In medicine, tumor markers are understood as a combination of biochemical substances and elements, the increase of which in the human body shows and signals a malignant, benign neoplasm or the presence of an inflammatory process. The body responds to the appearance of cancer cells by increasing the production of tumor markers. The person does not suspect that pathological processes are developing in the body, the onset of the disease is asymptomatic or the signs are not paid attention to. Detection of symptoms of a disease at the stage of its occurrence is often a matter of chance and depends entirely on the attentiveness of the patient and the therapist. The doctor’s task is to promptly identify possible deviations in the internal environment of the body in the early stages through examination, analyzes and tests.
The HE-4 tumor marker is a protein belonging to the family of human acidic tetradisulfide proteins. In the normal state, the protein is present in the organs of the genitourinary system, pancreas and upper respiratory tract. Present in men and women. The functional load of the HE-4 marker has not been fully studied. Scientists suggest that the marker is involved in the normal functioning of the epithelium and supports the functioning of the local immunity of the oral cavity and respiratory tract. Increased production of HE-4 is a feature of some types of cancer cells, which makes it possible to use it as a tumor marker. Researchers have found another property of HE-4 - enhancing the movement and adhesion of ovarian cancer cells. Therefore, it is advisable to use the marker for diagnostic and prognostic purposes for ovarian and endometrial tumors.
Stages of development of ovarian cancer
Advantages of HE-4 marker
The development of diagnostic medicine has not yet reached a level at which guaranteed and error-free detection of ovarian cancer at an early stage of deviation is possible. Traditionally, the CA 125 tumor marker is used to determine the presence of cancer in the organs of the reproductive system in women. The problem with its use lies in the weak ability to distinguish benign formations from malignant tumors.
Unlike CA 125, the HE-4 marker more accurately identifies malignant oncology. When prescribing examinations, oncologists give preference to a combination of CA 125 and HE-4 markers when diagnosing cancer cells in the ovaries. An algorithm for identifying the risk of ovarian cancer ROMA has been developed. Elevated levels of HE-4 protein are detected by a combination of clinical methods for quantitative determination of the concentration of the substance in the blood. Laboratory studies have confirmed the increased sensitivity of the HE-4 marker for recognizing cancer cells of the female genital organs at an early stage of the disease compared to other markers.
According to numerous foreign studies, if ovarian cancer is detected in the initial stages, then complete remission is 94%, while detection of a tumor at a later stage reduces the chance of survival (45%).
A low risk of developing ovarian cancer is reflected by the above-mentioned ROMA indicator, which is divided into two diagnostic parameters:
ROMA1 (during premenopause) – less than 7.4%.
ROMA 2 (during menopause) – less than 25.3%.
If the indicators are higher than or equal to the presented values, we are talking about an increased risk of cancer, the spread of metastases and the lack of effect of treating the disease. With such results, the patient is prescribed additional studies to localize a possible pathological process and adjust treatment. All diagnostic procedures and treatment prescriptions are carried out by doctors. Self-medication and unconventional practices without a therapist’s opinion are dangerous to life and health!

What is he 4
The he 4 tumor marker is a protein formation that can be present in a small concentration in the body of any healthy person. This glycoprotein blocks the proteinase enzyme.
Normally he 4 is located in:
- Epididymis in men. This protein is involved in sperm production;
- Endometrium - the mucous membrane of the uterus;
- Fallopian tube cells;
- Cells lining the bronchi.
The he 4 protein is specific for oncological processes, since it is actively produced in the presence of cancer cells, by these cells or by the human body. He 4 is produced under the influence of a special gene WFDC2, which is activated in malignant cells.
The he 4 tumor marker is used to diagnose ovarian cancer in women, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of therapy during treatment.
It should be noted that he 4 is extremely rarely synthesized by healthy cells of the female body, therefore, if its levels increase, additional examination should be carried out to clarify the diagnosis. If the concentration of this protein increases, then this laboratory sign alone does not indicate the presence of a cancerous tumor. The diagnosis is made after a comprehensive examination.
It is important that the collected blood is delivered to the laboratory for testing no later than 1.5 hours after its collection, and the tube must be stored in a special box where the temperature is maintained no higher than 8°C.
The protein structure of he 4 is not a sign of any malignant ovarian formation. It is more than 90% specific for epithelial cancer.
Only the tumor marker he 4 is detected in the blood long before the spread of the pathological process (early stage), that is, before the formation of metastases in neighboring organs and tissues. This in turn makes it possible to cure the patient and avoid serious complications.
What types of abnormalities are indicated by the HE-4 tumor marker?
Clinical studies have shown the ability of HE-4 for early diagnosis of ovarian and endometrial cancer.
Ovarian cancer (ovarian carcinoma) is a malignant tumor. It is the fifth leading cause of cancer death in women in the world. With early diagnosis and treatment, the 5-year survival rate is 94%. The cause of the disease is not fully understood. According to researchers, nulliparous women are more susceptible to ovarian carcinoma. The patient’s age and hereditary predisposition also play a role. The development of the disease may be affected by an increase in the amount of animal fats obtained from food, as well as gynecological disorders of various etiologies.
Endometrial cancer (endometrial carcinoma) is a malignant tumor of the epithelium of the uterine body. Discharge with blood from the vagina is the main symptom of the disease. Symptoms of endometrial cancer coincide with signs of other diseases of the pelvic organs. Among the risk factors that can provoke the disease are listed: hyperplasia of uterine tissue, excess body weight, infertility, irregularities in the menstrual cycles, taking certain hormonal contraceptives, hereditary predisposition.
The marker also signals the development of oncological processes in the following organs:
- lungs;
- colon;
- mammary gland.
The marker is less sensitive to benign formations and endometriosis of the female genital organs, which makes it possible to differentiate diagnoses. HE-4 is used in the diagnosis of the following diseases not associated with malignant neoplasms:
- An ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm. It has the shape of a bubble filled with liquid. It occurs in the absence of symptoms and is detected during diagnostic and preventive examinations. An ovarian cyst may be indicated by discomfort in the lower abdomen, disturbances in the healthy functioning of the intestines, frequent urge to urinate, and others. The level of HE-4 is elevated in cysts. It is advisable to use other diagnostic procedures to make a diagnosis.
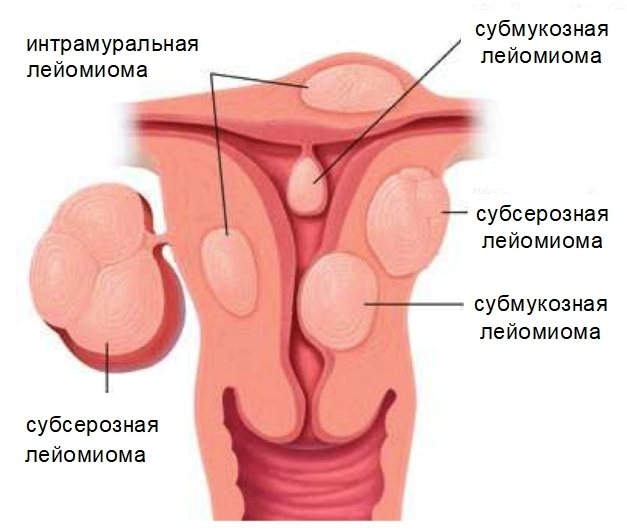
Types of uterine leiomyomas
- Myoma is a benign formation of the muscles of the uterus. A common disease in women over thirty years of age. One of the causes of uterine fibroids is hormonal imbalance. Like a cyst, fibroids do not have obvious signs of deviation. Pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, disruption of the normal menstrual cycle may indicate the presence of a disease. An increase in the tumor marker for fibroids is an additional trigger for a specialized examination in the gynecological office.
- Endometriosis is a pathology of the uterus in which endometrial tissue cells spread beyond the organ. Women of reproductive age are susceptible to the disease. Symptoms of endometriosis include pain and heavy discharge during menstruation and infertility. The marker value for endometriosis does not exceed the threshold values or is slightly increased.
In renal failure and liver diseases, the HE-4 tumor marker is shifted upward. To make a diagnosis, the patient must experience symptoms indicating abnormalities in these organs.
Also, using diagnostics with the HE-4 tumor marker, the results of treatment for detected cancer are monitored. For example, the concentration of HE-4 in patients with ovarian cancer at the initial stages of treatment was 300 pmol; as a result of successful treatment and during the period of remission, the figure decreased to 20 pmol.
The HE-4 marker is ineffective in diagnosing mucoid and germ cell forms of ovarian cancer, since it is not expressed in cells of these types of neoplasms.
Additional diagnostics
The He4 tumor marker, despite its high accuracy, cannot be used as the only method for diagnosing ovarian and endometrial cancer of the uterus. To make a diagnosis, determine the nature of the tumor and the stage of the disease, you need to undergo a complete examination of the body, which includes laboratory and instrumental methods.
General and biochemical blood tests can reveal the severity of the inflammatory process, hemoglobin level, and the concentration of vital enzymes in the blood. These are the most common studies prescribed for all diseases.
An examination by a gynecologist is mandatory if both malignant and benign tumors are suspected. The doctor examines the patient, takes smears and sends her for an ultrasound examination of the pelvis. Ultrasound is performed transabdominal and transvaginally to obtain more complete information.
Additional diagnostic methods:
- To determine metastases, a chest x-ray, abdominal ultrasound, and radioisotope study are performed.
- Computed tomography, MRI - allow you to accurately determine the location and size of the tumor, the presence of metastases.
- Laparoscopy - allows you to examine the structure of the ovary, examine the neoplasm and take material for a biopsy. Laparoscopy is also performed to remove the tumor or the ovary as a whole.
- Biopsy and histology - performed to determine the type of cancer.
Also, together with the tumor marker, the study of other cancer antigens is carried out. Most often together with the CA 125 marker, less often with the AFP and CEA antigens. It is also necessary to determine the level of hCG and estradiol, and, if necessary, other hormones.
Taking tests
For diagnostic purposes, blood from a vein is used. To increase the accuracy of analysis results, the following rules must be observed before donating blood samples for research:

- Do not smoke at least 30 minutes before donating blood for testing.
- Stop eating and drinking liquids, except boiled water, 8 hours before the procedure.
- Do not take medications for two days, if possible and will not harm the body.
- Avoid sexual intercourse for two days.
- A week before the tests, avoid alcoholic beverages.
- Avoid stressful activities, including physical ones.
- Limit consumption of fatty, fried and spicy foods.
On average, test results are ready within two days. The research takes place in laboratory conditions. Using a special catalyst, a glow reaction is started in the removed samples, after which the level of the required tumor marker HE-4 is determined and calculated.
Reasons for the increase in HE4 tumor marker
An overestimation of the tumor marker concentration primarily indicates malignant processes in the reproductive organs. The higher the He4, the more likely it is that the patient has cancer.
The main reasons for raising the marker:
- Mucinous or serous cystadenocarcinoma of the ovary.
- Endometrial cancer of the uterus.
Attention! Less commonly, high rates indirectly indicate malignant neoplasms in the respiratory tract and pancreas.
But the high concentration of tumor marker He4 does not always indicate oncological processes. A false positive result may indicate benign neoplasms and severe inflammatory processes.
Non-oncological reasons for increased antigen:
- benign ovarian cysts;
- polyps in the ovaries;
- endometriosis;
- fibroids and uterine fibroids;
- liver damage – hepatitis, cirrhosis;
- severe kidney dysfunction;
- cystic fibrosis;
- any inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
If the tumor marker level is high, you should not panic - you need to rule out a laboratory technician’s mistake, improper preparation before taking blood, and also retake the test and conduct additional examinations.
Interpretation of analyzes
The interpretation of the result is based on the possibility of increasing the threshold value of the HE-4 marker in other diseases, including lung cancer, renal failure, and renal fibrosis. According to researchers in the field of cancer diagnostics, the phase of the menstrual cycle does not affect the level of HE-4. If the level of tumor marker HE-4 is below normal, this is not critical. Increased indicators require attention, which may indicate the presence of pathological processes in a woman’s body.
Norm
Women have the tumor marker HE-4 in their blood. The normal amount depends on the age of the patient. The norm for women under 40 years of age is within 60 picomoles per liter. During the onset of menopause, the normal value should not exceed 140 picomoles, according to other sources, 104 picomoles. The marker value in pregnant patients is lower than in non-pregnant patients.
Table of indicators of normal levels of tumor marker HE-4 in women:
| Age, years | Norm, picomole |
| Up to 40 | No more than 60 |
| 40 – 49 | No more than 76 |
| 50 – 59 | No more than 74 |
| 60 – 69 | No more than 83 |
| After 70 | No more than 104 |
Deviations
An unambiguous diagnosis of the presence of the disease is made by the attending physician based on the results of a number of additional diagnostic procedures and studying the patient’s comprehensive medical history. After conducting diagnostic studies and confirming the positive dynamics of cancer cell growth, doctors develop an individual strategy to combat the disease. The main treatment for cancer is chemotherapy. If a positive effect is not achieved, surgical intervention and postoperative rehabilitation therapy are used. After the indicators return to normal, regular preventive examinations are carried out to monitor the level of the HE-4 tumor marker and other indicators.
Diagnostic errors
As in any other field, in diagnostic medicine there can be inaccuracies, inaccuracies and errors. The possibility of false-positive and false-negative results cannot be ruled out due to technical failures in diagnostic equipment, non-compliance with requirements when preparing for tests, or an error by a laboratory technician or diagnostician.

Indications for the purpose of analysis
The He 4 blood test is mandatory for all patients in whom the presence of a neoplasm was suspected based on the results of ultrasound diagnostics of pelvic organs and tissues or during a bimanual vaginal examination.
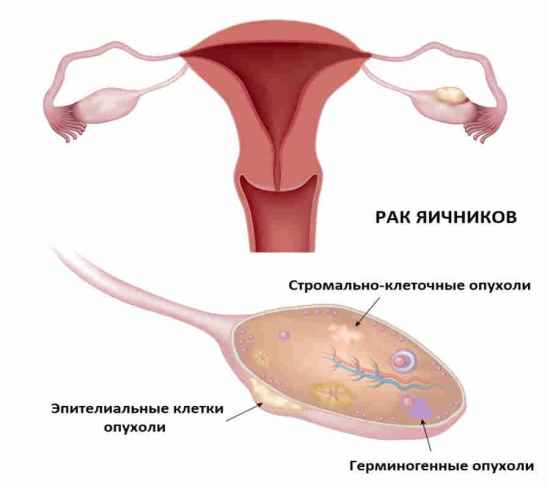
The study is also carried out for women in whom the development of a tumor has not been established, due to a combination of certain factors:
- complete loss of appetite;
- rapid, unexplained weight loss;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- inter-cycle discharge;
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- bloating, bulging or palpable formation;
- Irregularity of the menstrual cycle.
According to statistics, women over 50 years of age during postmenopause have an increased risk of developing cancer. The high-risk group also includes patients in whose family episodes of cancer have already been identified. Therefore, it is recommended that this particular category of people undergo routine laboratory diagnostics for tumor markers of ovarian cancer every year.
In a situation where the type of examination in question is carried out to assess the effectiveness of the chosen treatment tactics, monitoring the level of the tumor marker in question must be carried out once every 3 months. After a successful course of therapy, control measurements of this criterion are carried out once every six months.
Preventive actions
In order to minimize the risk of ovarian cancer, the following rules must be observed:
- Periodic examinations by gynecologists.
- Regular blood donation for analysis (general, biochemistry). This procedure is also indicated for people undergoing rehabilitation for ovarian cysts.
- Maintaining genital hygiene.
- Taking hormonal and contraceptive medications only after consultation with a therapist.
- In winter, choose a wardrobe with warm clothes, and not for the sake of fashion. Keep the pelvic organs warm.
- Complete cessation of drinking alcohol and smoking.
- Maintaining a routine and balanced diet. Increasing the consumption of plant antioxidants (vegetables, fruits, dried fruits).
- Losing excess weight. According to American researchers, overweight women are at risk of developing ovarian cancer. Moreover, the excess weight may be small. There is also a direct connection between excess kilograms and diseases such as breast cancer, colon cancer, endometrial cancer, kidney cancer, etc.
With the proper level of care for the body, timely and regular examinations and studying the research of international scientific organizations in the field of combating cancer, you can overcome the disease and live a full life.
HE 4 in combination with other tumor markers
The most optimal way to diagnose ovarian malignancy is to study a combination of tumor markers he 4 and ca 125. However, it should be noted that an increase in the concentration of ca 125 occurs at a later stage in the development of the pathological process than he 4. But he 4 is not sensitive to some types of ovarian cancer ( germinogenic and mucoid), and ca 125 increases.
Tumor markers he 4 and ca 125 are necessary to calculate the ROMA index. It is a calculation of the prognosis of the disease. To calculate this index, you need to know the results of the analysis for tumor markers and the woman’s age.
ROMA index in premenopausal women:
- If this index is less than 11.4, then the risk of developing epithelial ovarian cancer is very low;
- If this indicator is 11.4 or more, then this indicates a high risk of developing this pathology.
ROMA index in postmenopause:
- If ROMA is less than 29.9, then the risk is low;
- If this index is equal to or greater than 29.9, then the risk of developing ovarian cancer is extremely high.
Studying a combination of tumor markers leads to more accurate and timely detection of such a dangerous disease as cancer.
ROMA index norm
The World Health Organization has created instructions for decoding the ROMA index:
- Roma index 1 - during reproductive times - in premenopause - the probable norm is up to 7.39% (if the figure is lower than this, there is no cancer in the woman’s body and the chance of its occurrence is minimal, if higher, there is a suspicion of oncology).
- Roma index 2 - after the end of the reproductive period - in postmenopause - the limit norm is up to 25.29% (a minimum risk of a tumor is indicated by a figure below this, and a level above the norm indicates a greater danger of the existence of a cancerous tumor). The figure can often be higher than normal values, but after a new analysis it turns out that it remains at the same level, does not rise or decrease. This is a sign that a benign tumor is present in a woman’s body.
Decoding the results
The diagnosis is made by a gynecologist or oncologist based on the data obtained. The Roma index is calculated using special formulas. They vary depending on the phase of menopause and the age of the woman. It is quite difficult to make calculations on your own. An increase in the indicator does not always indicate the presence of cancerous tumors. The following factors can provoke an increase in CA125:
- liver diseases;
- cystic formations in the ovaries;
- pregnancy;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- infections in the genital tract;
- endometriosis;
- appendicitis.
An increase in HE4 almost always indicates the presence of malignant tumors. But in some cases it is the result of impaired kidney function, cirrhosis of the liver or the formation of fibroids. A diagnosis cannot be made based on data from one of the indicators. Both parameters need to be assessed. A false negative result is rare. It is possible only in the early stages, when the malignant tumor does not produce cells.
The doctor makes a conclusion about the patient’s health only after receiving the results of other studies. These include ultrasound monitoring of the pelvic organs, biopsy and gynecological examination. If the study was carried out in preparation for surgery, then the woman’s hereditary predisposition to cancer is determined. Surgical intervention is possible only if the woman does not have any problems.

Norm and deviation
The Roma index rate ranges from 11.4% to 29.9%. Premenopausal women are at risk with rates above 7.4%. In postmenopause, the possible development of oncology is indicated by a result of more than 25.3%. When interpreting analyses, various nuances are taken into account. If the indicator decreases over time, then the neoplasm is benign. An increase in the index over time indicates the presence of cancer. The results of ultrasound, biopsy, laparoscopy and additional tests are of great importance in making a diagnosis. Borderline indicators require special attention from women in relation to their health. In this case, there is a risk of developing cancer in the future. It is advisable to carry out additional diagnostic procedures to ensure the absence of a tumor.