At this stage of medical development, various diseases can be confirmed or excluded using a simple blood test. Due to the discovery of many tests, it is difficult to say when and what test to take.
The indication of tumor markers serves to identify and confirm the presence of tumors. Various factors other than tumors affect the test result. You need to know and follow the rules for taking the test. In gynecology, the most important tumor marker for ovarian tumors is CA-125.
Tumor markers and their significance
Tumor markers are specific proteins that are produced by malignant tumors or normal tissues in quantities exceeding the permissible limits due to the entry of cancer cells.
They cannot be used to make an accurate diagnosis, but detection of these substances in the blood and/or urine allows:
- suspect cancer and its location;
- distinguish a malignant tumor from a benign one;
- study the effectiveness of tumor therapy;
- detect relapse of the disease early;
- detect metastases before their clinical manifestation.
Types of tumor markers
Currently, scientists have identified more than 200 types of tumor markers, because all neoplasms secrete their antigens.
The most commonly used tumor markers in diagnostics include:
- Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) is determined to detect liver carcinoma, the formation of metastases of oncological pathologies in other organs and monitor the effectiveness of therapy;
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is a protein secreted by embryonic cells; its detection in an adult allows one to detect colorectal cancer with more than 50% accuracy, monitor postoperative relapse, and determine the stage of cancer;
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a marker that increases during pregnancy (it is the increase in the hormone that confirms its presence). If the indicator increases in men and non-pregnant women, testicular or ovarian cancer can be suspected, respectively;
- Prostate specific antigen (PSA ) is a polypeptide, a high level of which allows one to suspect a benign prostate tumor or prostate cancer in a patient;
- CA 15-3 (breast tumor marker) is a highly specific marker that allows you to diagnose breast cancer pathology in the initial stages, evaluate the effectiveness of therapy and identify relapses and metastases in the earliest period;
- CA 19-9 (pancreatic tumor marker ) is a glycoprotein that does not have sufficient specificity, suitable for studying the dynamics of tumor development and differential diagnosis with other formations of the pancreas;
- CA-125 is a specific high-molecular glycoprotein, a tumor marker used in the diagnosis of both ovarian cancer and its metastases;
- HE 4 (epididymal secretory protein) is a glycoprotein, increased production of HE4 has been detected in ovarian and endometrial cancer, rarely in lung adenocarcinoma; has greater sensitivity than CA-125 and is used together with it to confirm the presence of ovarian cancer.
What is SA-125?
CA-125, or mucin-16, carbohydrate antigen 125 is an antigen located on the membranes of ovarian cancer cells.
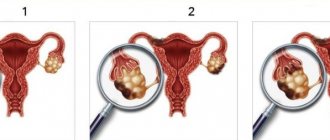
Ovarian tumors represent a serious gynecological problem in all age groups of patients.
In no other human organ is there such a histological diversity of tumors as in the ovaries.
The CA-125 protein belongs to a specific type of epithelium and is normally found in the endometrial tissue of healthy women of reproductive age.
In this situation, changes in CA-125 depend on the phase of the menstrual cycle: a slight increase in its level is observed during menstruation (especially in the presence of endometriosis), as well as during normal pregnancy during the third trimester.
Physiological is the content of CA-125 in the uterine fluid, while it does not penetrate into the bloodstream. Minimal amounts of the glycoprotein can be found in the mesothelial tissues of the thoracic and abdominal organs. Reference (threshold) protein values in laboratory diagnostics are up to 35 U/ml.
Tumor marker for ovarian cancer
In most cases, an analysis to detect the CA-125 marker in the blood is prescribed if the presence of a malignant ovarian tumor is suspected. Its level will depend on the stage of the disease. In the early stages of the development of the pathological process, a significant increase in the specific protein is observed in 50% of cases, in later stages - in almost all patients.
Ovarian cancer is dangerous because it can be asymptomatic for some time. And since a regular gynecological examination is not able to detect the disease, it can quickly progress to a more dangerous stage. When symptoms of a malignant process appear, the doctor prescribes a test to detect the tumor marker CA-125. If elevated values are obtained, it is necessary to conduct additional diagnostics to clarify the diagnosis. It is recommended to take the test multiple times to determine the dynamics of marker increase. If there is an increase in its values, we can talk about the progression of the tumor process or the development of a relapse. Following the course of treatment, the analysis should reveal a decrease in the concentration of CA-125 in the blood.
There are very rarely situations in which the tumor marker is within the normal range in the presence of ovarian cancer. This can occur when cancer cells do not produce enough marker for diagnostic purposes. Therefore, if an oncological process is suspected, it is necessary to perform a series of tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Who needs to get tested?
- First of all, this test must be taken by every woman who monitors her health. For screening purposes, the analysis is carried out for early detection and most effective treatment of cancer. The sooner an increase in tumor marker levels is detected, the greater the chances of successful treatment of the disease.
- It is important for those women whose relatives have been diagnosed with cancer to undergo the test. For this purpose, it is recommended to carry out the analysis once a year.
- If a woman has previously been diagnosed with benign neoplasms , such as leiomyoma, fibromyoma, functional ovarian cysts, neoplastic lesions, the doctor may prescribe a blood test for tumor markers to diagnose and differentiate tumors.
- It is mandatory for women who have symptoms of a malignant neoplasm to undergo the test. However, do not forget that a positive test for tumor markers is not specific and 100% confirmation of cancer, so additional instrumental research methods (ultrasound, tumor tissue biopsy, MRI) will be prescribed.
- After diagnosing a malignant tumor and carrying out conservative (chemotherapeutic, radiotherapeutic) and surgical (radical removal) treatments, the doctor prescribes repeated blood tests for CA-125 tumor markers. This is done to evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy.
- Subsequent analysis is carried out to identify metastases in distant organs, as well as for the early detection of tumor relapse. To do this, the test is taken monthly in the first year after treatment, then once every 2 months during the second year, and once every 3 months in the third year. In the absence of relapses and metastases, the test is performed 1-2 times a year until the end of the woman’s life.
Indications for analysis

A blood test to detect the tumor marker CA-125 is not standard. The doctor prescribes it for certain patient complaints. As a rule, this is the first test ordered when ovarian cancer is suspected. There are the most common symptoms that are indications for the procedure:
- Quite a strong weight loss in the absence of objective reasons for this.
- Increased body temperature for several months.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Painful sensations in the lower back and lower abdomen.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- The appearance of pain when urinating, frequent urges, which may be false.
- Enlarged lymph nodes, especially in the groin area.
- Stool and digestive disorders.
- Ascites.
- An increase in ESR in a general blood test.
- The appearance of spotting that is not associated with menstruation.
- Mucous discharge, including streaks of blood, may be disturbing.
- Weakness, depression, mood swings. The woman feels constantly tired.
The above signs can very easily be confused with manifestations of various diseases of the female genitourinary system. This significantly complicates diagnosis, and therefore dangerous pathologies progress, which can lead to advanced stages of cancer, in which the likelihood of positive treatment is significantly reduced.
How to take a tumor marker test correctly?
To obtain the most accurate result of a tumor marker test, you need to prepare and adhere to simple but very important rules:
- Blood from a vein must be taken on an empty stomach ; the patient must not eat 8 hours before taking blood for analysis. Only water is allowed among drinks to prevent distortion of results.
- It is better to take the test in the morning , between 8 and 11 o'clock.
- A woman should give up alcohol and smoking at least three days before taking the test.
- Immediately before the test, you need to calm down , because... Nervous strain, along with nicotine and alcohol, can affect the final result.
- For a certain number of days before the analysis, you should not engage in intense physical activity..
- It is necessary to exclude medical procedures (physiotherapy, massages, ultrasound examinations) 3-4 days before the test.
- It is very important to monitor your diet during the week before the test: avoid fatty, fried and spicy foods.
- Consult your doctor about taking medications before the test , because... some of them may affect the result of the analysis.
- If a woman has any inflammatory diseases , the test should be postponed and taken after they are completely eliminated.
- The test cannot be performed during menstruation , because... how this period can be accompanied by a physiological increase in the level of tumor marker in the blood.
If all these rules are followed, the analysis will be clearly and correctly interpreted by the doctor. The result can be expected within 1-2 days after delivery.
How to prepare the body for analysis
Modern medical equipment is used to carry out laboratory blood tests. But to obtain undistorted indicators, the patient needs to prepare for the procedure.
Preparation for analysis includes the following points:
- Venous blood is collected on an empty stomach. The interval between the procedure and analysis should be eight to ten hours. During this period of time, you can drink a couple of glasses of pure water without flavor impurities. This will relieve the feeling of hunger and bring a feeling of satiety and a full stomach.
- Avoid drinking tea and coffee on the day of the procedure. This will result in a distorted result and the test performed will not be accurate.
- Active and passive smoking must be stopped three days before the test. You should also avoid drinking alcoholic beverages. Ethanol quickly penetrates the blood and changes its composition. This changes the analysis indicators and makes them erroneous.
- Fatty, salty, fried foods contribute to an increase in CA 125. Therefore, the consumption of such foods should be kept to a minimum.
- Medicinal drugs affect the level of antigens in the blood. If it is impossible to suspend the course of therapy, then you must inform your doctor about taking the drug.
- Excessive physical activity and stress on the body negatively affect the performance of the test. During the period of preparation for the analysis, it is better to refrain from playing sports, visiting gyms and fitness centers.
- Stress, emotional tension and psychological stress distort the accuracy of the results. Therefore, during preparation for blood sampling, emotional shock and nervousness should be avoided.
- You should not donate blood during your menstrual cycle. At this time, hormonal processes occur in the body that affect the examination process.

Compliance with the above recommendations will allow you to obtain an accurate examination result and identify the disease. The intervals between repeated tests should be at least three months.
Decoding the results of the CA-125 analysis
After blood is drawn, it is sent to a laboratory where the tumor marker level is determined. After receiving certain numbers, a very important and responsible stage begins - deciphering the results. It requires a high level of professionalism for accurate verification of the diagnosis, and, accordingly, correctly selected treatment for the patient.
Results:
- Threshold values for protein in laboratory diagnostics are up to 35 U/ml.
- Under normal conditions, in the absence of pathology, the tumor marker level fluctuates between 10-15 U/ml.
- An increase in its level to 35 U/ml is observed in women during menstruation, as well as in the first trimester of pregnancy.
- If a woman’s screening examination revealed an increase in the level of the CA-125 tumor marker above 35 U/ml, you should not make hasty conclusions and think about the worst prognosis.
What does the tumor marker CA 125 mean, what does it show in women and men?
Modern diagnostics is not limited to just a doctor’s examination and now a definitive diagnosis for any disease is made using laboratory tests. The most productive discoveries in medicine have affected the field of oncology (cancer diseases). Many specialists conduct analyzes and actively search for cancer cells in the body in order to be able to diagnose the tumor in time and try to eliminate it.
CA-125 tumor markers will serve as assistants in these studies and biochemical analyses. At their core, these are groups of complex substances, the nature of which is based on protein (it is protein that is a product of the vital activity of cancer cells). Tumor markers diagnose the amount of protein in biological fluids, making it possible to make an accurate diagnosis.
IMPORTANT: It should be clearly understood that tumor markers will not give you 100% confidence in the presence or absence of cancer. They can only serve as the basis and beginning of a more serious diagnosis.
Tumor marker CA-125 has its own area of action and is capable of diagnosing ovarian cancer in women. The test should be done on blood (it is important that the blood is collected on an empty stomach). If during the examination the specialist discovered excessive levels of this tumor marker, this serves as the reason for an additional and more in-depth examination.
In addition, the CA-125 tumor marker may indicate diseases in the body such as:
| Name of the disease | % amount of tumor marker |
| Liver cirrhosis (oncology) | 70% |
| Hepatitis | 68% |
| Pancreatitis | 67-69% |
| Dysmenorrhea | 73-75% |
| Inflammation of the uterine appendages | 80% |
| Ovarian cyst | 82% |
| Sexual infections | 70% |
How to decipher the tumor marker CA-125?
SA-125 analysis indicators
An increase in the CA-125 antigen in the blood to 100 U/ml can result in various non-tumor processes in a woman’s body:
- inflammatory changes in the abdominal cavity (chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver, chronic pancreatitis, peritonitis),
- pelvis (pelvioperitonitis),
- cystic ovarian abnormalities,
- endometriosis,
- adnexitis,
- other gynecological infections, pleurisy, autoimmune diseases.
Cystic ovarian abnormality
Ovarian cysts are not true tumors, since in their presence blastomatous (cellular) growth is not observed in the tissues.
They are formed as a result of retention or accumulation of various contents and gland secretions in the cavity. Cysts can form due to tissue softening due to hemorrhage and necrosis.
The presence of cysts in a woman can affect the level of tumor marker CA-125 in the blood, which begins to reach 60-70 U/ml (up to 100 U/ml).
Correct differentiation of ovarian cysts, timely detection, and examination of patients is very important. To accurately confirm the diagnosis, a bimanual examination and ultrasound of the female genital organs are performed.
After a correct diagnosis, the doctor chooses the most appropriate treatment tactics: from conservative and expectant (functional cysts can resolve on their own) to surgical.
Women who have reached the age of menopause require a careful approach. If an elevated level of the CA-125 tumor marker is detected, it is necessary to undergo regular tests to monitor the course of the disease and take the necessary measures.
Endometriosis
This disease is benign and is characterized by the presence of endometrial (tissue inside the uterus) glands and cells outside the uterus.
In 75% of cases, it is observed in women aged 25-50 years, regardless of its location. The incidence of endometriosis in women during the reproductive and later periods averages 10-15%.
The level of tumor marker CA-125 in the blood with this pathology can reach 100 U/ml, which is significantly higher than normal.
Considering the fact that the disease is widespread, it is necessary to carefully differentiate it from malignant neoplasms when an elevated level of CA-125 protein is detected.
A histological examination of the biopsy material, as well as ultrasound data of the female genital organs, can help with this.
It should be remembered that patients with endometriosis are not cured until menopause. Drug therapy is carried out to suppress and reduce endometrioid lesions. For this purpose, properly selected hormonal treatment is used. If indicated, various surgical interventions are performed.
Uterine fibroids
A benign tumor develops from the smooth muscle tissue of the uterus and ranks first in frequency among tumors of the female reproductive system.
According to statistics, 20% of women over the age of 30 have uterine fibroids of various sizes.
The tumor usually does not appear until puberty, develops only during reproductive age and regresses after menopause.
Scientists associate its development with hormonal disorders in a woman’s body.
After the development of this pathology, the level of tumor marker CA-125 in the blood can reach 90-110 U/ml.
To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a bimanual examination and ultrasound of the female genital organs. Only a thorough examination and high professionalism of the doctor will help identify the cause of the increase in tumor markers, as well as take the necessary measures to treat the pathology.
The first step in the management of patients with uterine fibroids is to clarify the shape and growth rate of the tumor. Depending on this, the patient’s treatment tactics are chosen. The main component of conservative treatment is hormonal therapy with progestogens.
In the presence of large tumor sizes and the development of complications from the uterus and adjacent organs, surgical treatment is indicated.
Tumor marker level during pregnancy
In some cases, it is possible to detect elevated levels of CA-125 protein during a normal pregnancy in the first trimester.
This is due to the fact that during this period the female body undergoes significant hormonal changes, general changes in the body, and emotional instability.
Therefore, an increase in the level of CA-125 antigen in the blood is a physiological change. In addition, fetal cells are capable of producing this antigen, as a result of which its level in the blood increases.
Due to the above reasons, the level of CA-125 protein can reach the threshold level of 35 U/ml in the blood and even slightly exceed it. However, this situation only requires careful monitoring of the antigen level and additional examination of the woman. Subsequently, it is mandatory to donate blood again for analysis.
Menopause (menopause)
After menopause (cessation of menstruation), a woman’s body becomes more vulnerable, which is associated with changes in hormonal metabolism.
Detection of an increased level of the CA-125 tumor marker in the blood during this period will no longer be characteristic of pregnancy, menstrual irregularities, endometriosis (the disease regresses) or functional cystic ovarian abnormalities.
Detection of deviations from normal values requires additional research: ultrasound of the female genital organs, bimanual examination, repeated testing for tumor markers in the blood.
If the level of the CA-125 antigen increases and there is no increase in it, the presence of a benign tumor can be assumed. A significant increase, together with symptoms characteristic of the menopausal period (bleeding from the genital tract), will confidently indicate in favor of a malignant neoplasm.
Significance of CA-125 in ovarian cancer
The main purpose of testing for CA-125 in the blood is to laboratory confirm or exclude the presence of a malignant neoplasm in a woman.
In the case of ovarian cancer, the CA-125 antigen level increases more than 5 times compared to the threshold level, thus reaching numbers of more than 100 U/ml. Do not forget that in ovarian cancer the level of the CA-125 antigen may be normal.
This, in turn, should not be regarded as a clear exclusion of cancer. The diagnosis can be established only after conducting a double analysis with increasing indicators over time.
To clarify the diagnosis, if there are controversial indicators of the CA-125 protein, it is useful to take a test for HE-4, which is more sensitive. A combined test with the calculation of a special index makes it possible to identify oncopathology at an early stage, as well as differentiate malignant pelvic tumors from benign ones.
In the early stages of cancer, the CA-125 indicator increases slightly or does not change. As the tumor grows and the stages of the disease progress, its level in the blood may exceed the norm. Testing for this antigen can be used to predict the course of the disease: if the level decreases after starting treatment, patients have a significantly increased survival rate.
It is very important to monitor the woman after treatment in the tumor remission stage. During this period, the level of CA-125 protein is reduced to zero. Increasing it even to a threshold value may mean a relapse even before its clinical manifestation. This condition requires careful examination.
If a constant antigen level is established after the start of treatment, one can judge a poor response to the therapy and continued growth of oncological pathology.
False-positive results when assessing CA-125
Diseases that do not have a tumor origin lead to false-positive results when assessing the level of the CA-125 antigen. They are named as such because the main purpose of the test is to confirm and show the presence of cancer.
These pathologies include:
- inflammatory diseases of the abdominal cavity (peritonitis, chronic hepatitis, chronic pancreatitis);
- pelvic inflammatory diseases (pelvioperitonitis);
- inflammatory diseases of the chest cavity (pleurisy);
- autoimmune diseases;
- infectious lesions of the female genital organs.
Additional examination methods help in differentiating these diseases and oncological pathologies. It is important to promptly confirm and treat, or exclude any damage to internal organs.
What else can the CA-125 tumor marker indicate?
When a high level of protein is initially detected, it is necessary to carry out a qualitative and detailed differential diagnosis with other oncological diseases.
The CA-125 protein is not strictly specific for ovarian cancer; it is also detected in a number of other oncopathologies:
- mammary cancer,
- uterus, endometrium,
- pancreas,
- lungs,
- liver and stomach.
If there are no signs of ovarian cancer on ultrasound, MRI, or histological examination of biopsy material, it is necessary to conduct additional diagnostics of the pathologies of other organs listed above.
Definition
Tumor marker CA-125 is a highly specific protein that is located on the surface of a malignant ovarian tumor.
It is important to know that some amount of this protein is contained in the endometrium, in the serous and mucinous fluids of the uterus. Also, a certain amount of this marker is produced by the epithelium of the gallbladder, testes, stomach, bronchi, and pancreas. While maintaining biological barriers, CA-125 should not enter the bloodstream.
Don’t worry right away when getting tested for tumor markers. If CA-125 is elevated, you need to undergo a number of additional tests to clarify the cause.
Bottom line
When prescribing an analysis for a tumor marker, a woman must take preparations before it with complete seriousness, otherwise the result and further interpretation may be incorrect.
The following factors may affect the test, so it is worth preparing:
- eating before delivery;
- drinking alcohol and smoking several days in advance;
- drinking coffee, tea before delivery;
- use of medications;
- undergoing ultrasound and x-ray examinations;
- eating spicy, fatty and fried foods;
- stress;
- menstruation.
After eliminating these factors, it remains to correctly decipher the table of analysis results. This requires an excellent specialist and additional research methods. If necessary, the test is repeated.
In addition, an additional analysis for HE-4 may be prescribed. We must not forget that the absence or presence of an increased level of antigen cannot completely exclude or confirm the formation of a malignant tumor.
A timely diagnosis and correctly chosen treatment tactics are the key to an effective and speedy recovery for the patient!