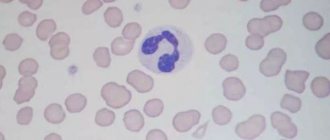
The mechanism of appearance of plasma cells
The function of plasma cells is protective
Unlike other immune cells, plasma cells are not constantly present in the blood. They are contained mainly in lymphatic tissues, spleen and bone marrow, leaving their shelters only in case of danger to the body. Their main function is the production of antibodies.
The mechanism of appearance occurs as follows:
- immune cells send a signal to the brain that pathogenic organisms of a certain type have invaded;
- the brain sends a signal to B lymphocytes with information about which particular virus or bacterium has penetrated;
- B lymphocytes move to the lymph nodes, where they transform into plasmocytes (plasma cells) to fight a specific pathogen;
- Plasmocytes begin to develop an immune response, forming several thousand molecules of protein compounds—antibodies—in a second.
During the transformation of B lymphocytes, some of the newly formed cells become so-called memory cells. They live for decades in the bone marrow, carrying antibodies against every bacteria or virus. Plasmocytes die within a few days after their birth.
Prevention
The preventative fight against any disease is a healthy lifestyle. Proper nutrition is the key to a strong body. It is recommended to exclude fried, salty and fatty foods from the diet.
Every day there should be fruits, vegetables, cereals, proteins, and clean water on the table. Be sure to eat greens and berries, they contain a large amount of vitamins and antioxidants. The simpler the food, the healthier the body. Do not leave the body without physical activity. Exercising and playing any sport strengthens the body. Due to the correct lifestyle, immunity is formed. It is difficult for viruses to attack a healthy body.
An important factor for health will be place of residence. Longevity is always where there is a lot of nature. A person should breathe fresh air, eat natural foods, drink clean water. When this is not possible, there is no need to blame the body. To improve your health, you need to get out into nature more often: relax at the sea, in the forest, near clean reservoirs. Be selective in your choice of food, water, and take vitamins.
Causes of plasma cells in blood tests

Infection of the body can lead to the appearance of plasma cells
Thus, plasma cells appear in the bloodstream only when it is necessary to produce antibodies. In the absence of a pathogenic factor, there is no need for plasma cells. If transformed B lymphocytes are found in a blood sample, then an infection is present in the body, or has been present in the recent past.
Factors that provoke the formation of plasma cells:
- flu,
- ORZ,
- ARVI,
- bacterial infection
- infectious diseases,
- mononucleosis,
- tuberculosis,
- dysbacteriosis,
- pathologies of an autoimmune nature,
- oncological tissue lesions.
When is the presence of plasma cells normal?

Plasmocytes may circulate for some time after infection
In a healthy adult, plasma cells should not be present in the bloodstream. They can appear in a ratio of 1-2 per 1000 leukocytes, so they are most often not detected when diagnosing a blood sample.
After the disease, transformed cells continue to circulate in the plasma for some time. Therefore, if plasma cells are detected, it is necessary to retake the test after a few days.
For children, the presence of a small percentage of plasma cells is normal. From the 5th day of life until the end of puberty, the blood may contain from 0.25 to 0.5% plasma cells. The percentage is calculated in relation to the total number of leukocytes.
What to do?
If a high level of plasma cells is detected in a general blood test, it is necessary to identify the cause . To do this, the doctor collects an anamnesis, after which he prescribes a number of mandatory tests to make the correct diagnosis. Self-medication in this case is inappropriate, since you need to know what to treat and how to treat it. And only a doctor has such knowledge.
Don't panic when thinking about cancer. High rates do not always indicate cancer.
This is how an infection or other disease can manifest itself, so before an accurate diagnosis is established, you should not suffer from guesswork and make diagnoses yourself, based on clinical manifestations.
Plasmocyte detection test
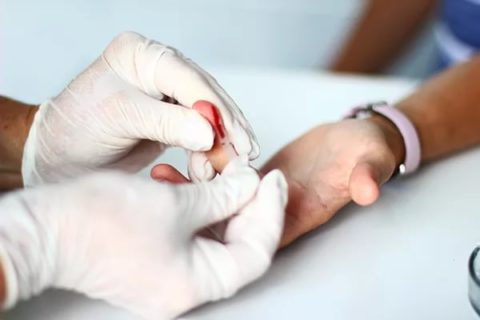
The plasma cell test requires minimal preparation
The doctor may refer you for an analysis to detect plasma cells if the patient is concerned about various ailments: aching joints, lethargy, causeless fatigue, low-grade fever, pain in the abdomen, swollen lymph nodes.
Plasmocytes are detected during a general blood test. Most often, a blood sample is taken from a finger, less often from a vein. Before blood collection, it is recommended not to eat for 8 hours.
If the analysis reveals the presence of plasma cells, it is necessary to undergo additional examinations to determine the cause. Only after this the doctor prescribes treatment.
What analysis is it determined by?
In the case when a person feels unwell and clinical signs of a cold appear, a simple blood test , taken from a finger, is sufficient. To do this, a small puncture is made in the ring finger, after which blood is drawn onto a glass slide using a capillary. Next, the resulting sample is examined under a microscope, where the total number of blood cells is assessed, as well as the presence or absence of plasma cells. In cases where additional diagnostics are required, blood is taken from a vein and the exact number of plasma cells is detected using PCR or other reactions. Most often, a blood test from a finger prick is sufficient. The second diagnostic method is used when a person does not experience any symptoms, but the plasma cell count remains high.
Factors influencing the result

Plasmocytes in a blood sample in children are not uncommon.
The presence of plasma cells in adults is a clear sign of a pathological process in the body. If the acute stage of the disease is not observed, the doctor may suspect a sluggish chronic infection, which may not manifest itself in any way externally. Subsequent research will reveal the factor that influenced the appearance of plasma cells.
In children, the immune system is just developing, encountering many viruses, fungi and bacteria. To create lasting immunity for life, white blood cells actively develop a response to every dangerous object. Plasmocytes can always be detected in a child’s blood sample. Therefore, the patient's age is one of the factors influencing the result.
An increase in the number of transformed cells is detected after vaccination. It is with the help of plasma cells and memory cells that an immune response is formed to virus particles introduced into the body, which allows the cells to fight back this virus in the future.
Threat of presence of plasma cells
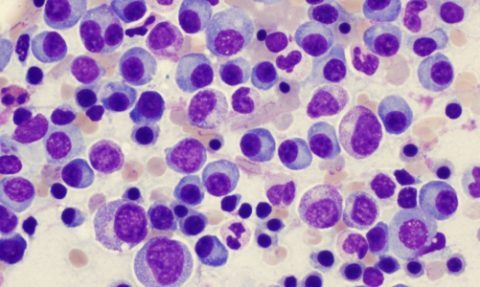
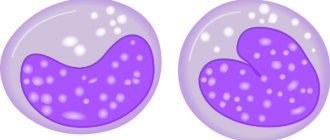
Blood smear from a patient with plasmacytoma
The presence of plasma cells in itself is a consequence of the inflammatory process in the body. If the pathogenic cause is eliminated, the cells will no longer circulate in the blood. However, under the influence of certain factors, plasma cells can form incorrectly and turn from friends of the immune system into its enemies.
This phenomenon is the most common concern of patients who receive a form about the content of plasma cells in the blood. The idea that all plasma cells pose a threat and are an indicator of oncological changes in the blood is erroneous. Such a failure at one of the stages of transformation of a B-lymphocyte into a plasma cell occurs in rare cases; a possible cause may be toxic damage to the body, exposure to radiation, or genetic disorders.
As a result of the failure, an atypical plasma cell appears, which, through continuous division, forms a plasmacytoma. The neoplasm is a malignant tumor of plasma cells and poses a danger to human life.
Treatment
The reasons why elevated test results are diagnosed most often lie in diseases of viral etiology. First of all, a person needs symptomatic treatment. He may suffer from fever, chills, and pain. Doctors prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that relieve these symptoms (Ibuklin, Ibuprofen). In the future, each diagnosis will have its own treatment.
Viral attacks are blocked by antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Viferon, Tamiflu, Kagocel, Celoferon), as tablets or injections. To relieve swelling of the nose and throat and eliminate skin symptoms, antihistamine therapy is needed (Zertec, Suprastin, Claretin). Antitumor drugs (special antibiotics, antimetabolites, hormones) are prescribed at the discretion of the doctor.
It fights autoimmune diseases by lowering immunity; antitumor and immunomodulatory therapy is also prescribed. Most often doctors use:
- Prednisolone (a hormonal drug that suppresses and limits certain functions in the body;
- "Cyclophosphamide", "Methotrexate" (chemotherapeutic agents, against tumors);
- "Azathioprine" (suppresses the body's defenses).

For cancer, the treatment process is very complex. It consists of several stages.
- Antitumor agents.
- Immunomodulatory therapy;
- Surgical method.
The course will depend on the stage of the disease; the higher it is, the more active the process itself. Cytostatics are usually prescribed:
- alkylating antineoplastic agents (promote the “dying” of the genome of cells that were copied during division);
- plant alkaloids (anticancer agent);
- antimetabolites (promote cell division).
Treatment and prevention

Treatment is aimed at the cause that caused the appearance of plasma cells
Treatment consists of identifying and eliminating the cause that caused the appearance of plasma cells in the blood. Depending on the factors that provoked the formation of plasma cells, drugs are prescribed:
- antiviral,
- antibacterial,
- antibiotics,
- antihistamines,
- anthelmintics,
- vitamin complexes.
If a cluster of atypical plasma cells forms, radiation and chemotherapy, the use of glucocorticosteroids, and surgery may be required.
Preventive measures include a balanced diet, proper rest, and the absence of physical and emotional stress. An important component is the absence of untreated diseases, in order to avoid their development into chronic forms.
Dangers and Consequences
In the case when high levels of plasma cells in the blood are detected by chance during a routine examination and the person does not experience any health problems, there is a need for a more accurate examination.
The fact is that the cause may be autoimmune diseases and oncology, the initial stages of which are asymptomatic.
In the absence of a timely search for the cause of what is happening, there is a high probability that the disease will progress, reducing the chances of a full recovery. Therefore, even if there are no health complaints, but these cells appear in the blood, it is necessary to consult a doctor and find out why this happened and what the dynamics are. If plasma cells are not detected during a repeated blood test, then there is no need to worry. But when their number is growing rapidly, there is a need for a more detailed examination.