in the form indicate the quantitative and qualitative indicators of blood components - leukocytes, platelets, etc. The RDW index refers to erythrocytes, or red blood cells - cells that carry oxygen and contain hemoglobin.
Why does the size of red blood cells change?
If RDW is elevated in a blood test, what does this mean? This is a common question. The simplest source of the problem of changes in blood cells is considered to be an unbalanced human diet. With a non-critical transformation of blood quality, the issue most likely lies in the deficiency of certain microelements, mainly such as B9, A, B12, folic acid, iron. If the reason lies in poor nutrition, then it is often enough to simply change the situation by adjusting it, that is, eating foods that contain the necessary nutrients in sufficient quantities.
If this indicator significantly exceeds the norm, then the person has reason to worry and immediately consult a doctor for a thorough examination.
Degrees of anisocytosis
Erythrocyte anisocytosis is divided into four stages:
- I degree. Diagnosed when 27% or 50% of red blood cells have a different volume.
- II degree. Occurs when 55% or 70% of red blood cells have a change in size.
- III degree. More than 75% of blood cells are modified and have different dimensions.
- IV degree. Almost 100% of blood cells are different from normal.
Clinical analysis reveals blood levels of rdw, ranging from a slight degree to a pronounced degree, when the highest percentage of deviation from the blood flow composition standards is detected. In ideal condition, the size of red blood cells should vary between 7-9 micrometers. According to the degree of change in the size of red blood cells in one direction or another, anisocytosis is classified into:
- Macroanacitosis - a larger number of red blood cells of increased volume.
- Microanacitosis is the predominant number of red blood cells of small diameter.
- Mixed type, combining macrocytes and microcytes.
There are also megalocytes, which have the maximum possible blood cell size of more than 12 microns. Macrocytes are red blood cells whose size is more than 8 microns. Their normal amount should be in the range of 12−15%. Microcytes include blood cells smaller than 6.9 microns. Mixed anisocytosis is characterized by the presence of both reduced and enlarged blood cells in the bloodstream. Combined studies are carried out using the calculation method using the Price-Jones curve.
Preparing for the study
To obtain a reliable and accurate result, it is important to follow the recommended rules for preparing for analysis. Therefore, experts advise adhering to the following recommendations:

You should donate blood on an empty stomach. The interval between food intake and collection of biomaterial should be at least eight hours
Therefore, doctors advise taking it in the morning. Before the analysis, avoid drinking alcoholic beverages the day before. It is recommended not to smoke a few hours before the diagnosis. An hour before the manipulation, it is important to eliminate physical and emotional stress. Immediately before the procedure, you need to sit quietly for at least 15 minutes. If a person took medications the day before, it is important to inform the laboratory assistant about this. After some diagnostic procedures, for example, after a rectal examination, it is advisable to donate blood after a certain time.
Some clinics recommend bringing disposable sterile gloves and a scarifier with you. They can be purchased at any pharmacy.
Red blood cell distribution index
An important informative method is the red blood cell distribution index (RDW), which means the complex chemical process of distribution of red blood cells by diameter. Using the method, it is possible to determine the number of deformed cells.
What is he talking about?
Healthy cells have the correct shape and color. Indicators change dramatically if an inflammatory process occurs in the body. Any deviations are associated with a malfunction at the cellular level, when the basic functions of red blood cells are disrupted. The average particle index and average volume in a child and an adult are interrelated, which is why the method is often prescribed simultaneously. There are two types of RDW indicators: CV and SD.
- The first value characterizes the ratio of cells as a percentage of their size.
- The second indicator indicates possible deviations, the difference between the sizes of two different cells.
What does it mean if the values are below normal in women and men, only a specialist can answer: a decrease in values often indicates the presence of a serious pathology.
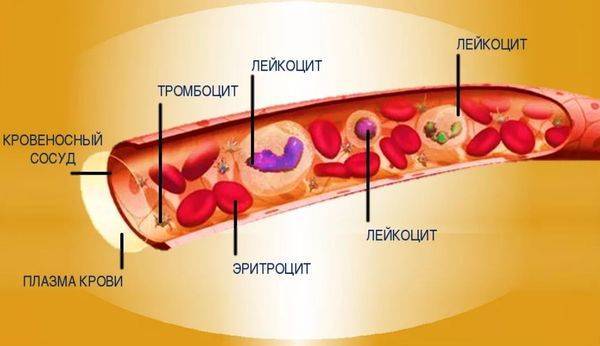
Blood composition
Functions of red blood cells
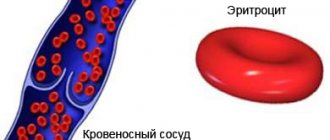
Red blood cells are blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body. This process is carried out using the hemoglobin protein located inside red blood cells. Hemoglobin consists of a protein molecule with iron atoms attached to it. Oxygen entering the lungs is attached to hemoglobin and red blood cells deliver it to all cells.
Red blood cells are small in size and biconcave in shape. Thanks to this, they are able to squeeze through the narrowest capillaries. In the entire body, only the cornea of the eye does not receive oxygen from red blood cells - because it does not contain blood vessels.
Other functions of red blood cells:
- maintaining the acid-base balance of the blood;
- amino acid transfer;
- collection and removal of toxins;
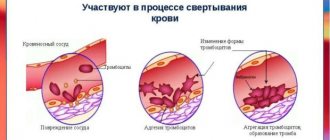
- participation in blood clotting.
If cells change their shape, the process of oxygen transfer is disrupted. This causes hypoxia and disruption of the functioning of internal organs.