What does hematocrit show?
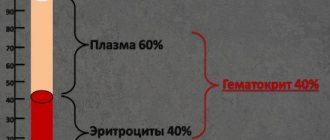
The value reflects the volume of the liquid part of the blood, which contains formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets) in the bloodstream. The hematocrit value is measured as a percentage. So, if the analysis indicates that the hematocrit is 40%, this means that 40% of red blood cells, platelets, etc. are present in 100 ml of blood.
A reduced hematocrit in the blood is observed in patients with a low number of red blood cells in the bloodstream. The indicator also takes into account the size of blood cells. Their decrease naturally affects the results of the analysis.
Measuring the hematocrit indicator is advisable in diagnosing anemia and hyperproteinemia, as well as in assessing the effectiveness of selected treatment methods. The test is performed on patients with dehydration to assess the severity of their condition. Included in the list of mandatory indicators for people who are planning a blood transfusion and for pregnant women.
Main article: What is hematocrit, why is it needed and what are its norms?
What is hematocrit in a blood test?
In medicine, the term “hematocrit number” is considered more correct. It is called for short among health workers. In more scientific language, hematocrit is the content of red blood cells, the calculation formula for which is expressed as a fraction or multiplied by 0.01, the unit of measurement is percentage. This indicator can be determined with the naked eye. When the blood settles, the red blood cells settle and their percentage of the total volume is easy to calculate. In laboratory conditions, other methods are used, because there is a risk of spontaneous sedimentation of blood cells.
Hematocrit is below normal - what does this mean?
A low hematocrit in an adult indicates a reduction in the number of red blood cells in the blood. In this case, the doctor will prescribe additional laboratory tests and instrumental diagnostic methods. Among the laboratory indicators, it is important to determine: the level of iron and ferritin, as well as evaluate the biochemical parameters of the blood. Of the instrumental methods, it is preferable to conduct an ultrasound examination of the digestive organs, liver and pelvis. Based on the results of a comprehensive examination and the patient’s collected medical history, the doctor determines the cause of the low hematocrit.
It should be borne in mind that if a woman submitted biomaterial for analysis during menstruation, then the hematocrit is below normal - this is a standard phenomenon. During this period, the woman loses a certain amount of blood, which means the level of red blood cells decreases somewhat.
It is important to follow the rules for preparing the patient, as well as taking and transporting biomaterial. During venipuncture, destruction of red blood cells in the tube (hemolysis) may occur. For example, due to strong or prolonged compression of the site of biomaterial collection with a tourniquet or due to incorrect storage temperature of the collected blood. The readings obtained cannot be considered reliable, and the patient will definitely need to take the biomaterial again.
When the hematocrit is low...
It is not difficult to guess that hematocrit values directly depend on red blood cells, or rather, on their size and quantity. If for some reason there are too many of them (hematocrit is increased) or too few (hematocrit is decreased) or their sizes due to certain circumstances begin to change towards decreasing or increasing. Of course, the volume of the cellular part of the blood will deviate proportionally in the corresponding direction. A low hematocrit is said to occur if its level drops to 20-25%, indicating anemia. As a rule, such changes are caused by factors involved in the formation of the pathological process.
A decrease in hematocrit can be caused by a drop in the level of red blood cells (erythropenia), excessive accumulation of water in the body, which dilutes the blood and changes the percentage of red blood cells and plasma (hyperhydration), or an excessive increase in the concentration of proteins (hyperproteinemia), which bind and retain water in the body. Such changes are observed under the following circumstances:
- Blood loss, but if the circulating blood volume (CBV) can be restored relatively quickly with infusion solutions, then it takes some time for red blood cells to return to normal.
- In the bone marrow, the formation of red blood cells is impaired (reduced) (anemia, leukemia, treatment with cytostatics and antitumor drugs, kidney paresis).
- Red blood cells are intensively destroyed: hereditary and acquired hemolytic anemias, poisoning with hemolytic poisons (pale grebe, salts of heavy metals), serious infections (typhoid fever, malaria).
- Intravenous administration of large amounts of fluid to patients with impaired renal function increases the total blood volume with normal red blood cells, naturally causing the hematocrit number to become lower.
- Hematocrit is also reduced during pregnancy, especially in the second half, which is due to an increase in plasma volume while maintaining the same level of red blood cells.
- Anemia of any kind and origin.
- Overhydration: BCC increases, the content of red blood cells remains unchanged - the hematocrit is reduced (water intoxication, circulatory failure, decreased functional abilities of the excretory system, etc.).
- Hyperproteinemia. It is formed by a wide range of conditions varying in severity: vomiting, diarrhea, acute infections, myeloma, Hodgkin's lymphoma, paraproteinemic hemoblastoses. An increase in protein in the blood ultimately leads to the accumulation of fluid in the body and an increase in blood volume (red blood cells remain indifferent to these changes).
For children, there are no specific reasons for low hematocrit, so a drop in the level of this indicator in a child is subject to the same law as in an adult, except that the baby’s body is more sensitive to such changes and the disease is often somewhat more severe.
Reasons for decreased hematocrit in adults
Only the attending physician can determine the exact cause in each specific case after a complete diagnosis. Let's look at the main causes of low hematocrit in adults.
Anemia (anemia) describes a group of similar syndromes, united by a total decrease in hemoglobin levels and the number of red blood cells. It should be noted that the isolated term “anemia”, without clarifying explanations, does not describe a specific disease. In this case, it is only a separate symptom of a disease.
How to increase and decrease Ht?
We recommend reading: Causes of elevated red blood cells in the blood
A decreased hematocrit is less common than an increased one. Treatment will depend on the causes of the decrease. That is, drugs are needed to eliminate the primary disease. If this is due to iron deficiency anemia, you should change your diet and include more foods containing iron in your menu. In addition, iron supplements are prescribed. All this will help increase the level of this indicator.
If both red blood cells and hematocrit are elevated, the question arises of lowering it. To do this, you can use the following tips:
- eat fewer foods that contain iron;
- drink more fluids, as dehydration increases this indicator;
- you should avoid alcohol and coffee, which have a diuretic effect and therefore lead to dehydration;
- eat grapefruit every day, which contains a flavonoid that leads to the natural disposal of red blood cells;
- There are foods rich in antioxidants, these include beans, prunes, and various berries.
Is low hematocrit dangerous?
The main function of red blood cells is to sufficiently supply cells and tissues with molecular oxygen. When they decrease, there is an insufficient supply of oxygen to the organs. This has a particularly negative effect on the functional activity of the brain. A person experiences a decrease in concentration, memory and mental activity.
Adults with a low hematocrit are more susceptible to infectious diseases, are unable to work fully, get tired more quickly and lose concentration. In the future, a lack of red blood cells can lead to the development of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys.
NBT in the blood test is increased
When a patient has an increased hematocrit in the blood, it is said to be thickening. This occurs against the background of an increase in the concentration of red blood cells in the human bloodstream. With a detailed diagnosis of the pathological condition, it is possible to establish the main provoking factors. As medical practice shows, they are associated with increased production of red blood cells (disturbance of bone marrow) or with an increase in the size of the cells themselves, which makes the blood thicker.
Hematocrit is increased - reasons
Even knowing why HCT is diagnosed in a blood test and what it is, patients often have no idea about the reasons for its increase. High hematocrit in most cases is due to the development of pathology of the circulatory system. Among the possible reasons causing an increase in hematocrit:
- Erythrocytosis.
- Erythremia (Vaquez disease) is the result of increased production of red blood cells. Accompanied by heaviness in the head, pain in the heart, unpleasant tingling in the fingers, redness of the skin.
- Compensatory reactions of the cardiovascular system - occur when the blood strives to saturate tissues with oxygen more: pulmonary failure, exposure to high altitudes.
- Heart defects.
- Leukemia.
- Renal pathology.
The following transient conditions may be the causes of a temporary increase in hematocrit:
- intestinal obstruction;
- breakthrough diarrhea;
- burn disease;
- peritonitis;
- hyperhidrosis (increased sweating).
Hematocrit is elevated - what to do?
When the NCT level in a blood test is elevated, doctors prescribe appropriate treatment. They try to normalize the condition with the help of symptomatic therapy. With severe erythremia, replacement of physiological fluid is indicated. The procedures are carried out every other day by bloodletting. During one procedure, up to 500 ml of blood is taken, which is replaced with rheopolyglucins - solutions that reduce blood viscosity.
Some patients are prescribed erythrocytapheresis. When it is carried out, a special apparatus is used to correct the composition of the blood outside the body. As part of complex therapy, doctors prescribe antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants (Curantil, Aspirin). The duration of therapy can be several months.
Methods for increasing hematocrit
You should not try to increase the level of red blood cells on your own. A specialist will select the necessary treatment based on the results of laboratory and instrumental studies. In case of prolonged fasting or dehydration, it is necessary to restore the normal diet and the amount of fluid consumed per day. In this case, the patient can do without drug therapy. It is also important to establish a daily routine and plan enough time for relaxation and walks in the fresh air.
If there is a lack of iron or other elements, the doctor will select the necessary medications, their dosage and determine the duration of the course of taking them. You should not interrupt the course of treatment on your own, even if the symptoms of anemia no longer bother you. Your diet should include foods rich in iron. For example, beef liver, seafood, lentils, red meat, nuts and pomegranate.
The use of traditional methods of treatment without prior approval from a doctor is unacceptable. It should be emphasized that these methods cannot be a sufficient alternative to the methods of official medicine. They can only complement treatment, provided that the selected components do not block the action of the medicinal components.
Ht reduced
A reduced hematocrit in the blood is detected in the following conditions:
- increase in plasma circulation volume during hyperproteinemia, during pregnancy (second half);
- overhydration - occurs when large volumes of liquid are introduced into the bloodstream, when swelling subsides;
- for anemia (B12-, iron-, folate deficiency);
- with cirrhosis of the liver;
- for oncological diseases of the bone marrow and blood.
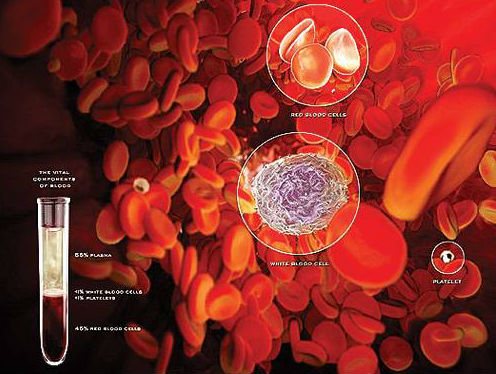
On average, the volume of the erythrocyte fraction is about 45% of the total blood volume
Stool analysis

Photo: fotofermer / Depositphotos A coprogram or stool analysis is a variant of a laboratory test that evaluates the parameters of the stool itself and the impurities in it. Used for suspected infectious and inflammatory diseases of the hollow (stomach, intestines) and parenchymal (liver, pancreas) organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
The consistency and color, the presence of pathological impurities (blood, mucus, dietary fiber, fat) are subject to evaluation. If an intestinal infection is suspected, microscopic examination is also used to identify bacteria, fungi, and protozoa.3
How to collect stool for analysis
- There are several standard rules for donating stool:
- You need to collect freshly excreted feces.
- Before collecting stool, you should stop taking medications (antibacterial, laxatives, castor and vaseline oil, stop administering rectal suppositories). Do not collect stool obtained after an enema or barium ingestion.
- You need to collect feces in a separate container, for example, in a pot, so that urine does not get there (you need to pee first). Before doing this, the pot needs to be washed with soap and rinsed with boiling water.
- To send stool to the laboratory, it is convenient to use a container with a spoon; it is enough to fill it ⅓ full. It is important not to touch the inside of the container to keep it sterile.
- The collected feces should be donated as quickly as possible, preferably within 3 hours after collection.
Important! Stool that was collected 5 or more hours before delivery or that was frozen will not be suitable for analysis.